Summary
Halophiles, thriving in harsh saline environments, capture scientific interest due to their remarkable ability to prosper under extreme salinity. This study unveils the distinct salt-induced activation of methionine sulfoxide reductases (MsrA) from Halobacterium hubeiense, showcasing a significant enhancement in enzymatic activity across various salt concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 3.5 M. This contrasts sharply with the activity profiles of non-halophilic counterparts. Through comprehensive molecular dynamics simulations, we demonstrate that salt ions stabilize and compact the enzyme’s structure, notably enhancing its substrate affinity. Mutagenesis analysis further confirms the essential role of salt bridges formed by the basic Arg168 residue in salt-induced activation. Mutating Arg168 to an acidic or neutral residue disrupts salt-induced activation, substantially reducing the enzyme activity under salt conditions. Our research provides evidence of salt-activated MsrA activity in halophiles, elucidating the molecular basis of halophilic enzyme activity in response to salts.
Subject areas: Biochemistry, Molecular genetics, Microbiology, Molecular microbiology
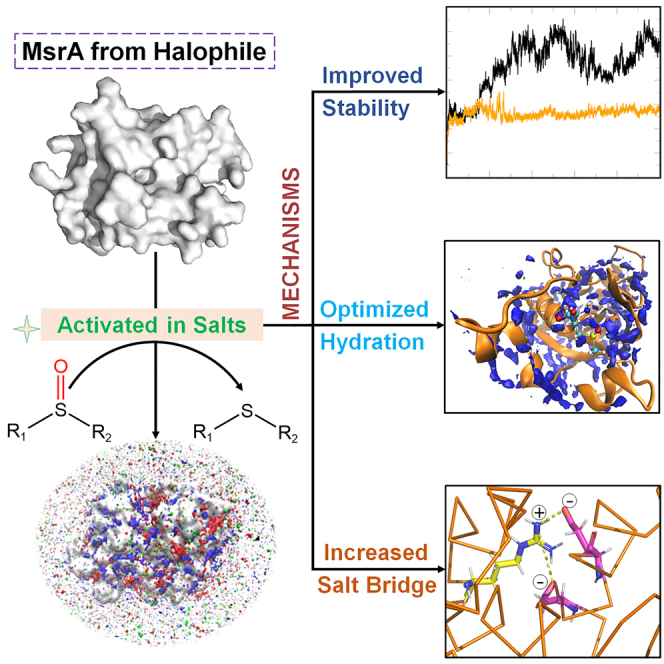
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
MsrA activity from halophiles is induced by salts
-
•
Salt ions stabilize MsrA structure and enhance substrate affinity
-
•
Salt bridges triggered by Arg168 are crucial and its mutation disrupts salt activation
Biochemistry; Molecular genetics; Microbiology; Molecular microbiology
Introduction
Extremophiles are microorganisms that thrive in extreme environments, such as extreme temperatures, high radiation, acidic or alkaline environments, and even the depths of the ocean floor.1 Their unique biochemical and physiological adaptations have garnered significant scientific interest due to their potential applications in various fields, including biotechnology, astrobiology, and environmental science.2,3,4,5,6,7 Halophiles constitute a fascinating group of extremophiles that thrive in saline or hypersaline environments.4,8 According to the optimum salt concentration required for their growth, halophiles can be categorized as slight halophiles (0.2–0.5 M salt), moderate halophiles (0.5–2.5 M salt), and extreme halophiles (2.5–5.2 M salt).9 Owing to their distinctive structural and physicochemical characteristics, halophiles have garnered significant attention in biotechnological applications, such as high-salt fermentation, high-salt wastewater treatment, biofuel production, and the exploration of enzymes derived from halophilic microorganisms.4,9,10,11,12 Furthermore, understanding the mechanisms by which these microorganisms adapt to high-salt environments has also been a fascinating pursuit for scientists.8,13,14,15,16,17
Halophiles have developed several remarkable adaptations to cope with high salinity, including the “salt-in strategy” involving potassium ion accumulation, the production of “halophilic proteins” to repel sodium ions, and the synthesis of “osmoprotectants” like betaine and trehalose to protect cellular structures from osmotic stress.17,18 These strategies collectively enable their survival in extreme saline environments. Usually, high salt concentration environments can denature and destabilize proteins, which may inhibit the catalytic activity and impair the structural integrity of enzymes.19 However, halophilic proteins generally remain stable and functional under high salt concentrations.20 These proteins feature negatively charged surfaces, contrasting with typical proteins with neutral or slightly positive charges, which allow them to repel positively charged ions.21,22,23 They also exhibit a more flexible structure, promoting efficient interaction with water molecules to counteract dehydration caused by high salt concentrations.24 Many halophilic proteins display enhanced thermostability, which is crucial in high-temperature, high-salt conditions.20 Additionally, some possess specialized salt-binding pockets, aiding stability and functionality in saline environments.25,26 A deeper understanding of how halophilic proteins maintain their structure and prevent aggregation in challenging environments could offer valuable insights for the field of biotechnology.
Methionine sulfoxide reductases (Msr) are a family of enzymes responsible for catalyzing the reduction of methionine sulfoxide (Met-O) back to its biologically active methionine (Met) form.27 In living cells, Met is relatively easily oxidized to sulfoxide under mild conditions.28 For many proteins, oxidation of Met residues to the Met-O results in the loss of their biological properties.29 Thus, Msr enzymes play a crucial role in cellular antioxidant defense mechanisms and the maintenance of protein functionality.30 On the other hand, oxidation of Met creates a chiral center at the sulfur atom, making the produced Met-O a mixture of S and R enantiomers.31 Therefore, different types of reductases, like MsrA and MsrB, are active on each enantiomer of Met-O due to their enantioselectivity.27 The excellent enantioselectivity of different types of Msr enzymes makes them outstanding biocatalysts for the green synthesis of enantiopure sulfoxide compounds in the field of biotechnology.32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41 As an outstanding protector of cells from the harmful effects of oxidative stress,42 the Msr enzymes probably play pivotal roles in the survival of halophilic cells in high-salt-stress environments. Recently, it has been reported that the MsrA from Haloferax volcanii exhibits ubiquitin-like (Ubl) protein modification activity, in addition to its well-known stereospecific reduction of Met-O. This discovery provides insights into oxidative stress responses that can induce Ubl modification within a cell.43 Nevertheless, the enzymatic characteristics and mechanisms of Msr in halophilic microorganisms in response to salts remain unexplored. In this study, we revealed that the activity of the MsrA enzyme from halophile Halobacterium hubeiense strain JI20-1 (named HhMsrA) was activated by high salt concentrations. We further elucidated the related mechanisms using molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and mutagenesis analysis, providing perspectives on understanding the mechanisms underlying salt ion activation in halophilic proteins.
Results and discussion
Recombinant expression and activity characterization of MsrA from halophile H. hubeiense strain JI20-1
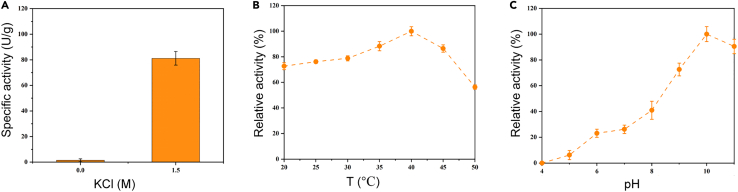
The DNA fragment of the HhMsrA gene (gene ID: 26659341) was first synthesized based on the GenBank database and cloned into the expression plasmid. The results of SDS-PAGE analysis confirmed that the target protein was effectively expressed in a soluble form after induction by isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (Figure S1). After purification using the His-tag, enzymatic studies revealed that HhMsrA exhibited minimal activity when Met-O was used as the substrate (Figure 1A). Considering the survival of Halobacterium genus in high-salt environments,44 we hypothesized that the activity of HhMsrA could be activated by high-salt conditions. Thus, KCl was added to the reaction at a final concentration of 1.5 M. The results showed a significant improvement in catalytic activity, with the specific activity reaching 81.2 ± 5.3 U/g (Figure 1A), strongly suggesting that high-salt ions were essential for the activity of MsrA in this haloarchaeon. In contrast, the activity of MsrA from a non-halophilic Pseudomonas monteilii strain (pmMsrA), which we isolated previously,32 was inhibited with increasing salt concentrations (Figure S2). These data demonstrate the activation of MsrA in halophiles by high concentrations of salt ions.
Figure 1.
Characterization of the enzymatic properties of HhMsrA
(A) Specific activity analysis of HhMsrA with 0 and 1.5 M KCl.
(B and C) Temperature and pH profiles of HhMsrA. The HhMsrA activities were assayed using the DTT-DTNB coupled colorimetric method. Each reaction was performed in the presence of 3 μM of pure enzyme, 3 mM of Met-O, and 1 mM of DTT for 45 min. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
Afterward, we evaluated temperature and pH characteristics of HhMsrA in the presence of 1.5 M KCl. Initially, the relative activities of HhMsrA over a temperature range of 20°C–50°C were determined. The enzyme exhibited its peak activity at 40°C, retaining over 80% of its activities within the 35°C–45°C range (Figure 1B). Previous studies have shown that enzymes from halophiles exhibit higher optimal reaction temperature and greater thermal stability.45,46 Our research is consistent with these studies, as the optimal reaction temperature of 40°C is higher than that of MsrA homologs from non-halophilic cells, which are usually around 30°C and sensitive to temperature.33,37,47 The enzyme’s exceptional temperature adaptability suggests potential advantages in the field of industrial biotechnology, where thermostability is deemed a critical parameter for assessing the feasibility of enzymes for industrial application.48 Subsequent investigations focused on the impact of pH on the activity of HhMsrA, spanning pH values from 4.0 to 11.0. The results indicated that the enzyme showed basophilic properties with the highest activity at pH 10.0, retaining over 90% of its activities between pH 10.0 and 11.0 (Figure 1C). However, the activity of HhMsrA was significantly reduced when the reaction pH was lower than 8.0. Based on these results, 40°C and pH 10.0 were designated as the reaction conditions for subsequent studies.
Effects of various salts on HhMsrA activity
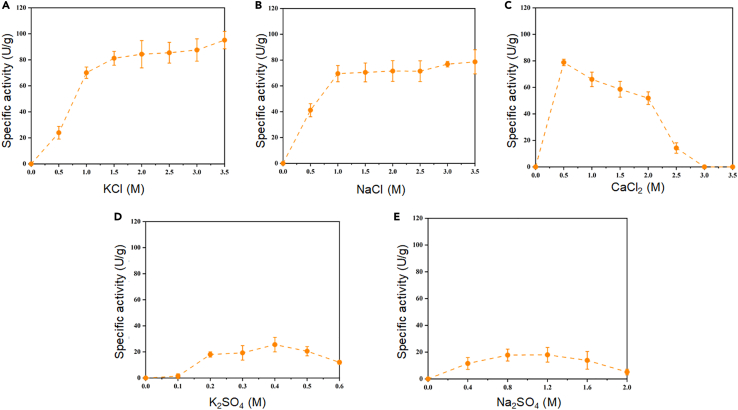
To further assess the impact of salts on the HhMsrA activity, the specific activities of HhMsrA were determined under various monovalent and bivalent neutral salts, including KCl, NaCl, CaCl2, K2SO4, and Na2SO4. The results revealed that all tested salts significantly activated the enzyme HhMsrA. Among them, KCl and NaCl exhibited the strongest activation, with similar profiles (Figures 2A and 2B). Enzyme activity was observed at concentrations higher than 0.5 M of KCl or NaCl and elevated with increasing salt concentrations. The activation effects of both KCl and NaCl were most pronounced between 0 and 1.0 M, and the peak activity was observed at the highest concentration of 3.5 M for both salts, achieving 95.1 ± 6.7 U/g and 78.6 ± 9.3 U/g, respectively. In addition, specific activities were slightly higher under KCl than under NaCl at most concentrations. While a previous report suggested that H. hubeiense JI20-1 required NaCl for growth,44 our findings indicate that the activating effect of K+ ions was more pronounced than that of Na+ ions on the HhMsrA enzyme. Regarding CaCl2, the activation effect was similar to that of NaCl, but the salt concentration required for activation was much lower. The enzyme exhibited peak activity under 0.5 M CaCl2, achieving 78.8 ± 3.4 U/g (Figure 2C), indicating that the activation effect of Ca2+ ions was much stronger than that of Na+ ions. However, unlike KCl and NaCl, the activities of HhMsrA decreased at concentrations higher than 0.5 M CaCl2 and were completely inhibited at 3.0 M, indicating that the high concentrations of Ca2+ ions could inhibit HhMsrA activity.
Figure 2.
Effects of various salts on HhMsrA’s activity
The activity of HhMsrA was assessed in the presence of different salts: KCl (A), NaCl (B), CaCl2 (C), K2SO4 (D), and Na2SO4 (E). Specific activities were assayed using the DTT-DTNB coupled colorimetric method, consistent with those in Figure 1, using Met-O as the substrates under conditions of 40°C and pH 10.0. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
For the two sulfates, K2SO4 and Na2SO4, their activation effects were much weaker compared to their chlorides (Figures 2D and 2E). Peak activities were observed at 0.4 M K2SO4 and 1.2 M Na2SO4, achieving only 25.6 ± 5.6 U/g and 18.0 ± 5.5 U/g, respectively. Unlike their chloride counterparts, the high concentrations of K2SO4 and Na2SO4 inhibited enzyme activities. To test whether these inhibitions are reversible or not, we first treated the enzyme in the presence of 2.0 M of Na2SO4 for 45 min, and then measured its activity under 1.0 and 2.0 M KCl conditions. The results showed that only 36% of residual activities were detected in both conditions (Figure S3), suggesting that high concentration of sulfates can result in irreversible inhibition of the enzyme. This irreversible inhibition suggests that sulfate ions may cause permanent structural changes and denaturation of the enzyme, as indicated by the observed protein precipitation after treatment.
Taken together, the activity of HhMsrA was activated by all test salts, with chlorides showing much stronger effects than the corresponding sulfates. Both monovalent Na+ and K+ ions, as well as bivalent Ca2+ ions, could activate the enzyme HhMsrA, with monovalent Na+ and K+ ions exhibiting a greater tolerance under higher concentrations in activating the enzyme. Considering the survival of H. hubeiense under high-salt conditions,44 the activation of MsrA by various salts may potentially contribute to protecting these cells from oxidative stress in high-salt conditions. Numerous reports have illustrated that halophiles developed several remarkable adaptations to cope with high salinity.18,20,25 This study implies that the MsrA-mediated antioxidation system could also play essential roles in the survival of these halophiles under high-salt conditions, providing insights into the mechanisms by which halophilic microorganisms survive in such environments.
Substrate specificity analysis of HhMsrA for various sulfoxide substrates
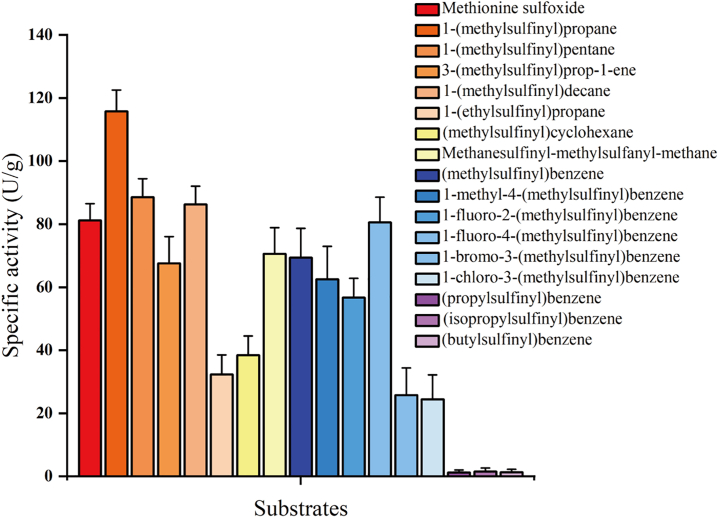
Previous studies have shown that MsrA homologs from non-halophilic species exhibited excellent activities toward a series of sulfoxide substrates.33,38,39 To further understand the substrate specificity of this HhMsrA enzyme, various aryl alkyl sulfoxides, dialkyl sulfoxides, and thioalkyl sulfoxides (Figure S4) were used as substrates to test its activity under the condition of 3.5 M KCl. The results revealed that the enzyme was active on all substrates containing a methyl/ethyl moiety on the sulfinyl group, with specific activities ranging from 24.4 ± 7.8 U/g to 115.8 ± 6.7 U/g, depending on their structures (Figure 3). As observed, HhMsrA exhibits maximal activity against 1-(methylsulfinyl)propane rather than the natural substrate Met-O and also shows higher activity against 1-(methylsulfinyl)pentane and 1-(methylsulfinyl)decane compared to Met-O. This substrate preference may be attributed to the specific structural features of HhMsrA’s active site, which likely favors the binding of these substrates due to better steric and hydrophobic interactions. The structural configuration of these substrates may align more effectively with the enzyme’s active site, enhancing catalytic efficiency. Further structural studies could provide more insights into these interactions. However, for substrates in which the methyl/ethyl moiety was substituted by a larger propyl/butyl moiety, such as (propylsulfinyl)benzene, (isopropylsulfinyl)benzene, and (butylsulfinyl)benzene, HhMsrA was inactive. These substrate profiles were also similar to those of homologs from non-halophilic species.33,38,39
Figure 3.
Specific activity analysis of HhMsrA toward a series of sulfoxide substrates
The reaction conditions are consistent with those in Figure 2 in the presence of 3.5 M KCl. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
Mechanism investigation of salt activation of HhMsrA
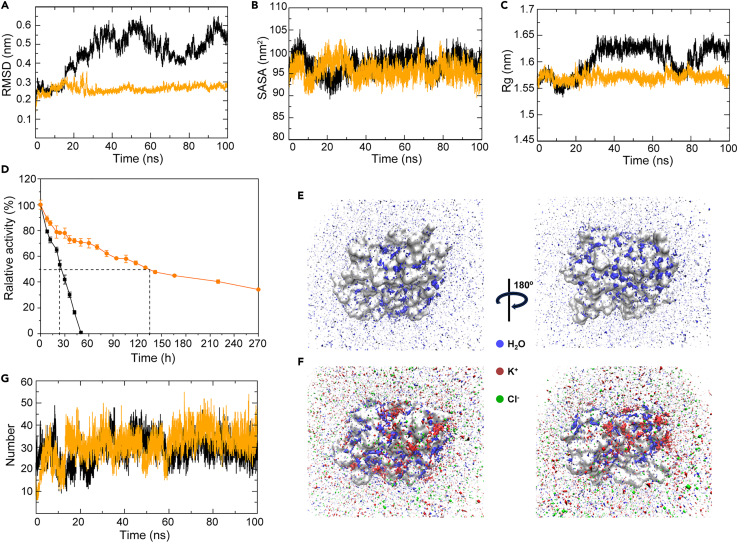
To elucidate the mechanism underlying the activation of HhMsrA by salts, 100 ns MD simulations of HhMsrA-substrate (Met-S-O) complexes were performed with and without the presence of KCl (1.0 M). The enzyme’s stability was compared by analyzing several parameters, including root-mean-square deviation (RMSD),49 solvent-accessible surface area (SASA),50 and radius of gyration (Rg).51 As illustrated in Figure 4A, the RMSD values of the enzyme displayed significant fluctuations after 20 ns in the absence of KCl. In contrast, in the presence of KCl, the system remained stable throughout the simulation, with an average RMSD value of 0.263 nm, significantly lower than that in the absence of KCl (0.459 nm). As a commonly used indicator for assessing protein structure stability throughout the simulation,49 the RMSD measurement indicates that the presence of KCl enhances the stability of HhMsrA. Furthermore, the enzyme exhibited lower SASA and Rg values in the presence of KCl, indicating a more compact structure (Figures 4B and 4C). Collectively, the data obtained through MD simulations indicate that the presence of KCl enhances the stability of the enzyme during catalytic processes.
Figure 4.
MD simulation and stability analysis of HhMsrA under conditions with or without KCl
Met-S-O was used as substrate for the simulation. The black and orange lines represent data obtained in the absence and presence of KCl, respectively.
(A) Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) for the main chain atoms.
(B) Solvent-accessible surface area (SASA).
(C) Radius of gyration (Rg).
(D) Half-life analysis of HhMsrA in the absence and presence of KCl, each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(E and F) Spatial distribution of water molecules, K+, and Cl− ions on the surface of the HhMsrA in the absence (E) and presence (F) of KCl. The protein surface, water molecules, K+ ions, and Cl− ions are shown in gray, blue, red, and green, respectively.
(G) Number of water molecules in the active site.
To further validate these data, the half-life of HhMsrA at 30°C was determined in both the absence and presence of KCl. As illustrated in Figure 4D, the half-life of HhMsrA was only 24.3 h without KCl. However, in the presence of KCl, this metric extended to 133.1 h, approximately 5 times longer than without salt. Moreover, we analyzed the pH-stability profile of the enzyme in the presence and the absence of KCl to further validate the stability. We analyzed the activity of HhMsrA pre-treated at pH 5.0, 7.0, and 11.0 with or without KCl, for durations of 2 and 10 h. The data showed that pre-treatment with salts under unfavorable pH conditions, such as pH 5.0, could greatly reduce the enzyme’s activity (Figure S5). However, the presence of salt was highly effective in maintaining the enzyme’s activity. For instance, after treatment for 10 h at pH 5.0, the residual activities of HhMsrA were 30.2% and 80.4% with and without KCl, respectively (Figure S5). These experiments validated the MD results and strongly verified that the presence of salts greatly enhances the enzyme’s stability.
Previous studies on the crystal structure of halophilic 2Fe-2S ferredoxin reveal that haloadaptation involves an enhanced water-binding capacity.52 Thus, the effect of KCl on the stability of the hydration layer around HhMsrA was investigated. We employed the spatial distribution function to visualize the distribution of the water molecules and ions around HhMsrA. As depicted in Figures 4E and 4F, the water molecules and ions (mainly K+) were distributed on the surface of the protein, with an increased number of water molecules in certain regions following the addition of KCl. Statistical analysis of the number of water molecules within the active site revealed that the addition of KCl increased the number of water molecules within the active pocket and reduced their fluctuations in this region (Figure 4G). These findings indicate that the KCl improves the distribution and quantity of water molecules of the enzyme, consequently optimizing its conformation and probably enhancing the enzyme-substrate binding.53,54 Thus, we determined the kinetic parameters of HhMsrA under low (0.8 M) and high salts (1.5 M). The Km and Kcat of the enzyme under low salt were 4.301 mM and 0.133 s−1, respectively (Table 1). Notably, with the increase in salt concentration, the Km was reduced to 0.503 mM, indicating that the high salt concentration greatly enhanced the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate. Combining the results of MD simulations, stability experiments, and enzymatic kinetics experiments, these findings suggest that the addition of salt enhances the structural stability of HhMsrA by reducing fluctuations and compacting the structure and strengthens the stability of the hydration layer. These combined factors contribute to the improved stability of the enzyme in salt-rich environments, consequently enhancing the enzyme-substrate affinity, which positively influences its activity.
Table 1.
Kinetic parameters of HhMsrA and variants
| Entry | Enzyme | KCl (M) | Km (mM) | Kcat (s−1) | Kcat/Km (s−1 · mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HhMsrA-WT | 0.8 | 4.301 | 0.133 | 0.031 |
| 2 | HhMsrA-WT | 1.5 | 0.503 | 0.169 | 0.336 |
| 3 | HhMsrA-R168K | 1.5 | 0.579 | 0.173 | 0.299 |
| 4 | HhMsrA-R168P | 1.5 | 1.411 | 0.110 | 0.078 |
Investigation of salt bridges regarding the activation of HhMsrA by salts
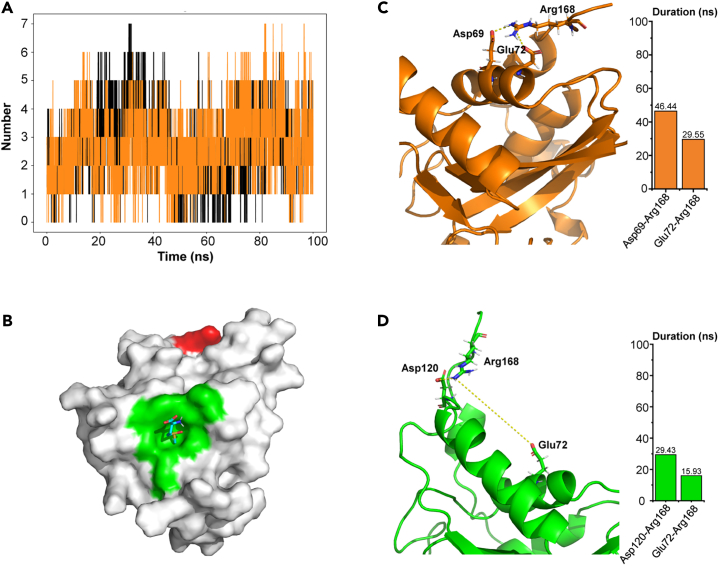
Salt bridges are pivotal for the structural stability of halophilic proteins, particularly in high-salt environments.45,55,56 They enhance internal electrostatic interactions within the protein, thereby preserving its three-dimensional structure and ultimately bolstering its stability. For instance, comparing the three-dimensional structures of halophilic malate dehydrogenase with its non-halophilic counterparts reveals a greater presence of salt bridges in halophilic malate dehydrogenase.21 We thus analyzed changes in salt bridges during the 100 ns MD simulations with or without KCl. Our analysis revealed that the presence of KCl leads to an increase in the total number and duration within HhMsrA and decrease in their fluctuations (Figure 5A). These data indicate that the addition of KCl could potentially enhance the enzyme’s interaction network favorably. Notably, we observed substantial variations in salt bridges triggered by the residue Arg168, which is located on the surface of the enzyme, far from the active center (Figure 5B). In the presence of KCl, this residue formed salt bridges with Asp69 and Glu72 with durations of 46.44 and 29.55 ns, respectively, during the 100 ns simulation (Figure 5C). However, in the absence of KCl, the enzyme underwent certain conformational changes, resulting in the reorientation of the positively charged side chain of Arg168 away from the acidic amino acids Asp69 and Glu72. This change led to the formation of substituted salt bridges between Arg168 and Asp120, and Arg168 and Glu72, with significantly shorter durations, lasting only 29.43 and 15.93 ns, respectively (Figure 5D).
Figure 5.
Analysis of salt bridge formations in HhMsrA during a 100 ns MD simulation
(A) Number of total salt bridges within HhMsrA during simulation. The black and orange lines represent data obtained in the absence and presence of KCl, respectively.
(B) 3D model of HhMsrA docking with substrate Met-S-O. The green and red regions represent the active center and Arg168, respectively. The sticks represent the substrate.
(C and D) Structure and duration analysis of residue Arg168 salt bridge in the presence (C) and absence of KCl (D).
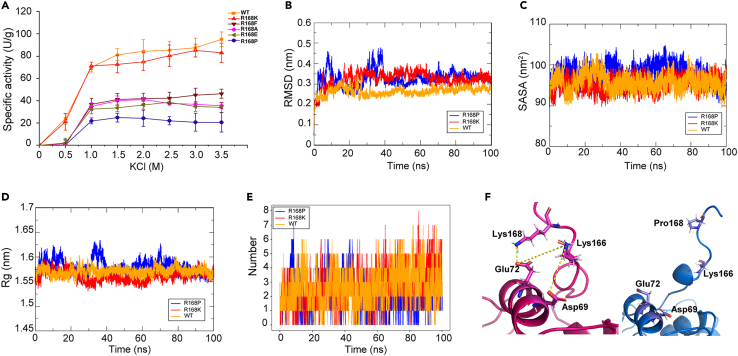
To further verify the essential role of the salt bridge formed by Arg168, mutagenesis analysis was conducted for this critical amino acid residue. We introduced mutations at this site, substituting the basic Arg168 with various other amino acids, including the basic Lys, acidic Glu, hydrophobic Ala and Pro, and aromatic Phe. All resulting variants were successfully expressed in soluble form and purified from E. coli (Figure S1). As shown in Figure 6A, when this Arg residue was replaced by another basic Lys (HhMsrA-R168K), the KCl profiles at all concentrations remained virtually unchanged, indicating that substituting amino acids with similar properties did not alter HhMsrA’s salt activation. Variants including HhMsrA-R168F, HhMsrA-R168A, HhMsrA-R168E, and HhMsrA-R168P exhibited minimal activities at 0.5 M of KCl. Even under optimal salt concentrations, their activities were less than half of those observed for HhMsrA-wild type (WT) and HhMsrA-R168K. Notably, the variant HhMsrA-R168P exhibited a peak activity of only 24.3 ± 7.4 U/g, which is a quarter of that of HhMsrA-WT. These findings underscore the critical role of the basic amino acid at position 168 in maintaining enzyme stability and facilitating salt activation.
Figure 6.
Mutagenesis analysis of key amino acid residue within HhMsrA
(A) Specific activities of HhMsrA-WT and its variants under various concentrations of KCl, each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(B–D) RMSD (B), SASA (C), and Rg (D) comparisons between HhMsrA-WT and the variants HhMsrA-R168K and HhMsrA-R168P.
(E) Total number of salt bridges within variants HhMsrA-R168K and HhMsrA-R168P during simulation.
(F) Structure analysis of salt bridge involving key residue 168 within variants HhMsrA-R168K (red) and HhMsrA-R168P (blue).
Variants HhMsrA-R168K and HhMsrA-R168P were then selected for MD simulations to assess their performances in the presence of 1.0 M KCl. As shown in Figures 6B–6D, the values of RMSD, SASA, and Rg values between enzymes HhMsrA-WT and HhMsrA-R168K exhibit relatively minor differences. However, for the variant HhMsrA-R168P, all these parameters were unfavorable compared to HhMsrA-WT and HhMsrA-R168K. These results suggest that substituting Arg168 with an amino acid sharing similar properties minimally affects enzyme stability, whereas substitution with other types of amino acids substantially weakens it. The half-life of HhMsrA-R168K variant at 30°C was determined, and the results were consistent with those of the WT enzyme (Figure S6). These results further confirmed that this mutagenesis did not alter the enzyme’s stability. However, substitution with other types of amino acids significantly weakened the salt activation effects. Furthermore, the salt bridge analysis revealed that mutating Arg168 to Pro significantly reduced both the total number and duration of salt bridges compared to those observed in the HhMsrA-WT and HhMsrA-R168K (Figure 6E). Notably, in the HhMsrA-R168K variant, although the salt bridge between Arg168 and Asp69 in HhMsrA-WT disappeared, the salt bridge between Arg168 and Glu72 shortened the distances between certain nearby amino acids. This, in turn, led to the formation of two new salt bridges between Lys166 and both Glu72 and Asp69, maintaining the stability of its spatial conformation (Figure 6F). Conversely, within the HhMsrA-R168P variant, the mutated Pro was far from the corresponding amino acids and failed to form any salt bridges with other residues, resulting in significant spatial conformation changes compared to the HhMsrA-WT enzyme (Figure 6F).
Moreover, the kinetic parameters of HhMsrA-R168K and HhMsrA-R168P under high salts (1.5 M) were compared. The results showed that the Km and Kcat values of HhMsrA-R168K were quite consistent with those of the WT enzyme (Table 1), indicating this mutagenesis did not cause significant changes to the enzymatic properties. However, the Km of HhMsrA-R168P was 1.141 mM, much higher than those of WT and HhMsrA-R168K, suggesting that the mutagenesis of basic Arg to hydrophobic Pro leads to a lower substrate affinity. In addition, the Kcat value of HhMsrA-R168P was also slightly lower, indicating this mutagenesis also resulted in a decrease in catalytic rate. All these data suggest that salt bridges formed by the basic residue at position 168 play crucial roles in the enzyme’s response to salts, enhancing its stability and ultimately activating its catalytic activity.
In summary, our study presents evidence that the activity of MsrA from halophile is activated by various salts, offering insights into the antioxidation roles contributing to the survival of halophiles in high-salt environments. Molecular docking, MD simulations, stability, and kinetic assays revealed that the presence of salts enhances the structural stability of the enzyme, resulting in improved enzyme-substrate binding and catalytic efficiency. Furthermore, site-directed mutagenesis experiments demonstrated the essential role of specific amino acid residues, particularly Arg168, in mediating the enzyme’s response to salts. Substitution of Arg168 with different amino acids significantly impacted enzyme stability and salt activation. These findings deepen the understanding of the molecular basis of salt adaptation in halophilic microorganisms and provide insights for the design of enzymes with enhanced stability and activity under extreme environmental conditions.
Limitations of the study
This study proposes that the salt bridge is an essential factor for the MsrA enzyme from halophiles in responding to high salinity, as evidenced by MD simulations and mutagenesis analysis. Further analysis of the crystal structure is required to confirm the significance of this factor. Moreover, since all HhMsrA variants retained a certain level of activity, future studies will explore other contributing factors influencing the enzyme’s response to high salinity.
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Jiawei Yang (yangjw@zmu.edu.cn).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Data and code availability
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request.
This paper does not report original code.
All other requests: Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported will be shared by the lead contact upon request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Guizhou Science and Technology Department (no. QKHJC-ZK-2023YB521 and QKHJC-ZK-2021-ZD028), National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 32260228 and 31960202), and the Zunyi Science and Technology Department (ZSKH-HZ2023-193 and QKPTRC-2021-1350-029).
Author contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and J.Y.; methodology, B.P., S.C., and X.X.; investigation, S.Z., B.P., X.K., and Y.Z.; software, B.P., Y.S., and L.L.; writing – original draft, S.Z., B.P., and X.K.; writing – review and editing, X.C. and J.Y.; funding acquisition, X.C. and J.Y.; resources, J.Y.; supervision, X.C. and J.Y.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| TOP10 Chemically Competent Cell | Beijing Tsingke Biotech Co., Ltd. | Cat: TSC-C12 |
| BL21 Star (DE3) Chemically Competent Cell | Beijing Tsingke Biotech Co., Ltd. | Cat: TSC-E01 |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| 50XTAE Buffer | Sangon Biotech | Cat: B548101-0500 |
| DNA Marker (250∼10000 bp) | Sangon Biotech | Cat: B600022-0050 |
| Coomassie Brilliant Blue Quick stain | Epizyme | Cat:PS111 |
| Omni-EasyTM instant protein loading buffer (denatured, reduced, 5 ×) | Epizyme | Cat:LT101S |
| Two-color pre-staining protein Marker 10 KDa∼250 KDa | Epizyme | Cat: WJ102 |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| Primer: R168K Forward: GAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCAAAG AGGAGTTCGCCGAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168K Reverse: CTCGGCGAACTCCTCTTTG ACCTTCGCGACCTTC |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168F Forward: GAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCTTTG AGGAGTTCGCCGAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168F Reverse: GAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCTTTGA GGAGTTCGCCGAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168A Forward: CGAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCGCGG AGGAGTTCGCCGAGAAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168A Reverse: CTTCTCGGCGAACTCCTCCGCG ACCTTCGCGACCTTCG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168E Forward: GAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCGAAGA GGAGTTCGCCGAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168E Reverse: CTCGGCGAACTCCTCTTCGAC CTTCGCGACCTTC |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168P Forward: GAAGGTCGCGAAGGTCCCGG AGGAGTTCGCCGAGAAG |
This paper | N/A |
| Primer: R168P Reverse: CTTCTCGGCGAACTCCTCCGGG ACCTTCGCGACCTTC |
This paper | N/A |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| Gel Mini Purification Kit | Zomanbio | Cat: ZP202 |
| Site-directed Mutagenesis Kit | Sangon Biotech | Cat: B639281-0020 |
| BeyoGold™ His-tag Purification Resin | Beyotime | Cat: P2218 |
| BCA protein concentration assay kit | Beyotime | Cat: P0009 |
| Easy PAGE color rapid gel preparation kit (10%) | Seven Biotech | Cat: SW143-02 |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| Origin 2022 | Origin | https://www.originlab.com/2022 |
| GraphPad Prism 9.5.0 | Prism | https://www.graphpad-prism.cn/ |
| Lasergene | Lasergene | https://www.dnastar.com/software/lasergene/ |
| Gromacs 2020.6 | Spoel et al.57 | https://manual.gromacs.org/2020.6/download.html |
| Python 3.9 | Python Software Foundation | https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-390/ |
| VMD version 1.9.3 | Humphrey et al.58 | https://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/vmd/ |
| PyMOL | DeLano et al.59 | https://pymol.org/ |
| Autodock Vina | Trott et al.60 | https://github.com/ccsb-scripps/AutoDock-Vina |
Experimental model and study participant details
Microbe strains
E. coli strains TOP10 and BL21 (DE3) were used for molecular cloning and the recombinant expression, respectively. The corresponding competent cells were purchased from Tsingke Biotech Co., Ltd, Beijing, China.
Methods details
Recombinant expression and purification of HhMsrA and variants
The gene sequence of MsrA from the halophile H. hubeiense strain JI20-1 was obtained from the GenBank database and synthesized by Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China). The corresponding DNA fragment was then cloned into the multiple cloning site (MCS) of the pET-28a vector using BamH I and Xho I restriction sites to construct the recombinant plasmid. To induce the soluble expression of recombinant enzymes, recombinant plasmids were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells. Overnight cultures of BL21 (DE3) cells harboring the expression plasmid were diluted at a 1:100 ratio in LB medium and incubated at 37°C until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached 0.6. Protein expression was then induced with 1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and the cultures were incubated at 20°C for 18 hours. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 10 min and lysed by sonication. The lysates were centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C to collect the crude enzymes. Purification of the recombinant HhMsrA and variants was achieved through Ni-NTA affinity chromatography using the His6-tagged within the proteins. Protein concentration was determined using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay and then converted to micromolar (μM) based on the molecular weight of the protein. The purity of the proteins was assessed by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis.
Enzyme activity assays
The enzymatic activities of the HhMsrA and its variants were determined using the dithiothreitol (DTT)-5,5'-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) coupled colorimetric assay, as previously reported with modifications.37,61 The consumption of co-factor DTT was used to represent the enzyme activity. For relative activity assays of pH and temperature profiles, reaction mixtures containing purified enzymes (3 μM), Met-O (3 mM), and DTT (1 mM) were combined in a 500 μL reaction system. After a 45 min reaction under different pH or temperature conditions, 50 μL of mixtures from each well were transferred to a 96-well ELISA plate, and 150 μL of DTNB solution were added to a final concentration of 2 mM. After incubation at 37°C for 15 min, the plate was placed into the microplate reader to measure the absorbance at 405 nm (A405). A blank system without enzyme was used as a control. The decrease in A405 was used to describe the relative activities to represent the pH and temperature profiles. For the specific activity assays, the same enzymatic reactions were performed at pH 10.0 and 40°C in the presence of various salts and substrates. The amount of enzyme that consumed 1 μM of DTT per minute was defined as 1 unit (U). For analysis of the reversible effect of salt inhibition, the enzyme was first incubated in 2.0 M of Na2SO4 for 45 min and then washed with 3 times via ultrafiltration centrifugation. The recovered enzyme was tested for the activity using method mentioned above. Differential significance analysis was conducted using the t-test method, with a p-value of less than 0.05 indicating a significant difference.
Half-life and pH stability analysis
To determine the half-life of HhMsrA-WT and HhMsrA-R168K, the enzymes were first incubated at 30°C for up to 50 h without KCl and 270 h with 1.5 M KCl. Enzyme activity was measured at specific time intervals throughout this period using methods described above. The initial activity was recorded, and subsequent measurements were taken to determine the remaining activity over time, allowing the calculation of the enzyme's half-life. The data were then fitted using Origin 2022 to calculate the enzyme's half-life. To determine the pH stability, the enzyme was incubated in solutions with pH 5.0, 7.0, and 11.0 for 2 h or 10 h with or without 1.5 M of KCl. Then, enzyme activity was measured using methods described above.
Kinetic parameters determination
To determine the kinetic parameters, 3 μM HhMsrA-WT of was incubated with the substrate Met-O, varying the concentrations from 0.2 to 20 mM (containing 0.1 to 10 mM of the S enantiomers) under high salt condition (1.5 M KCl). Additionally, 12 μM of HhMsrA-WT was incubated with the substrate Met-O, varying the concentrations from 0.4 to 30 mM (containing 0.2 to 15 mM of the S enantiomers) under low salt condition (0.8 M KCl). For the variants, 3 μM of HhMsrA-R168K and 15 μM of HhMsrA-R168P were incubated with the substrate Met-O, varying the concentrations from 0.2 to 20 mM (containing 0.1 to 10 mM of the S enantiomers). The initial rate at different substrate concentrations was determined by the above colorimetric assay after a 20 min incubation at 40°C. Kcat and Km values were calculated using nonlinear regression analysis in software Origin 2022, according to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
Site-directed mutagenesis
Site-directed mutagenesis of HhMsrA was performed via PCR using the Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Sangon Biotech, China). The PCR primers were listed in the key resources table, and the parameters were set as follows: 95°C for 5 min (1 cycle), 95°C for 30 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 68°C for 10 min (30 cycles). The PCR products were then digested with Dpn І at 30°C for 3 h to eliminate the template DNA. Subsequently, the products were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells, and sequencing was conducted to confirm the mutagenesis.
Molecular docking and MD simulations
The 3D models of both the wild-type HhMsrA and its variants were created using the SWISS-MODEL web server, with the Neisseria meningitidis Z2491 MsrA crystal structure (PDB ID: 3BQE) as the modeling template (43.71% of sequence identity). The substrate Met-S-O was sourced from PubChem. Autodock tools were used to produce PDBQT files for the substrate and protein, which were then docked using Vina in a semiflexible manner. The docking process was repeated three times to ascertain the most favorable binding affinity, selecting the best complex conformation. Visualization was done using PyMOL software. For molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, Gromacs 2022. 06 was employed, incorporating protein residues from the AMBER14SB force field and the substrate using the GAFF. The simulations used a periodic cubic box, ensuring a 10 Å buffer from the solute to the box edges, filled with TIP3P water molecules, and balanced with Na+, K+, and Cl- ions for neutrality. Energy minimization was conducted via the steepest descent method, followed by NVT (500 ps) and NPT (1,000 ps) equilibration phases, using the linear constraint solver for hydrogen bonds and the particle-mesh Ewald method for long-range interactions, setting a 1.0 nm cutoff for van der Waals forces. MD simulations were carried out at 303 K in 0 or 1 M KCl. The analysis utilized a suite of tools from Gromacs, such as gmx rms, rmsf, gyrate, sasa, and spatial, to evaluate various molecular dynamics parameters: RMSD, RMSF, Rg, SASA, SDF, and the molecular or atomic density distribution within the system. Trajectory analysis and the identification of salt bridges were conducted using Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD), applying a cutoff for oxygen-nitrogen distances at 4 Å.
Quantification and statistical analysis
All statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism 9.5.0. Data were derived from three independent biological replicates reported as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). The t-test or nonparametric test was used for the comparison of two independent samples, with p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
Published: August 23, 2024
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110806.
Contributor Information
Xiaoling Cheng, Email: xiaoling_cheng@qq.com.
Jiawei Yang, Email: yangjw@zmu.edu.cn.
Supplemental information
References
- 1.Dumorné K., Córdova D.C., Astorga-Eló M., Renganathan P. Extremozymes: A Potential Source for Industrial Applications. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017;27:649–659. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1611.11006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shrestha N., Chilkoor G., Vemuri B., Rathinam N., Sani R.K., Gadhamshetty V. Extremophiles for microbial-electrochemistry applications: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018;255:318–330. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barnard D., Casanueva A., Tuffin M., Cowan D. Extremophiles in biofuel synthesis. Environ. Technol. 2010;31:871–888. doi: 10.1080/09593331003710236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chettri D., Verma A.K., Sarkar L., Verma A.K. Role of extremophiles and their extremozymes in biorefinery process of lignocellulose degradation. Extremophiles. 2021;25:203–219. doi: 10.1007/s00792-021-01225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carré L., Zaccai G., Delfosse X., Girard E., Franzetti B. Relevance of Earth-Bound Extremophiles in the Search for Extraterrestrial Life. Astrobiology. 2022;22:322–367. doi: 10.1089/ast.2021.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Obulisamy P.K., Mehariya S. Polyhydroxyalkanoates from extremophiles: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021;325 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ye J.W., Lin Y.N., Yi X.Q., Yu Z.X., Liu X., Chen G.Q. Synthetic biology of extremophiles: a new wave of biomanufacturing. Trends Biotechnol. 2023;41:342–357. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Edbeib M.F., Wahab R.A., Huyop F. Halophiles: biology, adaptation, and their role in decontamination of hypersaline environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016;32:135. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Qiu J., Han R., Wang C. Microbial halophilic lipases: A review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021;61:594–602. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Amoozegar M.A., Safarpour A., Noghabi K.A., Bakhtiary T., Ventosa A. Halophiles and Their Vast Potential in Biofuel Production. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:1895. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xu T., Mitra R., Tan D., Li Z., Zhou C., Chen T., Xie Z., Han J. Utilization of gene manipulation system for advancing the biotechnological potential of halophiles: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024;70 doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yin J., Chen J.C., Wu Q., Chen G.Q. Halophiles, coming stars for industrial biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1433–1442. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Srivastava A.K., Srivastava R., Sharma A., Bharati A.P., Yadav J., Singh A.K., Tiwari P.K., Srivatava A.K., Chakdar H., Kashyap P.L., Saxena A.K. Transcriptome Analysis to Understand Salt Stress Regulation Mechanism of Chromohalobacter salexigens ANJ207. Front. Microbiol. 2022;13 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.909276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Onishi H., Kushner D.J. Mechanism of dissolution of envelopes of the extreme halophile Halobacterium cutirubrum. J. Bacteriol. 1966;91:646–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.646-652.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gunde-Cimerman N., Plemenitaš A., Oren A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018;42:353–375. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuy009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li P.S., Kong W.L., Wu X.Q. Salt Tolerance Mechanism of the Rhizosphere Bacterium JZ-GX1 and Its Effects on Tomato Seed Germination and Seedling Growth. Front. Microbiol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.657238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ventosa A., Nieto J.J., Oren A. Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998;62:504–544. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.2.504-544.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Csonka L.N., Hanson A.D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Norberg P., Kaplan J.G., Kushner D.J. Kinetics and regulation of the salt-dependent aspartate transcarbamylase of Halobacterium cutirubrum. J. Bacteriol. 1973;113:680–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.680-686.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Arakawa T., Yamaguchi R., Tokunaga H., Tokunaga M. Unique Features of Halophilic Proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017;18:65–71. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160617111140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dym O., Mevarech M., Sussman J.L. Structural features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from an archaebacterium. Science. 1995;267:1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.267.5202.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xia Y.L., Sun J.H., Ai S.M., Li Y., Du X., Sang P., Yang L.Q., Fu Y.X., Liu S.Q. Insights into the role of electrostatics in temperature adaptation: a comparative study of psychrophilic, mesophilic, and thermophilic subtilisin-like serine proteases. RSC Adv. 2018;8:29698–29713. doi: 10.1039/c8ra05845h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kennedy S.P., Ng W.V., Salzberg S.L., Hood L., DasSarma S. Understanding the adaptation of Halobacterium species NRC-1 to its extreme environment through computational analysis of its genome sequence. Genome Res. 2001;11:1641–1650. doi: 10.1101/gr.190201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang T.N., Guan Q.T., Pain A., Kaksonen A.H., Hong P.Y. Discovering, Characterizing, and Applying Acyl Homoserine Lactone-Quenching Enzymes to Mitigate Microbe-Associated Problems Under Saline Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:823. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mevarech M., Frolow F., Gloss L.M. Halophilic enzymes: proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys. Chem. 2000;86:155–164. doi: 10.1016/s0301-4622(00)00126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sivakumar N., Li N., Tang J.W., Patel B.K.C., Swaminathan K. Crystal structure of AmyA lacks acidic surface and provide insights into protein stability at poly-extreme condition. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2646–2652. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peng T., Cheng X., Chen Y., Yang J. Sulfoxide Reductases and Applications in Biocatalytic Preparation of Chiral Sulfoxides: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2021;9 doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.714899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Drazic A., Winter J. The physiological role of reversible methionine oxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1844:1367–1382. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stadtman E.R., Moskovitz J., Levine R.L. Oxidation of methionine residues of proteins: biological consequences. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2003;5:577–582. doi: 10.1089/152308603770310239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Achilli C., Ciana A., Minetti G. The discovery of methionine sulfoxide reductase enzymes: An historical account and future perspectives. Biofactors. 2015;41:135–152. doi: 10.1002/biof.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boschi-Muller S., Olry A., Antoine M., Branlant G. The enzymology and biochemistry of methionine sulfoxide reductases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005;1703:231–238. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yang J., Yuan Z., Zhou Y., Zhao J., Yang M., Cheng X., Ou G., Chen Y. Asymmetric reductive resolution of racemic sulfoxides by recombinant methionine sulfoxide reductase from a pseudomonas monteilii strain. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016;133:S588–S592. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2017.02.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yang J., Wen Y., Peng L., Chen Y., Cheng X., Chen Y. Identification of MsrA homologues for the preparation of (R)-sulfoxides at high substrate concentrations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019;17:3381–3388. doi: 10.1039/c9ob00384c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wen Y., Peng L., Zhou Y., Peng T., Chen Y., Cheng X., Chen Y., Yang J. Discovery and application of methionine sulfoxide reductase B for preparation of (S)-sulfoxides through kinetic resolution. Catal. Commun. 2020;136 doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2019.105908. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Peng T., Tian J., Zhao Y., Jiang X., Cheng X., Deng G., Zhang Q., Wang Z., Yang J., Chen Y. Multienzyme Redox System with Cofactor Regeneration for Cyclic Deracemization of Sulfoxides. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2022;61 doi: 10.1002/anie.202209272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhao Y., Jiang X., Zhou S., Tian J., Yang P., Chen Y., Zhang Q., Xu X., Chen Y., Yang J. Kinetic resolution of sulfoxides with high enantioselectivity using a new homologue of methionine sulfoxide reductase B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023;21:3417–3422. doi: 10.1039/d3ob00402c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang Q., Pan B., Yang P., Tian J., Zhou S., Xu X., Dai Y., Cheng X., Chen Y., Yang J. Engineering of methionine sulfoxide reductase A with simultaneously improved stability and activity for kinetic resolution of chiral sulfoxides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024;260 doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Anselmi S., Carvalho A.T.P., Serrano-Sanchez A., Ortega-Roldan J.L., Caswell J., Omar I., Perez-Ortiz G., Barry S.M., Moody T.S., Castagnolo D. Discovery and Rational Mutagenesis of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase Biocatalysts To Expand the Substrate Scope of the Kinetic Resolution of Chiral Sulfoxides. ACS Catal. 2023;13:4742–4751. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c00372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nosek V., Míšek J. Chemoenzymatic Deracemization of Chiral Sulfoxides. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2018;57:9849–9852. doi: 10.1002/anie.201805858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bierbaumer S., Schmermund L., List A., Winkler C.K., Glueck S.M., Kroutil W. Synthesis of Enantiopure Sulfoxides by Concurrent Photocatalytic Oxidation and Biocatalytic Reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2022;61 doi: 10.1002/anie.202117103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Achilli C., Ciana A., Minetti G. Kinetic resolution of phenyl methyl sulfoxides by mammalian methionine sulfoxide reductase A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017;58:4781–4782. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.11.022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Boschi-Muller S., Branlant G. Methionine sulfoxide reductase: chemistry, substrate binding, recycling process and oxidase activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2014;57:222–230. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2014.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fu X., Adams Z., Liu R., Hepowit N.L., Wu Y., Bowmann C.F., Moskovitz J., Maupin-Furlow J.A. Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A (MsrA) and Its Function in Ubiquitin-Like Protein Modification in Archaea. mBio. 2017;8 doi: 10.1128/mBio.01169-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jaakkola S.T., Pfeiffer F., Ravantti J.J., Guo Q., Liu Y., Chen X., Ma H., Yang C., Oksanen H.M., Bamford D.H. The complete genome of a viable archaeum isolated from 123-million-year-old rock salt. Environ. Microbiol. 2016;18:565–579. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wu Y., Hu J., Du Y., Lu G., Li Y., Feng Y., Chen L., Tu Y., Xiang M., Gui Y., et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Halophilic Xylosidase Xylo-1 and Its Role in Xylose Production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023;71:15375–15387. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bowers K.J., Wiegel J. Temperature and pH optima of extremely halophilic archaea: a mini-review. Extremophiles. 2011;15:119–128. doi: 10.1007/s00792-010-0347-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Peng L., Wen Y., Chen Y., Yuan Z., Zhou Y., Cheng X., Chen Y., Yang J. Biocatalytic preparation of chiral sulfoxides through asymmetric reductive resolution by methionine sulfoxide reductase A. ChemCatChem. 2018;10:3284–3290. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201800279. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xu Z., Cen Y.K., Zou S.P., Xue Y.P., Zheng Y.G. Recent advances in the improvement of enzyme thermostability by structure modification. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020;40:83–98. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1682963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cohen F.E., Sternberg M.J. On the prediction of protein structure: The significance of the root-mean-square deviation. J. Mol. Biol. 1980;138:321–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ali S.A., Hassan M.I., Islam A., Ahmad F. A review of methods available to estimate solvent-accessible surface areas of soluble proteins in the folded and unfolded states. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014;15:456–476. doi: 10.2174/1389203715666140327114232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Galzitskaya O.V., Garbuzynskiy S.O. Entropy capacity determines protein folding. Proteins. 2006;63:144–154. doi: 10.1002/prot.20851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Frolow F., Harel M., Sussman J.L., Mevarech M., Shoham M. Insights into protein adaptation to a saturated salt environment from the crystal structure of a halophilic 2Fe-2S ferredoxin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996;3:452–458. doi: 10.1038/nsb0596-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ebbinghaus S., Kim S.J., Heyden M., Yu X., Heugen U., Gruebele M., Leitner D.M., Havenith M. An extended dynamical hydration shell around proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:20749–20752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709207104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Halle B. Protein hydration dynamics in solution: a critical survey. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004;359:1207–1224. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Okajima R., Hiraoka S., Yamashita T. Environmental Effects on Salt Bridge Stability in the Protein-Protein Interface: The Case of Hen Egg-White Lysozyme and Its Antibody, HyHEL-10. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2021;125:1542–1549. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c09248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bandyopadhyay A.K., Islam R.N.U., Mitra D., Banerjee S., Yasmeen S., Goswami A. Insights from the salt bridge analysis of malate dehydrogenase from H. salinarum and E.coli. Bioinformation. 2019;15:95–103. doi: 10.6026/97320630015095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Groenhof G., Mark A.E., Berendsen H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005;26:1701–1718. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Trott O., Olson A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.DeLano W.L. 2002. The PyMOL molecular graphics system.https://www.pymol.org/ [Google Scholar]
- 60.Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996;14:33. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wu P.F., Zhang Z., Guan X.L., Li Y.L., Zeng J.H., Zhang J.J., Long L.H., Hu Z.L., Wang F., Chen J.G. A specific and rapid colorimetric method to monitor the activity of methionine sulfoxide reductase A. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2013;53:391–397. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request.
This paper does not report original code.
All other requests: Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported will be shared by the lead contact upon request.