Abstract
Advances in omics technologies have enabled the in-depth study of microbial communities and their metabolic profiles from all environments. Here metagenomes were sampled from piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus) and from river water from the Rio São Benedito (Amazon Basin). Shotgun metagenome sequencing was used to explore diversity and to test whether fish microbiomes are a good proxy for river microbiome studies. The results showed that the fish microbiomes were not significantly different from the river water microbiomes at higher taxonomic ranks. However, at the genus level, fish microbiome alpha diversity decreased, and beta diversity increased. This result repeated for functional gene abundances associated with specific metabolic categories (SEED level 3). A clear delineation between water and fish was seen for beta diversity. The piranha microbiome provides a good and representative subset of its river water microbiome. Variations seen in beta biodiversity were expected and can be explained by temporal variations in the fish microbiome in response to stronger selective forces on its biodiversity. Metagenome assembled genomes construction was better from the fish samples. This study has revealed that the microbiome of a piranha tells us a lot about its river water microbiome and function.
Keywords: Metagenomics, Serrasalmus rhombeus, Host-associated microbiome, Amazon river microbiome, Biotechnology
Subject terms: Biological techniques, Biotechnology, Ecology, Microbiology, Ecology, Environmental sciences
Introduction
Microbiomes are a trove of biological activity with the potential to advance the fields of biotechnology and industry 5.01. Next-generation sequencing has allowed us to delve deeper into microbiomes, bringing microbial ecology into the age of ‘big data’ where we can generate sequence data en-masse that can be parsed for metabolic or functional information of interest2–4. However, the habitats that host these precious bioproducts and their associated microbial candidates can often be highly complex and diverse. Approaches that simplify the community present an easier avenue to unravel the metabolic interactions within the target ecosystems5,6. One such strategy is through the gut microbiota of host organisms, which has been shown to produce a simplified subset of the greater environment7.
The gut microbiome presents a unique environment for bioprospecting as the commensal microorganisms are often involved with digestion and nutrient availability, containing enzymes that can improve the bioavailability of compounds8. Genome-resolved metagenomics of the collective data of the human gut microbiome alone has uncovered thousands of hitherto uncultured prokaryotes, along with protein sequences with no known functional representatives9. The exploration of gut microflora has shown promise towards the discovery of novel bioproducts, with searches expanding to non-human organisms. Where microbial candidates with plastic biodegradation potential from mealworms have been described10; bioactive compounds from fish and shellfish with health benefits in pharmaceutical or aquaculture settings reported11; enzymes with industrial applications from mud crabs described12, as well as cow dung microflora which hosts a range of potential enzymes and compounds for widespread applications in biotechnology and bioremediation13. Taken together, gut microbiomes provide a lens into wider environments by enriching and simplifying the environmental biodiversity within the resident hosts.
One group of organisms that shares a direct relationship with their ecosystems are fish, which due to the nature of their existence form an intimate holobiont with the aquatic environment and their gut microbiota14–17. The relationship between gut and environment in fish can often be distinguished over geographical regions, with distinct patterns appearing across spatial distances17–19, with the gut providing a relatively stable environment, free from environmental perturbations20. The investigation of fish microflora has improved aquaculture practices 11,21,22 and has been shown to be a source of novel antimicrobial compounds, which is key to combatting the growing horde of multidrug-resistant pathogens23,24. To investigate the ability of fish to act as a method for enriching taxa and functions from the aquatic environment, whole shotgun sequencing was used to compare the metagenomes of the Rio São Benedito, a river located in the Amazon Basin in Pará, Brazil and the gut microbiome of the endemic Redeye Piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus). Our aims were to investigate differences in microbial community composition between gut microbiome and environment, such as differential metabolic gene abundances, as well as the propagation of underrepresented taxa from the environment. In addition, we sought to evaluate the suitability of fish for their bioprospecting potential in freshwater environments.
Results
Taxonomic profile of the metagenomes
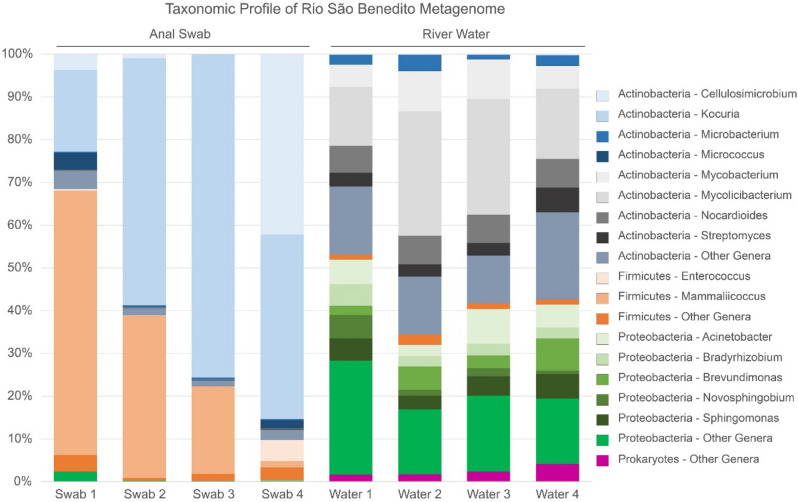
The study investigated two sample groups obtained from the São Benedito River, Brazil (Fig. 1): gut microbiota of Serrasalmus rhombeus via anal swabs (n = 4) and water microbiome samples (n = 4). Comparative analyses were performed on metagenomic sequences obtained from both sample groups, with a distinct difference in the overall distribution of prokaryotic taxa observed between the anal swab and river water metagenomes (Fig. 2). Bacterial phyla from Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria were present in all samples, with a minute representation of Bacteroidota, Deinococcus-Thermus, and Planctomycetota, along with archaeal representatives from Euryarchaeota within the river water samples (Supplementary Table 1). Anal swabs appear to be mostly represented by Actinobacteria and Firmicutes, whereas river water contains mainly members from Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria. At the genus level, a finer distinction between the anal swab and river water samples was observed. In the anal swab group, each phylum is dominated by only one or two genera—notably Kocuria and Cellulosimicrobium within the Actinobacteria, and Mammaliicoccus in the Firmicutes. In comparison, the river water samples had a more diverse representation of genera from each respective bacterial phylum reported. Mycobacterium and Mycolicibacterium are the major representatives of Actinobacteria, while Brevundimonas and Novosphingobium are the most abundant genera in Proteobacteria. Additionally, the Actinobacteria observed in the river water contained genera that were at negligible levels in the anal swabs and vice versa.
Fig. 1.
Photos of fish and river sampling on the Rio São Benedito, located in the Amazon Basin in Pará, Brazil. (a–c) Example specimens of the endemic Redeye Piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus) sampled in the study. (d) Demonstration of river water sampling using a Sterivex filter unit.
Fig. 2.
Taxonomic profile of the Rio São Benedito fish and water metagenomes. The graph shows distribution of the 15 most abundant prokaryotic genera from anal swab and water samples and their respective phyla.
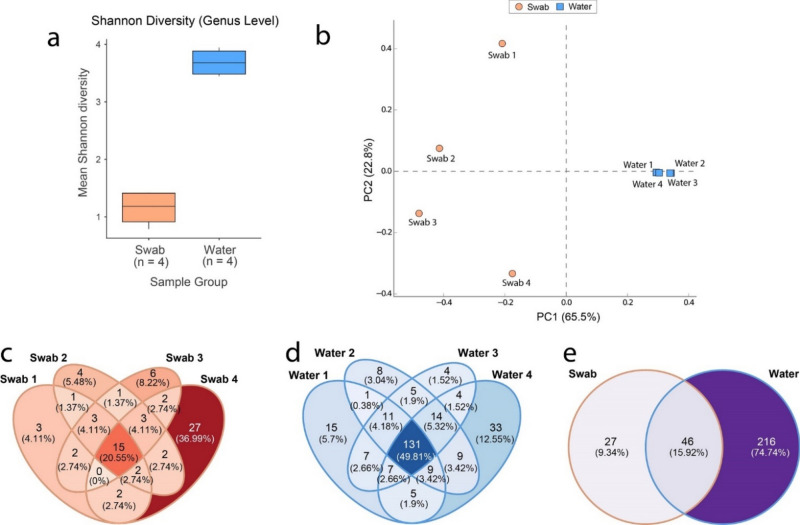
There appeared to be a significant difference in the alpha diversity at the genus level in the prokaryotic communities between the anal swab and river water metagenomes (Shannon index, one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001). In parallel to the taxonomic profile, the alpha diversity measured seemed to be much lower in the anal swab samples compared to the river water (Fig. 3a). Similarly, there was a significant difference observed between the community structures from the anal swab and river water metagenomes (PERMANOVA, with pseudo-F ratio, p < 0.01). The principal component analysis plot also suggests that the community structures of prokaryotes differ between the two sample groups (Fig. 3b). The river microbiome seems to cluster closely, suggesting a greater similarity in prokaryotic community structure, whereas the fish microbiota, appears to be dissimilar to the river water, as well as within their own sampling group. This was also seen in the unique genera count within the anal swab sampling group (Fig. 3c) which showed less overlap in common taxa compared to the river water (Fig. 3d). The prokaryotic genera count within the two sample groups from the Rio São Benedito shows that the river water sampling group has a much higher number of unique genera when compared to the anal swab sampling group (Fig. 3e). The relatively small overlap of taxa between the river and fish microbiomes appeared consistent with both the data from the taxonomic profile, as well as what was observed in the diversity measures. There appears to be a small group of prokaryotic genera that are unique to the anal swab microbiome, despite the fish microbiome being largely derived from the river water. This suggests that the conditions within the host-associated ecosystem may promote a subset of taxa that may be otherwise underrepresented within the aquatic environment of the river.
Fig. 3.
Diversity measures of Rio São Benedito water and piranha anal swab samples at the genus level for prokaryotic communities. (a) Alpha diversity represented by Shannon Index showing significant differences between anal swab and river samples (one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001). (b) Beta diversity represented by principal component analysis plot showing differences in the structure of prokaryotic communities from anal swab and river water samples. The axes show the Principal Components (PC), with PC1 and PC2 respectively explaining 65.5% and 22.8% of the total variance. Only entries where at least 10 reads were classified within a given sample from either swab or water metagenomes were used for diversity measures. Venn diagram representing unique and common counts of prokaryotic genera between (c) anal swabs, (d) water and (e) both sampling groups overall. For Venn Diagram counts, only entries where at least 10 counts were classified to a genus within an individual swab or river sample were included.
Functional profiles of metabolic gene abundances
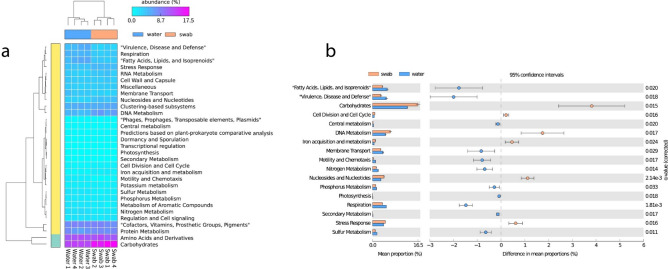
Differential abundance analyses of metabolic genes in the anal swab and river water samples showed differences at SEED Level 1, which provided a generalized overview of different metabolic categories (Fig. 4a). At SEED Level 1, significant differences in metabolic gene abundances were observed in several categories (Fig. 4b) with genes related to “Carbohydrates”, “Cell Division and Cell Cycle”, “DNA Metabolism”, “Iron acquisition and metabolism”, “Nucleosides and Nucleotides” and “Stress Response” significantly enriched in the fish microbiota. More categories of genes were significantly abundant in the river water, namely from “Central Metabolism,” “Fatty Acids, Lipids and Isoprenoids”, “Membrane Transport”, “Motility and Chemotaxis”, “Nitrogen Metabolism”, “Phosphorus Metabolism”, “Photosynthesis”, “Respiration”, “Secondary Metabolism”, “Sulfur Metabolism”, and “Virulence, Disease and Defense.”
Fig. 4.
Differential abundance of metabolic genes from the anal swab and river water metagenomes. Differences in relative abundance of metabolic gene groups categorized at SEED Level 1 were visualized via (a) heatmap of all classified functional genes with (b) the significant differences in differential abundance displayed as a bar plot with error bars (two-sided Welch’s t test, with Benjamin-Hochberg method for false discovery rate, q < 0.05).
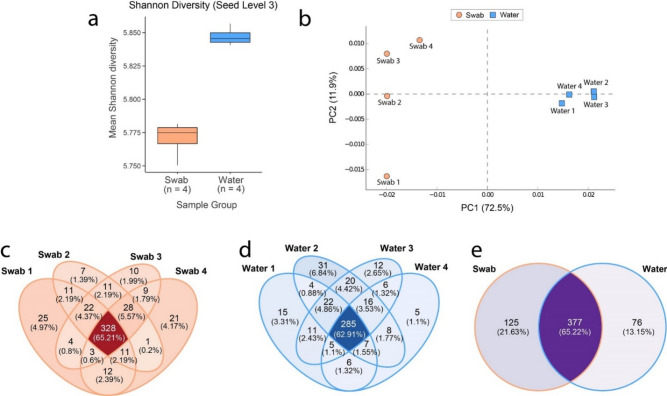
The Shannon Index shows close similarity of the alpha diversity of functional gene abundances in the anal swab and river water samples at SEED level 3, which consists of more specific metabolic categories (Fig. 5a). The beta-diversity of the functional profile as visualized by the principal component analysis plot, showed a clear delineation between the two sampling groups, with a tighter clustering in the water samples (Fig. 5b), which appears consistent with the data observed in the taxonomic diversity (Fig. 3b). The distinct community structures observed in the metabolic profile appeared to be significantly different (PERMANOVA, with pseudo-F ratio, p < 0.05). When compared to the taxonomic data, the classified metabolic genes showed > 60% overlap at the SEED Level 3 categories within and across respective sampling groups (Fig. 5c–e). This indicates that there are core metabolic processes that are critical for survival across both environments. The relative smaller group of unique metabolic genes observed in each respective sampling group, along with the observations seen in the taxonomic profile, are likely due to adaptations from ecological differences between an aquatic environment (river water) and a host-associated ecosystem (gut microbiota).
Fig. 5.
Diversity and abundance measures of Rio São Benedito water and piranha anal swab samples for functional genes at SEED level 3. (a) Alpha diversity represented by Shannon Index between anal swab and river samples. (b) Beta diversity represented by principal component analysis plot showing differences in the community metabolic structure from anal swab and river water samples. The axes show the Principal Components (PC), with PC1 and PC2 respectively explaining 72.5% and 11.9% of the total variance. Only entries where at least 10 reads were classified within a given sample from either swab or water metagenomes were used for diversity measures. Venn diagram representing unique and common counts of functional genes categorized at SEED level 3 between (c) anal swabs, (d) water and (e) both sampling groups overall. For Venn Diagram counts, only entries where at least 10 counts were classified to a category within an individual swab or river sample were included.
Recovery of metagenome-assembled genomes
Metagenomes from the anal swab and river water sampling group underwent co-assembly within their respective groups. The anal swab group co-assembly produced better assembly statistics compared to the river water co-assembly and read mapping information showed that substantially more of the reads (78.96% vs 5.30%) were utilized in the assembly process (Supplementary Table 2). Co-assembly of the river water metagenomes yielded no bins or metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs). Conversely, co-assembly of the metagenomes from anal swab samples produced four MAGs, with the genome quality and classification statistics available in Supplementary Table 3. Three recovered MAGS were identified by GTDB-tk as Kocuria rhizophila A (86.39% completeness), Kocuria marina (16.4% completeness), and Mammaliicoccus sciuri (36.78% completeness). The fourth MAG was unable to be classified by GTDB-tk. The recovered genomes appear to be from the highest represented genera from the taxonomic profile of the anal swab samples and were either underrepresented or not observed in the river water samples (Fig. 1). This suggests that the fish microbiota can enrich underrepresented taxa from the river environment, as well as provide a simplified microbiome with the potential for enabling shallow genome-resolved metagenomics.
Discussion
Our study revealed that the S. rhombeus gut microcosm presents taxonomically distinct communities when compared to the microbiome of the Rio São Benedito. Notably, the gut appears to enrich prokaryotic genera that were underrepresented in the river water and produces simplified communities (Fig. 2). As expected, the Shannon index was higher for the river samples, indicating that their communities are more diverse and uniform; while the fish gut metagenomes possessed more biased microbial communities which is probably explained by variable conditions in the gut environment. The beta diversity analysis showed that river water and fish gut metagenomes clearly clustered separately. Furthermore, the fish gut samples displayed greater intra sample variability in their microbial communities. This could be a result of a more dynamic gut microbiota, which is strongly affected by host factors such as stress and diseases25.
At the genus level, Kocuria, Mammaliicoccus, and Cellulosimicrobium are the dominant genera identified in the fish gut microbiome. Mammaliicoccus is a novel genus proposed by Madhaiyan, Wirth, and Saravanan (2020), who suggested the reassignment of five Staphylococcus species26. Interestingly, the type strains from this genus were isolated from mammals, namely ruminants as well as their meat and dairy products, other farm animals, along with canines27,28. Here, we report the discovery of Mammaliicoccus species in the Redeye piranha gut, sampled from the Amazon basin. On the other hand, we observed that Mycolicibacterium and Mycobacterium were the most abundant genera in the river water samples. However, it is worth mentioning that Mycolicibacterium is considered a taxonomic synonym to Mycobacterium29. Therefore, we can conclude that the São Benedito water metagenomes are composed of 20–40% of Mycobacterium species.
Considering that piranhas feed at all depths and move freely within river ecosystems, we hypothesized that they act as a lens to the river's microbial community. In this manner, they sample and enrich a small subset of the total river's microbial community, which allows for the recovery of nearly complete metagenome-assembled genomes30. In contrast, the metabolic gene profile, although containing differences between the gut and river microbiomes, appears to have much more overlap (Figs. 4, 5). This is explained as the fish gut microbiome has been observed to be derived from the aquatic habitat14,15, which in turn suggests that the functional traits of the core microbiome of the river water persist within the fish gut microbiome31. This indicates that the fish gut has the potential to present a simplified representative model, allowing for a more accessible lens to the ecological process and functional capacity of the more diverse river microbiome5,7.
Concerning the functional analyses, some of the categories displayed differentially abundant frequencies. We observed a differentially abundant profile for the respiration category in the water metagenomes (Fig. 4b). This could be because the Mycobacterium genus is more prevalent in these metagenomes and that Mycobacterium are obligate aerobes32. On the other hand, the gut metagenomes are mainly composed of representatives from the Kocuria genus, which are facultatively anaerobic33. Altogether, both these circumstances create conditions that justify the statistically different results. In addition, the fish gut metagenomes presented more abundant sequences for carbohydrate metabolism. A possible explanation could be the fact that piranha have a rich and diverse diet, allowing for a similarly diverse group of bacteria to metabolize more types of carbohydrates34.
As expected, the motility and chemotaxis systems were more abundant in the river water samples. In aquatic ecosystems, bacteria are divided into either particle-attached bacteria or free-living bacteria35. While particle-attached bacteria colonize those substrates and metabolize the organic matter, free-living bacteria depend on their ability to perceive chemical stimuli and move towards resources, oxygen concentration, and other environmental conditions via fimbriae, pili, and flagella. On the other hand, bacteria that colonize hosts, such as those from the fish gut, depend more on their ability to interact with the host cells and adhere to surfaces36.
The iron acquisition and metabolism group were statistically more abundant in the fish gut metagenomes. In most ecosystems, especially in open waters, iron is a limiting nutrient and as a result microorganisms have developed methods to capture and attract this element, such as via siderophores37. It is interesting to hypothesize that the iron acquisition and metabolism group may be more abundant in the fish gut metagenome samples due to the harshness and competitiveness found there. This is likely a microbial response to the host’s “nutritional immunity”, where trace elements such as iron is sequestered by the host to limit pathogenicity within the gut microbiome38.
The comparisons of the host-associated and environmental ecosystems in fish populations have recently provided a springboard towards the understanding of how the microbiome can be understood and utilized to improve fish health, combat pathogens, and provide sustainable aquaculture practices39,40. Delving into the beneficial microbes within the fish gut flora, provides an avenue for improving the likelihood of bioprospecting taxa with useful bioproducts41,42. Within the S. rhombeus gut, the study found several bacterial candidates of interest. Fish microbiomes are a source of metabolites against multidrug-resistant bacteria29. For instance, Kocuria rhizophila produces antimicrobial substances, namely bacteriocins30. Similarly, we identified Mammaliicoccus sciuri within the S. rhombeus gut flora, with some representatives harboring substances with probiotic properties which could be potential candidates for gut health therapies31. The exploration of the fish gut flora may also serve as a enrichment approach to elucidate underrepresented taxa from the environment43.
The lower complexity community of the fish gut microbiome may also provide a more accessible metagenome for in-silico studies. Genome mining has been a valuable technique for the discovery of bioproducts from genomic data44, but has also been pivotal in uncovering hitherto undiscovered enzymes and natural products with unknown activity45. The microbial MAGs uncovered by de novo recovery from the natural environment have been critical in expanding the tree of life46 and unlocked the massive biosynthetic potential of the world’s oceans47, but the massive computational power needed to process these high diversity communities make genome-resolved metagenomics costly and difficult48,49. The gut microbiota was able to bin several MAGs, one with over 88% completion, compared to no bins from the relatively diverse river sample (Supplementary Table 2). Although this represents only a small derivative of the river’s microbiome, this approach was able to recover MAGs from a relatively small sequencing dataset, presenting a more accessible approach for in-silico bioprospecting and genome mining.
Conclusion
Piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus) from the Rio São Benedito, a river in Amazon Basin in Brazil were selected as a model Amazon Basin fish to investigate and compare river and fish gut microbiomes. Taxonomic and functional diversity were compared between the water and fish with the results clearly indicating that the gut microbiome provides a lens on the river water diversity. A lens which both simplifies the waters microbiome complexity, enriches for taxa of biotechnological interest and genome mining while demonstrating that functional diversity is not lost in the less diverse fish microbiome. Using piranha to elucidate river water diversity and function s a new and promising science, but further studies are required with other fish species and in other rivers to test this hypothesis.
Methods
Sample collection and preparation
Piranha are a ubiquitous shoaling fish found throughout almost all the river in the Amazon basin. They feed at all depths in the water and move freely within river systems. A model fish that roams around within its environment and a good candidate to sample the river water environment and all in it. Fish and river water samples were collected from the Rio São Benedito, located in Pará, Brazil (Fig. 1, Supplementary Table 4, Supplementary Fig. 1) Wild fish were collected live and released unharmed, they varied in size from 15 to 25 cm, were not sexually dimorphic and gender not recorded, they were caught from the same general location near the Thaimacu Pousada (Supp Fig 1), all were caught within two hours. All experimental protocols with live animals were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations in agreement with ARRIVE https://arriveguidelines.org. The methodology was approved by the ethics committee of the Postgraduate Programme for Biotechnology at Centre for Health Sciences at UFRJ.
Fish used for sampling in this study were endemic S. rhombeus caught from the Rio São Benedito. Anal swabs for collecting individual fish microbiota samples were performed via a cotton wool bud inserted in anus to depth of 1cm (area of swab material), twisted 360° three times and removed. River water was sampled on location, with 500ml of water filtered via a Sterivex filter unit (Merck) with 0.22 µm pore size Millipore Express (PES) membrane at each sampling site to collect the microbiota present. Swab and filter samples collected from the river were frozen until use in downstream processing. DNA was extracted from the swab and filter samples using the DNeasy® PowerSoil® Pro Kit (QIAGEN, Cat. No./ID: 47014) following the manufacturer’s instructions and was quantified by Qubit (Invitrogen). Library preparation was performed using the Nextera XT DNA Library Prep kit v2 (Illumina) to prepare the DNA samples for whole genome sequencing. Samples were sent to LAGBIO (Paraná, Brazil) for sequencing on the Miseq platform (Illumina) using the 2 × 150 bp chemistry and produced an average of 207K reads per sample.
Metagenomic profiling and analyses
The quality control of raw reads was performed using fastp (0.23.2)50 with default parameters. Prior to comparative ecological analyses of the taxonomic and metabolic profiles, datasets were subsampled to an equal depth with the sample with the lowest read count using seqtk (1.3.1; https://github.com/lh3/seqtk). Taxonomic profiling was performed using Kraken2 (2.1.2)51 and the prebuilt Kraken2 “Standard” database (released on 06/05/2023), with classified data filtered for prokaryotes only. Functional profiling was done using SUPER-FOCUS (1.5)52 with diamond (0.9.14)53 as the aligner, and the DB_90 database option selected.
Taxonomic profile data was explored at the genus level, whereas functional gene profiles were investigated at the SEED Level 1 and 3 metabolic subcategories (Supplementary Table 5)54. Alpha diversity measures using the Shannon Index, as well as one one-way ANOVA, and PERMANOVA statistical calculations on taxonomic and metabolic abundance data were performed using the vegan R package (2.6.4)55, with the Shannon diversity visualized using ggplot2 (3.4.1)56. Unique taxa and functional genes between anal swab and river water samples were visualized using the ggVennDiagram (1.2.2)57 R package. STAMP (2.1.3)58 was used to visualize the beta-diversity of all samples at the SEED Level 3 functional profile, as well as at the genus level for the taxonomic profile, via a principal component analysis plot using an ANOVA test, with Tukey–Kramer post-hoc test for confidence interval and Benjamin-Hochberg method for false discovery rate correction. STAMP was also used to visualize differential abundances in functional genes at the SEED Level 1 subcategories between the anal swab and river water sampling groups, applying a two-sided Welch’s t test, with the Benjamin-Hochberg method for false discovery rate correction.
Metagenomic assembly and binning
De novo co-assembly was performed on all combined metagenomic reads for the anal swab samples, as well as respectively for the river water samples using MEGAHIT (1.2.9)59 with the default parameters. Read mapping of metagenomic reads to contigs assembled by MEGAHIT was conducted using Bowtie 2 (2.5.0)60. The subsequent mapping data processed by Samtools (1.15)61 for downstream analyses as well as for checking read mapping statistics. Binning was done with MetaBAT 2 (2.15)62 on the contigs and associated mapping data with minimum contig length set to 1500 base pairs. CheckM (1.2.2)63 was used to assess the completeness and contamination levels of the recovered metagenomic bins. All recovered MAGs were classified using GTDB-tk (2.3.2)64 with the R214 GTDB release data.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
AM thanks the Brazilian Federal Government funding agency CAPES for financial support from its ProInternational (PRINT) programme: grant code 001 that provided the financial support to visit UWA and CSIRO in Australia where some of the analyses were done. SS and JRVA thank the Brazilian Federal Government funding agency: CNPq for their PhD and Master’ Scholarship grants. AM and SSO thank the Rio de Janeiro State funding agency FAPERJ for APQ1 grants. SS thanks Dimensions Science for a bridging grant post-Ph.D. AM thanks Renato Ferreira de Oliveira and Barbara Peckle for laboratory support. AM and ASW thank Pousada Thaimacu for the accommodation and boats and Dale Smith, Steve Smith, Dan Marland, Michael Conner, Justin James Mytton Thornycroft and Bernard Woodcock for sampling, logistical and libation support. PV and PK thank Joel Andrew Bellesini for his preliminary work under the Pawsey Internship program. All authors thank the Programa de Pos-graduacao em Biotecnologia Vegetal e Bioprocessos (PBV) da Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), The University of Western Australia (UWA) and, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO), for their support, financial and otherwise. The authors also give thanks to the resources provided by the Pawsey Supercomputing Research Centre with funding from the Australian Government and the Government of Western Australia.
Author contributions
These authors contributed equally, as first authors: Sheila da Silva, Paton Vuong. These authors jointly supervised the work: Parwinder Kaur, Andrew Macrae. JRVA, SSO, VA, ABV, DJB, were involved in bioinformatic analyses and discussions. ASW, PK and AM were involved in experimental design, hypotheses, sampling, analyses and discussions. SS was involved in experimental design, sampling, bioinformatic analyses, discussions, manuscript drafting and editing. PV was involved in bioinformatic analyses, discussions and wrote the manuscript with SS, with input from all authors.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI repository, under BioProject ID PRJNA1064611.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Sheila da Silva and Paton Vuong.
These authors jointly supervised this work: Andrew Macrae and Parwinder Kaur.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-024-72329-8.
References
- 1.D’Hondt, K. et al. Microbiome innovations for a sustainable future. Nat. Microbiol.6, 138–142 (2021). 10.1038/s41564-020-00857-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Krüger, A., Schäfers, C., Busch, P. & Antranikian, G. Digitalization in microbiology—Paving the path to sustainable circular bioeconomy. New Biotechnol.59, 88–96 (2020). 10.1016/j.nbt.2020.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wani, A. K. et al. Bioprospecting culturable and unculturable microbial consortia through metagenomics for bioremediation. Clean. Chem. Eng.2, 100017 (2022). 10.1016/j.clce.2022.100017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gutleben, J. et al. The multi-omics promise in context: From sequence to microbial isolate. Crit. Rev. Microbiol.44, 212–229 (2018). 10.1080/1040841X.2017.1332003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Naylor, D. et al. Deconstructing the soil microbiome into reduced-complexity functional modules. mBio11, e01349–01320 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Zegeye Elias, K. et al. Selection, succession, and stabilization of soil microbial consortia. mSystems4, e00055–00019 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Sarkar, S. et al. Perspective: Simple state communities to study microbial interactions: Examples and future directions. Front. Microbiol.13, 65 (2022). 10.3389/fmicb.2022.801864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao, Y. et al. Potential roles of gut microbes in biotransformation of natural products: An overview. Front. Microbiol.13, 76 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Almeida, A. et al. A unified catalog of 204,938 reference genomes from the human gut microbiome. Nat. Biotechnol.39, 105–114 (2021). 10.1038/s41587-020-0603-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cf, S. F. et al. Bioprospecting of gut microflora for plastic biodegradation. Bioengineered12, 1040–1053 (2021). 10.1080/21655979.2021.1902173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Diwan, A. D., Harke, S. N., Gopalkrishna & Panche, A. N. Aquaculture industry prospective from gut microbiome of fish and shellfish: An overview. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr.106, 441–469 (2022). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Aman, A. M. & Mayenkar, S. Bioprospecting for industrially important biomolecules from gut microflora of the mud crab (Scylla serrata) from an estuary of the Mandovi River in Goa, India. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. India63, 94 (2021). [Google Scholar]
- 13.Behera, S. S. & Ray, R. C. Bioprospecting of cowdung microflora for sustainable agricultural, biotechnological and environmental applications. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci.2, 100018 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yang, H. et al. Quantifying the colonization of environmental microbes in the fish gut: A case study of wild fish populations in the Yangtze River. Front. Microbiol.12, 56 (2022). 10.3389/fmicb.2021.828409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xu, L. et al. Host species influence the gut microbiota of endemic cold-water fish in Upper Yangtze River. Front. Microbiol.13, 33 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Egerton, S., Culloty, S., Whooley, J., Stanton, C. & Ross, R. P. The gut microbiota of marine fish. Front. Microbiol.9, 45 (2018). 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim, P. S. et al. Host habitat is the major determinant of the gut microbiome of fish. Microbiome9, 166 (2021). 10.1186/s40168-021-01113-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hamilton, E. F. et al. Anadromous arctic char microbiomes: Bioprospecting in the high arctic. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.7, 12 (2019). 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pan, B. et al. Geographical distance, host evolutionary history and diet drive gut microbiome diversity of fish across the Yellow River. Mol. Ecol.32, 1183–1196 (2023). 10.1111/mec.16812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sylvain, F. -É. et al. Fish skin and gut microbiomes show contrasting signatures of host species and habitat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.86, e00789-e1720 (2020). 10.1128/AEM.00789-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen, C.-Z., Li, P., Liu, L. & Li, Z.-H. Exploring the interactions between the gut microbiome and the shifting surrounding aquatic environment in fisheries and aquaculture: A review. Environ. Res.214, 114202 (2022). 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gallo, B. D., Farrell, J. M. & Leydet, B. F. Fish gut microbiome: A primer to an emerging discipline in the fisheries sciences. Fisheries45, 271–282 (2020). 10.1002/fsh.10379 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Silva, S. D. et al.Aeromonas allosaccharophila strain AE59-TE2 is highly antagonistic towards multidrug-resistant human pathogens, what does its genome tell us?. Life12, 32 (2022). 10.3390/life12101492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tyagi, A., Singh, B., Billekallu Thammegowda, N. K. & Singh, N. K. Shotgun metagenomics offers novel insights into taxonomic compositions, metabolic pathways and antibiotic resistance genes in fish gut microbiome. Arch. Microbiol.201, 295–303 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.Sylvain, F. et al. Fish skin and gut microbiomes show contrasting signatures of host species and habitat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.86, 12 (2020). 10.1128/AEM.00789-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Madhaiyan, M., Wirth, J. S. & Saravanan, V. S. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.70, 5926–5936 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Schauer, B. et al. Diversity of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. and methicillin-resistant Mammaliicoccus spp. isolated from ruminants and New World camelids. Vet. Microbiol.254, 109005 (2021). 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nemeghaire, S. et al. The ecological importance of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group as a reservoir for resistance and virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol.171, 342–356 (2014). 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gupta, R. S., Lo, B. & Son, J. Phylogenomics and comparative genomic studies robustly support division of the genus Mycobacterium into an emended genus Mycobacterium and four novel genera. Front. Microbiol.9, 67 (2018). 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.van der Sleen, P. & Albert, J. S. Field Guide to the Fishes of the Amazon, Orinoco, and Guianas. (Princeton University Press, 2018).
- 31.Neu, A. T., Allen, E. E. & Roy, K. Defining and quantifying the core microbiome: Challenges and prospects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA118, e2104429118 (2021). 10.1073/pnas.2104429118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cook, G. M. et al. Physiology of mycobacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol.55(81–182), 318–189 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kandi, V. et al. Emerging bacterial infection: Identification and clinical significance of Kocuria species. Cureus8, e731 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kolmann, M. A. et al. Phylogenomics of Piranhas and Pacus (Serrasalmidae) uncovers how dietary convergence and parallelism obfuscate traditional morphological taxonomy. Syst. Biol.70, 576–592 (2021). 10.1093/sysbio/syaa065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hu, Y. et al. The relationships between the free-living and particle-attached bacterial communities in response to elevated eutrophication. Front. Microbiol.11, 9 (2020). 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pfister, C. A. et al. Conceptual exchanges for understanding free-living and host-associated microbiomes. mSystems7, e0137421 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Park, J. et al. Siderophore production and utilization by marine bacteria in the North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr.68, 1636–1653 (2023). 10.1002/lno.12373 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spiga, L. et al. Iron acquisition by a commensal bacterium modifies host nutritional immunity during Salmonella infection. Cell Host Microbe31, 1639-1654.e1610 (2023). 10.1016/j.chom.2023.08.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Quero, G. M. et al. Host-associated and environmental microbiomes in an open-sea Mediterranean gilthead sea bream fish farm. Microb. Ecol. (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 40.Kumar, V. et al. Microbial inoculums improve growth and health of Heteropneustes fossilis via biofloc-driven aquaculture. Microb. Cell Factor.22, 106 (2023). 10.1186/s12934-023-02107-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Loh, J. Y. & Ting, A. S. Y. Mining of Microbial Wealth and MetaGenomics. 161–182 (Springer Singapore, 2017).
- 42.Silva, S. D. et al.Aeromonas allosaccharophila strain AE59-TE2 is highly antagonistic towards multidrug-resistant human pathogens, what does its genome tell us?. Life12, 1492 (2022). 10.3390/life12101492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lewis, W. H., Tahon, G., Geesink, P., Sousa, D. Z. & Ettema, T. J. G. Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.19, 225–240 (2021). 10.1038/s41579-020-00458-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Albarano, L., Esposito, R., Ruocco, N. & Costantini, M. Genome mining as new challenge in natural products discovery. Mar. Drugs18, 124 (2020). 10.3390/md18040199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yee, D. A. et al. Genome mining for unknown–unknown natural products. Nat. Chem. Biol.19, 633–640 (2023). 10.1038/s41589-022-01246-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Parks, D. H. et al. Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol.2, 1533–1542 (2017). 10.1038/s41564-017-0012-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Paoli, L. et al. Biosynthetic potential of the global ocean microbiome. Nature607, 111–118 (2022). 10.1038/s41586-022-04862-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Prosser, J. I. Dispersing misconceptions and identifying opportunities for the use of “omics” in soil microbial ecology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.13, 439–446 (2015). 10.1038/nrmicro3468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ayling, M., Clark, M. D. & Leggett, R. M. New approaches for metagenome assembly with short reads. Brief. Bioinform.21, 584–594 (2020). 10.1093/bib/bbz020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y. & Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics34, i884–i890 (2018). 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wood, D. E., Lu, J. & Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol.20, 257 (2019). 10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Silva, G. G. Z., Lopes, F. A. C. & Edwards, R. A. Protein Function Prediction: Methods and Protocols (ed. Kihara, D.). 35–44 (Springer, 2017).
- 53.Buchfink, B., Reuter, K. & Drost, H.-G. Sensitive protein alignments at tree-of-life scale using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods18, 366–368 (2021). 10.1038/s41592-021-01101-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Overbeek, R. et al. The subsystems approach to genome annotation and its use in the project to annotate 1000 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res.33, 5691–5702 (2005). 10.1093/nar/gki866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Oksanen, J. S. G. et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package (2023).
- 56.Wickham, H., Chang, W. & Wickham, M. H. Package ‘ggplot2’. In Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. Version 2. 1–189 (2016).
- 57.Gao, C.-H., Yu, G. & Cai, P. ggVennDiagram: An intuitive, easy-to-use, and highly customizable R package to generate Venn diagram. Front. Genet.12, 130 (2021). 10.3389/fgene.2021.706907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Parks, D. H., Tyson, G. W., Hugenholtz, P. & Beiko, R. G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics30, 3123–3124 (2014). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li, D., Liu, C.-M., Luo, R., Sadakane, K. & Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics31, 1674–1676 (2015). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Langmead, B., Wilks, C., Antonescu, V. & Charles, R. Scaling read aligners to hundreds of threads on general-purpose processors. Bioinformatics35, 421–432 (2019). 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty648 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li, H. et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics25, 2078–2079 (2009). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kang, D. D. et al. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ7, e7359 (2019). 10.7717/peerj.7359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Parks, D. H., Imelfort, M., Skennerton, C. T., Hugenholtz, P. & Tyson, G. W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res.25, 1043–1055 (2015). 10.1101/gr.186072.114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chaumeil, P.-A., Mussig, A. J., Hugenholtz, P. & Parks, D. H. GTDB-Tk v2: Memory friendly classification with the genome taxonomy database. Bioinformatics38, 5315–5316 (2022). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI repository, under BioProject ID PRJNA1064611.