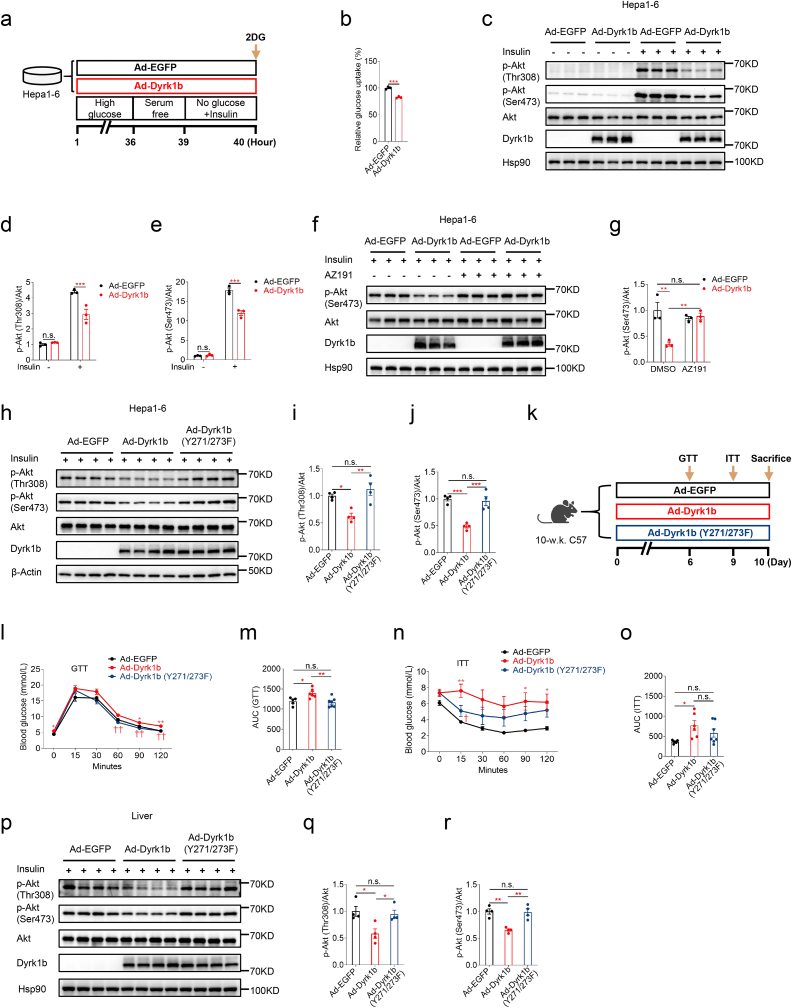
Fig. 2.
Dyrk1b overexpression attenuates insulin signaling in a kinase activity-dependent manner. (a) Experimental designs following Ad-Dyrk1b or Ad-EGFP infection of Hepa1-6 cells. (b) Glucose uptake of Hepa1-6 cells infected with Ad-EGFP or Ad-Dyrk1b (MOI = 100) (n = 3). Unpaired Student's t-test (two-sided) was performed for Fig. 2b. (c–e) Western blot and densitometry quantification of Hepa1-6 cells infected with Ad-EGFP or Ad-Dyrk1b (MOI = 100) (n = 3). Two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc test was performed for Fig. 2d and e. (f–g) Western blot and densitometry quantification of Hepa1-6 cells infected with Ad-EGFP or Ad-Dyrk1b in the absence or presence of AZ191 (1 μM) (n = 3). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test was performed for Fig. 2g. (h–j) Western blot and densitometry quantification of Hepa1-6 cells infected with adenovirus expressing wild-type Dyrk1b or kinase-defective Dyrk1b with Y271/273F mutation. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's post-hoc test was performed for Fig. 2i and j. (k) Experimental designs for female C57 mice injected with adenovirus expressing wild-type or kinase-defective Dyrk1b. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (l) and AUC of GTT curves (m) of mice injected with adenovirus expressing wild-type or kinase-defective Dyrk1b (n = 5–7). Insulin tolerance test (n) and AUC of ITT curves (o) of mice injected with adenovirus expressing wild-type or kinase-defective Dyrk1b (n = 6–7). One-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test was performed for Fig. 2l–o. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 for mice injected with Ad-EGFP versus Ad-Dyrk1b. †P < 0.05 and ††P < 0.01 for mice injected with Ad-Dyrk1b versus Ad-Dyrk1b (Y271/273F). (p–r) Western blot and densitometry quantification of livers from mice injected with adenovirus expressing wild-type or kinase-defective Dyrk1b (n = 4). One-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test was performed for Fig. 2q and r. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant.