Abstract
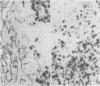
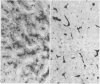
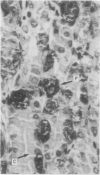
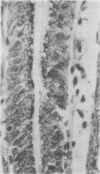
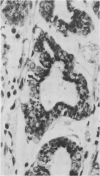
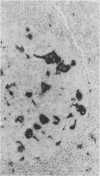
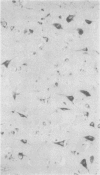
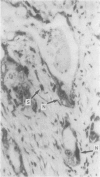
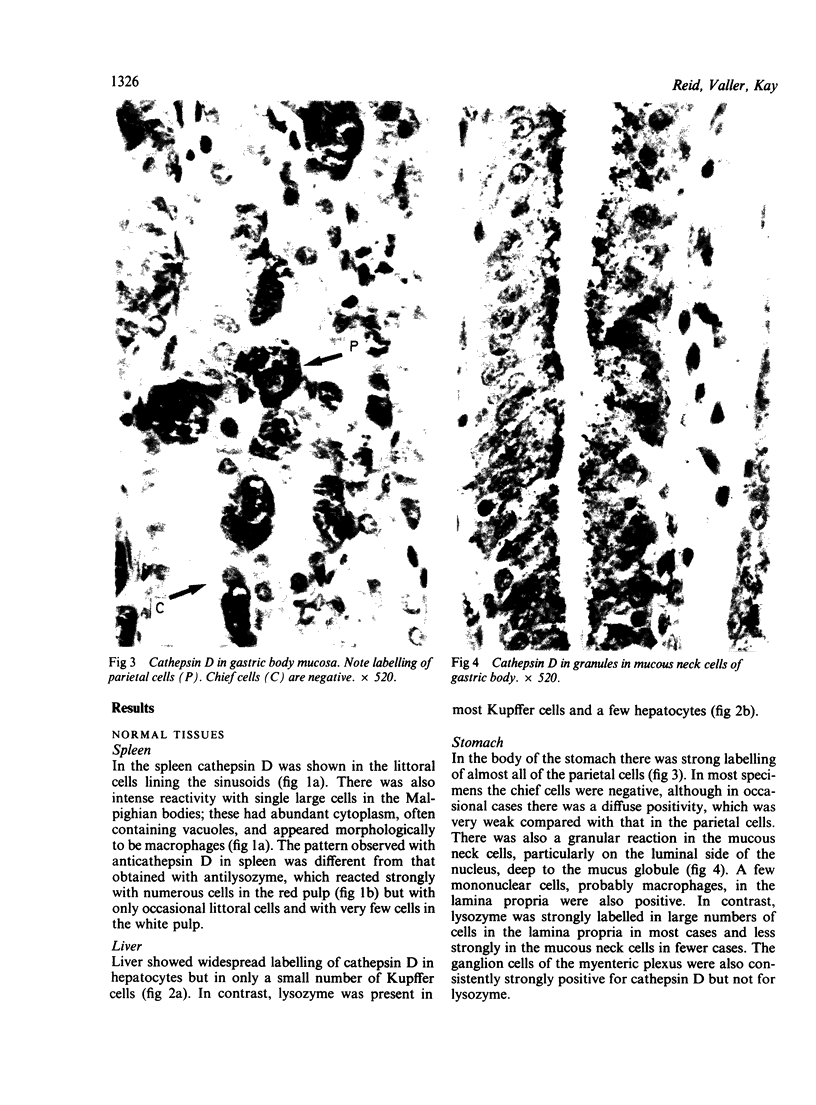
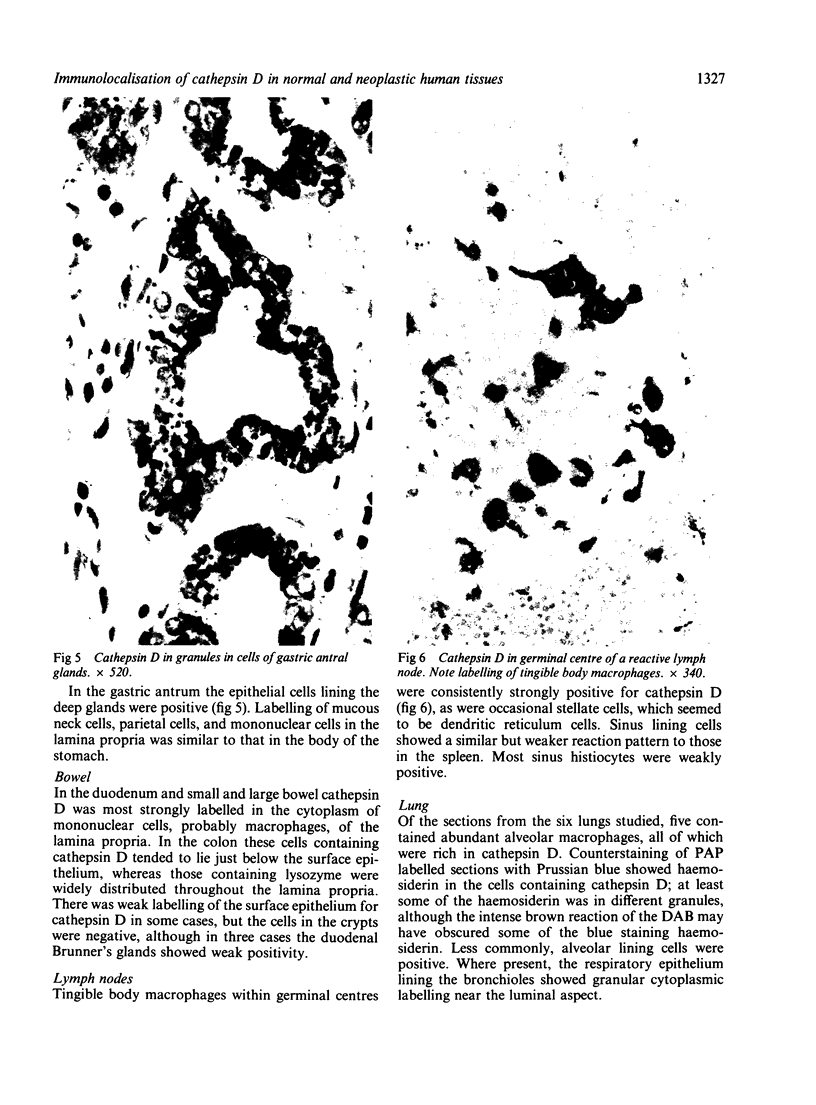
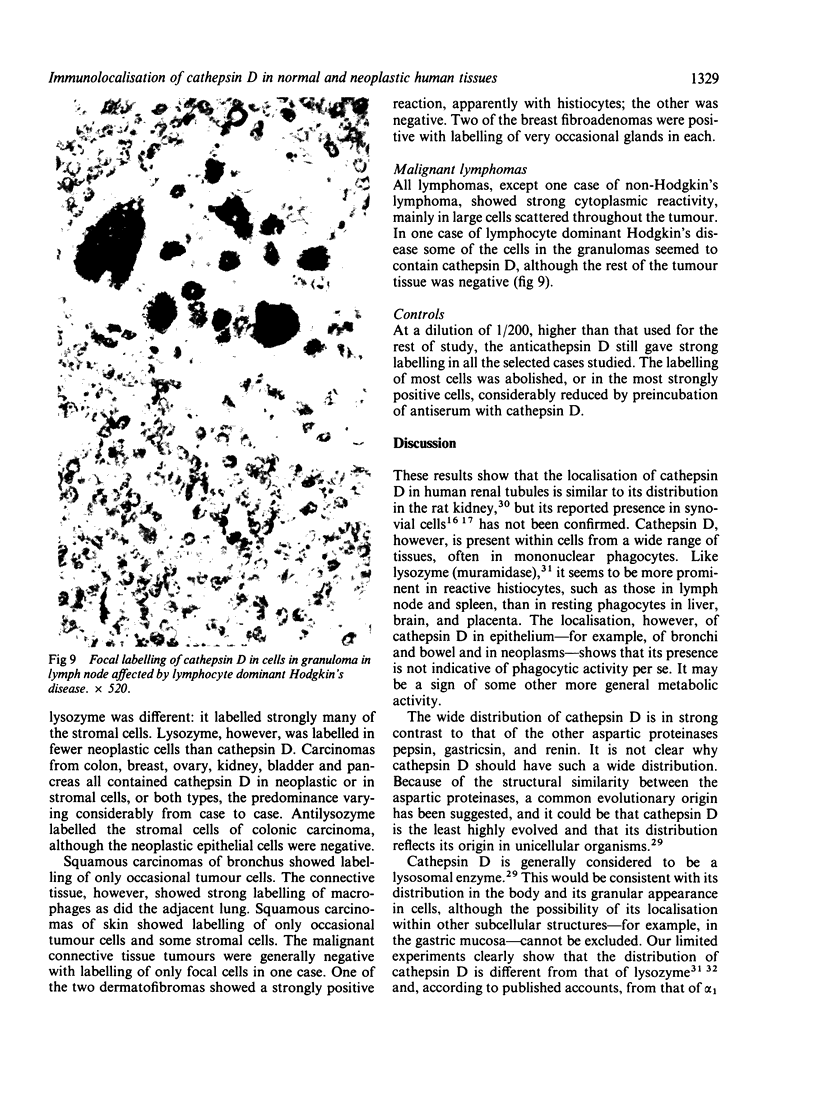
The aspartic proteinase cathepsin D was purified from human spleen and localised in various formalin fixed paraffin embedded human tissues using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) technique. Cathepsin D was shown not only in macrophages but also in other connective tissue cells, and in epithelium. It was present in spleen (littoral cells and cells within Malpighian bodies), liver (hepatocytes and Kupffer cells), lung (alveolar macrophages and bronchial epithelium), brain (neurones), lymph nodes (histiocytes in germinal centres, sinusoid lining cells) and stomach (parietal and mucous neck cells). Cathepsin D was also found in carcinomas of bronchus, stomach, colon, kidney, breast, ovary, bladder and pancreas, both in neoplastic epithelium and in stromal cells, but was seldom present in connective tissue neoplasms. A group of malignant lymphomas also contained the enzyme within scattered cells. The distribution of cathepsin D seems to be much wider than that of the structurally related aspartic proteinases pepsin, gastricsin, and renin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afting E. G., Recker M. L. Two-step affinity-chromatographic purification of cathepsin D from pig myometrium with high yield. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj1970519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baricos W. H., Shah S. V. Increased cathepsin D-like activity in cortex, tubules, and glomeruli isolated from rats with experimental nephrotic syndrome. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2230393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J. W., Schwartz W. N., Spanier A. M. Degradation of myofibrillar proteins by cathepsins B and D. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(11-12):1587–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Taylor J. M., Murakami K., Michelakis A. M., Inagami T. Isolation and characterization of renin-like enzymes from mouse submaxillary glands. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4286–4293. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker J., Burnett D., Jones E. L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of cathepsin B in the macrophages of benign and malignant lymphoid tissues. J Pathol. 1984 Jan;142(1):87–94. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Ferraro C., Nahmod V. E., Goldstein D. J., Finkielman S. Angiotensin and renin in rat and dog brain. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):353–361. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum L. M., Sutherland J. H. Host cathepsin D response to tumor in the normal and pepstatin-treated mouse. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2584–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobart P. M., Fogliano M., O'Connor B. A., Schaefer I. M., Chirgwin J. M. Human renin gene: structure and sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5026–5030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie A. J., Burnett D., Crocker J. The distribution of cathepsin B in human tissues. J Pathol. 1985 Apr;145(4):307–314. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T., Clemens D. L., Hirose S., Okamura T., Naruse K., Takii Y., Yokosawa H. Brain renin. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(4-5):607–622. doi: 10.3109/10641968209061602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P., Jones D. B., Millward-Sadler G. H., Judd M. A., Payne S. Alpha-1-antitrypsin in human macrophages. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):982–990. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama T., Takahashi K. A cathepsin D-like acid proteinase from human gastric mucosa. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1980 Mar;87(3):725–735. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J., Siemankowski R. F., Siemankowski L. M., Goll D. E. Degradation of smooth-muscle myosin by trypsin-like serine proteinases. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):267–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2010267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockars M., Reitamo S. Tissue distribution of lysozyme in man. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Dec;23(12):932–940. doi: 10.1177/23.12.1104708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindop G. B., Fleming S. Renin in renal cell carcinoma--an immunocytochemical study using an antibody to pure human renin. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):27–31. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Taylor C. R. The distribution of muramidase (lysozyme) in human tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Feb;28(2):124–132. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews I. T., Decker R. S., Knight C. G. The localization of cathepsin D with a biotin-labelled pepstatin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto N., Arai K. M., Tani S. Purification and properties of a cathepsin D-like acid proteinase from rat gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 30;745(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Dingle J. T., Barrett A. J. The immunocytochemical demonstration of cathepsin D. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Apr;20(4):261–265. doi: 10.1177/20.4.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. A., Liddle C. N., Svasti J., Kay J. Gastricsin in the benign and malignant prostate. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jun;38(6):639–643. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.6.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. A., Thompson W. D., Kay J. Pepsinogen in gastric carcinoma cells. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Feb;36(2):137–139. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. A., Vongsorasak L., Svasti J., Valler M. J., Kay J. Identification of the acid proteinase in human seminal fluid as a gastricsin originating in the prostate. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;236(3):597–600. doi: 10.1007/BF00217228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M. Cellular localization of group I pepsinogens in human gastric mucosa by immunofluorescence. Gastroenterology. 1971 Aug;61(2):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Liebman W. M. Cellular localization of the group II pepsinogens in human stomach and duodenum by immunofluorescence. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jul;65(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewale J. G., Tang J. Amino acid sequence of porcine spleen cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3703–3707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara E., Ito H., Taniyama K., Yokozaki H., Hata J. Alpha 1-antitrypsin, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, and alpha 2-macroglobulin in human gastric carcinomas: a retrospective immunohistochemical study. Hum Pathol. 1984 Oct;15(10):957–964. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Bertorini T. E., Mendell J. R. Immunocytochemical studies of cathepsin D in human skeletal muscle. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]