Abstract
Patient: Female, 23-year-old
Final Diagnosis: Pheochromocytoma
Symptoms: Headcahe
Clinical Procedure: —
Specialty: Endocrinology and Metabolic
Objective:
Challenging differential diagnosis
Background:
Pheochromocytoma, a rare catecholamine-secreting tumor, often presents with paroxysmal or sustained hypertension, tachycardia, headache, and diaphoresis. Timely diagnosis is essential to prevent adverse complications. Less common presentations include pheochromocytoma crisis, with severe neurological and cardiac complications.
Case Report:
We report a unique case of a 25-year-old woman who initially presented with pheochromocytoma-induced hypertensive encephalopathy and acute coronary syndrome. Echocardiography revealed takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy, and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Initial treatment focused on controlling her blood pressure and supporting cardiac function. Due to her recovering from immediate crisis and absence of further symptoms, the patient refused further follow-up. However, she eventually experienced another episode of hypertensive crisis 2 years later. Subsequent investigations with 24-h urine tests revealed elevated vanillylmandelic acid levels (7.93 mg/24 h), normetanephrine (2638.72 µg/24 h), and normetanephrine to creatinine ratio (3546.67) and normal urine metanephrine levels (195.92 µg/24 h) and metanephrine to creatinine ratio (263.33). Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen revealed a 4.3×3.1×4-cm mass in the right adrenal gland. A DOTATATE positron emission tomography scan revealed a 3.9×4.3×2.7-cm localized right adrenal pheochromocytoma. Biochemical testing and adrenal imaging revealed a previously undiagnosed pheochromocytoma. Following targeted medical therapy and right adrenalectomy, the patient achieved complete resolution of her hypertension and associated symptoms.
Conclusions:
Our case is a unique simultaneous presentation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy, highlighting the importance to consider pheochromocytoma in acute neurological and cardiac presentations, even in the absence of typical symptoms.
Key words: Endocrinology, Hypertensive Encephalopathy, Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy, Pheochromocytoma, Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Introduction
Pheochromocytoma is a “great masquerader” and is known for its protean manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic hypertension to organ failure. Patients can present with symptoms suggestive of accelerated hypertension or hypertensive encephalopathy, including migraines, seizures, visual impairment, transient ischemic attack, or stroke. A few patients can even be normotensive (5–15%) or rarely hypotensive [1,2]. These varying clinical features are due to the different forms and amounts of catecholamines secreted by tumors. The typical triad of headache, sweating, and palpitations is observed in only 25% of patients with pheochromocytoma [3–5]. However, pheochromocytoma mimic other disorders, such as headache syndromes, panic disorder, acute abdomen, sepsis, Takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy (TLC), pre-eclampsia, hypertensive crisis, and hypertensive encephalopathy, often leading to missed diagnosis for several years, as the clinical manifestations are diverse [3,4]. However, pheochromocytoma crisis presenting as TLC and hypertensive encephalopathy is rare [6].
Our case report highlights this diagnostic challenge, showcasing a 25-year-old woman who presented with these very concerns – a 2-year history of undiagnosed pheochromocytoma masquerading as a rare combination of TLC and hypertensive encephalopathy. We also explore the potential underlying mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for managing this uncommon presentation of combined TLC and hypertensive encephalopathy in patients with pheochromocytoma. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to cure this condition and prevent serious cardiovascular and neurological complications.
Case Report
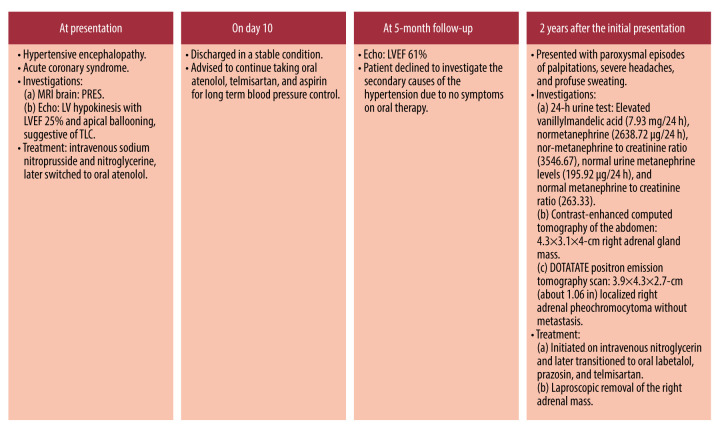
A 23-year-old woman presented with a headache, non-localizing neurological symptoms, including agitation, refusal to eat, acute confusional state, and concurrent chest pain, all of which had manifested over the course of 1 day. Upon examination, the patient was afebrile, conscious but confused, and did not follow verbal commands. Her Glasgow Coma Scale score was 13/15 (E4V4M5), pulse rate was 112 beats/min, and blood pressure was 210/114 mmHg. Pupillary reflexes were normal, and the rest of the physical examination, including funduscopy, was unremarkable. Her diagnostic workup was suggestive of acute coronary syndrome, as evidenced by elevated troponin I levels, coupled with sinus tachycardia and ST-segment depression in leads II, III, aVF, and V3-V6 on the electrocardiogram (EKG). The random blood glucose level was 92 mg/dL (Table 1). Because of the possibility of hypertensive encephalopathy, the patient was started on intravenous sodium nitroprusside and nitroglycerine until her blood pressure was controlled. Subsequently, intravenous antihypertensive medications were switched to oral atenolol. In the next 24 h, her blood pressure spikes normalized to 124/76 mmHg, and the sensorium gradually improved. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain revealed vasogenic edema, predominantly involving the watershed areas of the bilateral parieto-occipital lobes on T2-weighted images. This finding strongly supported the diagnosis of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)-type hypertensive encephalopathy. Echocardiography performed 5 days after admission demonstrated global left ventricular (LV) hypokinesia, with a severely depressed LV ejection fraction (LVEF) of 25% and apical ballooning, suggestive of TLC (Table 1). A thorough history review did not reveal any obvious stressors typically associated with the onset of TLC. The patient’s blood pressure normalized on treatment, and neurological symptoms resolved completely. After a 10-day hospital stay, she was discharged in a stable condition, with no residual neurologic deficit. She was advised to continue taking oral atenolol, telmisartan, and aspirin for long-term blood pressure control. Her LVEF demonstrated a significant improvement, rising to 34% after 1 month and normalizing at 5 months on follow-up echocardiography.
Table 1.
Investigation reports of prior hospitalization in the outside hospital.
| Investigation | Value/impression |
|---|---|
| Troponin I | 1.6 µg/L |
| MRI brain | Multiple T2/(FLAIR) hyperintense lesions involving the deep white matter of bilateral frontal and parietal lobe, suggestive of hypertensive encephalopathy |
| Electrocardiogram | Acute ischemic changes in the form of ST-segment depression and T-wave inversion, non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction |
| Echocardiography (on day 5 of admission) | Global LV hypokinesia with apical ballooning. LVEF of 25% and mild mitral regurgitation |
| Echocardiography (after 1 month) | Global LV hypokinesia, no apical ballooning. Significant improvement in LVEF (34%) |
| Echocardiography (after 5 months) | Normal LVEF (61%) and no diastolic dysfunction |
FLAIR – fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; LV – left ventricle; EF – ejection fraction.
In view of hypertensive encephalopathy and TLC, initial attention was turned to urgently treat the patient. Subsequently, the patient was advised to follow up for investigate potential secondary causes of hypertension as an outpatient; however, the patient declined further evaluations due to the absence of symptoms on oral therapy.
Two years after her initial presentation, the patient presented to our institute with paroxysmal episodes of palpitations, severe headaches, and profuse sweating for the past month. Notably, she denied any history of fever, visual disturbances, seizures, neck swelling, or menstrual irregularities. On admission, her pulse rate was 96 beats/min and blood pressure was 260/170 mmHg in the supine position and 190/110 mmHg in the sitting position. The rest of the systemic examinations, including the fundus examination, were normal. The laboratory investigations are shown in Table 2. Urine pregnancy test results were negative. The patient was treated with intravenous nitroglycerin until her blood pressure was controlled and was later transitioned to oral labetalol, prazosin, and telmisartan. While initial investigations for secondary causes of hypertension, including serum electrolytes, thyroid function tests, and morning fasting serum cortisol levels, were within the normal range, a 24-h urine test provided a critical clue. As shown in Table 2, her 24-h urine tests revealed elevated levels of vanillylmandelic acid (7.93 mg/24 h; reference range: <6.8 mg/24 h), elevated normetanephrine (2638.72 µg/24 h; reference range: <600 µg/24 h), elevated normetanephrine to creatinine ratio (3546.67), normal urine metanephrine level (195.92 µg/24 h), and normal metanephrine to creatinine ratio (263.33). Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen revealed a 4.3×3.1×4-cm mass in the right adrenal gland (Figure 1). A DOTATATE positron emission tomography scan revealed an intense tracer uptake in a heterogeneously enhancing soft tissue lesion (3.9×4.3×2.7 cm), suggestive of localized right adrenal pheochromocytoma, and confirmed the absence of metastatic disease. Echocardiography revealed a normal LVEF and functioning heart valves. A stress thallium study of the heart was also normal. After a multidisciplinary team discussion, the patient underwent laparoscopic removal of the right adrenal mass. The intraoperative blood pressure was elevated to a maximum of 170/100 mmHg, which was successfully managed with intravenous phenoxybenzamine and nitroglycerine. Histopathological examination of the removed mass confirmed the suspected diagnosis – a benign pheochromocytoma. The patient remained stable postoperatively, and 2 weeks later, she was discharged from the hospital, no longer requiring any antihypertensive medications. Follow-up appointments over the past 2 years have consistently shown normal blood pressure readings, indicating a complete resolution of her condition (Figure 2).
Table 2.
Comprehensive list of laboratory investigations done in the patient at our hospital.
| Investigation | Value |
|---|---|
| Serum sodium | 140.3 mmol/L |
| Serum potassium | 4.25 mmol/L |
| Serum cortisol (PM) | 163.9 nmol/L (normal 171–536 nmol/L) |
| Serum cortisol (AM) | 364.3 nmol/L |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone | 23.41 pg/mL |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate | 74.76 µg/dL |
| Luteinizing hormone | 4.65 mIU/mL |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | 4.68 mIU/mL |
| Prolactin | 12.61 ng/mL |
| Parathyroid hormone | 93.10 pg/mL (reference range 15–65 pg/mL) |
| Calcifediol-25(OH)D3 | 6.67 ng/mL (reference range 11.1–42.9 ng/mL) |
| 24-h urine metanephrine | 195.92 µg/24 h (reference range <350 µg/24 h) |
| 24-h urine nor-metanephrines | 2638.72 µg/24 h (reference range <600 µg/24 h) |
| 24-h urine protein | 216 mg/TV (reference range 0–150 mg/TV) |
TV – total volume of urine.
Figure 1.
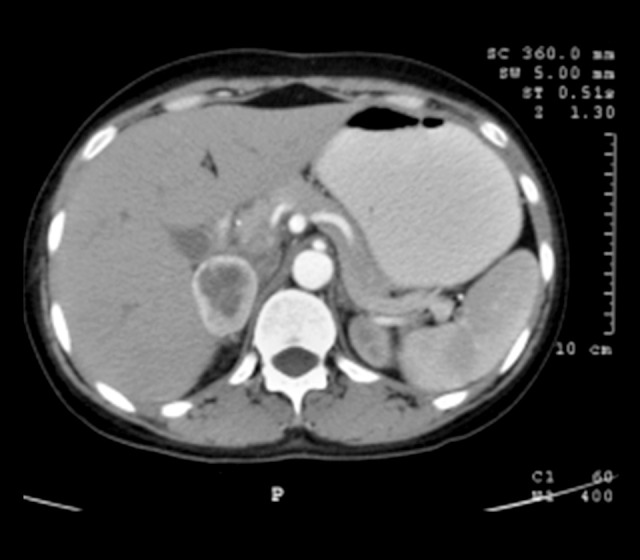
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen showing right adrenal pheochromocytoma. Arrow showing right (4×3 cm) adrenal pheochromocytoma.
Figure 2.
Timeline of the disease progression.
Discussion
Our case highlights the complexity in the diagnosis of a pheochromocytoma. An unconventional presentation with the TLC and PRES further increases the diagnostic challenge. Despite of the initial misdiagnosis, diligent follow-up and comprehensive testing led to the detection of the localized right adrenal pheochromocytoma.
In patients with pheochromocytoma, cardiovascular and neurological manifestations usually dominate the clinical picture, with 95% of patients having hypertension and 90% having headaches at presentation [7–9]. Hypertension is either sustained (50%) or paroxysmal (45%) and is more commonly associated with norepinephrine-secreting tumors. Further, postural hypotension in patients with pheochromocytoma is uncommon. Although, the exact etiology is unclear, postural hypotension is most probably precipitated due to the fluctuation in vascular tone, suppression of baroceptor signaling, and/or hypovolemia and/or downregulation of adrenergic receptors [10–14]. Other severe cardiovascular manifestations include arrhythmia, hypotension, shock, myocardial ischemia, cardiomyopathy, aortic dissection, and extremity ischemia [15]. However, presentation with pheochromocytoma-induced TLC is very rare, with fewer than 100 cases reported in the literature [16]. Most of these patients were female (approximately two-thirds), and chest pain was the most common presenting symptom, followed by classical symptoms of pheochromocytoma (headache, palpitation, and sweating), and less commonly, symptoms of heart failure. Antecedent triggers are reported in only 20% to 30% of patients, with surgery being the most common stressor, followed by emotional stressors. We could not identify any triggers in our patient. Investigations usually reveal LV dysfunction of varying severity, with regional wall motion abnormalities that are global or present in the distribution of multiple coronary arteries, elevated myocardial enzymes, and ECG abnormalities [4,16]. The diagnosis of pheochromocytoma-induced TLC is based on the International Takotsubo Diagnostic Criteria or Mayo diagnostic criteria [17,18]. Our patient also had typical symptoms of acute coronary syndrome, severe LV dysfunction with global LV hypokinesia and apical ballooning, elevated troponin I levels, and EKG changes. Pheochromocytoma-induced TLC is more commonly reported in norepinephrine-secreting tumors. It has been proposed that catecholamines, especially norepinephrine, increase myocardial oxygen demand, induce microvascular dysfunction, and induce severe epicardial coronary vasospasm [19,20]. Furthermore, excess catecholamines, especially norepinephrine, are oxidized and produce a direct toxic effect on the myocardium by increasing the sarcolemmal permeability and cellular calcium influx. This results in reduced myocyte viability, cardiac contractility, and distortion of the conductive system. All of these can induce cardiomyopathy, myocardial ischemia, and various EKG changes, including deep symmetric T-wave inversion, prolongation of QT interval and ST-T segment abnormalities, and arrhythmias [5]. Importantly, all these changes are reversible and resolve after the administration of phenoxybenzamine and resection of pheochromocytoma [4,5,21]. Furthermore, recurrence of pheochromocytoma-induced TLC after adrenalectomy has never been reported [15,22].
After cardiovascular disease, neurological manifestations are the second most common presenting symptoms, present in 75% of patients with pheochromocytoma. However, severe neurological manifestations, including intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, PRES, and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, are very rare and are usually dominant in patients with pheochromocytoma crisis. However, the pathophysiology of PRES is unclear, and there are 2 potential processes. One involves the disruption of cerebral autoregulation, which causes a rise in blood-brain barrier permeability and vasogenic edema. The term “cerebral hyperperfusion” refers to this notion. Sympathetic innervations, which are less widespread in the vertebrobasilar circulation than in the anterior circulation, mediate the autoregulatory system. Vasogenic edema is therefore anticipated to be mostly observed in the subcortical white matter and parieto-occipital cortex. The alternative approach, referred to as the “toxic/immunogenic theory”, centers on the endothelial dysfunction caused by endogenous or exogenous toxins, such as sepsis or (pre) eclampsia, immunosuppressive medications, or chemotherapy. Both ideas lead to disruption of the blood-brain barrier [23–25].
In PRES, blood pressure surges beyond the limits of cerebral autoregulation, leading to hyperperfusion-induced cerebrovascular endothelial injury, vasogenic edema, and, rarely, hemorrhage, and catecholamine excess results in severe cerebral vasoconstriction with hypoperfusion, ischemia, and vasogenic edema. The predominant symptoms include headache, drowsiness, confusion, coma, stroke, seizures, and delirium. Almost 4% to 5% of patients with pheochromocytoma develop ischemic stroke, and intracerebral hemorrhage is mostly associated with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome [26,27]. Hypertensive encephalopathy usually develops due to PRES and presents with headache, altered sensorium, papilledema, or ischemic stroke [28]. The pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy in pheochromocytoma is related to the loss of the “Bayliss effect”, an auto-regulatory response to maintain cerebral perfusion. In healthy individuals, an increase in systemic blood pressure leads to the activation of α-1 receptors in cerebral vessels, resulting in vasoconstriction and normalization of cerebral perfusion pressure. However, during the pheochromocytoma crisis, this protective mechanism becomes dysfunctional, resulting in vasodilation, reduced cerebral perfusion pressure, and ischemia, leading to hypertensive encephalopathy. Timely diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact neurological morbidities and improve outcomes, as seen in our patient. Importantly, for PRES to be reversible, it requires early diagnosis and treatment with antihypertensive medications to reduce 20% to 30% of blood pressure or to a mean diastolic blood pressure of about 100 mmHg within a few hours of the onset of hypertensive encephalopathy [26,29].
The concomitant presence of TLC and hypertensive encephalopathy is very rare in patients with or without pheochromocytoma. Most reported patients were female, and physical or emotional triggers were reported in most patients. We did not find any triggers in our patient. In both disorders, endotheliopathy due to excess catecholamines and inflammation has been proposed as a potential underlying mechanism. This hypothesis was further supported by the presence of vasogenic cerebral edema in PRES and myocardial edema in TLC on cardiac MRI. Both conditions are usually reversible with appropriate management for control of blood pressure but can be life-threatening in the acute phase [6,26,30–32]. These patients may be very sick at presentation, and their condition is usually dictated by the severity of heart failure. Patients who present with heart failure and cardiogenic shock can require mechanical ventilation for respiratory support and mechanical circulatory support to improve organ perfusion. In these patients, fluid administration and the use of antihypertensive medications and inotropes should be judicious and guided by the Swan-Ganz catheter, to promptly manage control blood pressure [6,26]. With appropriate management, cessation of the trigger, and the abolition of catecholamine surge, patients usually develop complete myocardial and neurological recovery, as reported in the literature. Clinical recovery usually precedes investigational recovery, since the resolution of myocardial and cerebral edema can take a few weeks to months [6,26,30–32]. In our patient, the sensorium recovered completely, without neurological deficit, with the control of blood pressure. However, cardiac function was recovered at the 5-month follow-up echocardiography. No repeat brain MRI was performed to determine the resolution of the cerebral edema.
In our patient, the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma was missed at the initial presentation, and the patient was treated with beta-blockers alone and was at risk of developing hypertensive crisis and pulmonary edema due to unopposed α-receptor over-activity. However, our patient did not develop pulmonary edema. TLC and hypertensive encephalopathy resolved completely after medical management, and the patient remained asymptomatic for 2 years on beta-blockers alone. There are 2 possible explanations for this finding. First is desensitization of adrenergic receptors either by reduced adrenergic receptors on the cell surface due to internalization or a decrease in the affinity of the adrenergic receptors to bind with the catecholamines [33]. Second, norepinephrine has a high affinity for the β-1 receptor, which is responsible for tachycardia, tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, and myocardial dysfunction. Epinephrine has a higher potency for β2 and α receptors. Therefore, in epinephrine-secreting tumors, unopposed α action in the presence of β-blockers alone can lead to accelerated hypertension [34]. Our patient had a norepinephrine-secreting pheochromocytoma. Therefore, the administration of β-blockers can treat tachycardia and tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy by blocking β-1 receptors.
It is important to improve awareness among physicians to always suspect the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma in any patient with unexplained hypertension or heart failure; otherwise, diagnosis can be delayed for a long time, owing to the overlapping presenting symptoms of pheochromocytoma with many other conditions. Gagnon et al, in a review of 14 patients with pheochromocytoma, reported a mean delay of 21 months after an episode of pheochromocytoma-induced TLC [22]. In our patient, the diagnosis was delayed for 2 years.
Conclusions
Patients with pheochromocytoma often receive misdiagnoses, due to the absence of the classic triad of headache, diaphoresis, and palpitations. Pheochromocytoma can mimic many clinical conditions, such as hypertensive emergencies or TLC. It is crucial to have a high level of suspicion in any young patients presenting with hypertension crisis and cardiac manifestations. After initial stabilization, thorough laboratory and imaging investigations are necessary to identify patients with pheochromocytoma. Surgery is usually curative in most patients, without the need for antihypertensive medications and no recurrence of hypertensive encephalopathy or TLC.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher
Department and Institution Where Work Was Done
Division of Internal Medicine, PGIMER, Chandigarh, India.
Declaration of Figures’ Authenticity
All figures submitted have been created by the authors who confirm that the images are original with no duplication and have not been previously published in whole or in part.
References:
- 1.Zuber SM, Kantorovich V, Pacak K. Hypertension in pheochromocytoma: Characteristics and treatment. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011;40(2):295–311. vii. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2011.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sharkey SW, McAllister N, Dassenko D, et al. Evidence that high catecholamine levels produced by pheochromocytoma may be responsible for tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(11):1615–18. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.02.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gu YW, Poste J, Kunal M, Schwarcz M, Weiss I. Cardiovascular manifestations of pheochromocytoma. Cardiol Rev. 2017;25(5):215–22. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Awadji FB, Sasmita BR, Huang B, et al. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy induced by pheochromocytoma: a case report. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2023;2023(2) doi: 10.1093/omcr/omad011. omad011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wu HY, Gao TJ, Cao YW, Liang L. Case report: Pheochromocytoma in a 59-year-old woman presenting with hypotension. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:648725. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.648725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Petrie J, Lockie C, Paolineli A, et al. Undiagnosed phaeochromocytoma masquerading as eclampsia. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012 doi: 10.1136/bcr.10.2011.4922. bcr1020114922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rupala K, Mittal V, Gupta R, Yadav R. Atypical presentation of pheochromocytoma: Central nervous system pseudovasculitis. Indian J Urol. 2017;33(1):82–84. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.195760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Anderson NE, Chung K, Willoughby E, Croxson MS. Neurological manifestations of phaeochromocytomas and secretory paragangliomas: A reappraisal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84(4):452–57. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-303028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Manger WM, Gifford RW. Pheochromocytoma. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2002;4(1):62–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.01452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Koch CA, Rodbard JS, Brouwers FM, et al. Hypotension in a woman with a metastatic dopamine-secreting carotid body tumor. Endocr Pract. 2003;9(4):310–14. doi: 10.4158/EP.9.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Streeten DH, Anderson GH., Jr Mechanisms of orthostatic hypotension and tachycardia in patients with pheochromocytoma. Am J Hypertens. 1996;9(8):760–69. doi: 10.1016/0895-7061(96)00057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ganguly A, Grim CE, Weinberger MH, Henry DP. Rapid cyclic fluctuations of blood pressure associated with an adrenal pheochromocytoma. Hypertension. 1984;6(2 Pt 1):281–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mathew J, Menon PS, Shah NS, Supe AN. A man with recurrent abdominal pain and hypotension. J Postgrad Med. 2005;51(3):234–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Manger WM, Gifford RB., Jr . Clinical and experimental pheochromocytoma. Blackwell Science; Cambridge, USA: 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meijs AC, Snel M, Corssmit EPM. Pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma crisis: Case series from a tertiary referral center for pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Hormones (Athens) 2021;20(2):395–403. doi: 10.1007/s42000-021-00274-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang L, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Yang Z. Pheochromocytoma with takotsubo syndrome and acute heart failure: A case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02704-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ghadri JR, Wittstein IS, Prasad A, et al. International Expert Consensus Document on Takotsubo Syndrome (Part I): Clinical characteristics, diagnostic criteria, and pathophysiology. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(22):2032–46. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Scantlebury DC, Prasad A. Diagnosis of takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2014;78(9):2129–39. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-14-0859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Menke-van der Houven van Oordt CW, Twickler TB, van Asperdt FG, et al. Pheochromocytoma mimicking an acute myocardial infarction. Neth Heart J. 2007;15(7–8):248–51. doi: 10.1007/BF03085991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sharkey SW, McAllister N, Dassenko D, et al. Evidence that high catecholamine levels produced by pheochromocytoma may be responsible for tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(11):1615–18. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.02.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cheng Y, Qin L, Chen L. Pheochromocytoma mimicking acute coronary syndrome: A case report. Front Oncol. 2022;12:879714. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gagnon N, Mansour S, Bitton Y, Bourdeau I. Takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy in a large cohort of patients with pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Endocr Pract. 2017;23(10):1178–92. doi: 10.4158/EP171930.OR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(9):914–25. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00111-8. [Erratum in: Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(9):874] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fischer M, Schmutzhard E. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neurol. 2017;264(8):1608–16. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8377-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bartynski WS, Boardman JF, Zeigler ZR, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in infection, sepsis, and shock. Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(10):2179–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dominedò C, D’Avino E, Martinotti A, Cingolani E. A rare pheochromocytoma complicated by cardiogenic shock and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021;5(2) doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaa513. ytaa513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Anderson NE, Chung K, Willoughby E, Croxson MS. Neurological manifestations of phaeochromocytomas and secretory paragangliomas: A reappraisal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84(4):452–57. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-303028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Madhok J, Kloosterboer A, Venkatasubramanian C, Mihm FG. Catecholamine-induced cerebral vasospasm and multifocal infarctions in pheochromocytoma. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2020;2020:20–0078. doi: 10.1530/EDM-20-0078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Caplan LR, Biller J, Leary M, et al. 2nd ed. San Diego: Elsevier Science Publishing Co Inc; 2017. Primer on cerebrovascular diseases. pp. 733–37. Chapter 139: Hypertensive Encephalopathy. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stuetz M, Templin C, Templin-Ghadri JR, et al. Acute heart and brain failure: A case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2020;4(6):1–8. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaa352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grimaldi S, Doche E, Rey C, et al. Association of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and transient apical ballooning syndrome (takotsubo): First case report of a man and review of the literature. Case Rep Neurol. 2017;9(2):173–78. doi: 10.1159/000474933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Summers MR, Madhavan M, Chokka RG, et al. Coincidence of apical ballooning syndrome (tako-tsubo/stress cardiomyopathy) and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Potential common substrate and pathophysiology? J Card Fail. 2012;18(2):120–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M, Pacak K. Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet. 2005;366(9486):665–75. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pacak K. Preoperative management of the pheochromocytoma patient. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(11):4069–79. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]