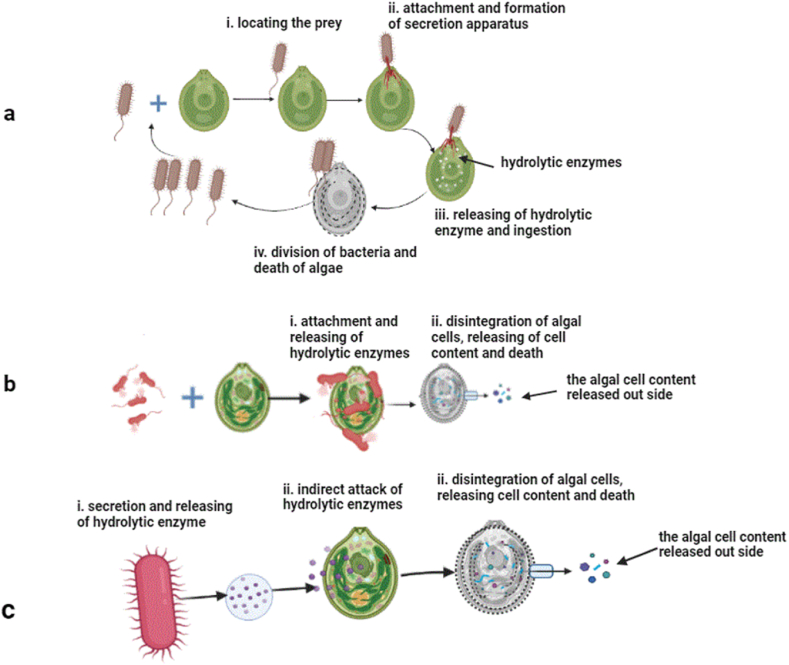
Fig. 3.
An illustration depicting a) the direct and indirect attack with an exemplary predatory lifestyle of Vampirovibrio chlorellavorus where sections indicating the bacterium locating the prey-the bacterium seeks out the host (C. vulgaris) cells via chemotaxis and flagella (i), attachment and formation of secretion apparatus (ii), ingestion-hydrolytic enzymes are transferred to the prey cells where they degrade algal cell contents (iii), binary division-algal cell exudates are ingested by V. chlorellavorus allowing it to replicate by binary division, and releasing of progeny (iv), the illustration depicted based on Soo et al. [172], b) the direct and indirect attack of bacteria on microalgae, and c) indirect attack of bacteria by secretion of hydrolytic enzymes.