Abstract
The KRAS protein, a product of the KRAS gene (V-ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog), functions as a small GTPase that alternates between an active GTP-bound state (KRAS(ON)) and an inactive GDP-bound state (KRAS(OFF)). The KRASG12C mutation results in the accumulation of KRASG12C(OFF), promoting cell cycle survival and proliferation primarily through the canonical MAPK and PI3K pathways. The KRASG12C mutation is found in 13% of lung adenocarcinomas. Previously considered undruggable, sotorasib and adagrasib are the first available OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors, but treatment resistance is frequent. In this review, after briefly summarizing the KRAS pathway and the mechanism of action of OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors, we discuss primary and acquired resistance mechanisms. Acquired resistance is the most frequent, with "on-target" mechanisms such as a new KRAS mutation preventing inhibitor binding; and "off-target" mechanisms leading to bypass of KRAS through gain-of-function mutations in other oncogenes such as NRAS, BRAF, and RET; or loss-of-function mutations in tumor suppressor genes such as PTEN. Other "off-target" mechanisms described include epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and histological transformation. Multiple co-existing mechanisms can be found in patients, but few cases have been published. We highlight the lack of data on non-genomic resistance and the need for comprehensive clinical studies exploring histological, genomic, and non-genomic changes at resistance. This knowledge could help foster new treatment initiatives in this challenging context.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, KRASG12C mutation, KRASG12C inhibitor resistance, translational research, sotorasib, adagrasib
1. Introduction
The RAS (rat sarcoma viral oncogene) protein is a small guanosine triphosphate hydrolase (GTPase) that alternates between an active GTP-bound state (RAS(ON)) and an inactive GDP-bound state (RAS(OFF)). Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) regulate the transition from RAS(ON) to RAS(OFF) and from RAS(OFF) to RAS(ON) (1). RAS(ON) promotes several important signaling pathways, primarily the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway and the RAS-PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, thus playing an important role in cell survival and cell cycle proliferation (2).
Growth factors can induce rapid dimerization and autophosphorylation of their receptors (GFRs). Specific tyrosine residues in noncatalytic regions of autophosphorylated GFRs can interact with the SH2 domain of the Grb2 protein. Coupled with the Son of Sevenless (Sos) protein, the Grb2-Sos complex stimulates the exchange of GDP for GTP on RAS, thus leading to RAS(ON) promotion. The Grb2-Sos complex is the primary GEF (3, 4).
Even though RAS possesses intrinsic low GTPase activity, additional proteins are needed to accelerate GTP hydrolysis. Those GAPs (such as RASA1, neurofibromin, or DAB2IP) aid, via their arginine finger, in the structural rearrangement and assembly of a catalytically competent active site, leading to nucleotide release (4, 5). Regulation of RAS signaling thus depends on a balance between GEFs and GAPs.
The RAS(ON) protein binds to RAS binding domains (RBD) located on RAS effectors, which are proteins with a strong affinity to RAS(ON). RAF (rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma) is a critical RAS effector that triggers the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway. PI3K is another important RAS effector that activates the RAS-PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway (4).
Four isoforms of the RAS protein are found in humans: HRAS, NRAS, KRAS4A, and KRAS4B (6), with RAS mutations detected in 19% of cancer patients (75% in KRAS, 17% in NRAS, and 7% in HRAS) (7).
KRAS mutations are frequent in lung adenocarcinomas, accounting for 43% of cases (8), while NRAS and HRAS mutations account collectively for approximately 1.2% of cases. Furthermore, 80% of NSCLC-KRAS mutations involve a glycine on position 12 substitution (KRASG12C , KRASG12V , KRASG12D …) and 11% involve a glycine on position 13 substitution (KRASG13C , KRASG13D , KRASG13R …).
The most frequent KRAS mutation is KRASG12C , present in 13% of lung adenocarcinomas (9). This glycine at position 12 substitution to cysteine in the KRASG12C protein prevents interaction with GAPs through steric blockade, resulting in reduced GTPase activity responsible for the accumulation of active KRASG12C-GTP bound protein (KRASG12C(ON)). Unlike other oncogenic mutations such as EGFR's classical L858R exon 21 mutation or exon 19 deletions, KRAS mutations are predominantly seen in the majority of patients with a history of smoking and co-mutations are not rare (mainly TP53, STK11, and KEAP1). However, KRAS mutations are considered mutually exclusive with other NSCLC driver alterations, such as EGFR mutations, EML4-ALK fusions, or ROS1 fusions.
Long deemed undruggable due to its lack of apparent hydrophobic pockets and its picomolar affinity for GTP/GDP, new KRASG12C inhibitors are finally under investigation in preclinical and clinical studies (10). These treatments bind covalently to an H95 residue located in an allosteric binding pocket behind switch-II, referred to as P2, near the mutated cysteine 12, in the inactive KRASG12C-GDP bound protein (KRASG12C(OFF) ( Figure 1 ). This covalent binding in the P2 pocket induces the blocking of nucleotide exchange from GDP to GTP (10) thereby inhibiting RAS-effector interaction in KRASG12C mutant cells. Despite the KRASG12C mutation inducing the accumulation of KRASG12C(ON) protein, 25% of proteins in each cell remain in a GDP-bound inactive state, explaining the potential for protein inhibition (11).
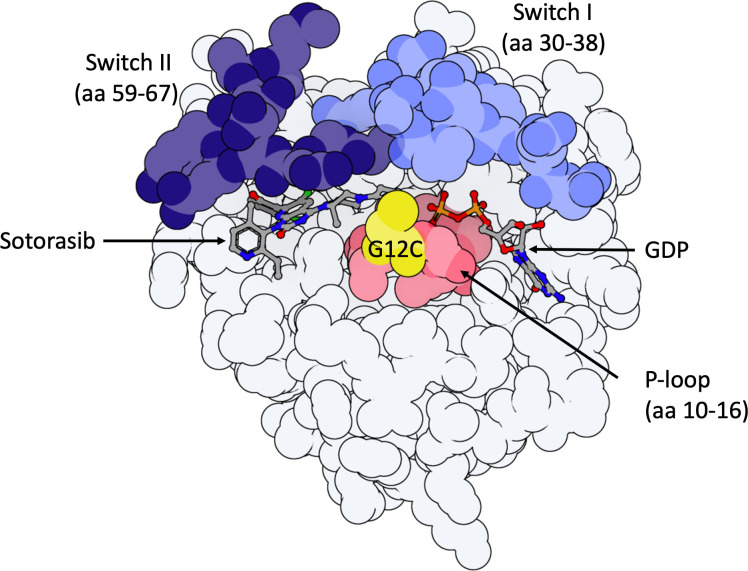
Figure 1.
Model of KRASG12C-protein in the inactive GDP-bound state with important domains highlighted. 3D molecule was rendered with ProteinImager (http://3dproteinimaging.com) based on the crystal structure (PBD ID: 6OIM, rcsb.org/structure/6OIM). The structure of the KRAS gene comprises a G-domain coding region and a hypervariable region, including the conserved CAAX motif, a membrane anchor sequence (C: cysteine, A: aliphatic amino acids, X: any amino acid and residues coding for a lipid tail; not shown here). Selected structural regions of the KRAS protein G-domain are highlighted: the phosphate-binding loop (P-loop, amino acids (aa) 10 to 16) and the two switch regions (switch I (aa 30 to 38) and switch II (aa 59 to 67)). Both switch regions change conformation to make hydrogen bonds with the gamma-phosphate in GTP-bound-KRAS. Sotorasib is observed in its binding pocket (P2, behind Switch II region, near mutated Cysteine-12). The mutated Cystein-12 residue is shown in yellow. Adagrasib interacts with the P2 binding pocket in the same way as sotorasib.
Sotorasib is the first-in-class OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitor, available in France since early 2021 through an early access program. The phase III open-label randomized controlled trial (RCT) CodeBreak 200 demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) over docetaxel (median PFS 5.6 months (4.3-7.8) in the sotorasib group vs 4.5 months (3.0-5.7) in the docetaxel group; 12-month PFS rate of 24.8% with sotorasib vs 10.1% with docetaxel) (12). However, the overall survival (OS) did not reach statistical significance, partly due to a decrease in sample size after protocol amendment and a 26% cross-over rate in the docetaxel group.
Adagrasib is another OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitor with results from the recently published phase I/II KRYSTAL-1 study (13) showing promising outcomes with adagrasib in the same second-line setting as sotorasib. A phase III randomized controlled trial (NCT04685135) is in progress. Additionally, studies investigating sotorasib and adagrasib (alone or combined with chemo- or immunotherapy) in the first-line and the second-line settings are ongoing (34 trials listed on clinicaltrials.gov). A summary of the main efficacy results in the second-line setting is described in Table 1 .
Table 1.
Efficacy data from Phase II/III trials involving KRASG12C inhibitors sotorasib and adagrasib in pretreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
| KRASG12C Inhibitor | Study | Phase | Control | Number of patients | Objective Response
a
- %, (95% CI) |
Median duration of response b , mo (95% IC) | Median PFS, mo (95% IC) |
Median OS, mo (95% IC) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | KRASG12Ci | Control | KRASG12Ci | Control | KRASG12Ci | Control | KRASG12Ci | Control | KRASG12Ci | ||||
| Sotorasib | CodeBreak 100 | II15 | 126 | 37.1 (28.6-46.2) |
11.1 (6.9-NE) |
6.8 (5.1-8.2) |
12.5 (10-NE) |
||||||
| CodeBreak 200 | III13 | Docetaxel | 174 | 174 | 13.2 (8.6-19.2) |
28.1 (21.5-35.4) |
6.8 (4.3-8.3) |
8.6 (7.1-18.0) |
4.5 (3.0-5.7) |
5.6 (4.3-7.8) |
11.3 (9.0-14.9) |
10.6 (8.9-14.0) |
|
| Adagrasib | Krystal-1 | II14 | 116 | 42.9 (33.5-52.6) |
8.5 (6.2-13.8) |
6.5 (4.7-8.4) |
12.6 (9.2-19.2) |
||||||
Objective response was defined as a complete or partial response.
Duration of response was evaluated based on patients with a complete or partial response. KRASG12Ci, KRASG12C inhibitor; CI, confidence interval; mo, months; NE, not evaluated.
Despite promising efficacy, resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors occurs in virtually all patients. Notably, one-third of patients experienced early disease progression (PFS < 3 months) on sotorasib in the CodeBreaK100 study. Primary and early adaptative resistance mechanisms may drive early disease progression (14). Recent preclinical and clinical datasets suggest that resistance mechanisms to the KRASG12C inhibitors sotorasib and adagrasib may be categorized into two distinct groups: genetic and non-genetic mechanisms, which can explain early and delayed resistance at different levels.
This review aims to describe and examine emerging mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors in KRASG12C -mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and to demonstrate how this body of data is shaping the therapeutical development in KRASG12C targeting.
2. Genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors
2.1. Genetic determinants of primary resistance
Genomic alterations were correlated with long-term benefit (PFS ≥ 12 months) versus early progression (PFS < 3 months) in the CodeBreaK100 study dataset (14). The most significant enrichment in patients with early progression was observed with mutant KEAP1. Aggregated with other emerging data, co-occurring mutations in KEAP1, SMARCA4, and CDKN2A are associated with worse clinical outcomes with sotorasib or adagrasib therapy (14–16). The biological mechanisms driving early progression in this subgroup of patients with co-occurring KEAP1, SMARCA4, and CDKN2A mutations are not clearly understood.
2.2. Genetic mechanisms of acquired resistance
Mechanisms of acquired resistance have been partly described following treatment with sotorasib and adagrasib. Resistance has been categorized as "on-target" or "off-target", with the majority of published data focusing on "on-target" mechanisms. Figure 2 summarizes acquired mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors (11).
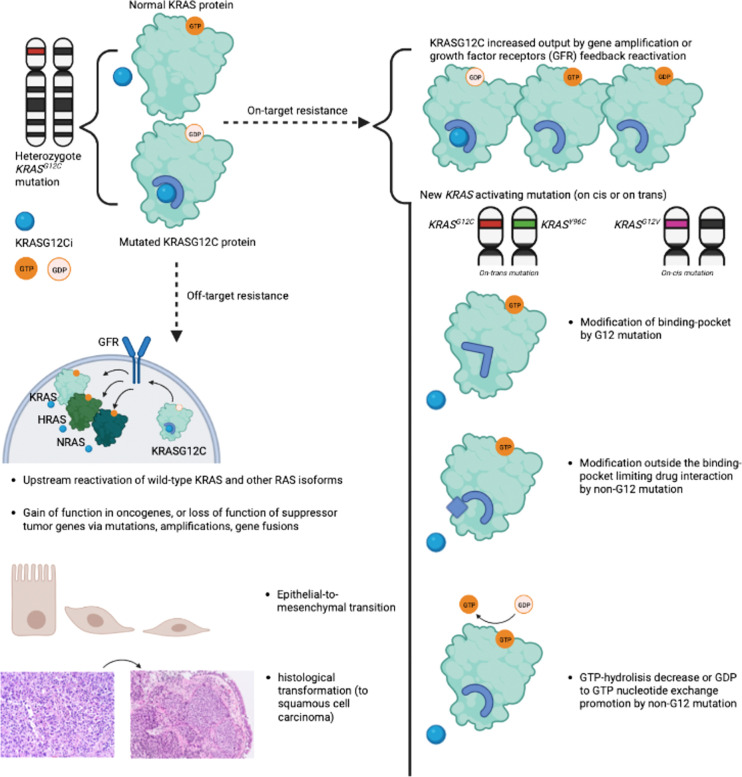
Figure 2.
Summary of "on-target" and "off-target" resistance mechanisms to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors. Summary of "on-target" and "off-target" resistance mechanisms described with OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors sotorasib and adagrasib. "On-target" resistance encompasses new KRAS activating mutations and increased KRASG12C output due to growth factor receptors' feedback reactivation. "Off-target" resistance mechanisms include amplification or mutations of other oncogenes, upstream reactivation of wild-type KRAS and other RAS isoforms, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and adeno-to-squamous transition. The illustration was created with BioRender.com. KRASG12Ci, OFF state KRASG12C inhibitor; GFR, Growth Factor Receptor.
2.2.1. "On-target" genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors
"On-target" genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors encompass mutations of the KRAS G12C codon to another mutant variant on the same allele (cis) or a secondary KRAS mutation on the trans-KRAS allele. CfDNA analysis of a 67-year-old patient with KRASG12C -mutant NSCLC after progression on adagrasib showed a new (trans) KRASG12V mutation (11), coexisting with the (cis) KRASG12C mutation and probably arising from the wild-type KRAS allele. The persistence of a wild-type KRAS allele in multiple KRAS-mutated lung cancer cell lines was observed in preclinical studies (17). Acquired KRASG12D/R/V/W mutations in other patients led to the reactivation of the KRAS downstream pathway (18). Non-KRASG12 mutations affecting switch II pocket and precluding drug binding, such as KRASY96C , KRASR68S , or KRASH95D/Q/R , were described (18). Other KRAS mutations, like KRASG13D or KRASA59S , induce resistance by decreasing GTP hydrolysis or promoting GDP to GTP nucleotide exchange (18).
KRASG12C allele amplification or copy number gain were the only identifiable resistance mechanisms in two patients treated with adagrasib (18).
Upstream reactivation of associated proteins such as Aurora Kinase A (AURKA), a serine/threonine kinase essentially involved in mitosis and DNA repair, has been shown to facilitate effector activation by stabilizing the interaction between newly formed KRASG12C protein and RAF, thus aiding cell cycle progression in in vitro models (19).
In summary, the inhibition of KRASG12C(OFF) downregulates physiological negative feedback mechanisms, leading to the upregulation of GFR (19). Similar resistance mechanisms have already been described with MEK inhibitors (20) and BRAF inhibitors (21).
2.2.2. "Off-target" genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors
"Off-target" genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASF12C inhibitors include:
- Amplifications or mutations of upstream RTK genes (such as EGFR).
- Bypass of KRASG12C through activating mutation in downstream pathway components, including MEK, BRAF, or PI3KCA.
- Activating mutation in NRAS or HRAS.
In an analysis of 38 patients with KRASG12C-mutant cancers resistant to adagrasib (18), a putative resistance mechanism was seen in only 17 patients. These mechanisms included multiple acquired bypass resistances (such as EGFR, RET, NRAS, BRAF, PI3K, and PTEN mutations), acquired gene fusions (e.g., EML4-ALK), or amplification (e.g., MET). An important limitation of this study was the limited number of tissue samples, with most analyses conducted using cfDNA sequencing. Interestingly, multiple co-resistance mechanisms were found in patients.
For example, one patient developed a KRASG12D and KRASQ61H mutation (an "on-target" resistance mechanism) associated with a BRAFV600E bypass mutation and a CCD6-RET fusion (an "off-target" resistance mechanism). The MET amplification was found in vitro to bypass the RAS pathway through the HGF/MET pathway, leading to AKT and ERK activation, but also reactivating the RAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK pathway through other RAS isoforms (22)
3. Non-genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors
A large majority of patients have no identifiable genetic mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors, suggesting that resistance may arise from non-genetic alterations.
3.1. Upstream reactivation of growth factor receptors
Rapid adaptative resistance may be driven by GFR reactivation (19, 23) The upstream reactivation of GFRs (including multiple tyrosine kinase receptors (RTKs)) not only increases KRASG12C output but also activates wild-type KRAS and other RAS isotypes (NRAS and HRAS), which can at least partially restore MAPK signaling. This rebound mechanism, with higher concentrations of NRAS(ON) and HRAS(ON) and downstream pathway reactivation (shown by phosphorylation of downstream MAPK proteins ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinases) and RSK (ribosomal s6 kinase)), was seen in the first 48h following KRASG12C inhibition in KRASG12C -mutant cell lines (19). RTKs such as EGFR, but also HER2, FGFR, and cMET were activated with different levels in different cell lines. RTK reactivation can activate the downstream ERK pathway via SHP2 tyrosine phosphatase interaction with Grb2. This has been shown in vitro with the rapid increase of SHP2 activation in multiple KRAS-mutant lung, colon, and pancreatic cell lines after initial reduction following MEK inhibition (23).
3.2. Histological transdifferentiation and cell lineage plasticity
Histological transdifferentiation and cell lineage plasticity may play a role in the resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors. Two KRASG12C mutant lung adenocarcinomas treated with adagrasib showed squamous cell carcinoma histology in biopsies at progression, with no genomic alterations explaining the resistance otherwise (18). Transcriptomic and genomic analysis on pre-treatment biopsies from patients in the KRYSTAL-1 trial revealed that patients presenting a baseline high expression of squamous cell carcinoma-related genes and STK11/LKB1 co-mutations had a shorter treatment duration with adagrasib (24). STK11/LKB1 co-mutations are frequent in KRASG12C mutant lung adenocarcinomas, and LKB1 is a regulator of chromatin accessibility linked with cellular plasticity (25, 26). Its inactivation induced squamous transition in KRASG12D -mutant lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. In a preclinical study, adagrasib-resistant KRAS/LKB1 mutant NSCLC showed enrichment in adenosquamous transition-associated genes, including Wnt4, Sfn, Aqp3, and Krt6a (24). In another preclinical study, KRAS inhibition was associated with the transition of lung adenocarcinoma alveolar type 2 cells to alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells. AT1 cells exhibited less dependency on KRAS and more quiescent activity (27). Both mechanisms have been described with EGFR and ALK inhibitors in EGFR-mutation-positive and ALK-fusion-positive NSCLC models (28).
3.3. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been observed in KRASG12C-mutated cancer cell lines after induced resistance to sotorasib. EMT, the process by which epithelial cells acquire mesenchymal features, is associated in cancer with tumor invasion, initiation, metastasis, and resistance to therapy (29), notably with EGFR and ALK inhibitors in EGFR-mutation-positive and ALK-fusion-positive NSCLC models (30, 31). EMT can be induced by numerous biological drivers such as TGFβ, TNF-α, HIF-α, Wnt signaling, interleukins, Hedgehog, and Hippo pathways (32). Genes related to EMT were enriched in sotorasib-resistant NSCLC cell lines (33). Induction of EMT via chronic TGFβ treatment was sufficient to induce resistance to sotorasib. In this population of EMT-induced cells, rebound activation of ERK and S6 was observed. Cell growth was inhibited after the addition of a PI3K inhibitor to sotorasib, implying that KRASG12C-independent AKT activation is a cause of resistance to sotorasib in EMT-induced KRASG12C -mutant NSCLC cell lines. These results were confirmed in a xenograft mouse model. EMT dependence on CDK-4 (cyclin-dependent kinase 4) has also been described in in vitro models, with promising efficacy for CDK4 inhibitors in reducing tumor volume in a murine model with autochthonous mesenchymal-like lung cancer with a KRASG12D mutation (34).
3.4. Tumor microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) associated with KRAS-mutant tumor cells is highly immunosuppressive (35). The TME is transiently converted to a less immunosuppressive state following RAS inhibition and may increase susceptibility to immunotherapies.
Due to a lack of data, other non-genomic resistance mechanisms to KRASG12C cannot be described to date. For example, no data about epigenetic dysregulation in this context are yet available.
4. Lessons from known mechanisms of resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors and therapeutical perspectives
Co-mutations in key tumor suppressor genes (KEAP1, SMARCA4, and CDKN2A) define different subgroups of KRASG12C-mutant NSCLC with clearly different clinical outcomes with OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors. These co-mutations may serve as biomarkers of clinical activity for OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors, should be integrated as stratification factors in clinical trials, and may guide escalated or de-escalated treatment strategies. The key role of co-mutations in defining patient subgroups with primary resistance and the diversity of on-target mechanisms of resistance explaining early and acquired resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors suggest that KRASG12C-mutant lung adenocarcinomas are highly genetically heterogeneous. This intra-tumoral genetic heterogeneity could partially explain the high proportion of early progressors and the low proportion of durable responders. Pan-RAS/KRAS inhibitors may prevent the emergence of acquired on-target mutations on KRAS and partly address the role of genetic heterogeneity in resistance to KRAS inhibition. For example, RMC-6236 is an ON-state RAS multi-selective noncovalent inhibitor of the active, GTP-bound state of both mutant and wild-type variants of RAS isoforms (36). RMC-6236 exhibited potent anticancer activity across RAS-addicted tumor models and showed early clinical activity (36, 37).
Amplifications or mutations of upstream RTK and upstream reactivation of GFR that drive RTK-driven pathway rebound can be prevented by RMC-6236 and ON/OFF-state direct inhibitors such as FMC-376 (38).
Upstream and downstream dysregulation of the RAS signaling pathway induced by OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors offer attractive targets for combination therapies. SOS1 and SHP2 are activated by RTK and regulate the switch of RAS from the OFF state to the ON state. Inhibition of SOS1 and SHP2 activity stabilizes GDP-bound RAS in an inactive form (39–41). Several combinations including SOS1 and SHP2 inhibitors are under clinical evaluation (42).
Other combinations under clinical evaluation include anti-PD-(L)1 with sotorasib or adagrasib (43). Sotorasib induced a proinflammatory tumor microenvironment highly sensitive to immunotherapy in a preclinical study (44). The combination of sotorasib and anti-PD-1 therapy resulted in a higher response rate and more durable responses in mice compared to sotorasib monotherapy or anti-PD-1 monotherapy (44). However, this strategy with sotorasib is limited in clinical practice due to higher rates of side effects, mainly hepatotoxicity, when sotorasib is prescribed in combination with or following anti-PD(L)1 therapy (45, 46). Preliminary results from the KRYSTAL-7 phase II trial did not show a higher rate of hepatotoxicity with adagrasib and pembrolizumab, hinting at a possible non-class effect (47). Multiple ongoing studies are investigating OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors and anti-PD(L)1 agents (43).
5. Conclusion
Several phase III trials comparing OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors (sotorasib, adagrasib, divarasib, olomorasib, opnurasib) to standard-of-care chemotherapy and immunotherapy in NSCLC are ongoing (47–49). They will provide highly valuable data on the benefit of these drugs, the optimal sequencing strategy, and hopefully, insights into mechanisms of resistance to these drugs. The design of these trials mainly relies on patient selection according to KRASG12C mutation and PD-L1 biomarkers.
The understanding of resistance mechanisms to KRASG12C inhibitors is in its early stages. It relies on data generated with OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors, mainly sotorasib and adagrasib, but provides an essential framework for future rationally designed therapeutic development. Thus, the early emergence of RAS-MAPK signaling reactivation through acquired resistance mutations and upstream reactivation of GFR underscores the strong need for RAS signaling in KRASG12C -mutant cancers as well as the major role of tumor heterogeneity in resistance to OFF-state KRASG12C inhibitors. As a result, therapeutic strategies based on strong inhibition of RAS signaling (ON- or ON/OFF-state RAS inhibitors), broad inhibition of the RAS pathway (pan-RAS inhibitors), and combination strategies that target upstream or downstream of the RAS pathway are relevant and currently being evaluated in clinical trials. There is a strong biological rationale supporting KRASG12C inhibitors and immunotherapy, specifically anti-PD-(L1) agents, and combination strategies, and multiple clinical trials are evaluating the safety and clinical activity of such combinations. Overall, the clinical evaluation of drug combination strategies is the way to address the problem of primary and acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors. These efforts should focus on understanding the biology driving KRASG12C-targeting clinical efficacy and selecting the most effective and relevant combination strategy and predictive biomarker of efficacy for future development, especially through phase III trials. Therapeutic platforms such as Master Protocols can effectively evaluate multiple combination strategies in KRASG12C-mutant NSCLC. ctDNA sample analysis can be a highly valuable tool for identifying early signals of efficacy and understanding mechanisms of resistance that may drive future preclinical and clinical development.
Funding Statement
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by INCa-DGOS-INSERM-ITMO cancer_18003 awarded to MD.
Author contributions
AC: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. A-CT: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. EB: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MD: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Conflict of interest
A-CT reports personal fees from AMGEN, during the conduct of the study; personal fees and non-financial support from Novartis, personal fees and non-financial support from Vifor Pharma, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, personal fees and non-financial support from MSD, personal fees and non-financial support from Takeda, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, personal fees and non-financial support from Astra Zeneca, personal fees and non-financial support from BMS, personal fees from Takeda, outside the submitted work. MD reports a membership of an advisory council or committee for BMS, GSK, Sanofi, MSD, AstraZeneca, Abbvie, Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merus, Amgen, Guardant, Pfizer; consulting fees from Roche, BMS, MSD, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gamamabs Pharma, Pfizer; research grants from Takeda, NanoString, Lilly, Blueprint.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Simanshu DK, Nissley DV, McCormick F. RAS proteins and their regulators in human disease. Cell. (2017) 170:17–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Huang L, Guo Z, Wang F, Fu L. KRAS mutation: from undruggable to druggable in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:386. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00780-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Buday L, Downward J. Many faces of Ras activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2008) 1786:178–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR, Albert S. Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2007) 1773:1177–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hennig A, Markwart R, Esparza-Franco MA, Ladds G, Rubio I. Ras activation revisited: role of GEF and GAP systems. Biol Chem. (2015) 396:831–48. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ostrem JML, Shokat KM. Direct small-molecule inhibitors of KRAS: from structural insights to mechanism-based design. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2016) 15:771–85. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Fleur LL, Falk-Sörqvist E, Smeds P, Berglund A, Sundström M, Mattsson JS, et al. Mutation patterns in a population-based non-small cell lung cancer cohort and prognostic impact of concomitant mutations in KRAS and TP53 or STK11. Lung Cancer. (2019) 130:50–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Cox AD, Der CJ. Ras history. Small GTPases. (2010) 1:2–27. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.1.1.12178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Biernacka A, Tsongalis PD, Peterson JD, de Abreu FB, Black CC, Gutmann EJ, et al. The potential utility of re-mining results of somatic mutation testing: KRAS status in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genet. (2016) 209:195–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2016.03.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Molina-Arcas M, Samani A, Downward J. Drugging the undruggable: advances on RAS targeting in cancer. Genes (Basel). (2021) 12. doi: 10.3390/genes12060899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Reita D, Pabst L, Pencreach E, Guérin E, Dano L, Rimelen V, et al. Direct targeting KRAS mutation in non-small cell lung cancer: focus on resistance. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:1321. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. de Langen AJ, Johnson ML, Mazieres J, Dingemans AMC, Mountzios G, Pless M, et al. Sotorasib versus docetaxel for previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer with KRASG12C mutation: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401(10378):P733–46. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(23)00221-0/fulltext. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Jänne PA, Riely GJ, Gadgeel SM, Heist RS, Ou SHI, Pacheco JM, et al. Adagrasib in non-small-cell lung cancer harboring a KRASG12C mutation. N Engl J Med. (2022) 387:120–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2204619 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Dy GK, Govindan R, Velcheti V, Falchook GS, Italiano A, Wolf J, et al. Long-term outcomes and molecular correlates of sotorasib efficacy in patients with pretreated KRAS G12C-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: 2-year analysis of codeBreaK 100. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:JCO2202524. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Skoulidis F, Li BT, Dy GK, Price TJ, Falchook GS, Wolf J, et al. Sotorasib for lung cancers with KRAS p.G12C mutation. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2371–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2103695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Negrao MV, Araujo HA, Lamberti G, Cooper AJ, Akhave NS, Zhou T, et al. Comutations and KRASG12C inhibitor efficacy in advanced NSCLC. Cancer Discovery. (2023) 13:1556–71. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-1420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Baldelli E, El Gazzah E, Moran JC, Hodge KA, Manojlovic Z, Bassiouni R, et al. Wild-type KRAS allele effects on druggable targets in KRAS mutant lung adenocarcinomas. Genes (Basel). (2021) 12:1402. doi: 10.3390/genes12091402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Awad MM, Liu S, Rybkin II, Arbour KC, Dilly J, Zhu VW, et al. Acquired resistance to KRAS(G12C) inhibition in cancer. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2382–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Xue JY, Zhao Y, Aronowitz J, Mai TT, Vides A, Qeriqi B, et al. Rapid non-uniform adaptation to conformation-specific KRAS(G12C) inhibition. Nature. (2020) 577:421–5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1884-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Little AS, Balmanno K, Sale MJ, Newman S, Dry JR, Hampson M, et al. Amplification of the driving oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, underpins acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. Sci Signal. (2011) 4:ra17. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Corcoran RB, Ebi H, Turke AB, Coffee EM, Nishino M, Cogdill AP, et al. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discovery. (2012) 2:227–35. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0341 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Suzuki S, Yonesaka K, Teramura T, Takehara T, Kato R, Sakai H, et al. KRAS inhibitor resistance in MET-amplified KRAS (G12C) non-small cell lung cancer induced by RAS- and non-RAS-mediated cell signaling mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:5697–707. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Mainardi S, Mulero-Sánchez A, Prahallad A, Germano G, Bosma A, Krimpenfort P, et al. SHP2 is required for growth of KRAS-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer in vivo. Nat Med. (2018) 24:961–7. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0023-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Tong X, Patel AS, Kim E, Li H, Chen Y, Li S, et al. Adeno-to-squamous transition drives resistance to KRAS inhibition in LKB1 mutant lung cancer. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:413–428.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Han X, Li F, Fang Z, Gao Y, Li F, Fang R, et al. Transdifferentiation of lung adenocarcinoma in mice with Lkb1 deficiency to squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3261. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4261 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhang H, Fillmore Brainson C, Koyama S, Redig AJ, Chen T, Li S, et al. Lkb1 inactivation drives lung cancer lineage switching governed by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:14922. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Li Z, Zhuang X, Pan CH, Yan Y, Thummalapalli R, Hallin J, et al. Alveolar differentiation drives resistance to KRAS inhibition in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discovery. (2024) 14:308–25. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Cooper AJ, Sequist LV, Lin JJ. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:499–514. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00639-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Pastushenko I, Blanpain C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. (2019) 29:212–26. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.12.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Recondo G, Mezquita L, Facchinetti F, Planchard D, Gazzah A, Bigot L, et al. Diverse resistance mechanisms to the third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:242–55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Huang L, Fu L. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2015) 5:390–401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. (2009) 119:1420–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI39104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Adachi Y, Ito K, Hayashi Y, Kimura R, Tan TZ, Yamaguchi R, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a cause of both intrinsic and acquired resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitor in KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:5962–73. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Padhye A, Konen JM, Rodriguez BL, Fradette JJ, Ochieng JK, Diao L, et al. Targeting CDK4 overcomes EMT-mediated tumor heterogeneity and therapeutic resistance in KRAS-mutant lung cancer. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e148392. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Molina-Arcas M, Downward J. Exploiting the therapeutic implications of KRAS inhibition on tumor immunity. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:338–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Jiang J, Jiang L, Maldonato BJ, Wang Y, Holderfield M, Aronchik I, et al. Translational and therapeutic evaluation of RAS-GTP inhibition by RMC-6236 in RAS-driven cancers. Cancer Discovery. (2024) 14:OF1–24. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Arbour KC, Punekar S, Garrido-Laguna I, Hong DS, Wolpin B, Pelster MS, et al. 652O Preliminary clinical activity of RMC-6236, a first-in-class, RAS-selective, tri-complex RAS-MULTI(ON) inhibitor in patients with KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S458. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.1838 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Patel S, Bhhatarai B, Calses P, Erlanson D, Everley R, Fong S, et al. Abstract 1142: Discovery of FMC-376 a novel orally bioavailable inhibitor of activated KRASG12C. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:1142. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2023-1142 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Liu C, Lu H, Wang H, Loo A, Zhang X, Yang G, et al. Combinations with allosteric SHP2 inhibitor TNO155 to block receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:342–54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Nichols RJ, Haderk F, Stahlhut C, Schulze CJ, Hemmati G, Wildes D, et al. RAS nucleotide cycling underlies the SHP2 phosphatase dependence of mutant BRAF-, NF1- and RAS-driven cancers. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) 20:1064–73. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0169-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Fedele C, Li S, Teng KW, Foster CJR, Peng D, Ran H, et al. SHP2 inhibition diminishes KRASG12C cycling and promotes tumor microenvironment remodeling. J Exp Med. (2021) 218. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Singhal A, Li BT, O’Reilly EM. Targeting KRAS in cancer. Nat Med. (2024) 30:969–83. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02903-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Miyashita H, Kato S, Hong DS. KRAS G12C inhibitor combination therapies: current evidence and challenge. Front Oncol. (2024) 14. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1380584/full. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Canon J, Rex K, Saiki AY, Mohr C, Cooke K, Bagal D, et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature. (2019) 575:217–23. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1694-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Li BT, Falchook GS, Durm GA, Burns TF, Skoulidis F, Ramalingam SS, et al. OA03.06 codeBreaK 100/101: first report of safety/efficacy of sotorasib in combination with pembrolizumab or atezolizumab in advanced KRAS p.G12C NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 17:S10–1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.07.025 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Chour A, Denis J, Mascaux C, Zysman M, Bigay-Game L, Swalduz A, et al. Severe sotorasib-related hepatotoxicity and non-liver adverse events associated with sequential anti-PD(L)1 and sotorasib therapy in KRASG12C-mutant lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:S1556–0864(23)00572-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.05.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Jänne PA, Smit EF, de Marinis F, Laskin J, Gomez MD, Gadgeel S, et al. LBA4 Preliminary safety and efficacy of adagrasib with pembrolizumab in treatment-naïve patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a KRASG12C mutation. Immuno-Oncology Technol. (2022) 16:100360. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2022.100360 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Barlesi F, Felip E, Popat S, Solomon BJ, Wolf J, Li BT, et al. Sotorasib versus pembrolizumab in combination with platinum doublet chemotherapy as first-line treatment for metastatic or locally advanced, PD-L1 negative, KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC (CodeBreaK 202). JCO. (2024) 42:TPS8653–TPS8653. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.TPS8653 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Mok TSK, Yao W, Duruisseaux M, Doucet L, Azkárate Martínez A, Gregorc V, et al. KRYSTAL-12: Phase 3 study of adagrasib versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a KRASG12C mutation. JCO. (2024) 42:LBA8509–LBA8509. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.17_suppl.LBA8509 [DOI] [Google Scholar]