Abstract
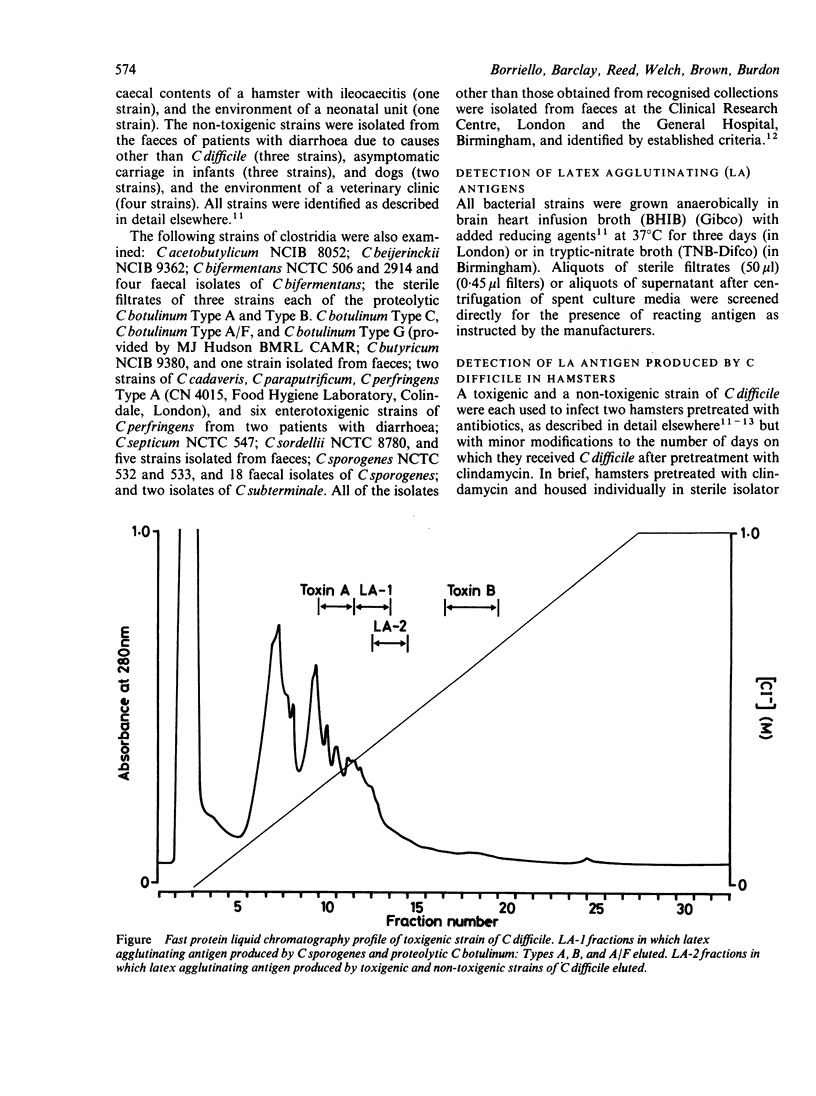
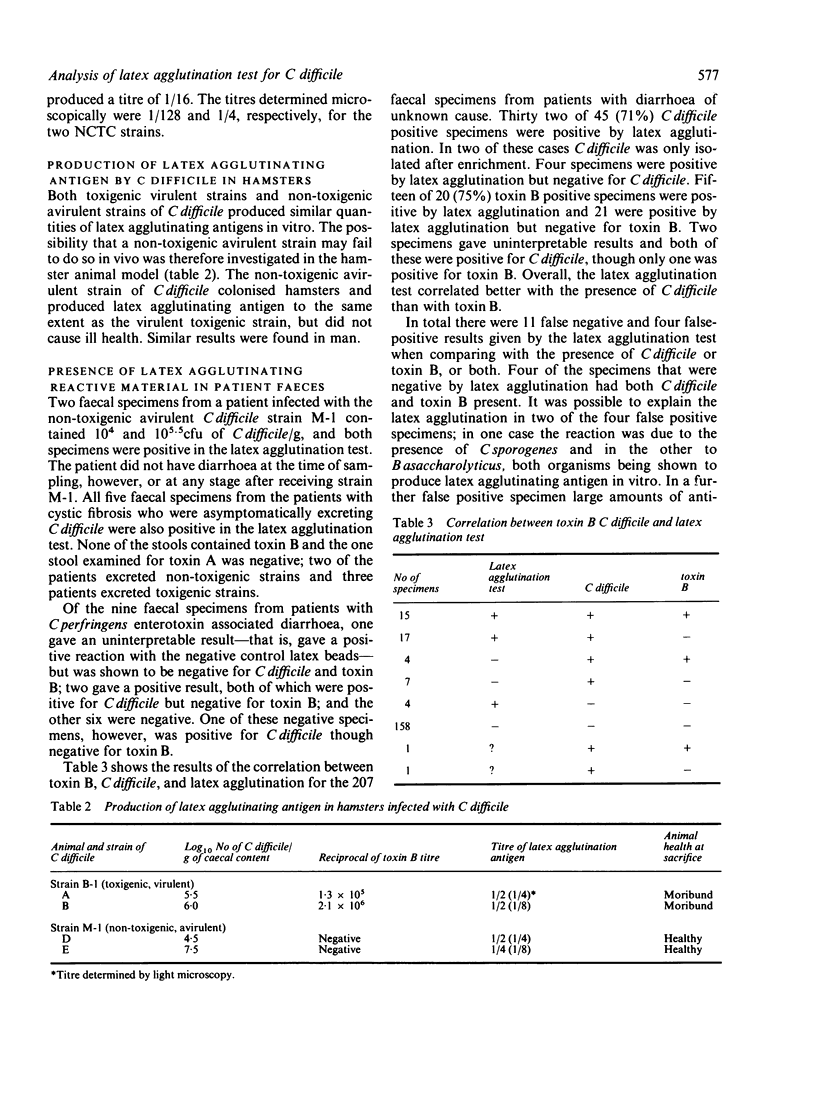
Virulent toxigenic and avirulent non-toxigenic strains of Clostridium difficile gave a positive result in the latex agglutination test (LAT) for C difficile toxin A (D-1). Similar concentrations of latex agglutinating antigen were produced by these strains in vivo. Positive reactions were also given by C sporogenes, proteolytic C botulinum Types A, B, and A/F, and Bacteroides assaccharolyticus. The latex agglutinating antigen was denatured by boiling for 10 minutes, but not by heating at 56 degrees C for 30 minutes. The reaction was abolished by incubation of test material with crude C difficile antitoxin but not with other clostridial antitoxins or specific antitoxin to C difficile toxin A. The latex agglutinating antigen present in C difficile eluted between 0.39% and 0.47% M sodium chloride, and that produced by the other clostridia, between 0.35% and 0.43% M sodium chloride by fast protein liquid chromatography. The latex agglutinating antigen of C difficile was neither cytotoxic nor mouse lethal and was distinct from toxin A and toxin B. In the analysis of faecal specimens from patients with diarrhoea the latex agglutination test correlated better with the presence of C difficile than with toxin B and detected both toxigenic and non-toxigenic strains. The latex agglutination test should only be used in the laboratory as an alternative to culture for C difficile and not as a method for the detection of C difficile toxins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borriello S. P., Barclay F. E. Protection of hamsters against Clostridium difficile ileocaecitis by prior colonisation with non-pathogenic strains. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):339–350. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon D. W., George R. H., Mogg G. A., Arabi Y., Thompson H., Johnson M., Alexander-Williams J., Keighley M. R. Faecal toxin and severity of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;34(5):548–551. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.5.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya S., Nakamura S., Yamakawa K., Nishida S. Evaluation of a commercially available latex immunoagglutination test kit for detection of Clostridium difficile D-1 toxin. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(2):177–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb00932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzynski T. A., Cembrowski G. S., Kimball J. L. The use of CIE for the detection of Clostridium difficile toxin in stool filtrates: laboratory and clinical correlation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;79(3):370–374. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Borriello S. P. Epidemiology of experimental enterocecitis due to Clostridium difficile. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):408–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Viscidi R. P., Gdovin S. L., Yolken R. H., Bartlett J. G. Enzyme immunoassays for detection of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in fecal specimens. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):781–788. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lawrence A. J., Manson J. I. Quantitation of Clostridium botulinum organisms and toxin in the feces of an infant with botulism. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.1-4.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach S. L., Borriello S. P., Gaya H., Barclay F. E., Welch A. R. Asymptomatic carriage of Clostridium difficile in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Sep;39(9):1013–1018. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.9.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihn B., Scheftel J. M., Girardot R., Monteil H. A new purification procedure for Clostridium difficile enterotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):690–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. W., Brown J. E., Diecidue A., Foret D. A. Differential cytotoxic effects of toxins A and B isolated from Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):324–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.324-331.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E., Gaffney D., Coderre S. E., Gordon R., Pai C. H. Latex agglutination test for detection of Clostridium difficile toxin in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):339–341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.339-341.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Pellett S., Wilkins T. D. Purification and characterization of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1032-1040.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


