Abstract
Many fungal pH responses depend upon conserved Rim101p/PacC transcription factors, which are activated by C-terminal proteolytic processing. The means by which environmental pH is sensed by this pathway are not known. Here, we report a screen of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae viable deletion mutant library that has yielded a new gene required for processed Rim101p accumulation, DFG16. An S. cerevisiae dfg16Δ mutant expresses Rim101p-repressed genes at elevated levels. In addition, Candida albicans dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ mutants are defective in alkaline pH-induced filamentation, and their defect is suppressed by expression of truncated Rim101-405p. Thus, Dfg16p is a functionally conserved Rim101p pathway member. Many proteins required for processed Rim101p accumulation are members of the ESCRT complex, which functions in the formation of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Staining with the dye FM4-64 indicates that the S. cerevisiae dfg16Δ mutant does not have an MVB defect. We find that two transcripts, PRY1 and ASN1, respond to mutations that affect both the Rim101p and MVB pathways but not to mutations that affect only one pathway. The S. cerevisiae dfg16Δ mutation does not affect PRY1 and ASN1 expression, thus confirming that Dfg16p function is restricted to the Rim101p pathway. Dfg16p is homologous to Aspergillus nidulans PalH, a component of the well-characterized PacC processing pathway. We verify that the previously recognized PalH homolog, Rim21p, also functions in the S. cerevisiae Rim101p pathway. Dfg16p is predicted to have seven membrane-spanning segments and a long hydrophilic C-terminal region, as expected if Dfg16p were a G-protein-coupled receptor.
The recognition of environmental cues and presentation of an appropriate response are central to the survival of microorganisms. The range of possible responses is broad and may affect metabolic activities, organelle biogenesis, cell division, or differentiation. For pathogens, environmental response pathways are typically critical for virulence. Our interests are in how diverse responses are coordinated and how coordination mechanisms may have evolved.
For the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the environmental pH affects growth as well as differentiation to permit invasive growth or meiotic sporulation. Among gene products that are required for adaptation to alkaline pH, haploid invasive growth, and sporulation is the zinc finger transcription factor Rim101p (19, 22, 31, 32). Microarray analysis and chromatin immunoprecipitation studies (18) have shown that S. cerevisiae Rim101p functions as a repressor through the target site TGCCAAG. Among its key repression targets are two transcription factor genes, SMP1 and NRG1. Epistasis tests indicate that Smp1p mediates effects of Rim101p on invasive growth and sporulation, whereas Nrg1p mediates effects on adaptation to alkaline pH and ion tolerance (18).
Rim101p homologs include Candida albicans Rim101p, Yarrowia lipolytica Rim101p, and the very well-studied Aspergillus nidulans PacC (reviewed in reference 25). Functional analysis indicates that Rim101p/PacC family proteins play a key role in pH-dependent responses in these organisms. Full-length Rim101p/PacC family members are biologically inactive and are activated by proteolytic removal of the C-terminal region. The N-terminal cleavage product, containing the zinc finger region, is an active repressor in the case of S. cerevisiae Rim101p. More complex cleavage patterns are seen with A. nidulans PacC (reviewed in reference 25) and C. albicans Rim101p (21), and these proteins may function as activators as well as repressors (2, 25, 26).
Genetic screens in A. nidulans, S. cerevisiae, and Y. lipolytica have identified conserved gene products that are required for Rim101p/PacC processing, including Rim13p/PalB, a cysteine protease that presumably cleaves Rim101p/PacC; Rim20p/PalA, a protein that binds to the Rim101p/PacC C-terminal region; Rim8p/PalF, a protein with similarity to arrestins; and Rim9p/PalI and Rim21p/PalH, two proteins with multiple predicted membrane-spanning segments (reviewed in reference 25). Homologs of these processing proteins are specified by many fungal genomes. Therefore, the Rim101p/PacC processing pathway and its overall biological role may be broadly conserved among fungi.
Recent findings in S. cerevisiae and C. albicans indicate that subunits of the ESCRT complex are also required for Rim101p processing (17, 37). The ESCRT complex is well-known for its role in eukaryotic vesicle trafficking: it is required for formation of multivesicular bodies (MVBs), a specialized class of vesicle that delivers cargo proteins to the vacuole or lysosome (reviewed in reference 16). These MVB cargo proteins include plasma membrane receptors that have been removed through endocytosis and are destined for vacuolar/lysosomal degradation. Other MVB cargo proteins are biosynthetic precursors of resident vacuolar/lysosomal hydrolases. The ESCRT complex is required to promote invagination of the limiting vesicular membrane to create an MVB. Eight ESCRT subunits (Snf7p/Vps32p, Vps20p, Snf8p/Vps22p, Vps25p, Vps36p, Vps23p, Vps28p, and Vps37p), which form what has been called the core ESCRT complex (3), function in both MVB formation and Rim101p processing (17, 37). Other proteins required for MVB formation and trafficking, including Vps27p, Vps2p, Vps24p, Vps4p, Bro1p, Doa4p, and Vps60p, are not required for Rim101p processing (17, 37). Two-hybrid studies (13) and functional analysis (36, 37) have led to the model that the core ESCRT subunits may bridge the interaction between the protease Rim13p and the substrate complex Rim20p-Rim101p (37).
Here, we report the characterization of a new gene that is required for Rim101p processing in S. cerevisiae. Its role is conserved, as evidenced by analysis of its C. albicans homolog. Our findings provide new insight into the Rim101p/PacC pathway and its relationship to ESCRT subunit function.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and media.
The haploid S. cerevisiae deletion strain libraries derived from the parental strain, BY4741 (MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0) and BY4742 (MATα his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 lys2Δ0 ura3Δ0), were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Strain YKB167 was derived from the RIM101-HA2 epitope-tagged strain WXY169 (36). The dfg16Δ::kanMX4 mutation was introduced by PCR product-directed gene disruption using genomic DNA from the dfg16Δ::kanMX4 yeast deletion clone (Invitrogen) as a template along with the primers TTC TTT TGT TGT TTC GGG GTG (forward) and TGC CAG AAG GAT TTG GAA CA (reverse).
All C. albicans strains were derived from strain BWP17 (ura3Δ::λimm434/ura3Δ::λimm434 his1::hisG/his1::hisG arg4::hisG/arg4::hisG) through standard transformation methods (35). The dfg16Δ::URA3/dfg16Δ::ARG4 strain, KBC033, was generated by PCR product-directed gene disruption using the primers AGA TCG AAA CAC TTG ATT TTA ATT TAT ATC GGG TTT TGT TAG GAC AGC AGA TCG AAA AAG TAA TAA TAC CAA CTA TTT CTT TCC CAG TCA CGA CGT T (forward) and AAG CTA TAC AAA TAA TTC TAT ACT TTG CTT CAG GAC CTA TAA TGA TGA AAG TTG TTT ACA TTT CTA TTGA AAG AAT GGA GTG GAA TTG TGA GCG GAT A (reverse). The genotypes of three independent homozygotes (each derived from an independent heterozygote) were verified by PCR using the primer pair ATT TTC TTG TTC GCA CGA CC (forward) and CAA AGC ACT CTG ATT GGT GAA (reverse). The deletion removed the entire DFG16 open reading frame.
Transformations.
Yeast deletion library strains were transformed in 96-well microtiter plates using a lithium acetate transformation method modified from a method described previously by Gietz and Woods (10). Strains were grown overnight in 200 μl of yeast-peptone-dextrose (YPD) medium at 30°C before harvesting cells by centrifugation at 1,500 × g. Cells were washed once in 200 μl sterile water and twice in 200 μl 0.1 M lithium acetate and then suspended in 25 μl 0.1 M lithium acetate. A 120-μl volume of 50% polyethylene glycol was mixed into each well, followed by 55 μl transformation mix (50 μg boiled salmon sperm DNA, 330 mM lithium acetate, and 300 to 500 ng transforming DNA) before incubation overnight at 30°C. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 1,500 × g and resuspended in 10 μl water. Transformations were spotted onto selective plates (24 per plate) and grown at 30°C for 2 to 4 days. Once colonies had appeared, they were replica plated onto new selective plates and grown for 1 day at 30°C before β-galactosidase assays were performed.
For electroporations, S. cerevisiae strains were grown overnight at 30°C with shaking. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 15,000 × g for 10 s and washed twice with cold 1 M sorbitol containing 20 mM HEPES before being resuspended in the same solution with a volume equal to the packed cell volume. If the transforming DNA contained any salts, it was ethanol precipitated before approximately 1 μg was mixed with 40 μl of yeast cells and placed into electroporation cuvettes that had been chilled on ice. Electroporation was carried out at 1.6 V, 200 Æ, and 25 μF using a Bio-Rad Genepulser. Cells were immediately resuspended in 0.2 ml cold 1 M sorbitol and plated on selective medium.
Electroporation of Escherichia coli was carried out at 2.5 V, 200 Æ, and 25 μF. Cells were immediately resuspended in 0.9 ml LB medium and grown for 1 h at 37°C with shaking before plating.
Plasmids.
The Rim101p repression reporter plasmid pAED39 has been described previously (18). The URA3-V5-RIM101 fusion gene, used to detect Rim101p processing activity, was inserted into a CEN-LEU2 vector, pRS315, creating plasmid pKJB011. The fusion gene includes native RIM101 5′ sequences to drive expression of an epitope-tagged URA3-V5 coding region fused in frame to RIM101 codons 501 to 628 and native 3′ sequences. The construction and characterization of this fusion gene will be reported elsewhere (W. Xu and A. P. Mitchell, unpublished results).
Complementation studies in C. albicans were carried out using plasmid pKJB024. This plasmid was created by amplifying DFG16 from BWP17 genomic DNA by PCR using the primers TGT GGA AAG CAA ACA CTG TG (forward) and CAA AGC ACT CTG ATT GGT GAA (reverse). After cloning into pGem-T Easy (Promega, Madison, WI), an NgoMIV-SapI fragment was released for in vivo recombination in S. cerevisiae with NotI-cut pDDB78 (30). Suppression studies were carried out using plasmids pDDB61 (RIM101) and pDDB71 (RIM101-405) as described previously (4).
β-Galactosidase assays.
A 0.45-μm 85-mm nitrocellulose membrane (Millipore Corporation, Bedford, MA) was placed on a selective plate and a YPD plate for replica plating of each plate of transformations before incubation overnight at 30°C. Membranes were removed from the plates and placed at −80°C for 1 h to permeabilize the cells. Disks of 3M filter paper (Whatman) were soaked in 3 ml Z buffer (60 mM Na2HPO4 [anhydrous], 60 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM KCl, 1 mM MgSO4) containing 35 μl 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactoside (50 μg μl−1 stock solution in dimethylformamide), and the membranes were placed on top. Membranes were incubated for 1 h at 30°C. The reaction was stopped by removing the membranes from the filter paper, and results were scored immediately.
Immunoblots.
Cells were grown overnight in selective medium at 30°C and used to inoculate YPD at an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.25. After two doublings, cells were pelleted, resuspended at an OD600 of 50 in 3× Laemmli buffer, vortexed with glass beads, and boiled for 5 min. After centrifugation, 20 to 60 μl of the supernatant was fractionated on a 9% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to nitrocellulose. For V5 epitope detection, the filter was probed with anti-V5-horseradish peroxidase antibody (Invitrogen) (1:5,000 dilution in phosphate-buffered saline-Tween). For hemagglutinin (HA) epitope detection, the filter was probed with anti-HA-peroxidase antibody (3F10; Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN) (1:10,000 dilution in phosphate-buffered saline-Tween). Peroxidase activity was visualized using ECL detection reagents (Amersham, Piscataway, NJ).
Transcript analysis.
For analysis of transcription after an alkaline shift, strains were inoculated in YPD medium at an OD600 of 0.05 and grown to an OD600 of 0.25. Cells were collected and resuspended in YPD medium containing 0.1 mM HEPES (pH 8). After the wild-type strain had doubled (approximately 4 h), all strains were harvested and snap frozen in a dry ice/ethanol bath. Isolation of RNA was carried out using a hot-phenol method (29).
Microarrays and Northern blotting were performed as previously described (18). Analysis was performed using the Affymetrix Microarray Suite, version 5, analysis program. Data were manipulated with Microsoft Excel worksheet functions.
Northern probes were generated by PCR using BY4741 genomic DNA as a template with the following oligonucleotide pairs: for PRY1, TGC AAG GCG TAG TTT ATG TCG (forward) and CGG GGT CGT AAC TAC AGA TGA (reverse); for ASN1, GAC ACT ATC ACT GCA TTC CCA (forward) and ATT TCA TCG GAA CCT TCA CC (reverse); for ENO1, CCA AGC AAC TGC TTA TCA ACA (forward) and GAA CTG GCA AAA CGT ATG GA (reverse). The NRG1 and SMP1 oligonucleotides have been described elsewhere previously (18). ImageQuant software, version 1.2 (Molecular Dynamics), was used for quantification of Northern blots.
Membrane staining.
Staining with N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(p-diethylaminophenyl-hexatrienyl)-pyridinium dibromide (FM4-64; Molecular Probes) followed the procedure previously described by Amerik et al. (1), with slight modifications. Cells were grown for two doublings to mid-log phase in 10 ml YPD medium at 30°C and then harvested and resuspended in 166 μl YPD to which 0.4 μl 16 mM FM4-64 in dimethyl sulfoxide was added. The tubes were wrapped in foil and incubated at 30°C for 20 min on a shaker. The cells were harvested, washed once with 200 μl YPD medium, resuspended in 200 μl YPD medium, and incubated at 30°C for 60 min on a shaker. Membrane staining was visualized immediately after the second incubation by fluorescence microscopy with a Nikon Eclipse E800 microscope equipped with a Plan Apo 100×/1.4 objective. Images were preserved with Improvision software.
RESULTS
Screen for Rim101p repression and processing defects.
To identify new genes that may function in the Rim101p pathway, we screened the S. cerevisiae haploid deletion strain library with a Rim101p-repressible reporter plasmid. The plasmid contains four PacC sites inserted between the upstream activation sequence and TATA regions of a CYC1-lacZ fusion (18). This CYC1pacC-lacZ reporter gene is expressed at much lower levels in wild-type cells, which contain processed Rim101p, than in a rim101Δ strain, which lacks Rim101p, or in a rim13Δ strain, which contains only unprocessed Rim101p (18). We used reporter plasmid expression as an indication that a strain is defective in Rim101p-dependent repression.
The 4,828 MATa deletion library strains were transformed with the reporter plasmid, and 84% of the strains yielded transformants. There were 40 strains that showed higher reporter expression than the parent strain (Table 1) after several assays. These strains included all six deletion mutants lacking previously known Rim101p pathway genes and all eight deletion mutants lacking core ESCRT subunits. The group also included the deletion mutant lacking the corepressor Tup1p, as expected (18). The remaining 25 strains had deletions of genes not associated previously with the Rim101p pathway.
TABLE 1.
Results of CYC1PacC-lacZ reporter screen
| Name | Alias | ORFa | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RIM101 | RIM1 | YHL027W | Transcriptional repressor, response to pH, sporulation, meiosis |
| RIM8 | PAL3 | YGL045W | Regulator of IME2, RIM101 pathway member |
| RIM9 | YMR063W | Regulator of IME2, RIM101 pathway member, probably a transmembrane protein | |
| RIM13 | CPL1 | YMR154C | Cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in Rim101p processing |
| RIM20 | YOR275C | Regulator of IME2, RIM101 pathway member, scaffold protein that interacts with Rim20p and Snf7p | |
| RIM21 | PAL2 | YNL294C | Regulator of IME2, RIM101 pathway member, probably a transmembrane protein |
| STP22 | VPS23 | YCL008C | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-I |
| VPS28 | VPT28 | YPL065W | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-I |
| SRN2 | SRN10, VPS37 | YLR119W | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-I |
| VPS36 | VAC3, VPL11, GRD12 | YLR417W | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-II |
| VPS25 | VPT25 | YJR102C | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-II |
| SNF8 | VPS22 | YPL002C | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-II |
| VPS20 | YMR077C | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-III | |
| SNF7 | DID1, VPS32 | YLR025W | Vacuolar protein sorting, ESCRT-III |
| TUP1 | AAR1, AER2, AMM1, CRT4, CYC9, FLK1, ROX4, SFL2, UMR7 | YCR084C | General repressor of transcription (with Ssn6p); mediates glucose repression |
| ATG21 | MAI1 | YPL100W | AuTophaGy-related vacuolar protein involved in processing/maturation |
| BRR1 | YPR057W | RNA binding, spliceosome assembly | |
| CIT1 | CS1, LYS6 | YNR001C | Citrate synthase |
| CKA2 | YOR061W | Casein kinase II alpha subunit | |
| CKB1 | YGL019W | Beta (38-kDa) subunit of protein kinase CK2 | |
| DFG16 | ECM41, ZRG11 | YOR030W | Defective in flocculant growth |
| DIA2 | YOR080W | Digs into agar | |
| DRS2 | FUN38, SWA3 | YAL026C | Integral membrane Ca2+-ATPase |
| FUN12 | YAL035W | GTPase activity, translation initiation factor activity | |
| GPH1 | YPR160W | Glycogen phosphorylase | |
| GRR1 | CAT80, COT2, SSU2 | YJR090C | F-box protein component of the SCF ubiquitin-ligase complex |
| IES6 | YEL044W | Protein associates with INO80 chromatin remodeling complex under low-salt conditions | |
| SIT4 | LGN4 | YDL047W | Similar to catalytic subunit of bovine type 2A protein phosphatase |
| SPE1 | ORD1, SPE10 | YKL184W | Ornithine decarboxylase |
| SPE2 | YOL052C | S-Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase | |
| SPE3 | YPR069C | Putrescine aminopropyltransferase | |
| SPT3 | YDR392W | Subunit of the SAGA and SAGA-like transcriptional regulatory complexes | |
| SRB8 | GIG1, NUT6, SSN5 | YCR081W | Negative regulation of transcription from PolII promoter |
| SSN6 | CRT8, CYC8 | YBR112C | General repressor of transcription (with Cyc8p); also acts as part of a transcriptional coactivator complex that recruits the SWI/SNF and SAGA complexes to promoters |
| TAF14 | SWP29, TAF30, TFG3, ANC1 | YPL129W | Subunit (30 kDa) of TFIID, TFIIF, and SWI/SNF complexes |
| THI6 | YPL214C | Thiamine biosynthetic bifunctional enzyme | |
| UBR1 | PTR1 | YGR184C | Ubiquitin-protein ligase |
| VAC8 | YEB3 | YEL013W | Vacuolar membrane protein that interacts with Atg13p, required for cytoplasm-to- vacuole targeting (Cvt) pathway |
| YGR122W | YGR122W | Unknown | |
| YPR116W | YPR116W | Uncharacterized |
ORF, open reading frame.
We used a URA3-V5-RIM101 fusion gene to determine whether any repression-defective deletion strains may be defective in Rim101p processing. This fusion gene consists of an epitope-tagged URA3-V5 gene fused in frame to RIM101 codons 501 to 628, which specify the Rim101p C-terminal segment, and is expressed from the RIM101 5′ region. Immunoblots showed that the wild-type strain contained both processed and unprocessed forms of Ura3-V5-Rim101p (Fig. 1A, lane 2), whereas a control rim20Δ strain contained only the unprocessed form (lane 1). A control rim101Δ strain contained the processed form of the protein (lane 3), thus indicating that Rim101p repression activity is not required for Rim101p processing.
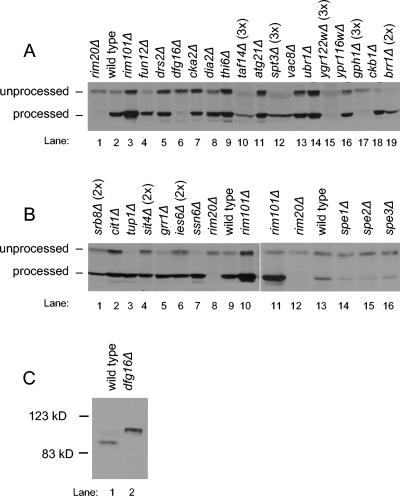
FIG. 1.
Processing of Ura3-V5-Rim101p and Rim101-HA2p. (A, B) Protein extracts from MATa deletion library S. cerevisiae strains containing a URA3-V5-RIM101 plasmid were analyzed on an anti-V5 immunoblot to visualize the unprocessed and processed forms of the protein. Protein amounts loaded were approximately equal, as determined by Ponceau-S staining, with the exception of panel A, lanes 10, 12, 15, 17, and 19, and panel B, lanes 1, 4, and 6. These lanes were intentionally loaded with two or three times as much protein, as indicated above the lane, in order to detect the epitope. (C) Protein extracts from yeast strains WXY169 (RIM101-HA2 DFG16) and YKB167 (RIM101-HA2 dfg16Δ) were analyzed on an anti-HA immunoblot to visualize the processing of the epitope-tagged Rim101p, expressed from the native RIM101 locus.
Among the deletion strains, accumulation of Ura3-V5-Rim101p forms fell into three categories (Fig. 1). In the first category, both unprocessed and processed forms were apparent. This group included drs2Δ, cka2Δ, dia2Δ, thi6Δ, atg21Δ, vac8Δ, ubr1Δ, ypr116wΔ, cit1Δ, fun12Δ, ckb1Δ, tup1Δ, grr1Δ, ssn6Δ, spe1Δ, spe2Δ, and spe3Δ deletion strains. These genes may be required for processed Rim101p repression activity or DNA binding ability. In the second category, overall levels of Ura3-V5-Rim101p were low. This group included taf14Δ, spt3Δ, ygr122wΔ, gph1Δ, brr1Δ, srb8Δ, sit4Δ, and ies6Δ deletion strains. The low protein level may represent decreased transcription, translation, protein stability, or, perhaps, plasmid stability. The final category comprised strains that accumulated only unprocessed Ura3-V5-Rim101p. The dfg16Δ strain clearly had this property (Fig. 1A, lane 6). The ygr122wΔ and gph1Δ strains might fit into this category as well (Fig. 1A, lanes 15 and 17), but their low levels of Ura3-V5-Rim101p made it difficult to distinguish processed Ura3-V5-Rim101p from a faint background band. These results indicate that Dfg16p may be required for Rim101p processing.
We used two approaches to confirm that the dfg16Δ deletion and not a secondary mutation causes a defect in processed Rim101p accumulation. First, the Ura3-V5-Rim101p plasmid was transformed into an independently constructed dfg16Δ strain from the MATα deletion library. The transformant also accumulated only unprocessed Ura3-V5-Rim101p (data not shown). This result argues that the dfg16Δ mutation is the cause of the defect. Second, we introduced a dfg16Δ mutation into a strain expressing functional epitope-tagged Rim101-HA2p and analyzed processing on an immunoblot (Fig. 1C). The DFG16 parent strain expressed primarily processed Rim101-HA2p of ∼90 kDa, whereas the dfg16Δ mutant expressed only unprocessed Rim101-HA2p of ∼98 kDa. Therefore, the dfg16Δ mutation does not simply affect the Ura3-V5-Rim101p fusion protein, it affects native Rim101p as well. We conclude that Dfg16p is required for accumulation of processed Rim101p.
Requirement for Dfg16p in Rim101p pathway function.
If Dfg16p is required for processed Rim101p accumulation, then dfg16Δ and rim101Δ mutants should have similar phenotypes. One promising indication is that Dfg16p, like Rim101p, is known to be required for haploid invasive growth (24). In order to investigate Dfg16p function in control of Rim101p-responsive genes, we performed microarray analysis on the dfg16Δ mutant in parallel with the isogenic wild-type and rim101Δ strains. In addition, we included rim21Δ and snf7Δ deletion strains. Rim21p has several similarities to Dfg16p (see Discussion) and has been implicated in the Rim101p/PacC pathways in A. nidulans and Y. lipolytica (11, 25). However, it has not been characterized in S. cerevisiae. Snf7p is of interest as an ESCRT subunit that functions in both the Rim101p processing pathway and the MVB pathway (17, 37), a point that is elaborated upon below. Because the Rim101p pathway is responsible for adaptation to alkaline conditions in yeast, this analysis was carried out on RNA that had been isolated from yeast grown in standard YPD medium (pH 6.6) and then shifted to alkaline YPD medium (pH 8) for approximately 4 h. (The entire data set is available in the supplemental material.) We found that 14 of 16 genes that had been up-regulated in rim101Δ mutants in the SK-1 and YC11 strain backgrounds (18) were up-regulated in the rim101Δ strain analyzed here. These 14 genes include all genes known to be repressed directly by Rim101p: YJR061W, YOR389W, YPL277C, RIM8, PRB1, NRG1, and SMP1 (18). However, we did not detect increased expression in the rim101Δ strain of CTS1, which we had previously detected only in SK-1 strains, or YPL088W. We also found that 11 of 17 genes that had been down-regulated in the previously studied rim101Δ mutants were down-regulated in the rim101Δ strain analyzed here. The weaker correspondence among down-regulated genes may reflect the fact that they are regulated by Rim101p indirectly.
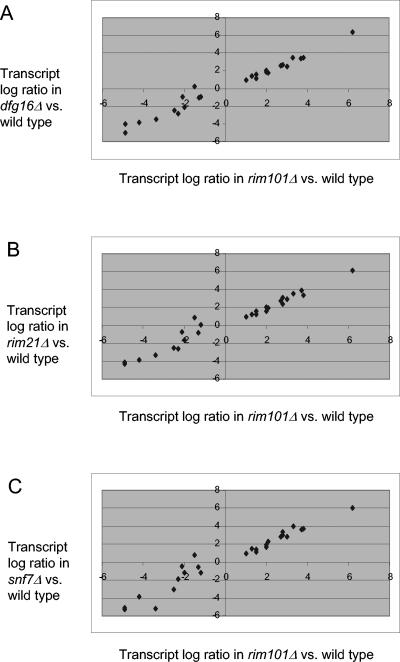
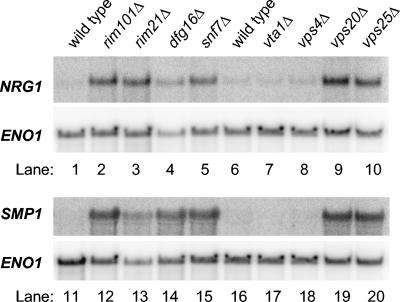
If Dfg16p is required for Rim101p processing, then we expect that the genes whose expression is altered by a rim101Δ mutation will be similarly altered by a dfg16Δ mutation. We focused on the 25 genes discussed above that respond to a rim101Δ mutation in all S. cerevisiae strain backgrounds examined thus far. A plot of their expression ratios (Fig. 2A) shows that the majority of transcripts responded similarly to the dfg16Δ and rim101Δ mutations (Pearson coefficient, 0.987). The results with rim21Δ and snf7Δ strains showed a similar correlation with the rim101Δ strain (Pearson coefficients of 0.979 and 0.970, respectively [Fig. 2B and C]). NRG1 and SMP1 are the two repression targets whose function in Rim101p-dependent responses has been demonstrated (18), and we verified their increased expression in each of the mutants through Northern analysis (Fig. 3, lanes 1 to 5 and 11 to 15). These results indicate that Dfg16p, like Rim21p and Snf7p, is required for Rim101p-dependent effects on expression of native S. cerevisiae genes.
FIG. 2.
Comparison of gene expression changes in the rim101Δ strain to dfg16Δ, rim21Δ, and snf7Δ strains. Microarray signals were expressed as log2 ratios of each S. cerevisiae mutant strain compared to the wild-type strain (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material), and all 25 Rim101p-responsive transcripts (18) that differed by at least twofold in the comparison of rim101Δ to the wild type reported here were selected. The log2 expression ratio in each comparison of mutant and wild type is plotted on the ordinate, and the log2 expression ratio in the comparison of rim101Δ and the wild type is plotted on the abscissa. Mutants include the dfg16Δ strain (A), the rim21Δ strain (B), and the snf7Δ strain (C).
FIG. 3.
Northern blot analysis of Rim101p-repressed genes. Wild-type and mutant S. cerevisiae strains, as indicated above each lane, were grown in YPD medium and then shifted to YPD medium, pH 8, for approximately 4 h before RNA was isolated. Each lane contained 20 μg total RNA; lanes 1 to 10 and 11 to 20 show two different Northern blots prepared in parallel. The blots were probed for NRG1 or SMP1, as indicated on the left of each panel, and then stripped and probed for the loading control, ENO1.
Relationship of Dfg16p and Rim21p to the MVB pathway.
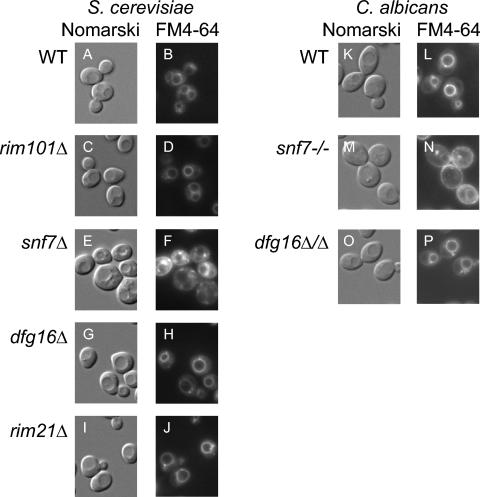
The fact that many gene products are required for both the MVB and Rim101p pathways raises the question of whether Dfg16p and Rim21p may be required for MVB pathway function. We addressed this question through comparison of live-cell staining with the lipophilic dye FM4-64. This dye stains the vacuole of wild-type cells vividly but accumulates in prevacuolar class E compartments in MVB pathway mutants (16, 34). Control wild-type and rim101Δ strains displayed vacuolar staining, as indicated by comparison of Nomarski images (Fig. 4A and C), in which the vacuole appears as a large indentation in the middle of the cell, and FM4-64 fluorescence images (Fig. 4B and D), in which the periphery of the indentation is fluorescent. The known MVB-defective snf7Δ mutant showed pronounced accumulation of FM4-64 in compartments surrounding the vacuole and little vacuolar staining (Fig. 4E and F). The dfg16Δ and rim21Δ mutants showed clear vacuolar staining patterns (Fig. 4G to J) very similar to those of the wild-type and rim101Δ strains. These results argue that Dfg16p and Rim21p are not required for MVB pathway function.
FIG. 4.
Staining of vacuolar and prevacuolar compartments with FM4-64. Wild-type (WT) and mutant S. cerevisiae strains (A to J) and C. albicans strains (K to P), as indicated to the left of the micrographs, were stained with FM4-64. Cells were visualized with visible Nomarski optics (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, and O). FM4-64 fluorescence was visualized for the same fields (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, and P). All images are shown at the same magnification.
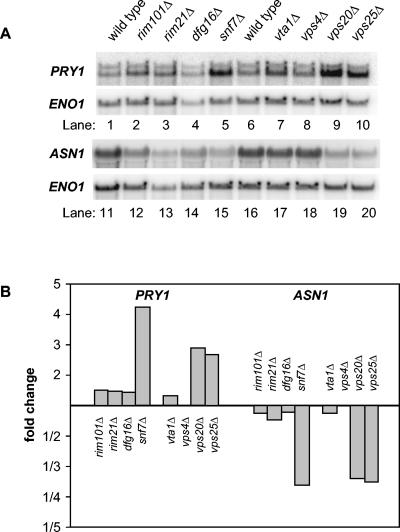
We sought to develop an independent criterion that might be diagnostic of MVB pathway defects. Hughes et al. have shown that large-scale mutant gene expression profiles are useful indicators of functional relationships among genes, even if the genes in question are not transcription factors themselves (12). Therefore, we turned to our microarray results to identify transcripts that respond to the snf7Δ mutation and not the rim101Δ mutation, with the rationale that these transcripts might be solely responsive to MVB pathway defects. We found 103 up-regulated transcripts and 222 down-regulated transcripts with these properties. We focused on two genes, PRY1 and ASN1, whose signal intensities indicated that they would be detectable by Northern analysis. PRY1 was expressed at fourfold-higher levels in the snf7Δ mutant than in the wild type (Fig. 5A, lanes 1 and 5, and B). Also, ASN1 was expressed at 3.5-fold-lower levels in the snf7Δ mutant than in the wild type (Fig. 5A, lanes 11 and 15, and B). A rim101Δ mutation had little effect on expression of these genes (Fig. 5A, lanes 2 and 12, and B). These results argue that PRY1 and ASN1 respond to Snf7p through a mechanism that is not solely dependent upon Rim101p function.
FIG. 5.
Northern blot analysis of Snf7p-responsive genes. (A) Wild-type and mutant S. cerevisiae strains, as indicated above each lane, were grown in YPD medium and then shifted to YPD medium, pH 8, for approximately 4 h before RNA was isolated. Each lane contained 20 μg of total RNA; lanes 1 to 10 and 11 to 20 show two different Northern blots prepared in parallel. The blots were probed for PRY1 or ASN1, as indicated on the left of each panel, and then stripped and probed for the loading control, ENO1. (B) Probe intensities relative to the wild type were normalized for loading against the ENO1 signal for the Northern blots in panel A.
To determine the relationship of the Snf7p-responsive genes to the MVB pathway, we examined the effects of four MVB pathway-defective mutations (Fig. 5). The vps20Δ and vps25Δ mutants expressed PRY1 and ASN1 at levels similar to that of the snf7Δ mutant. Vps20p and Vps25p are ESCRT subunits that function in both the MVB and Rim101p pathways (37). In contrast, vta1Δ and vps4Δ mutants expressed PRY1 and ASN1 similarly to the wild type. Vps4p functions only in the MVB pathway and not in the Rim101p pathway (17, 37). Vta1p functions in the MVB pathway (28, 39) and has not been tested for a role in the Rim101p pathway. However, we found that the vta1Δ mutant failed to derepress NRG1 and SMP1 (Fig. 3, lanes 6, 7, 16, and 17) and failed to express CYC1pacC-lacZ in our initial screen, thus indicating that Vta1p is not required for Rim101p function. These results indicate that PRY1 and ASN1 respond to mutations that cause combined defects in the MVB and Rim101p pathways.
We used Northern analysis to determine whether Dfg16p and Rim21p govern PRY1 and ASN1 expression (Fig. 5). Transcript levels of PRY1 and ASN1 were unaffected in dfg16Δ and rim21Δ strains. These observations indicate that Dfg16p and Rim21p are functionally distinguishable from the ESCRT subunits that function in both the MVB and Rim101p pathways. These findings support the conclusion that Dfg16p and Rim21p are not required for both Rim101p and MVB pathway function.
Conservation of Dfg16p function in C. albicans.
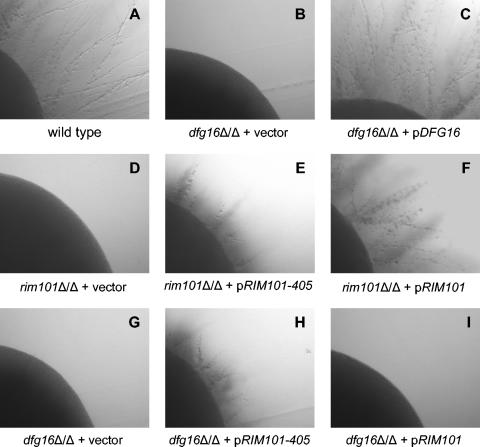
The C. albicans ORF19.881 (IPF9013) gene product is that organism's closest homolog of S. cerevisiae Dfg16p. (We refer to the C. albicans gene here as DFG16 based on the results below.) To determine whether this protein is required for C. albicans Rim101p pathway function, we examined the phenotype of C. albicans dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ deletion strains. In alkaline media, C. albicans produces hyphae, and this response depends upon Rim101p (4, 27). As expected, the wild-type reference strain displayed filamentous growth around the periphery of colonies on pH 8 plates, and a rim101Δ/rim101Δ mutant did not (Fig. 6A and D). We observed that a dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ mutant failed to yield filamentous growth, and this ability was restored by an ectopic copy of the wild-type DFG16 gene (Fig. 6B and C). Similar results were obtained with two additional dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ deletion strains that had been constructed independently (data not shown). Therefore, C. albicans DFG16 is required for filamentation in this alkaline medium.
FIG. 6.
Filamentation of C. albicans wild-type and mutant strains. Colonies were grown on M199 (pH 8) plates for 3 days at 37°C. The wild-type C. albicans reference strain DAY185 (A) was compared to C. albicans strains with mutations rim101/rim101Δ (D) and dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ (B) and to a dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ strain that had been complemented through integration of HIS1-DFG16 plasmid pKJB026 at the HIS1 locus (C). Both mutant C. albicans strains were transformed with plasmids pRIM101-405 (E, H) and pRIM101 (F, I) integrated into the RIM101 locus and empty vector controls (D, G). All strains in this comparison were prototrophic. All images are shown at the same magnification.
If the requirement for DFG16 in filamentation reflects a Rim101p pathway defect, then filamentation should be restored by introduction of the RIM101-405 allele. This allele specifies a C-terminally truncated product that suppresses filamentation defects of all tested Rim101p pathway mutants (4, 17, 37). We found that a copy of RIM101-405 restored filamentation to the dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ mutant, much as it did to a control rim101Δ/rim101Δ mutant (Fig. 6H and E). The suppression was not simply a result of increased overall RIM101 gene dosage, because a copy of wild-type RIM101 had no effect on dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ filamentation (Fig. 6I). These two results were verified with the two independent dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ deletion strains (data not shown). Function of the wild-type RIM101 copy was verified by its ability to complement the rim101Δ/rim101Δ mutant (Fig. 6F). These results support the conclusion that Dfg16p functions in the C. albicans Rim101p pathway.
To assess whether C. albicans Dfg16p may function in the MVB pathway, we again compared live-cell FM4-64 staining. The control wild-type C. albicans strain showed vacuolar staining (Fig. 4K and L). A control snf7/snf7 strain showed little vacuolar staining (Fig. 4M and N). These findings are in keeping with the extensive analysis by Kullas et al. (17). The dfg16Δ/dfg16Δ strain showed clear vacuolar staining (Fig. 4O and P). These results argue that Dfg16p is not required for MVB pathway function in C. albicans.
DISCUSSION
We describe here a new S. cerevisiae Rim101p pathway gene, DFG16, and show that its function is conserved in C. albicans. It is one of three predicted membrane proteins that function in the Rim101p pathway and, as such, is a candidate for an environmental sensor that promotes Rim101p processing. Recent findings indicate that the Rim101p and MVB pathways intersect, and FM4-64 staining indicates that Dfg16p does not function in the MVB pathway. We have borrowed the “compendium” strategy of Hughes et al. (12) on a small scale to develop a new criterion for genes at the Rim101p-MVB pathway intersection. These findings are of interest in providing new insight into MVB pathway function. They also invite speculation about the evolutionary pressures that co-opted the complex ESCRT machinery to participate in what might otherwise have been a simple protease-substrate reaction.
Rim101p pathway gene identification.
Our screen employed a CYC1pacC-lacZ reporter that is a direct assay for Rim101p function (18). The screen might have been simplified by using functional profiling results (9) to select the subset of strains that are sensitive to both NaCl and alkaline pH (7, 19). Unfortunately, rim101Δ mutations have a mild effect on these phenotypes in the S288c genetic background that is the platform for the deletion collection. Our screen of 84% of the deletion library led to the clear identification of one new gene that is required for processed Rim101p accumulation, DFG16. It also implicated two genes, YGR122W and GPH1, that may have a more complex relationship to Rim101p, perhaps affecting both processing and expression. Finally, it has provided numerous candidate genes that may govern RIM101 gene expression and Rim101p repression activity. These are areas that have received little attention. The overall results of the screen are preliminary, but promising signs of veracity are the cases in which known functionally related genes yielded similar mutant phenotypes. Examples include CKA2-CKB1, TUP1-SSN6, and SPE1-SPE2-SPE3. In addition, the spe1Δ, spe2Δ, and spe3Δ repression defects were reversed by supplementation of their spermidine auxotrophy (unpublished results). Thus, we expect that the results will be sufficiently reliable to make them useful.
Dfg16p function.
We focused here on DFG16 because the mutant's defects in haploid invasive growth (24) and processed Rim101p accumulation resemble other Rim101p pathway mutant defects. These observations, combined with microarray and Northern analysis for S. cerevisiae, and with mutant and suppressor analysis in C. albicans, indicate clearly that Dfg16p functions in the Rim101p pathway.
Dfg16p has some noteworthy features that frame a simple hypothesis for its mechanistic function. The Dfg16p sequences of S. cerevisiae and C. albicans are predicted by EMBOSS and SPLIT programs to have seven membrane-spanning segments and a long hydrophilic C-terminal region (see http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/protein?sgdid = S000005556 and http://split.pmfst.hr/split/). The EMBOSS prediction for S. cerevisiae Dfg16p includes a signal sequence as well. Either predicted architecture is shared with G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), leading to the hypothesis that Dfg16p may function as such a receptor. Dfg16p does not fall into a recognized GPCR subclass (15), so this model is quite speculative at present. However, it makes two simple, testable predictions. First, Rim8p (25, 31), which has homology to GPCR-interacting proteins of the β-arrestin family (20), may interact with Dfg16p to govern its localization or activity. Second, there may be a G protein that relays a Dfg16p-dependent signal. Therefore, while our findings do not establish a mechanistic role for Dfg16p, they provide a new framework to guide further investigation.
Rim21p may have seven transmembrane segments as well (25), though EMBOSS and SPLIT analysis programs predict that it has only six such segments. Nonetheless, the fact that Dfg16p and Rim21p are predicted membrane proteins suggests that they may function together, perhaps alongside the third predicted membrane protein, Rim9p. The closest A. nidulans homolog of Rim21p is PalH (E value, 8.0e-96; 68.3% aligned), as has long been appreciated (11). Interestingly, the closest A. nidulans homolog of Dfg16p is also PalH (E value, 2.0e-88; 59.1% aligned). Our results here confirm that Rim21p is an S. cerevisiae Rim101p pathway component, so the homology of both Rim21p and Dfg16p to PalH seems to be meaningful. Whether either S. cerevisiae protein, or perhaps both together, carries out a function equivalent to that of A. nidulans PalH is an interesting question. Given that there are homodimeric GPCRs (23), it seems possible that heterodimeric GPCRs may exist as well. One thought is that Dfg16p and Rim21p function as a heterodimeric receptor.
Functional interaction of MVB and Rim101p pathways.
It has seemed likely that the core ESCRT subunits that govern both MVB and Rim101p pathways may have additional unique functions (3, 28). For example, Bowers et al. (3) showed that almost all of the core ESCRT mutants are hypersensitive to LiCl and CaCl2. Sensitivity to LiCl is shared with Rim101p pathway mutants (18), but neither Rim101p pathway mutants nor other MVB pathway mutants are hypersensitive to CaCl2. In addition, Shiflett et al. (28) showed that almost all core ESCRT mutants are resistant to the cell wall inhibitor calcofluor white, unlike other MVB pathway mutants. Our finding that PRY1 is up-regulated and that ASN1 is down-regulated in three core ESCRT mutants, but not in rim101Δ or vps4Δ mutants, strengthens the case for a unique role of core ESCRT subunits. Four conditions, nitrogen depletion, amino acid starvation, stationary phase, and postdiauxic growth, cause an increase in PRY1 expression and a decrease in ASN1 expression in wild-type strains (6, 8). A simple inference is that the core ESCRT mutants respond to nitrogen or carbon limitation after a shift to pH 8, the conditions under which we examined gene expression. Indeed, the core ESCRT subunits Snf7p and Snf8p were first characterized genetically for their role in SUC2 derepression in response to glucose limitation (33, 38), an independent indication that they may affect a carbon-sensing pathway. We suggest two simple models to explain this unique role. One model is that the core ESCRT subunits function in a third pathway in addition to the MVB and Rim101p pathways; glucose- or nitrogen-sensing pathways are good candidates. This model is intriguing because it implies that the core ESCRT complex coordinates diverse cellular responses. A second model is that the MVB and Rim101p pathways have a redundant function, perhaps in nutrient limitation responses. Thus, defects in either pathway alone do not affect PRY1 and ASN1 expression because the other pathway provides a compensating function. However, a defect in both pathways, as is caused by core ESCRT subunit mutations, eliminates the compensating functions and causes altered PRY1 and ASN1 expression. This model is satisfying because it provides an explanation for the sharing of eight gene products by the two pathways: the postulated redundant function may be necessary in response to a particular level of ESCRT activity or MVB pathway flux. Thus, evolution may have favored a fungal progenitor that augmented a core ESCRT-dependent starvation response through its coordination with a Rim101p-dependent response.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Vincent Bruno and Clarissa Nobile for providing strains, plasmids, discussions, and comments on the manuscript.
This work was supported by RO1 grant GM39531 from the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://ec.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Amerik, A. Y., J. Nowak, S. Swaminathan, and M. Hochstrasser. 2000. The Doa4 deubiquitinating enzyme is functionally linked to the vacuolar protein-sorting and endocytic pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 11:3365-3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bensen, E. S., S. J. Martin, M. Li, J. Berman, and D. A. Davis. 2004. Transcriptional profiling in Candida albicans reveals new adaptive responses to extracellular pH and functions for Rim101p. Mol. Microbiol. 54:1335-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bowers, K., J. Lottridge, S. B. Helliwell, L. M. Goldthwaite, J. P. Luzio, and T. H. Stevens. 2004. Protein-protein interactions of ESCRT complexes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Traffic 5:194-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Davis, D., R. B. Wilson, and A. P. Mitchell. 2000. RIM101-dependent and -independent pathways govern pH responses in Candida albicans. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:971-978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Davis, D. A., V. M. Bruno, L. Loza, S. G. Filler, and A. P. Mitchell. 2002. Candida albicans Mds3p, a conserved regulator of pH responses and virulence identified through insertional mutagenesis. Genetics 162:1573-1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.DeRisi, J. L., V. R. Iyer, and P. O. Brown. 1997. Exploring the metabolic and genetic control of gene expression on a genomic scale. Science 278:680-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Futai, E., T. Maeda, H. Sorimachi, K. Kitamoto, S. Ishiura, and K. Suzuki. 1999. The protease activity of a calpain-like cysteine protease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for alkaline adaptation and sporulation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260:559-568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gasch, A. P., P. T. Spellman, C. M. Kao, O. Carmel-Harel, M. B. Eisen, G. Storz, D. Botstein, and P. O. Brown. 2000. Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes. Mol. Biol. Cell 11:4241-4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Giaever, G., A. M. Chu, L. Ni, C. Connelly, L. Riles, S. Veronneau, S. Dow, A. Lucau-Danila, K. Anderson, B. Andre, A. P. Arkin, A. Astromoff, M. El-Bakkoury, R. Bangham, R. Benito, S. Brachat, S. Campanaro, M. Curtiss, K. Davis, A. Deutschbauer, K. D. Entian, P. Flaherty, F. Foury, D. J. Garfinkel, M. Gerstein, D. Gotte, U. Guldener, J. H. Hegemann, S. Hempel, Z. Herman, D. F. Jaramillo, D. E. Kelly, S. L. Kelly, P. Kotter, D. LaBonte, D. C. Lamb, N. Lan, H. Liang, H. Liao, L. Liu, C. Luo, M. Lussier, R. Mao, P. Menard, S. L. Ooi, J. L. Revuelta, C. J. Roberts, M. Rose, P. Ross-Macdonald, B. Scherens, G. Schimmack, B. Shafer, D. D. Shoemaker, S. Sookhai-Mahadeo, R. K. Storms, J. N. Strathern, G. Valle, M. Voet, G. Volckaert, C. Y. Wang, T. R. Ward, J. Wilhelmy, E. A. Winzeler, Y. Yang, G. Yen, E. Youngman, K. Yu, H. Bussey, J. D. Boeke, M. Snyder, P. Philippsen, R. W. Davis, and M. Johnston. 2002. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418:387-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gietz, R. D., and R. A. Woods. 2002. Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods Enzymol. 350:87-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gonzalez-Lopez, C. I., R. Szabo, S. Blanchin-Roland, and C. Gaillardin. 2002. Genetic control of extracellular protease synthesis in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Genetics 160:417-427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hughes, T. R., M. J. Marton, A. R. Jones, C. J. Roberts, R. Stoughton, C. D. Armour, H. A. Bennett, E. Coffey, H. Dai, Y. D. He, M. J. Kidd, A. M. King, M. R. Meyer, D. Slade, P. Y. Lum, S. B. Stepaniants, D. D. Shoemaker, D. Gachotte, K. Chakraburtty, J. Simon, M. Bard, and S. H. Friend. 2000. Functional discovery via a compendium of expression profiles. Cell 102:109-126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ito, T., T. Chiba, R. Ozawa, M. Yoshida, M. Hattori, and Y. Sakaki. 2001. A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:4569-4574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kaiser, C., S. Michaelis, and A. Mitchell. 1994. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 15.Karchin, R., K. Karplus, and D. Haussler. 2002. Classifying G-protein coupled receptors with support vector machines. Bioinformatics 18:147-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Katzmann, D. J., G. Odorizzi, and S. D. Emr. 2002. Receptor downregulation and multivesicular-body sorting. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:893-905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kullas, A. L., M. Li, and D. A. Davis. 2004. Snf7p, a component of the ESCRT-III protein complex, is an upstream member of the RIM101 pathway in Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 3:1609-1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lamb, T. M., and A. P. Mitchell. 2003. The transcription factor Rim101p governs ion tolerance and cell differentiation by direct repression of the regulatory genes NRG1 and SMP1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:677-686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lamb, T. M., W. Xu, A. Diamond, and A. P. Mitchell. 2001. Alkaline response genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their relationship to the RIM101 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276:1850-1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lefkowitz, R. J., and E. J. Whalen. 2004. β-Arrestins: traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16:162-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li, M., S. J. Martin, V. M. Bruno, A. P. Mitchell, and D. A. Davis. 2004. Candida albicans Rim13p, a protease required for Rim101p processing at acidic and alkaline pHs. Eukaryot. Cell 3:741-751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li, W., and A. P. Mitchell. 1997. Proteolytic activation of Rim1p, a positive regulator of yeast sporulation and invasive growth. Genetics 145:63-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Milligan, G. 2004. G protein-coupled receptor dimerization: function and ligand pharmacology. Mol. Pharmacol. 66:1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mosch, H. U., and G. R. Fink. 1997. Dissection of filamentous growth by transposon mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 145:671-684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Penalva, M. A., and H. N. Arst, Jr. 2002. Regulation of gene expression by ambient pH in filamentous fungi and yeasts. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 66:426-446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ramon, A. M., and W. A. Fonzi. 2003. Diverged binding specificity of Rim101p, the Candida albicans ortholog of PacC. Eukaryot. Cell 2:718-728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ramon, A. M., A. Porta, and W. A. Fonzi. 1999. Effect of environmental pH on morphological development of Candida albicans is mediated via the PacC-related transcription factor encoded by PRR2. J. Bacteriol. 181:7524-7530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shiflett, S. L., D. M. Ward, D. Huynh, M. B. Vaughn, J. C. Simmons, and J. Kaplan. 2004. Characterization of Vta1p, a class E Vps protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 279:10982-10990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Spellman, P. T., G. Sherlock, M. Q. Zhang, V. R. Iyer, K. Anders, M. B. Eisen, P. O. Brown, D. Botstein, and B. Futcher. 1998. Comprehensive identification of cell cycle-regulated genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by microarray hybridization. Mol. Biol. Cell 9:3273-3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Spreghini, E., D. A. Davis, R. Subaran, M. Kim, and A. P. Mitchell. 2003. Roles of Candida albicans Dfg5p and Dcw1p cell surface proteins in growth and hypha formation. Eukaryot. Cell 2:746-755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Su, S. S., and A. P. Mitchell. 1993. Identification of functionally related genes that stimulate early meiotic gene expression in yeast. Genetics 133:67-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Su, S. S., and A. P. Mitchell. 1993. Molecular characterization of the yeast meiotic regulatory gene RIM1. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:3789-3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tu, J., L. G. Vallier, and M. Carlson. 1993. Molecular and genetic analysis of the SNF7 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 135:17-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Vida, T. A., and S. D. Emr. 1995. A new vital stain for visualizing vacuolar membrane dynamics and endocytosis in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 128:779-792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wilson, R. B., D. Davis, and A. P. Mitchell. 1999. Rapid hypothesis testing with Candida albicans through gene disruption with short homology regions. J. Bacteriol. 181:1868-1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Xu, W., and A. P. Mitchell. 2001. Yeast PalA/AIP1/Alix homolog Rim20p associates with a PEST-like region and is required for its proteolytic cleavage. J. Bacteriol. 183:6917-6923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xu, W., F. J. Smith, Jr., R. Subaran, and A. P. Mitchell. 2004. Multivesicular body-ESCRT components function in pH response regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Mol. Biol. Cell 15:5528-5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yeghiayan, P., J. Tu, L. G. Vallier, and M. Carlson. 1995. Molecular analysis of the SNF8 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 11:219-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yeo, S. C., L. Xu, J. Ren, V. J. Boulton, M. D. Wagle, C. Liu, G. Ren, P. Wong, R. Zahn, P. Sasajala, H. Yang, R. C. Piper, and A. L. Munn. 2003. Vps20p and Vta1p interact with Vps4p and function in multivesicular body sorting and endosomal transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 116:3957-3970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.