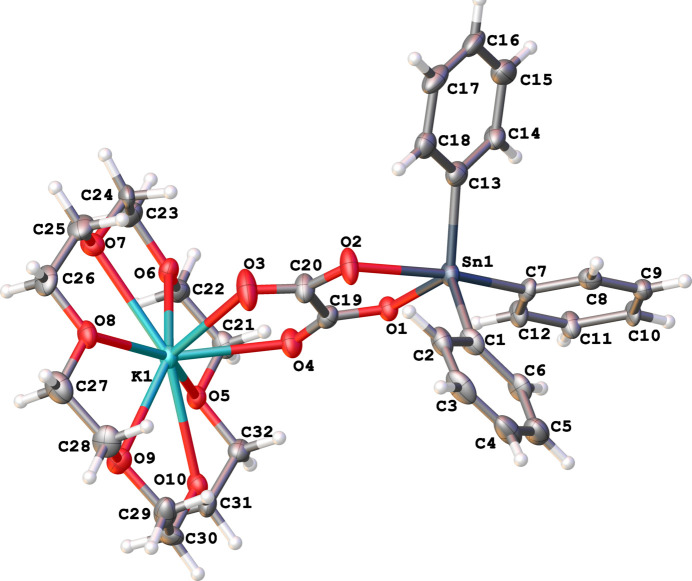
The single-crystal X-ray structure of [(18-crown-6)K][SnPh3(ox)] (ox = C2O42−) is reported. Integrity between neighboring molecules in the solid state is maintained by an array of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions.
Keywords: crystal Structure, triphenylstannate, oxalato, 18-crown-6, potassium
Abstract
The title complex, (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(μ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1′,O2′)triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV), [KSn(C6H5)3(C2O4)(C12H24O6)] or K[18-Crown-6][(C6H5)3SnO4C2], was synthesized. The complex consists of a potassium cation coordinated to the six oxygen atoms of a crown ether molecule and the two oxygen atoms of the oxalatotriphenylstannate anion. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system within the space group P21. The tin atom is coordinated by one chelating oxalate ligand and three phenyl groups, forming a cis-trigonal–bipyramidal geometry around the tin atom. The cations and anions form ion pairs, linked through carbonyl coordination to the potassium atoms. The crystal structure features C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms of the oxalate group and the hydrogen atoms of the phenyl groups, resulting in an infinite chain structure extending along a-axis direction. The primary inter-chain interactions are van der Waals forces.
1. Chemical context
Organotin carboxylates are one of the most significant classes of compounds, valued not only for their theoretical and structural properties but also for their industrial and agricultural applications (Zuckermann et al., 1976 ▸). Organotin(IV) carboxylates are particularly notable for their diverse and important biological activities, serving as anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal agents, as well as wood preservatives and pesticides (Davies & Smith, 1980 ▸; Smith et al., 1978 ▸; Thayer et al., 1984 ▸; Blunden et al., 1985 ▸; Evans & Karpel, 1985 ▸; Angham et al., 2019 ▸; Talebi et al., 2023 ▸). Metal complexes of dicarboxylic acids, such as oxalic acid, have garnered significant interest due to their promising magnetic and electrochemical properties. The appeal of oxalate-based coordination compounds lies in their high structural diversity, attributed to the oxalate ligand’s ability to adopt 17 different coordination modes and function as a mono-, bi-, tri-, or tetradentate ligand (Krishnamurty & Harris, 1961 ▸; Rao et al., 2004 ▸). This results in a vast, yet largely unexplored, compositional area. Notably, there are very few reports of organotin complexes of oxalic acid in the literature.
The author has been interested in designing and preparing ionic organotin complexes to improve aqueous solubility through ionization. Since the pioneering work of Pedersen (Pedersen, 1988 ▸; Izatt, 2017 ▸), crown ethers and their complexes with metal cations have attracted considerable attention. Their remarkable selectivity on metal cations, especially alkali and alkaline earth metal cations, is a topic of fundamental interest in both coordination chemistry and biological chemistry (Bajaj et al., 1988 ▸; Hay & Rustad, 1994 ▸; Lehn et al., 1988 ▸; Lee et al., 1996 ▸). Literature reports show that crown ethers can be utilized in solid-solid and solid-liquid processes to capture alkali metal and ammonium cations in extended hydrogen-bonded networks formed by inorganic acid anions, such as hydrogen sulfate and di-hydrogen phosphate, as well as organic acid anions (Braga et al., 2005 ▸, 2007 ▸, 2008 ▸, 2009 ▸). In this context, we present and discuss the crystal structure of a crown ether-stabilized potassium salt of oxalatotriphenylstannate, 1.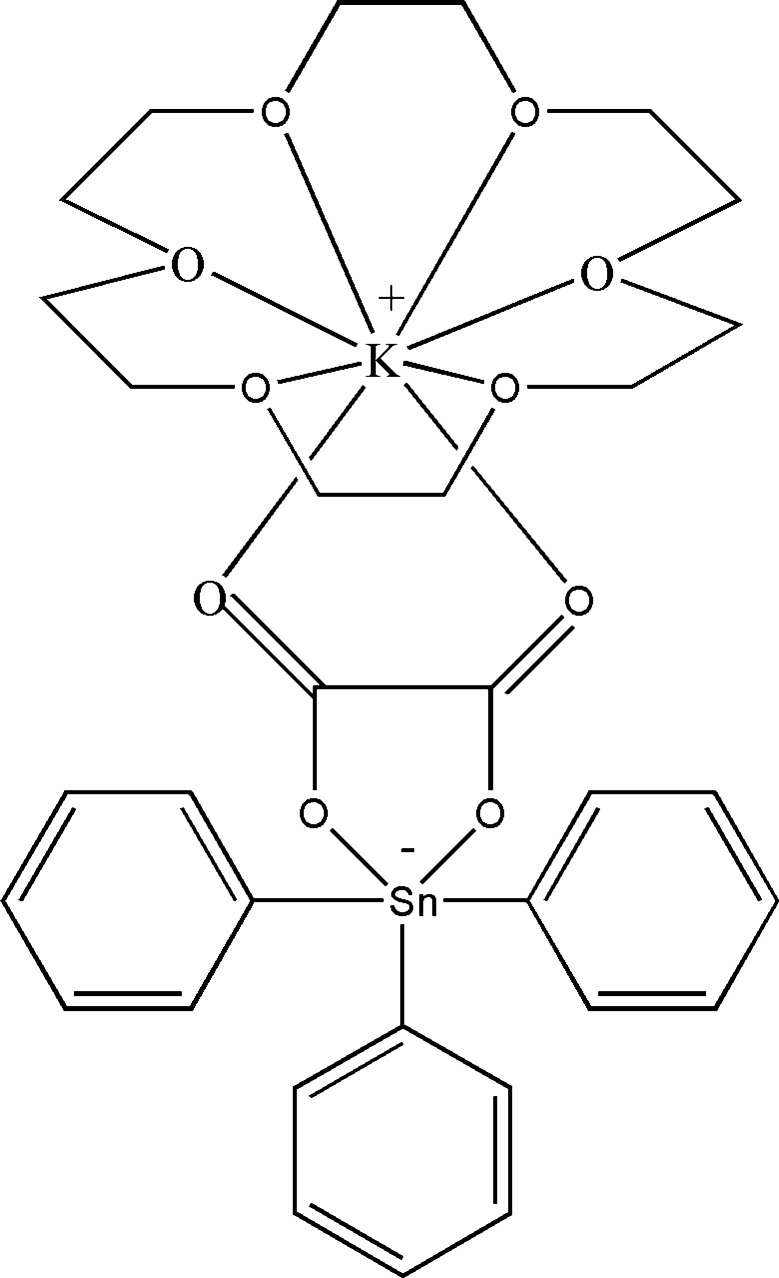
2. Structural commentary
The stannate anionic unit of the title compound 1 features a cis-tbp [Ph3Snox]− anion, with Sn1—O1 measuring 2.071 (5) Å and Sn1—O2 measuring 2.290 (6) Å, and an O1—Sn1—O2 bond angle of 73.4 (2)° (Fig. 1 ▸). This anion is coordinated via its two oxalate carbonyl groups (O3 and O4) to a K[18-crown-6] cation, with K1—O3 at 2.785 (7) Å, K1—O4 at 2.654 (6) Å, and an O3—K1—O4 bond angle of 61.3 (2)° (Fig. 1 ▸). The oxalate acts as a bidentate ligand to both tin and potassium, forming two five-membered chelate rings that are coplanar, with a dihedral angle of approximately 0°.
Figure 1.
The asymmetric unit and molecular structure of crystal [(18-crown-6)K][SnPh3(ox)] (1) with anisotropic displacement ellipsoids set to the 50% probability level.
In the [Ph3Snox]− portion, the axial Sn-O bond [Sn1—O2 at 2.290 (6) Å] is significantly longer than the equatorial Sn-O bond [Sn1—O1 at 2.071 (5) Å]. The bite angle of 73.4 (2)° is similar to those found in other chelated oxalato triphenylstannates (Ng et al., 1992 ▸; Ng & Kumar Das, 1993 ▸; Ng, 1996 ▸). The axial Sn—C bond [Sn1—C7 at 2.188 (7) Å] is somewhat longer than the equatorial Sn—C bonds [Sn1—C1 at 2.136 (7) Å and Sn1—C13 at 2.138 (7) Å]. The axial structure is notably bent, with an O2—Sn1—C7 angle of 160.8 (3)°, and the Sn atom is displaced out of the equatorial plane [Σ angles at Sn = 354.9 (3)°] towards the axial C7 atom by 0.119 Å.
The oxalate group in the [Ph3Snox]− ion consists of two similar carboxylate (–COO−) entities. Both bind to the Sn1 and K1 atoms, with slightly different C—O bond lengths: those bonded to tin [C—O = 1.266 (11) and 1.303 (10) Å] are slightly longer than those bonded to potassium [C—O = 1.233 (11) and 1.202 (10) Å]. The two negative charges appear to be delocalized over the four oxygen atoms in the oxalate group.
In the [K(18-crown-6)]+ complex cation, the potassium atom deviates by 0.614 Å from the root-mean-square plane of the six oxygen atoms in the 18-crown-6 ligand towards the oxalate group. This deviation is due to the coordination of two oxygens from the oxalate group. A similar observation has been reported in the literature (Gjikaj et al., 2005 ▸; Liebing et al., 2016 ▸; Sellin & Malischewski, 2019 ▸) when potassium has axial coordination to other heteroatoms. The K—O bond lengths with the 18-crown-6 ligand range from 2.802 (6) to 2.976 (6) Å, which are slightly longer than those reported for other [K(18-crown-6)]+ complexes in the literature. The increased average K—O bond length with 18-crown-6 is attributed to the strong coordination with the oxalate group, where the two K—O bond lengths with the oxalate group are 2.654 (6) Å and 2.785 (7) Å. The coordination number of the K+ cation is 8. The coordination polyhedron of the potassium cation can be described as a distorted hexagonal pyramid with a bifurcated vertex at the O3 and O4 atoms.
3. Supramolecular features
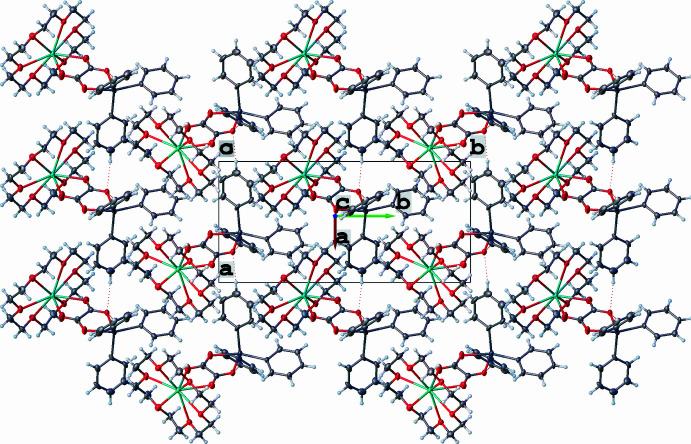
The title complex 1 exhibits a supramolecular structure that is consolidated by two weak intermolecular hydrogen bonds: C4—H4⋯O1 and C16—H16⋯O1, with C⋯O distances of 3.360 (11) and 3.332 (9) Å, respectively (Fig. 2 ▸; symmetry codes as in Table 1 ▸). These intermolecular hydrogen bonds result in the formation of a ‘shoulder-to-shoulder’ arrangement of the complex molecules, creating a supramolecular layer parallel to the (001) plane, as depicted in Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸.
Figure 2.
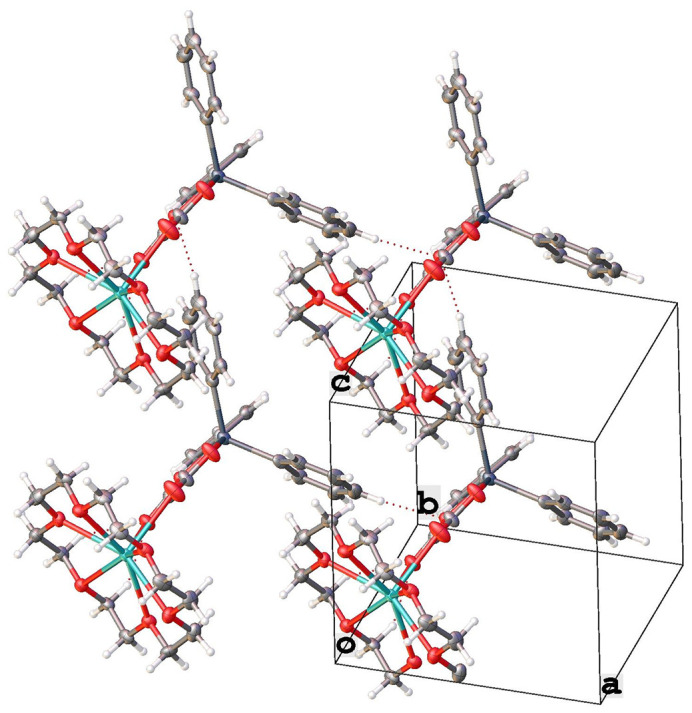
Crystal packing in the crystal structure showing C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, denoted by dashed lines, between neighboring molecules.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.360 (11) | 172 |
| C16—H16⋯O1ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.332 (9) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 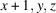 ; (ii)
; (ii) 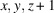 .
.
Figure 3.
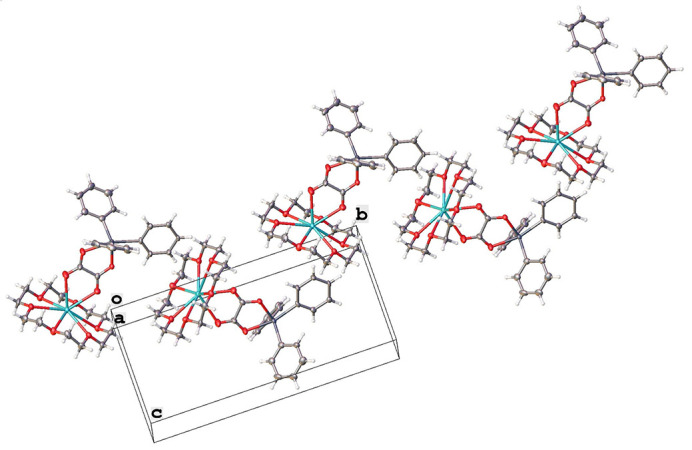
Partial packing plot of 1 along the b axis showing the 1-D chain formed through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding.
Figure 4.
Packing plot of 1 viewed approximately along [001] showing a layer of molecules perpendicular to the c axis.
In supramolecular chemistry, weak hydrogen bonds such as C—H⋯π and π–π interactions play significant roles in the structural integrity of crystal structures (Meyer et al., 2003 ▸; Nishio, 2004 ▸). The effectiveness of these interactions is primarily influenced by the distance between the hydrogen atom of the C—H bond and the plane of the aromatic ring, which should be less than 2.9 Å (the combined van der Waals radii), and the C—H⋯π access angles, ideally ranging from 140 to 180° (Takahashi et al., 2001 ▸).
In the crystal under investigation, relatively weak C—H⋯π interactions are observed. The analysis of these interactions reveals C—H⋯centroid phenyl distances of 2.936 and 2.937 Å (for H26A⋯C11) and distances of 2.937 and 2.949 Å (for H27B⋯C13). The corresponding access angles are 158° for C1 and 162° for C13. Despite the parallel alignment of phenyl groups (C7–C12) along the (101) direction, significant π–π interactions are absent. This is attributed to a large separation distance of 7.006 Å between the planes, which greatly exceeds the critical distance of 4 Å, and an inter-centroid distance of 9.406 Å, surpassing the 6 Å threshold (Ninković et al., 2011 ▸).
4. Database survey
A survey of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD; Groom et al., 2016 ▸; Conquest version 2024.1.0, Build 401958; Bruno et al., 2002 ▸) reveals thirteen reports of oxalatotriphenylstannate compounds with ammonium ions as counter-ions. Examples include di-iso-propylammonium (Ng & Hook, 1999 ▸), di-cyclo-hexylammonium (Ng & Rae, 2000 ▸), dibenzylammonium (Gueye et al., 2012 ▸), and di-iso-butylammonium (Thorpe et al., 2013 ▸). A further search for metal salts of triphenylstannate came out with one hit, in which a sodium salt of triphenylstannate named sodium bis[2-(3′,6′,9′-trioxadecyl)-1,2-dicarba-closododecaboane-1-carboxylato]triphenylstannate was reported (Bregadze et al., 2004 ▸). In this reported stannate, the sodium ion is stabilized by coordination to the carbonyl oxygen and five oxygen atoms of trioxadecyl substituents. In contrast, in the title compound 1, the potassium salt of triphenylstannate is described for the first time, where the potassium ion is primarily stabilized through coordination to 18-crown-6.
5. Synthesis and crystallization
The title coordination complex of triphenyltin was synthesized by reacting 1 mmol of oxalic acid, 1 mmol of potassium bicarbonate, 1 mmol of 18-crown-6, and 1 mmol of triphenyltin hydroxide in 30 mL of ethanol. The mixture was refluxed at 373 K with stirring for 1 h. The resulting solution, which was slightly cloudy, was filtered to yield a clear ethanol solution. This filtrate was then allowed to evaporate slowly at 300 K over the course of one week, resulting in colorless crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The H atoms in compound 1 were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H distances of 0.93 Å (ring H atoms) and 0.97 Å (methylene H atoms), and N—H distances of 0.98 Å, with Uiso(H) values of 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms. Reflections were merged by SHELXL according to the crystal class for the calculation of statistics and refinement. The Friedel fraction is defined as the number of unique Friedel pairs measured divided by the number that would be possible theoretically, ignoring centric projections and systematic absences. Ther crystal studied was refined as a two-component twin. Completeness statistics refer to single and composite reflections containing twin component 1 only.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [KSn(C6H5)3(C2O4)(C12H24O6)] |
| M r | 741.42 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.4060 (3), 19.3779 (4), 9.4225 (3) |
| β (°) | 97.925 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 1701.02 (8) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.93 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.06 × 0.06 × 0.03 × 0.02 (radius) |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S dual wavelength Mo/Cu |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2022 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.913, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 15412, 7113, 6792 |
| R int | 0.040 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.033, 0.105, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 7113 |
| No. of parameters | 398 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.28, −0.52 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 2807 quotients [(I+)−(I−)]/[(I+)+(I−)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.08 (3) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007Isup3.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007Isup4.hkl
CCDC reference: 2375984
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Crystal data
| [KSn(C6H5)3(C2O4)(C12H24O6)] | F(000) = 760 |
| Mr = 741.42 | Dx = 1.448 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.4060 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 9822 reflections |
| b = 19.3779 (4) Å | θ = 2.9–31.1° |
| c = 9.4225 (3) Å | µ = 0.93 mm−1 |
| β = 97.925 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1701.02 (8) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.06 × 0.06 × 0.03 × 0.02 (radius) mm |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Data collection
| Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S dual wavelength Mo/Cu diffractometer | 7113 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus sealed X-ray tube, Rigaku PhotonJet-S | 6792 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror optics monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −12→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2022) | k = −23→25 |
| Tmin = 0.913, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −11→10 |
| 15412 measured reflections |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0708P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.08 | Δρmax = 1.28 e Å−3 |
| 7113 reflections | Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3 |
| 398 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 2807 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: −0.08 (3) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Sn1 | 0.41008 (5) | 0.58376 (2) | 0.45935 (5) | 0.02209 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.2517 (6) | 0.5552 (3) | 0.2950 (6) | 0.0223 (10) | |
| O2 | 0.3969 (8) | 0.4658 (3) | 0.4651 (8) | 0.0369 (16) | |
| O3 | 0.2847 (9) | 0.3760 (4) | 0.3470 (9) | 0.0484 (19) | |
| O4 | 0.1482 (7) | 0.4720 (3) | 0.1562 (7) | 0.0312 (14) | |
| C1 | 0.6233 (8) | 0.5741 (5) | 0.4077 (8) | 0.0256 (19) | |
| C2 | 0.7115 (10) | 0.5176 (4) | 0.4492 (9) | 0.0306 (18) | |
| H2 | 0.677139 | 0.480378 | 0.500564 | 0.037* | |
| C3 | 0.8536 (11) | 0.5166 (5) | 0.4135 (11) | 0.039 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.913985 | 0.478341 | 0.441871 | 0.047* | |
| C4 | 0.9046 (10) | 0.5691 (5) | 0.3399 (10) | 0.040 (3) | |
| H4 | 1.000617 | 0.568146 | 0.319164 | 0.048* | |
| C5 | 0.8163 (11) | 0.6238 (5) | 0.2954 (12) | 0.038 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.850759 | 0.659627 | 0.240293 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.6788 (9) | 0.6274 (4) | 0.3295 (10) | 0.0280 (17) | |
| H6 | 0.620610 | 0.666331 | 0.300060 | 0.034* | |
| C7 | 0.3592 (8) | 0.6911 (4) | 0.4013 (9) | 0.0211 (15) | |
| C8 | 0.4450 (8) | 0.7424 (4) | 0.4748 (8) | 0.0237 (15) | |
| H8 | 0.519593 | 0.729495 | 0.548454 | 0.028* | |
| C9 | 0.4225 (8) | 0.8126 (4) | 0.4413 (8) | 0.0232 (14) | |
| H9 | 0.480264 | 0.846932 | 0.492962 | 0.028* | |
| C10 | 0.3137 (8) | 0.8314 (4) | 0.3306 (8) | 0.0225 (15) | |
| H10 | 0.298609 | 0.878641 | 0.305833 | 0.027* | |
| C11 | 0.2278 (9) | 0.7806 (4) | 0.2571 (9) | 0.0265 (16) | |
| H11 | 0.152693 | 0.793270 | 0.183718 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 0.2525 (9) | 0.7106 (4) | 0.2917 (9) | 0.0246 (16) | |
| H12 | 0.195505 | 0.676187 | 0.239377 | 0.030* | |
| C13 | 0.3708 (7) | 0.5795 (7) | 0.6773 (8) | 0.0273 (15) | |
| C14 | 0.2974 (10) | 0.6343 (5) | 0.7297 (9) | 0.0282 (17) | |
| H14 | 0.262058 | 0.670815 | 0.667257 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 0.2754 (11) | 0.6360 (5) | 0.8732 (11) | 0.038 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.226304 | 0.673758 | 0.908593 | 0.046* | |
| C16 | 0.3256 (8) | 0.5824 (8) | 0.9638 (8) | 0.0354 (17) | |
| H16 | 0.310981 | 0.583366 | 1.061508 | 0.042* | |
| C17 | 0.3963 (10) | 0.5280 (6) | 0.9124 (10) | 0.038 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.429710 | 0.491448 | 0.975628 | 0.045* | |
| C18 | 0.4207 (9) | 0.5247 (5) | 0.7686 (9) | 0.0307 (18) | |
| H18 | 0.469574 | 0.486627 | 0.734140 | 0.037* | |
| C19 | 0.2277 (8) | 0.4908 (4) | 0.2599 (9) | 0.0227 (15) | |
| C20 | 0.3101 (10) | 0.4379 (4) | 0.3672 (10) | 0.0287 (16) | |
| K1 | 0.10867 (17) | 0.33895 (8) | 0.09631 (17) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| O5 | −0.0911 (6) | 0.4275 (3) | −0.0971 (6) | 0.0229 (11) | |
| O6 | −0.1562 (6) | 0.3828 (3) | 0.1682 (6) | 0.0248 (12) | |
| O7 | −0.0356 (7) | 0.2587 (4) | 0.2852 (7) | 0.0275 (15) | |
| O8 | 0.2230 (7) | 0.2108 (3) | 0.2005 (7) | 0.0292 (12) | |
| O9 | 0.2918 (8) | 0.2593 (4) | −0.0621 (8) | 0.0294 (16) | |
| O10 | 0.1753 (6) | 0.3845 (3) | −0.1714 (6) | 0.0250 (12) | |
| C21 | −0.1744 (9) | 0.4682 (4) | −0.0123 (9) | 0.0258 (16) | |
| H21A | −0.241853 | 0.497889 | −0.075143 | 0.031* | |
| H21B | −0.110542 | 0.498315 | 0.053253 | 0.031* | |
| C22 | −0.2558 (11) | 0.4209 (6) | 0.0720 (11) | 0.029 (2) | |
| H22A | −0.319867 | 0.447871 | 0.126044 | 0.035* | |
| H22B | −0.315664 | 0.389015 | 0.006764 | 0.035* | |
| C23 | −0.2230 (12) | 0.3420 (6) | 0.2648 (12) | 0.035 (2) | |
| H23A | −0.286849 | 0.307414 | 0.211248 | 0.042* | |
| H23B | −0.281701 | 0.371518 | 0.319785 | 0.042* | |
| C24 | −0.1089 (10) | 0.3064 (4) | 0.3645 (9) | 0.0276 (17) | |
| H24A | −0.040179 | 0.340835 | 0.411697 | 0.033* | |
| H24B | −0.152538 | 0.281731 | 0.439726 | 0.033* | |
| C25 | 0.0662 (11) | 0.2172 (5) | 0.3752 (10) | 0.035 (2) | |
| H25A | 0.016438 | 0.190038 | 0.442444 | 0.042* | |
| H25B | 0.137948 | 0.247248 | 0.431986 | 0.042* | |
| C26 | 0.1389 (11) | 0.1701 (4) | 0.2836 (10) | 0.0339 (19) | |
| H26A | 0.201246 | 0.137366 | 0.344216 | 0.041* | |
| H26B | 0.066709 | 0.143313 | 0.219869 | 0.041* | |
| C27 | 0.2983 (11) | 0.1707 (5) | 0.1108 (11) | 0.039 (2) | |
| H27A | 0.229728 | 0.144494 | 0.041901 | 0.047* | |
| H27B | 0.361344 | 0.137377 | 0.168962 | 0.047* | |
| C28 | 0.3872 (10) | 0.2180 (5) | 0.0311 (11) | 0.036 (2) | |
| H28A | 0.449335 | 0.247442 | 0.099552 | 0.044* | |
| H28B | 0.449059 | 0.190529 | −0.024455 | 0.044* | |
| C29 | 0.3694 (10) | 0.3065 (5) | −0.1418 (11) | 0.035 (2) | |
| H29A | 0.439272 | 0.280956 | −0.191382 | 0.043* | |
| H29B | 0.422566 | 0.340498 | −0.076177 | 0.043* | |
| C30 | 0.2618 (11) | 0.3427 (5) | −0.2491 (10) | 0.032 (2) | |
| H30A | 0.311547 | 0.371631 | −0.313522 | 0.038* | |
| H30B | 0.201563 | 0.308548 | −0.307951 | 0.038* | |
| C31 | 0.0763 (10) | 0.4239 (5) | −0.2660 (10) | 0.027 (2) | |
| H31A | 0.010250 | 0.392884 | −0.326933 | 0.032* | |
| H31B | 0.128454 | 0.452511 | −0.329063 | 0.032* | |
| C32 | −0.0073 (9) | 0.4696 (4) | −0.1780 (8) | 0.0253 (16) | |
| H32A | 0.059398 | 0.498412 | −0.112634 | 0.030* | |
| H32B | −0.070902 | 0.500531 | −0.241853 | 0.030* |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Sn1 | 0.0258 (2) | 0.01459 (18) | 0.0242 (2) | 0.0024 (3) | −0.00227 (13) | 0.0011 (3) |
| O1 | 0.026 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.024 (3) | 0.002 (2) | −0.0018 (19) | 0.001 (2) |
| O2 | 0.045 (4) | 0.016 (3) | 0.043 (4) | −0.001 (3) | −0.018 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| O3 | 0.061 (5) | 0.022 (3) | 0.053 (5) | −0.004 (3) | −0.024 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| O4 | 0.034 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.031 (3) | −0.003 (2) | −0.007 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C1 | 0.027 (3) | 0.021 (5) | 0.027 (3) | 0.014 (3) | −0.005 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.038 (5) | 0.020 (4) | 0.030 (5) | 0.006 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C3 | 0.036 (5) | 0.034 (5) | 0.043 (5) | 0.023 (4) | −0.008 (4) | −0.012 (4) |
| C4 | 0.030 (4) | 0.046 (8) | 0.044 (5) | 0.001 (4) | 0.005 (3) | −0.022 (5) |
| C5 | 0.039 (5) | 0.032 (5) | 0.043 (6) | 0.002 (4) | 0.013 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
| C6 | 0.028 (4) | 0.020 (4) | 0.035 (5) | 0.012 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C7 | 0.022 (4) | 0.012 (3) | 0.030 (5) | 0.002 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C8 | 0.024 (4) | 0.023 (4) | 0.024 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C9 | 0.028 (4) | 0.020 (3) | 0.023 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C10 | 0.032 (4) | 0.008 (3) | 0.027 (4) | 0.002 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C11 | 0.035 (4) | 0.018 (3) | 0.024 (4) | 0.002 (3) | −0.008 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C12 | 0.030 (4) | 0.013 (4) | 0.028 (5) | 0.004 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C13 | 0.026 (3) | 0.028 (4) | 0.027 (3) | −0.005 (5) | −0.001 (2) | 0.001 (5) |
| C14 | 0.038 (5) | 0.022 (4) | 0.023 (4) | −0.004 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C15 | 0.039 (5) | 0.040 (5) | 0.038 (5) | −0.010 (4) | 0.012 (4) | −0.005 (4) |
| C16 | 0.039 (4) | 0.034 (4) | 0.032 (4) | −0.016 (6) | 0.004 (3) | 0.009 (6) |
| C17 | 0.038 (5) | 0.041 (5) | 0.030 (4) | −0.015 (4) | −0.006 (3) | 0.017 (4) |
| C18 | 0.027 (4) | 0.029 (4) | 0.035 (5) | −0.008 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.000 (4) |
| C19 | 0.021 (4) | 0.020 (4) | 0.027 (4) | 0.001 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C20 | 0.032 (5) | 0.020 (4) | 0.029 (5) | −0.001 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| K1 | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0168 (7) | 0.0240 (8) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0001 (5) | −0.0004 (5) |
| O5 | 0.026 (3) | 0.017 (2) | 0.026 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.0027 (19) | −0.0001 (19) |
| O6 | 0.022 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| O7 | 0.033 (4) | 0.026 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.001 (3) |
| O8 | 0.039 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.000 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| O9 | 0.026 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.037 (4) | 0.004 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| O10 | 0.030 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C21 | 0.023 (4) | 0.021 (4) | 0.031 (4) | 0.009 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C22 | 0.027 (5) | 0.032 (5) | 0.029 (5) | 0.000 (4) | 0.006 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C23 | 0.039 (5) | 0.028 (5) | 0.042 (5) | −0.007 (4) | 0.018 (4) | −0.001 (4) |
| C24 | 0.041 (5) | 0.015 (4) | 0.027 (4) | −0.006 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C25 | 0.048 (5) | 0.031 (4) | 0.025 (4) | −0.002 (4) | 0.001 (4) | 0.012 (4) |
| C26 | 0.045 (5) | 0.018 (4) | 0.035 (5) | 0.003 (4) | −0.005 (4) | 0.011 (3) |
| C27 | 0.047 (6) | 0.029 (5) | 0.040 (5) | 0.014 (4) | −0.004 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C28 | 0.028 (4) | 0.030 (4) | 0.049 (6) | 0.014 (4) | 0.001 (4) | 0.003 (4) |
| C29 | 0.029 (4) | 0.025 (4) | 0.054 (6) | 0.000 (4) | 0.011 (4) | −0.005 (4) |
| C30 | 0.041 (5) | 0.031 (5) | 0.025 (4) | 0.005 (4) | 0.013 (4) | −0.003 (4) |
| C31 | 0.032 (5) | 0.019 (4) | 0.027 (5) | −0.007 (3) | 0.000 (4) | 0.001 (3) |
| C32 | 0.028 (4) | 0.026 (4) | 0.020 (4) | −0.003 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Sn1—O1 | 2.071 (5) | K1—O7 | 2.845 (7) |
| Sn1—O2 | 2.290 (6) | K1—O8 | 2.827 (6) |
| Sn1—C1 | 2.136 (7) | K1—O9 | 2.878 (7) |
| Sn1—C7 | 2.188 (7) | K1—O10 | 2.823 (6) |
| Sn1—C13 | 2.138 (7) | O5—C21 | 1.430 (9) |
| O1—C19 | 1.303 (10) | O5—C32 | 1.425 (9) |
| O2—C20 | 1.266 (11) | O6—C22 | 1.418 (12) |
| O3—C20 | 1.233 (11) | O6—C23 | 1.417 (11) |
| O3—K1 | 2.785 (7) | O7—C24 | 1.426 (10) |
| O4—C19 | 1.202 (10) | O7—C25 | 1.435 (11) |
| O4—K1 | 2.654 (6) | O8—C26 | 1.425 (11) |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (12) | O8—C27 | 1.408 (11) |
| C1—C6 | 1.411 (13) | O9—C28 | 1.415 (11) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | O9—C29 | 1.443 (12) |
| C2—C3 | 1.422 (14) | O10—C30 | 1.421 (11) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | O10—C31 | 1.419 (11) |
| C3—C4 | 1.356 (15) | C21—H21A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C21—H21B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (14) | C21—C22 | 1.493 (13) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C22—H22A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.377 (13) | C22—H22B | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C23—H23A | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.401 (11) | C23—H23B | 0.9900 |
| C7—C12 | 1.389 (11) | C23—C24 | 1.494 (14) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C24—H24A | 0.9900 |
| C8—C9 | 1.406 (10) | C24—H24B | 0.9900 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C25—H25A | 0.9900 |
| C9—C10 | 1.405 (11) | C25—H25B | 0.9900 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9500 | C25—C26 | 1.486 (13) |
| C10—C11 | 1.396 (11) | C26—H26A | 0.9900 |
| C11—H11 | 0.9500 | C26—H26B | 0.9900 |
| C11—C12 | 1.407 (10) | C27—H27A | 0.9900 |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C27—H27B | 0.9900 |
| C13—C14 | 1.394 (15) | C27—C28 | 1.508 (15) |
| C13—C18 | 1.406 (14) | C28—H28A | 0.9900 |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C28—H28B | 0.9900 |
| C14—C15 | 1.396 (13) | C29—H29A | 0.9900 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9500 | C29—H29B | 0.9900 |
| C15—C16 | 1.385 (16) | C29—C30 | 1.502 (14) |
| C16—H16 | 0.9500 | C30—H30A | 0.9900 |
| C16—C17 | 1.370 (18) | C30—H30B | 0.9900 |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | C31—H31A | 0.9900 |
| C17—C18 | 1.407 (13) | C31—H31B | 0.9900 |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C31—C32 | 1.506 (13) |
| C19—C20 | 1.567 (11) | C32—H32A | 0.9900 |
| K1—O5 | 2.976 (6) | C32—H32B | 0.9900 |
| K1—O6 | 2.802 (6) | ||
| O1—Sn1—O2 | 73.4 (2) | O8—K1—O9 | 58.88 (19) |
| O1—Sn1—C1 | 114.0 (3) | O9—K1—O5 | 111.35 (18) |
| O1—Sn1—C7 | 87.6 (3) | O10—K1—O5 | 58.09 (15) |
| O1—Sn1—C13 | 120.4 (3) | O10—K1—O7 | 156.01 (19) |
| C1—Sn1—O2 | 88.5 (3) | O10—K1—O8 | 117.67 (18) |
| C1—Sn1—C7 | 101.9 (3) | O10—K1—O9 | 58.80 (19) |
| C1—Sn1—C13 | 120.5 (3) | C21—O5—K1 | 108.9 (4) |
| C7—Sn1—O2 | 160.8 (3) | C32—O5—K1 | 108.0 (4) |
| C13—Sn1—O2 | 85.5 (4) | C32—O5—C21 | 111.7 (6) |
| C13—Sn1—C7 | 102.5 (4) | C22—O6—K1 | 122.3 (5) |
| C19—O1—Sn1 | 121.9 (5) | C23—O6—K1 | 118.3 (6) |
| C20—O2—Sn1 | 116.1 (5) | C23—O6—C22 | 112.9 (7) |
| C20—O3—K1 | 117.5 (6) | C24—O7—K1 | 106.3 (5) |
| C19—O4—K1 | 121.4 (5) | C24—O7—C25 | 112.6 (7) |
| C2—C1—Sn1 | 123.1 (7) | C25—O7—K1 | 109.8 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.1 (7) | C26—O8—K1 | 117.6 (5) |
| C6—C1—Sn1 | 118.8 (6) | C27—O8—K1 | 118.3 (5) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C27—O8—C26 | 112.8 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.1 (8) | C28—O9—K1 | 110.8 (5) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C28—O9—C29 | 111.0 (7) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C29—O9—K1 | 108.2 (5) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.4 (8) | C30—O10—K1 | 119.7 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C31—O10—K1 | 121.5 (5) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C31—O10—C30 | 110.8 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.5 (9) | O5—C21—H21A | 110.0 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 | O5—C21—H21B | 110.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | O5—C21—C22 | 108.6 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.0 (9) | H21A—C21—H21B | 108.3 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C22—C21—H21A | 110.0 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.6 | C22—C21—H21B | 110.0 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.8 (8) | O6—C22—C21 | 108.5 (7) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.6 | O6—C22—H22A | 110.0 |
| C8—C7—Sn1 | 117.3 (5) | O6—C22—H22B | 110.0 |
| C12—C7—Sn1 | 123.7 (6) | C21—C22—H22A | 110.0 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 118.9 (7) | C21—C22—H22B | 110.0 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 108.4 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.1 (7) | O6—C23—H23A | 110.0 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 | O6—C23—H23B | 110.0 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 | O6—C23—C24 | 108.5 (8) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.3 (7) | H23A—C23—H23B | 108.4 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 | C24—C23—H23A | 110.0 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 | C24—C23—H23B | 110.0 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.8 (7) | O7—C24—C23 | 109.1 (7) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 | O7—C24—H24A | 109.9 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 | O7—C24—H24B | 109.9 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.0 (7) | C23—C24—H24A | 109.9 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 | C23—C24—H24B | 109.9 |
| C7—C12—C11 | 120.9 (8) | H24A—C24—H24B | 108.3 |
| C7—C12—H12 | 119.6 | O7—C25—H25A | 109.9 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 | O7—C25—H25B | 109.9 |
| C14—C13—Sn1 | 118.1 (7) | O7—C25—C26 | 108.9 (7) |
| C14—C13—C18 | 119.9 (7) | H25A—C25—H25B | 108.3 |
| C18—C13—Sn1 | 122.0 (7) | C26—C25—H25A | 109.9 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 | C26—C25—H25B | 109.9 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.5 (8) | O8—C26—C25 | 108.3 (7) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.8 | O8—C26—H26A | 110.0 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.1 | O8—C26—H26B | 110.0 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 119.7 (9) | C25—C26—H26A | 110.0 |
| C16—C15—H15 | 120.1 | C25—C26—H26B | 110.0 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 | H26A—C26—H26B | 108.4 |
| C17—C16—C15 | 120.0 (8) | O8—C27—H27A | 109.9 |
| C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 | O8—C27—H27B | 109.9 |
| C16—C17—H17 | 119.1 | O8—C27—C28 | 108.8 (8) |
| C16—C17—C18 | 121.7 (9) | H27A—C27—H27B | 108.3 |
| C18—C17—H17 | 119.1 | C28—C27—H27A | 109.9 |
| C13—C18—C17 | 118.1 (9) | C28—C27—H27B | 109.9 |
| C13—C18—H18 | 121.0 | O9—C28—C27 | 107.8 (8) |
| C17—C18—H18 | 121.0 | O9—C28—H28A | 110.1 |
| O1—C19—C20 | 114.2 (7) | O9—C28—H28B | 110.1 |
| O4—C19—O1 | 124.3 (8) | C27—C28—H28A | 110.1 |
| O4—C19—C20 | 121.5 (8) | C27—C28—H28B | 110.1 |
| O2—C20—C19 | 113.8 (7) | H28A—C28—H28B | 108.5 |
| O3—C20—O2 | 128.3 (8) | O9—C29—H29A | 110.2 |
| O3—C20—C19 | 117.9 (8) | O9—C29—H29B | 110.2 |
| O3—K1—O5 | 128.47 (19) | O9—C29—C30 | 107.7 (8) |
| O3—K1—O6 | 99.3 (2) | H29A—C29—H29B | 108.5 |
| O3—K1—O7 | 83.7 (2) | C30—C29—H29A | 110.2 |
| O3—K1—O8 | 77.22 (19) | C30—C29—H29B | 110.2 |
| O3—K1—O9 | 104.4 (2) | O10—C30—C29 | 107.5 (7) |
| O3—K1—O10 | 119.8 (2) | O10—C30—H30A | 110.2 |
| O4—K1—O3 | 61.30 (19) | O10—C30—H30B | 110.2 |
| O4—K1—O5 | 68.16 (17) | C29—C30—H30A | 110.2 |
| O4—K1—O6 | 75.94 (18) | C29—C30—H30B | 110.2 |
| O4—K1—O7 | 117.6 (2) | H30A—C30—H30B | 108.5 |
| O4—K1—O8 | 138.06 (19) | O10—C31—H31A | 110.0 |
| O4—K1—O9 | 123.7 (2) | O10—C31—H31B | 110.0 |
| O4—K1—O10 | 81.05 (18) | O10—C31—C32 | 108.5 (7) |
| O6—K1—O5 | 57.71 (16) | H31A—C31—H31B | 108.4 |
| O6—K1—O7 | 59.86 (18) | C32—C31—H31A | 110.0 |
| O6—K1—O8 | 119.38 (18) | C32—C31—H31B | 110.0 |
| O6—K1—O9 | 154.6 (2) | O5—C32—C31 | 109.2 (6) |
| O6—K1—O10 | 115.80 (18) | O5—C32—H32A | 109.8 |
| O7—K1—O5 | 112.53 (18) | O5—C32—H32B | 109.8 |
| O7—K1—O9 | 113.74 (19) | C31—C32—H32A | 109.8 |
| O8—K1—O5 | 153.77 (17) | C31—C32—H32B | 109.8 |
| O8—K1—O7 | 59.61 (19) | H32A—C32—H32B | 108.3 |
| Sn1—O1—C19—O4 | −171.7 (6) | K1—O3—C20—C19 | 6.8 (13) |
| Sn1—O1—C19—C20 | 9.4 (10) | K1—O4—C19—O1 | 179.9 (6) |
| Sn1—O2—C20—O3 | 179.5 (10) | K1—O4—C19—C20 | −1.3 (11) |
| Sn1—O2—C20—C19 | 0.0 (11) | K1—O5—C21—C22 | −59.3 (7) |
| Sn1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.2 (6) | K1—O5—C32—C31 | 60.9 (7) |
| Sn1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.2 (7) | K1—O6—C22—C21 | −35.7 (10) |
| Sn1—C7—C8—C9 | 178.1 (5) | K1—O6—C23—C24 | 29.9 (9) |
| Sn1—C7—C12—C11 | −178.2 (7) | K1—O7—C24—C23 | 65.7 (7) |
| Sn1—C13—C14—C15 | −176.6 (7) | K1—O7—C25—C26 | −60.8 (8) |
| Sn1—C13—C18—C17 | 176.8 (6) | K1—O8—C26—C25 | −37.5 (9) |
| O1—C19—C20—O2 | −5.7 (12) | K1—O8—C27—C28 | 38.8 (9) |
| O1—C19—C20—O3 | 174.8 (9) | K1—O9—C28—C27 | 59.3 (8) |
| O4—C19—C20—O2 | 175.4 (9) | K1—O9—C29—C30 | −64.4 (8) |
| O4—C19—C20—O3 | −4.2 (14) | K1—O10—C30—C29 | −34.4 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (13) | K1—O10—C31—C32 | 33.9 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.1 (13) | O5—C21—C22—O6 | 63.9 (9) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.7 (14) | O6—C23—C24—O7 | −65.8 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.7 (15) | O7—C25—C26—O8 | 66.3 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.8 (14) | O8—C27—C28—O9 | −66.0 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.1 (12) | O9—C29—C30—O10 | 66.4 (9) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −1.1 (11) | O10—C31—C32—O5 | −64.5 (8) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.7 (13) | C21—O5—C32—C31 | −179.4 (7) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.1 (11) | C22—O6—C23—C24 | −177.8 (7) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.5 (13) | C23—O6—C22—C21 | 173.2 (8) |
| C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.8 (14) | C24—O7—C25—C26 | −179.0 (7) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 1.4 (12) | C25—O7—C24—C23 | −174.0 (7) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.7 (14) | C26—O8—C27—C28 | −178.2 (8) |
| C14—C13—C18—C17 | −1.0 (12) | C27—O8—C26—C25 | 179.2 (8) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.1 (14) | C28—O9—C29—C30 | 173.8 (7) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.3 (14) | C29—O9—C28—C27 | 179.6 (8) |
| C16—C17—C18—C13 | 0.2 (13) | C30—O10—C31—C32 | −177.4 (7) |
| C18—C13—C14—C15 | 1.3 (13) | C31—O10—C30—C29 | 176.3 (7) |
| K1—O3—C20—O2 | −172.6 (9) | C32—O5—C21—C22 | −178.5 (7) |
(1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaoxacyclooctadecane-1κ6O)(µ-oxalato-1κ2O1,O2:2κ2O1',O2')triphenyl-2κ3C-potassium(I)tin(IV) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O1i | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.360 (11) | 172 |
| C16—H16···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.332 (9) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x, y, z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by National Science Foundation grant 2117621 to Xueqing Song and Feddie Dixon; National Science Foundation grant 1622811 to Freddie Dixon; National Science Foundation grant 1833656 to Xueqing Song.
References
- Angham, G. H., Khudheir, J., Dina, S. A. & Emad, Y. (2019). Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 10, 26–31.
- Bajaj, A. V. & Poonia, N. S. (1988). Coord. Chem. Rev.87, 55–213.
- Blunden, S. J., Cusack, P. & Hill, R. (1985). The Industrial Uses of Tin Chemicals. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
- Braga, D., Curzi, M., Lusi, M. & Grepioni, F. (2005). CrystEngComm, 7, 276–278.
- Braga, D., d’Agostino, S., Polito, M., Rubini, K. & Grepioni, F. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 1994–2002.
- Braga, D., Gandolfi, M., Lusi, M., Polito, M., Rubini, K. & Grepioni, F. (2007). Cryst. Growth Des.7, 919–924.
- Braga, D., Modena, E., Polito, M., Rubini, K. & Grepioni, F. (2008). New J. Chem.32, 1718–1724.
- Bregadze, V. I., Glazun, S. A., Petrovskii, P. V., Starikova, Z. A., Buyanovskaya, A. G., Takazova, R. U., Gielen, M., de Vos, D., Kemmer, M., Biesemans, M. & Willem, R. (2004). Appl. Organom Chem.18, 191–194.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Edgington, P. R., Kessler, M., Macrae, C. F., McCabe, P., Pearson, J. & Taylor, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 389–397. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Davies, A. G. & Smith, P. J. (1980). Adv. Inorg. Chem. Radiochem.23, 1–77.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
- Evans, C. J. & Karpel, S. (1985). J. Organomet. Chem. 16.
- Gjikaj, M., Adam, A., Duewel, M. & Brockner, W. (2005). Z. Kristallogr.220, 67–68.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gueye, N., Diop, L., Molloy, K. C. & Kociok-Köhn, G. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, m854–m855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hay, B. P. & Rustad, J. R. (1994). J. Am. Chem. Soc.116, 6316–6326.
- Izatt, R. M. (2017). Chem. Soc. Rev.46, 2380–2384. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurty, K. V. & Harris, G. M. (1961). Chem. Rev.61, 213–246.
- Lee, H. S., Yang, X. Q., McBreen, J., Choi, L. S. & Okamoto, Y. J. (1996). J. Electrochem. Soc.143, 3825–3829.
- Lehn, J. M. (1988). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.27, 89–112.
- Liebing, P., Zaeni, A., Olbrich, F. & Edelmann, F. T. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 1757–1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E. A., Castellano, R. K. & Diederich, F. (2003). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.42, 1210–1250. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ng, S. W. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 2990–2992.
- Ng, S. W. & Hook, J. M. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 310–312.
- Ng, S. W. & Kumar Das, V. G. (1993). J. Organomet. Chem.456, 175–179.
- Ng, S. W., Kumar Das, V. G., Gielen, M. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (1992). Appl. Organomet. Chem.6, 19–25.
- Ng, S. W. & Rae, A. D. (2000). Z. Kristallogr.215, 199–204.
- Ninković, D. B., Janjić, G. V., Veljković, D. Ž., Sredojević, D. N. & Zarić, S. D. (2011). ChemPhysChem, 12, 3511–3514. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M. (2004). CrystEngComm, 6, 130–158.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C. J. (1988). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.27, 1021–1027.
- Rao, C. N. R., Natarajan, S. & Vaidhyanathan, R. (2004). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.43, 1466–1496. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2022). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sellin, M. & Malischewski, M. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 1871–1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Smith, P. J. (1978). Toxicological Data on Organotin Compounds. ITRI Publication 538. London: International Tin Research Institute.
- Takahashi, O., Kohno, Y., Iwasaki, S., Saito, K., Iwaoka, M., Tomoda, S., Umezawa, Y., Tsuboyama, S. & Nishio, M. (2001). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 74, 2421–2430.
- Talebi, Z. A., Farhood, A. S. & Hadi, A. G. (2023). Int. J. Pharm. Bio Med. Sci.3, 181–184.
- Thayer, J. S. (1984). Organometallic Compounds and Living Organisms. Orlando: Academic Press.
- Thorpe, D., Callejas, A., Royzman, D., Pike, R. D., Eng, G. & Song, X. (2013). J. Coord. Chem.66, 3647–3659.
- Zuckermann, J. J. (1976). Adv. Chem. Series 157. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007Isup3.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024007758/ny2007Isup4.hkl
CCDC reference: 2375984
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report