Abstract
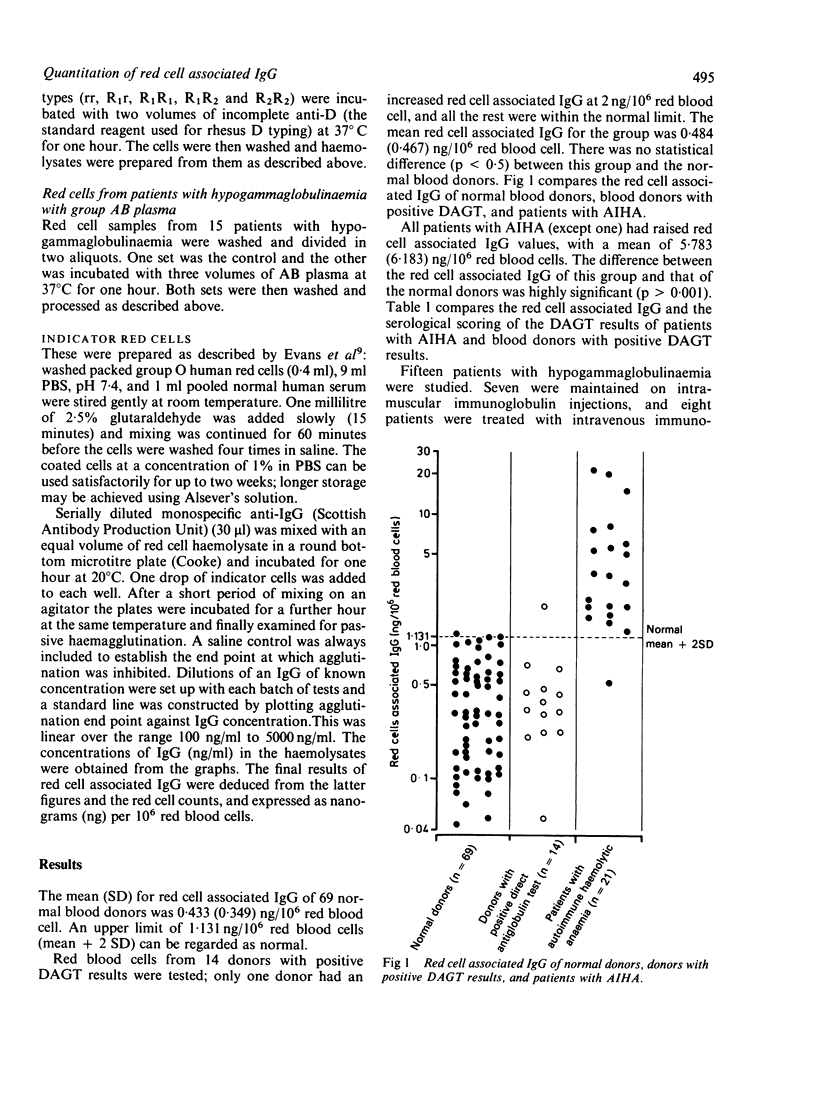
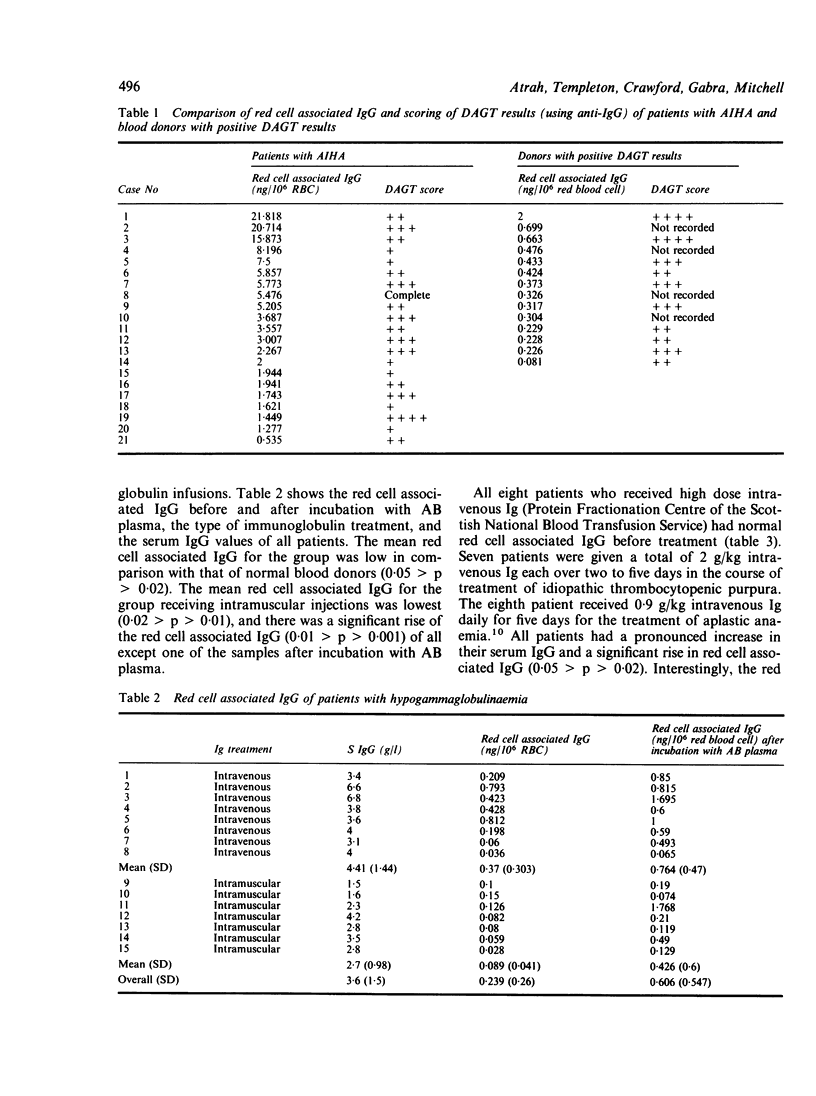
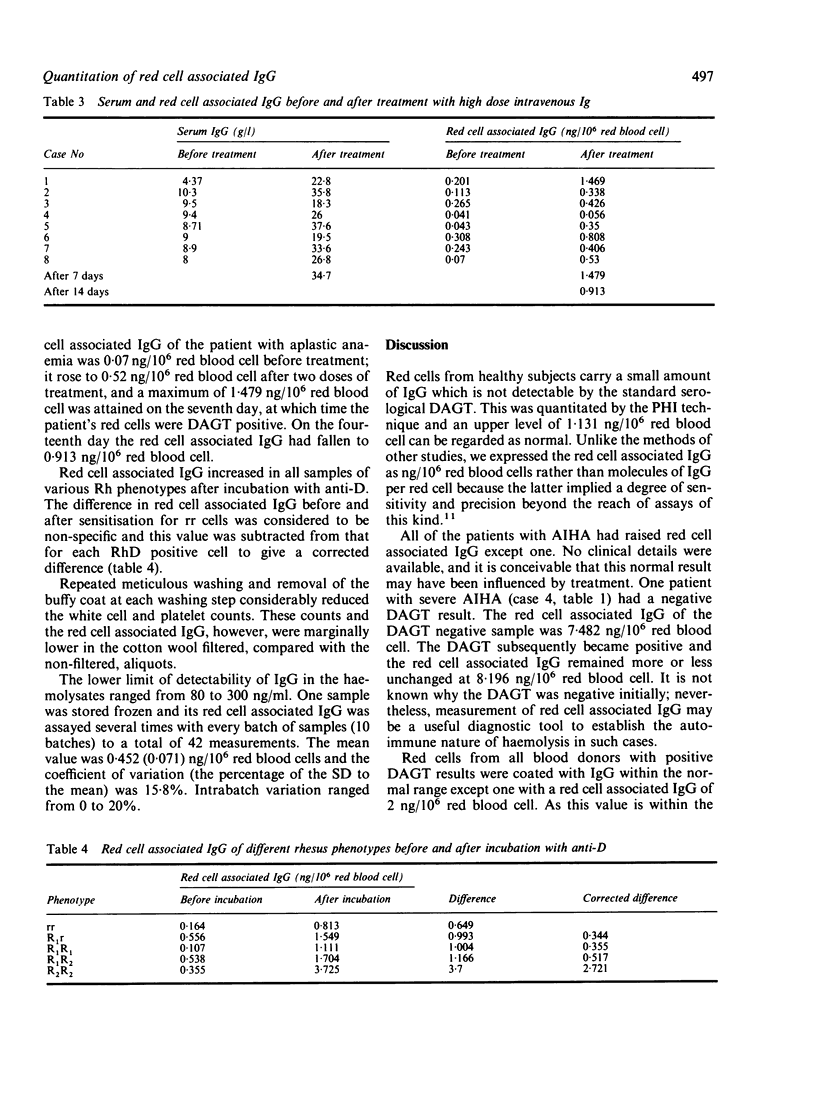
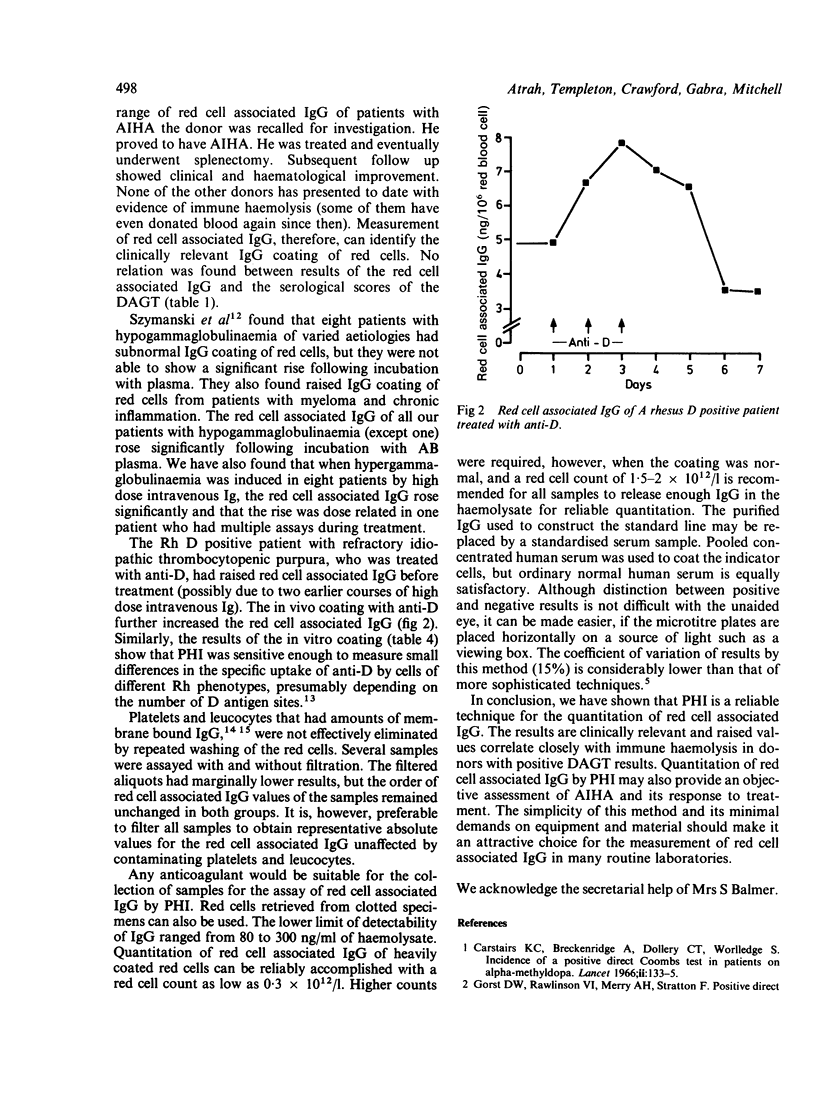
Passive haemagglutination inhibition (PHI) was adapted to quantitate red cell associated IgG. Twenty one patients with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia (AIHA) had a raised red cell associated IgG, mean (SD) = 5.783 (6.183) ng/10(6) red blood cell compared with that of 69 subjects with a red cell associated IgG of 0.433 (0.349) ng/10(6) red blood cell. Thirteen of 14 blood donors with a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAGT) had a normal red cell associated IgG. The only blood donor with positive DAGT and raised red cell associated IgG had AIHA. Studies of red cell associated IgG in other groups of patients were also undertaken. The technique is simple, does not require the use of sophisticated equipment, and is suitable as a routine test in hospital laboratories. The results of red cell associated IgG by PHI are reproducible and clinically relevant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atrah H. I., Crawford R. J., Gabra G. S., Forwell M. A., Mitchell R., Islam S. I., Ramsay D., Sandilands G. P. Modulation of suppressor T-cells for the treatment of aplastic anaemia. Lancet. 1985 Aug 10;2(8450):339–340. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstairs K. C., Breckenridge A., Dollery C. T., Worlledge S. M. Incidence of a positive direct coombs test in patients on alpha-methyldopa. Lancet. 1966 Jul 16;2(7455):133–135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J., Steel M., Arthur E. A hemagglutination inhibition technique for detection of immunoglobulins in supernatants of human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland B. C., Baxter E., Evans R. S. Red-cell antibodies in acquired hemolytic anemia with negative antiglobulin serum tests. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 29;285(5):252–256. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107292850503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorst D. W., Rawlinson V. I., Merry A. H., Stratton F. Positive direct antiglobulin test in normal individuals. Vox Sang. 1980 Feb;38(2):99–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeje M. O., Blajchman M. A., Steeves K., Horsewood P., Kelton J. G. Quantitation of red cell-associated IgG using an immunoradiometric assay. Transfusion. 1984 Nov-Dec;24(6):473–476. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24685066803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Giles A. R., Neame P. B., Powers P., Hageman N., Hirsch J. Comparison of two direct assays for platelet-associated IgG (PAIgG) in assessement of immune and nonimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logue G. Felty's syndrome: granulocyte-bound immunoglobulin G and splenectomy. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):437–442. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry A. H., Thomson E. E., Rawlinson V. I., Stratton F. A quantitative antiglobulin test for IgG for use in blood transfusion serology. Clin Lab Haematol. 1982;4(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1982.tb00483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama A., Kiefel V., Amberg R., Mueller-Eckhardt C. Treatment of autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura with rhesus antibodies (anti-Rh0(D). Blut. 1984 Jul;49(1):29–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00320381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton F., Rawlinson V. I., Merry A. H., Thomson E. E. Positive direct antiglobulin test in normal individuals. II. Clin Lab Haematol. 1983;5(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1983.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymanski I. O., Odgren P. R., Fortier N. L., Snyder L. M. Red blood cell associated IgG in normal and pathologic states. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meulen F. W., van der Hart M., Fleer A., von dem Borne A. E., Engelfriet C. P., van Loghem J. J. The role of adherence to human mononuclear phagocytes in the destruction of red cells sensitized with non-complement binding IgG antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1978 Apr;38(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


