Abstract
Background and aim
Appendiceal adenocarcinoma, an exceedingly rare malignancy, sparks debate on the optimal surgical approach—appendectomy or right hemicolectomy—for early-stage cases. This study aims to investigate the impact of these two surgical methods on the survival prognosis of patients with early appendiceal adenocarcinoma.
Method
Utilizing a multicenter medical database, we gathered data from 168 patients diagnosed with T1 stage appendiceal adenocarcinoma admitted between January 2008 and January 2015. This study aims to compare the impact of different treatment modalities on the prognosis of appendiceal adenocarcinoma in these two groups.
Result
In patients diagnosed with T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma, the survival prognosis was not significantly improved with right hemicolectomy compared to appendectomy. Out of one hundred twenty-seven patients undergoing right colon resection, only three exhibited lymphatic metastasis, resulting in a rate of 2.3%.
Conclusion
Simple appendectomy can fulfill the objective of achieving radical tumor resection, rendering right hemicolectomy unnecessary.
Keywords: T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma, Surgical approach, Survival prognosis
Subject terms: Gastrointestinal cancer, Cancer, Diseases, Oncology, Gastrointestinal system
Introduction
Appendiceal adenocarcinoma is a rare cancer, with an annual incidence of approximately 1 per 100,000 person-years1. Given its uncommon occurrence, the vast majority of surgeons lack a comprehensive understanding of the overall survival outcomes associated with appendiceal adenocarcinoma. Moreover, they often lack relevant experience in managing and treating this infrequently encountered disease2. In light of the difficulty in preoperative diagnosis for early appendiceal adenocarcinoma, a considerable number of cases are identified during emergency surgeries for acute appendicitis, revealing malignancy upon subsequent pathology examination. The prevailing perception deems appendiceal adenocarcinoma as a highly malignant tumor, often prompting the recommendation for right hemicolectomy, as endorsed by the guidelines of the American Society of Colorectal Surgeons3. Nonetheless, certain scholars argue that when the tumor lesion is highly localized, lacking external invasion, and devoid of lymph node metastasis, opting for additional right hemicolectomy may be unnecessary. A radical cure, they contend, can be effectively attained through appendectomy alone4.
Against the backdrop of the ongoing discourse, this study aims to scrutinize the potential advantages of right hemicolectomy over appendectomy in the management of patients diagnosed with T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma. By doing so, it endeavors to establish a vital theoretical foundation for shaping future treatment strategies and prognostic considerations in clinical T1 appendiceal cancer.
Materials and methods
Study design and population
This study utilized a multicenter database to compile data on patients diagnosed with appendiceal adenocarcinoma admitted to Tongji Hospital, Hubei Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhongshan People’s Hospital, and Xiaogan Central Hospital from January 2008 to January 2015. Inclusion criteria encompassed patients meeting the following conditions: (1) confirmed pathological diagnosis of appendiceal adenocarcinoma; (2) AJCC 7th edition T stage identified as T1; (3) availability of comprehensive survival prognosis information; and (4) receipt of surgical intervention, either through simple appendectomy or right hemicolectomy. Exclusion criteria consisted of: (1) patients exhibiting distant metastasis; (2) individuals with incomplete clinical or prognosis information; and (3) patients undergoing surgical procedures extending beyond the right colon or involving resection of adjacent organs; (4) insufficient data (N = 2). Data collected included patient age, gender, Body Mass Index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists score (ASA), tumor diameter, TNM staging of the tumor, and the surgical approach. Ethical approval has been obtained from the ethics committees of Tongji Hospital, Hubei Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhongshan People’s Hospital, and Huangshi Central Hospital, and the study adheres to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was secured from all participating patients.
Postoperative follow-up and endpoints
After surgery, patients are scheduled for regular follow-ups every 4–6 months during the initial year and annually thereafter. The follow-up protocol includes abdominal CT, chest CT or chest X-ray, blood routine, and monitoring tumor markers CA199 and CEA. Overall survival (OS) is characterized as the duration from the surgery date to either the patient’s demise or the latest follow-up, while Recurrence-free survival (RFS) is delineated as the duration from the surgery date to the initial postoperative tumor recurrence or the most recent follow-up.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented as median (range) or mean ± standard deviation (SD), while categorical variables were reported as numbers (n) or percentages (%). Statistical comparisons for continuous variables were conducted using either the student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test, and categorical variables were assessed through the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test. Survival curves were generated utilizing the Kaplan-Meier method, and the log-rank test was employed for comparing the survival outcomes between the two surgical approach groups. All statistical analyses were performed using the R language (version 3.6.2), and data visualization was accomplished with R packages such as table one, survival, and survminer. A significance threshold of P < 0.05 was adopted to denote statistically significant differences.
Result
Clinical data of patients
Among the 168 patients diagnosed with T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma, 41 individuals (24.4%) opted for a simple appendectomy, while 127 patients (75.6%) underwent right hemicolectomy. Within the hemicolectomy group, 18 patients (10.7%) underwent primary right hemicolectomy based on intraoperative pathology suggestive of adenocarcinoma. Additionally, 109 patients (64.9%) underwent emergency appendectomy for appendicitis, followed by secondary right hemicolectomy due to postoperative pathology indicating appendiceal adenocarcinoma. The overall study population comprised 59 patients (35.1%) below the age of 60, with 109 patients (64.9%) aged 60 or older. Gender distribution consisted of 87 males (51.8%) and 81 females (48.2%), with the majority falling into stage I and II (88.1%), while 20 cases (11.9%) were classified as stage III and IV(Stage I indicates that the tumor is confined to the mucosa of the intestine without metastasis. Stage II indicates tumor invasion into the intestinal wall but without metastasis. Stage III indicates tumor invasion into extraintestinal tissues but without distant metastasis. Stage IV indicates tumor metastasis to lymph nodes or beyond the peritoneum). Regarding tumor N stage, 165 cases (98.2%) were categorized as N0, with only 3 cases (1.8%) identified as N1. All N1 cases were part of the right hemicolectomy group, presenting a positive rate of 2.4%. Histopathologically, mucinous carcinoma was predominant (145 cases), followed by intestinal adenocarcinoma, with signet-ring cell adenocarcinoma representing the smallest proportion. Laparoscopic procedures accounted for 119 cases (70.8% of the total). The number of cases of mucinous appendiceal neoplasms (PMP) is 0. PMP usually refers to mucinous tumors that have spread to the abdominal cavity, rather than typical lymph node metastasis. However, we do identify PMP as a subtype of late recurrence. The number of lymph nodes in the two groups are 13.2 ± 3.8 and 14.2 ± 4.1, respectively. No statistically significant differences were observed in the basic clinical data between patients undergoing simple appendectomy or right hemicolectomy, ensuring comparability (Table 1).
Table 1.
Relationship between clinical characteristics and surgical methods in patients with early appendiceal adenocarcinoma.
| Variable | Overall (168) | Appendectomy (n = 41) | Hemicolectomy (n = 127) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (%) | < 60years | 59 (35.1) | 12 (29.3) | 47 (37.0) | 0.475 |
| ≥ 60years | 109 (64.9) | 29 (70.7) | 80 (63.0) | ||
| Gender (%) | Female | 81 (48.2) | 21 (51.2) | 60 (47.2) | 0.792 |
| Male | 87 (51.8) | 20 (48.8) | 67 (52.8) | ||
| ASA (%) | ≤ 3 | 134 (79.8) | 31 (75.6) | 103 (81.1) | 0.591 |
| > 3 | 34 (20.2) | 10 (24.4) | 24 (18.9) | ||
| Stage (%) | I + II | 148 (88.1) | 33 (80.5) | 115 (90.6) | 0.146 |
| III + IV | 20 (11.9) | 8 (19.5) | 12 (9.4) | ||
| N stage (%) | N0 | 165 (98.2) | 41 (100.0) | 124 (97.6) | 0.753 |
| N1 | 3 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.4) | ||
| Histology (%) | Mucinous | 145 (87.3) | 34 (82.9) | 111 (88.8) | 0.217 |
| Intestinal | 18 (10.8) | 7 (17.1) | 11 (8.8) | ||
| Signet ring | 3 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.4) | ||
| BMI (SD) | 26.39 (2.56) | 26.32 (2.52) | 26.41 (2.58) | 0.852 | |
| Laparoscopic (%) | Yes | 119 (70.8) | 31 (75.6) | 88 (69.3) | 0.564 |
| No | 49 (29.2) | 10 (24.4) | 39 (30.7) | ||
| Number of lymph nodes | N ± s | 13.2 ± 3.8 | 14.2 ± 4.1 | 0.169 |
ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists score; BMI, body mass index; SD, standard deviation.
Overall survival (OS) after appendectomy alone versus right hemicolectomy in patients with T1 appendiceal cancer
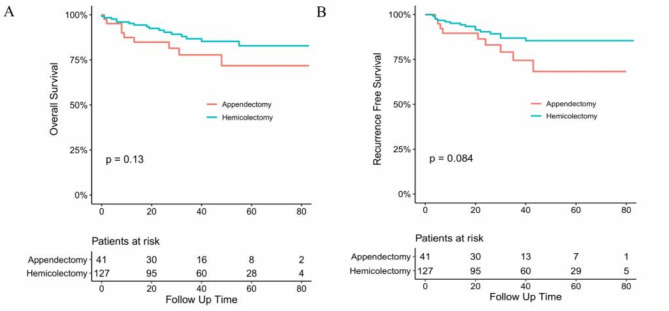
Throughout the entire cohort, patients underwent a follow-up period lasting 37 months. The overall survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years post-operation were 87.4%, 84.8%, and 71.8% in the simple appendectomy group, and 95.2%, 91.4%, and 82.8% in the right hemicolectomy group. Concerning recurrence-free survival, the rates at 1, 3, and 5 years post-surgery were 89.6%, 83.1%, and 68.3% in the appendectomy-alone group, and 95.1%, 90.4%, and 81.3% in the right hemicolectomy group. Importantly, there was no statistically significant difference in the overall survival and recurrence-free survival rates between the two groups of patients with early appendiceal adenocarcinoma who underwent different surgical methods (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Overall (A) and Recurrence-free (B) survival curve of patients with appendiceal adenocarcinoma in appendectomy group and Hemicolectomy group.
The recurrence pattern after surgery
After appendectomy, recurrence forms of appendiceal tumors manifested in 13 patients, with 10 experiencing local recurrence, 2 developing peritoneal metastasis, and 1 developing Pseudomyxoma Peritonei;
After undergoing right hemicolectomy, a total of 24 patients experienced recurrence, with 18, 4, and 2 patients experiencing three different types of recurrence, respectively (Table 2).
Table 2.
Recurrence pattern after surgery.
| Recurrence pattern | Appendectomy (N = 41) | Right hemicolectomy(N = 127) |
|---|---|---|
| Local Recurrence | 10 (24.4%) | 18 (14.2%) |
| Peritoneal Metastasis | 2 (4.9%) | 4 (3.1%) |
| Pseudomyxoma Peritonei (PMP) | 1 (2.4%) | 2 (1.6%) |
| Total Recurrence | 13 (31.7%) | 24 (18.9%) |
PMP, pseudomyxoma peritonei.
Discussion
The incidence of primary appendiceal adenocarcinoma is exceedingly rare, and the optimal treatment for early-stage appendiceal cancer remains a subject of controversy4. The primary treatment modalities include surgical approaches such as simple appendectomy and right hemicolectomy. Relevant literature on the appropriate surgical treatment of appendiceal adenocarcinoma published in the past is summarized in Table 3. While some studies, such as those by Aburahma, A. F., Yantiss R.K., and others4–9, have concluded that a simple appendectomy is sufficient for treating early appendiceal adenocarcinoma, others, such as those by Hopkins, G.B., and others2,10,11, have suggested that right hemicolectomy is the primary treatment for primary appendiceal cancer. In light of this ongoing debate, we sought to investigate the prognostic impact of the surgical approach for early appendiceal adenocarcinoma. Utilizing a multicenter database, our findings suggest that right hemicolectomy does not confer improved survival outcomes when compared with appendectomy alone in patients with T1-stage appendiceal adenocarcinoma. This aligns with the conclusions drawn by Japanese scholar Keisuke Hata and others4,12,13, who also emphasized that appendectomy is appropriate solely for early appendiceal adenocarcinoma limited to the submucosa, specifically T1 or better differentiated cases. A recent multicenter study by Stephanie et al. reported that the long-term survival rates among patients who underwent right hemicolectomy or extended cecal resection were comparable to those who underwent appendectomy8,14. Additionally, a study by Forster et al. demonstrated that the type of surgery was not correlated with recurrence rates or patient mortality15.
Table 3.
Published series reporting clinical outcomes of appendiceal adenocarcinoma.
| Study | Cases | Appendectomy | Extended resection | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J. V. Gahagan et al. | 2315 | 178 | 2137 | ER for all invasive appendiceal adenocarcinomas |
| H. Ito et al. | 36 | 1 | 35 | ER for T2 or higher stage appendiceal cancer |
| K. Hata et al. | 25 | 5 | 20 | AP for T1 or lower stage appendiceal cancer |
| Gonzalez-Moreno, S. et al. | 478 | 198 | 280 | ER does not improve outcome in appendiceal adenocarcinoma |
AP, appendectomy; ER, extended resection.
In the existing literature, there is a broad spectrum of indications regarding whether right hemicolectomy should be performed for appendiceal tumors, with a crucial factor being the presence of lymph node invasion16. Our study, focusing on patients with T1-stage appendiceal adenocarcinoma, revealed that only three patients experienced lymphatic metastases, indicating a very low probability of lymphatic invasion. In general, our findings align with previous literature reports17. Considering the oncological biological characteristics of T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma, the extent of tumor invasion is often limited, suggesting that extended surgical resection may be unnecessary. Gahagan, J. V, et al.11,18 considered the appendix as a colonic orifice, supporting the rationale to treat T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma similarly to malignant colonic polyps, a perspective reinforced by our data.
The observation of recurrence in the appendectomy group has prompted consideration of the underlying mechanisms driving the disease progression. Specifically, the lack of lymph node involvement in most recurrent cases suggests that recurrence may not primarily be attributed to lymph node metastasis. This hypothesis is supported by several factors. Firstly, analysis of the patterns of recurrence in recurrent lesions reveals features inconsistent with lymph node metastasis, such as local disease progression and peritoneal spread. These findings indicate alternative pathways for disease recurrence beyond lymphatic dissemination. Secondly, the surgical approach commonly employed in the appendectomy group typically involves lymph node clearance, further reducing the likelihood of postoperative lymph node metastasis, with no signs of lymph node metastasis detected in postoperative imaging. Furthermore, a review of the existing literature on appendiceal tumors emphasizes previous studies, with results from Takeyama’s multicenter study showing no lymph node metastasis in any T1 tumors19. These studies suggest a low rate of lymph node metastasis after surgery for early-stage appendiceal cancer and underscore the limited contribution of lymphatic spread to disease recurrence.Our study is subject to certain limitations. 1. Appendiceal adenocarcinoma encompasses various histological types, with mucinous adenocarcinoma being the most common. Prognosis varies across different pathological types, with mucinous adenocarcinoma having the best prognosis, followed by the colonic type, and the signet-ring cell carcinoma type exhibiting the worst prognosis9,20,21. In our study, the number of cases in each pathological subtype was small, preventing a detailed analysis. Does the study’s conclusions apply uniformly to different histological types? This aspect warrants further investigation in future studies. Additionally, being a retrospective study, there are inherent confounding factors.
We acknowledge that although our initial analysis did not reveal a statistically significant difference between appendectomy and right hemicolectomy, there seems to be a trend towards higher recurrence rates in the appendectomy group. It is important to emphasize the potential limitations of the study, including the relatively small sample size in the appendectomy group. The observed trend of higher recurrence rate in this group, particularly with a p-value of 0.084, suggests the possibility of Type II error, where a true difference in recurrence-free survival may exist but was not detected due to inadequate statistical power. With a slightly larger sample size in the appendectomy group, significant differences in recurrence-free survival may be observed. Additionally, the clinical significance of these findings warrants serious consideration. Appendiceal tumors represent a heterogeneous group with different biological behaviors and clinical outcomes. Decisions regarding the extent of surgical resection must balance oncological efficacy with preservation of organ function and quality of life. Appendectomy offers less invasive surgical intervention and lower morbidity compared to right hemicolectomy, but the potential for higher recurrence rates raises concerns regarding long-term tumor control. Given these considerations, future studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up periods are necessary to further elucidate the optimal surgical management of appendiceal tumors. Furthermore, integration of molecular analysis and prognostic biomarkers may facilitate risk stratification and personalized therapeutic approaches for this patient population.In conclusion, this study demonstrates that patients with appendiceal adenocarcinoma exhibiting tumor invasion limited to the submucosa (T1) experience favorable long-term survival outcomes. T1 appendiceal adenocarcinoma patients have a low likelihood of regional lymphatic metastasis, and appendectomy alone suffices for achieving a positive survival prognosis. Right colon resection does not confer a superior survival prognosis for these patients. Our findings can aid clinicians in selecting an appropriate treatment strategy for incidentally discovered appendiceal adenocarcinoma, steering clear of unnecessary two-stage extended resection.
Acknowledgements
Qiao Zhang, Guobing Xia and Ali Mo have contributed equally to this work. They are listed as co-author.
Abbreviations
- ASA
American Society of Anesthesiologists score
- BMI
Body mass index
- SD
Standard deviation
- OS
Overall survival
- RFS
Recurrence-free survival
Author contributions
QZ, GBX and Ali Mo wrote the paper. ZFG provided the ideas. FX, QZ, GBX, ZFG, YS provided data. FP reviewed and edited the manu-script. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [This data involves other studies by our team] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.This retrospective observational study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tongji Hospital, Hubei Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhongshan People’s Hospital, Huangshi Central Hospital. All patients provided written informed consent to the use and publication of their information.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These two authors have contributed equally to this work. They are listed as co-author.
References
- 1.McCusker, M. E., Cote, T. R., Clegg, L. X. & Sobin, L. H. Primary malignant neoplasms of the appendix: A population-based study from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and end-results Program, 1973–1998. Cancer 94(12), 3307–3312 (2002). 10.1002/cncr.10589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Whitfield, C. G., Amin, S. N. & Garner, J. P. Surgical management of primary appendiceal malignancy. Colorectal Dis. 14(12), 1507–1511 (2012). 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2012.03052.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Glasgow, S. C. et al. The American Society of Colon and rectal surgeons, clinical practice guidelines for the management of appendiceal neoplasms. Dis. Colon Rectum 62(12), 1425–1438 (2019). 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hata, K., Tanaka, N., Nomura, Y., Wada, I. & Nagawa, H. Early appendiceal adenocarcinoma. A review of the literature with special reference to optimal surgical procedures. J. Gastroenterol. 37(3), 210–214 (2002). 10.1007/s005350200023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aburahma, A. F. Primary adenocarcinoma of the vermiform appendix: Report of five new cases and review of the literature. W V Med. J. 73(11), 296–301 (1977). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sieracki, J. C. & Tesluk, H. Primary adenocarcinoma of the vermiform appendix. Cancer 9(5), 997–1011 (1956). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yantiss, R. K. et al. Prognostic significance of localized extra-appendiceal Mucin deposition in appendiceal mucinous neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 33(2), 248–255 (2009). 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31817ec31e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gonzalez-Moreno, S. & Sugarbaker, P. H. Right hemicolectomy does not Confer a survival advantage in patients with mucinous carcinoma of the appendix and peritoneal seeding. Br. J. Surg. 91(3), 304–311 (2004). 10.1002/bjs.4393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ito, H. et al. Appendiceal adenocarcinoma: Long-term outcomes after surgical therapy. Dis. Colon Rectum 47(4), 474–480 (2004). 10.1007/s10350-003-0077-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hopkins, G. B., Tullis, R. H. & Kristensen, K. A. Primary adenocarcinoma of the vermiform appendix: Report of seven cases and review of the literature. Dis. Colon Rectum 16(2), 140–144 (1973). 10.1007/BF02589930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gahagan, J. V. et al. Lymph node positivity in appendiceal adenocarcinoma: Should size matter? J. Am. Coll. Surg. 225(1), 69–75 (2017). 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.01.056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chicago Consensus Working G. The Chicago consensus on peritoneal surface malignancies: Management of appendiceal neoplasms. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 27(6), 1753–1760 (2020). 10.1245/s10434-020-08316-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kelly, K. J. Management of appendix cancer. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 28(4), 247–255 (2015). 10.1055/s-0035-1564433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Young, S. et al. Surgical management of appendiceal mucinous neoplasm: Is appendectomy sufficient? J. Surg. Oncol. 122(6), 1173–1178 (2020). 10.1002/jso.26108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Foster, J. M. et al. Right hemicolectomy is not routinely indicated in pseudomyxoma peritonei. Am. Surg. 78(2), 171–177 (2012). 10.1177/000313481207800234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shaib, W. L. et al. Appendiceal mucinous neoplasms: Diagnosis and management. Oncologist 23(1), 137 (2018). 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0081erratum [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sugarbaker, P. H. When and when not to perform a right colon resection with mucinous appendiceal neoplasms. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 24(3), 729–732 (2017). 10.1245/s10434-016-5632-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Aarons, C. B., Shanmugan, S. & Bleier, J. I. Management of malignant colon polyps: Current status and controversies. World J. Gastroenterol. 20(43), 16178–16183 (2014). 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takeyama, H. et al. Clinical significance of lymph node dissection and lymph node metastasis in primary appendiceal tumor patients after curative resection: A retrospective multicenter cohort study. J. Gastrointest. Surg.: Off. J. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract. 26(1), 128–140 (2022). 10.1007/s11605-021-05070-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McGory, M. L., Maggard, M. A., Kang, H., O’Connell, J. B. & Ko, C. Y. Malignancies of the appendix: Beyond case series reports. Dis. Colon Rectum 48(12), 2264–2271 (2005). 10.1007/s10350-005-0196-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Walters, K. C. et al. Treatment of appendiceal adenocarcinoma in the United States: Penetration and outcomes of current guidelines. Am. Surg. 74(11), 1066–1068 (2008). 10.1177/000313480807401105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [This data involves other studies by our team] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.