Abstract
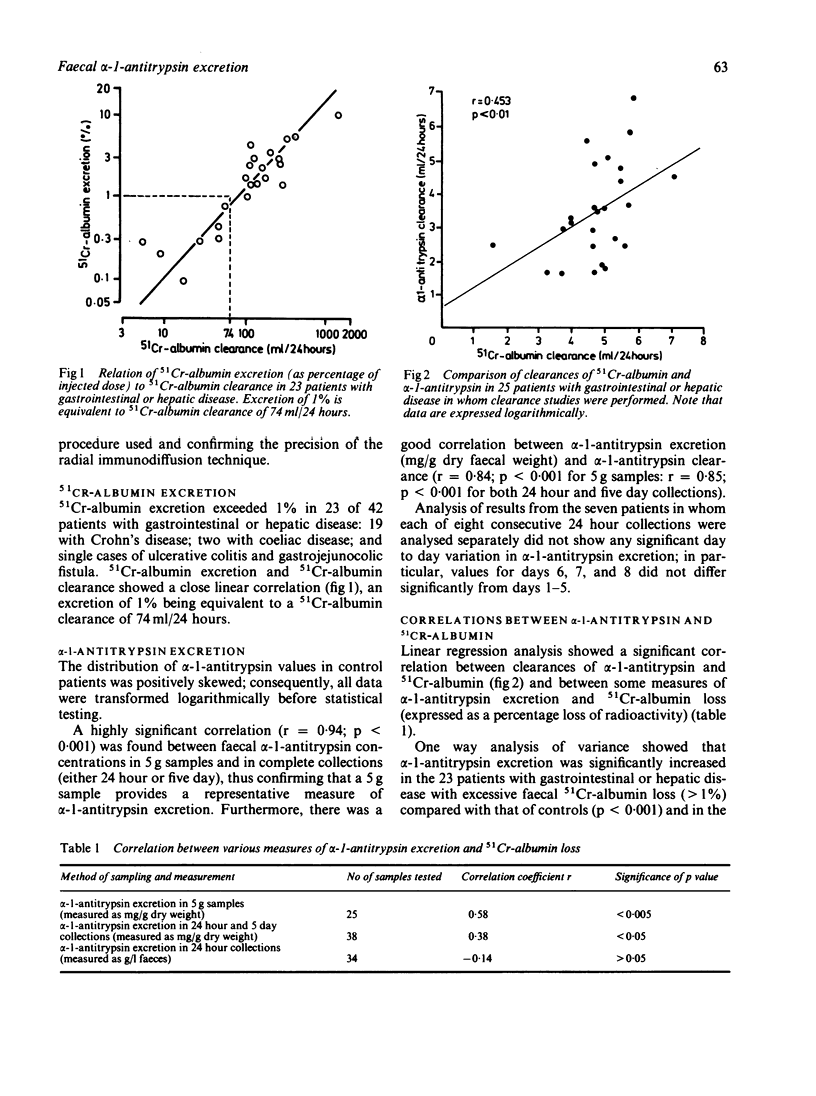
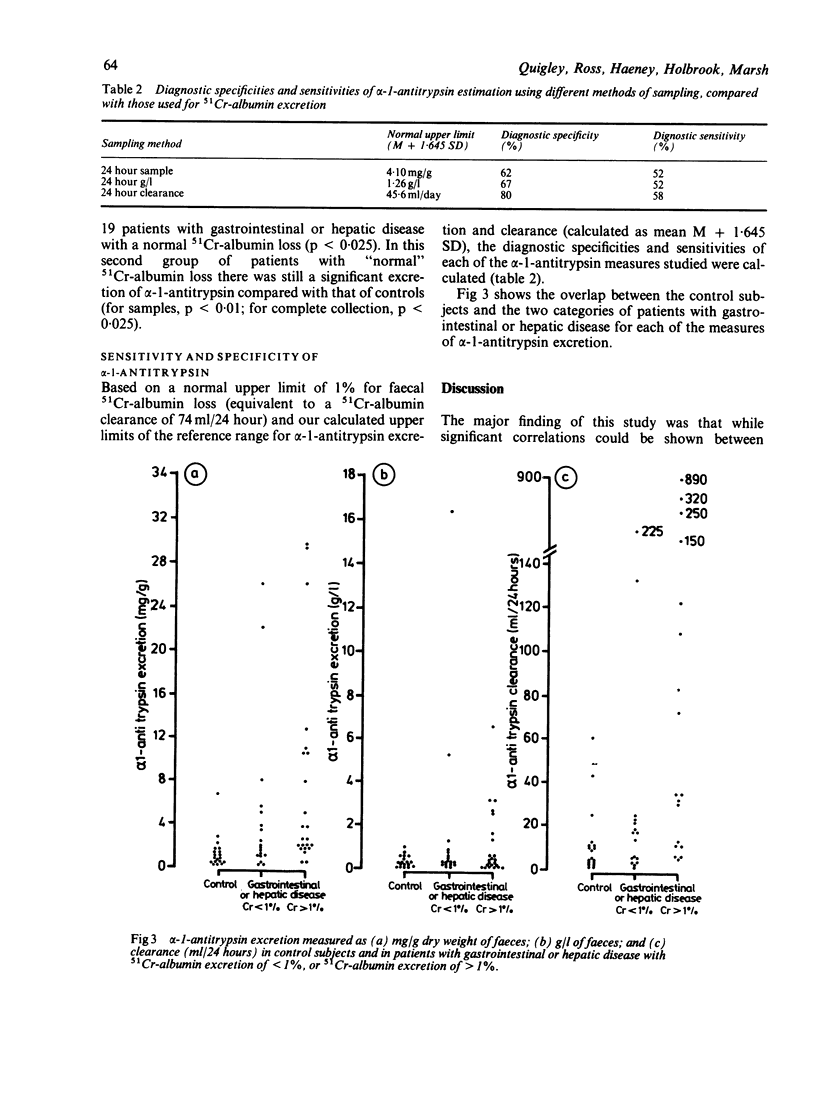
Faecal alpha-1-antitrypsin and 51Cr-albumin losses in 42 patients with either gastrointestinal or hepatic disease were compared. The reference range was derived from measurements in 20 controls without gastrointestinal disease. Alpha-1-antitrypsin excretion was increased in patients with excessive 51Cr-albumin loss, and correlations were found between alpha-1-antitrypsin clearance and 51Cr-albumin excretion. Because of the considerable overlap of faecal alpha-1-antitrypsin excretion between controls and patients, sensitivity and specificity of the test were only 58% and 80%, respectively. This poor reliability could not be explained by sampling error or temporal variations in alpha-1-antitrypsin excretion. These results show that although faecal alpha-1-antitrypsin excretion correlates with 51Cr-albumin excretion when whole groups of patients are studied, its poor sensitivity makes it an unreliable measure of enteric protein loss.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernier J. J., Florent C., Desmazures C., Aymes C., L'Hirondel C. Diagnosis of protein-losing enteropathy by gastrointestinal clearance of alpha1-antitrypsin. Lancet. 1978 Oct 7;2(8093):763–764. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92650-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretagne J. F., Lemee P., Esvant E., Gastard J. Evaluation de l'entéropathie exsudative chez le patient cirrhotique par la mesure de la clairance intestinal de l'alpha 1-antitrypsine. Sem Hop. 1982 Mar 11;58(10):575–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffone G. J., Shulman R. J. Characterization and evaluation of immunochemical methods for the measurement of fecal alpha 1-antitrypsin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;83(3):326–330. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke E. A., Anderson T. W. Does screening by "Pap" smears help prevent cervical cancer? A case-control study. Lancet. 1979 Jul 7;2(8132):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley J. R., Elliott R. B. Simple method for diagnosing protein-losing enteropathies. Br Med J. 1977 Feb 12;1(6058):428–429. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6058.428-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr R. M., Du Bois J. J., Holt P. R. Use of 125-I- and 51-Cr-labeled albumin for the measurement of gastrointestinal and total albumin catabolism. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2064–2082. doi: 10.1172/JCI105694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyaw-Myint T. O., Howell A. M., Murphy G. M., Anderson C. M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin in duodenal fluid and gallbladder bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Feb 22;59(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINI M. E., SHEEHY T. W. Exudative enteropathy. I. A comparative study of Cr51-Cl and I-131-PVP. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Dec;58:892–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart W. H., Weigand K., Kappeler M., Roesler H., Halter F. Comparison of gastrointestinal loss of alpha-1-antitrypsin and chromium-51-albumin in Ménétrier's disease and the influence of ranitidine. Digestion. 1983;26(4):192–196. doi: 10.1159/000198889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel J. M., Johnstone F., Duncan L. J. Abnormal infants of diabetic mothers. Lancet. 1980 Apr 5;1(8171):771–771. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Wochner R. D., Strober W. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in plasma protein metabolism. Studies with 51Cr-albumin. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


