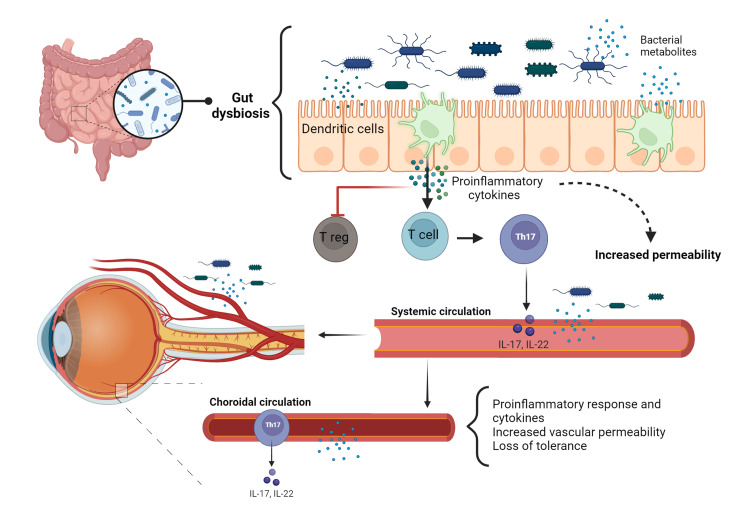
Figure 1. Mechanisms involved in the gut-eye axis.
Dysbiosis in the gut activates dendritic cells, which secretes proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, and IL-1B), leading to the activation of specific retina T cells as proinflammatory T cells (Th17) and the inhibition of T-regulatory. Once these T cells reach the eye, they begin the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, increased vascular permeability, loss of ocular microbiome tolerance, complement activation, and neovascularization. Also, TMAO, a metabolite produced by pathogen bacteria, is linked with the development of vascular conditions such as age-related macular degeneration; these bacteria and metabolites can travel through the systemic circulation and reach the eyes.
IL-6: interleukin-6, TNF-alpha: tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-1B: interleukin-1B, TMAO: trimethylamine oxide, IL-17: interleukin-17, IL-22: interleukin-22
Figure created with BioRender
All credits to Barbara Abreu Lopez