Abstract
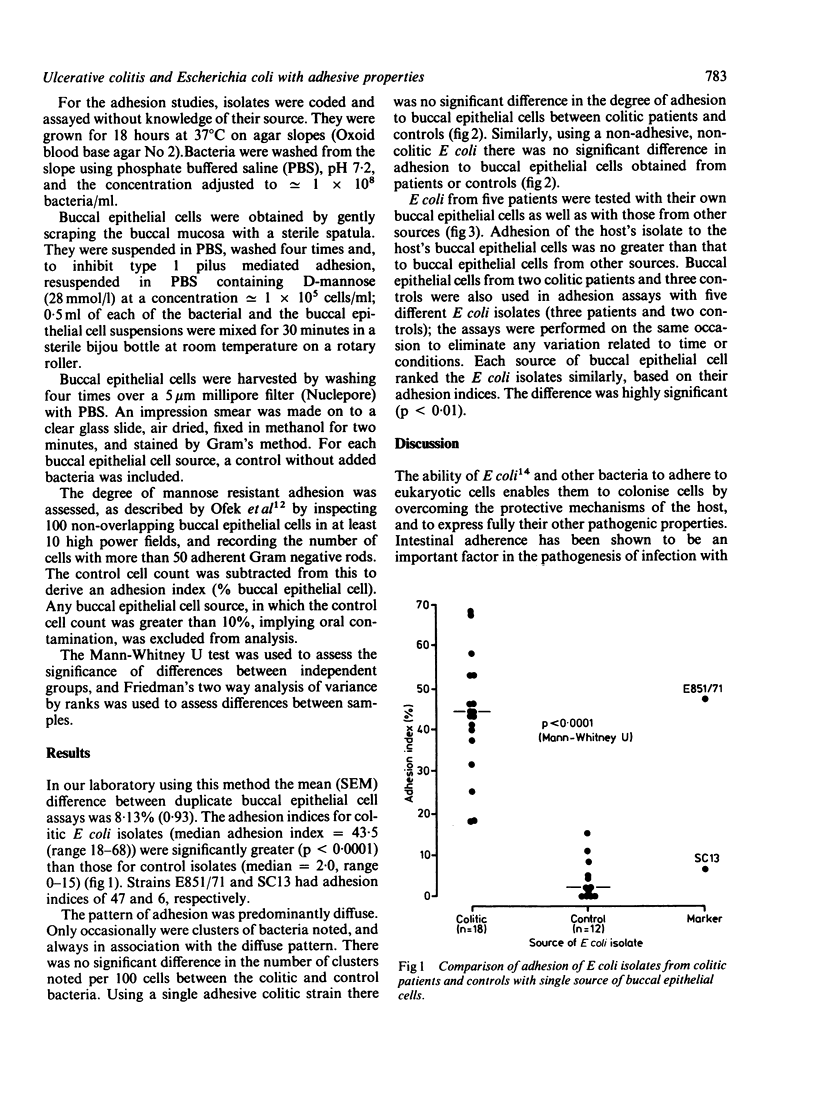
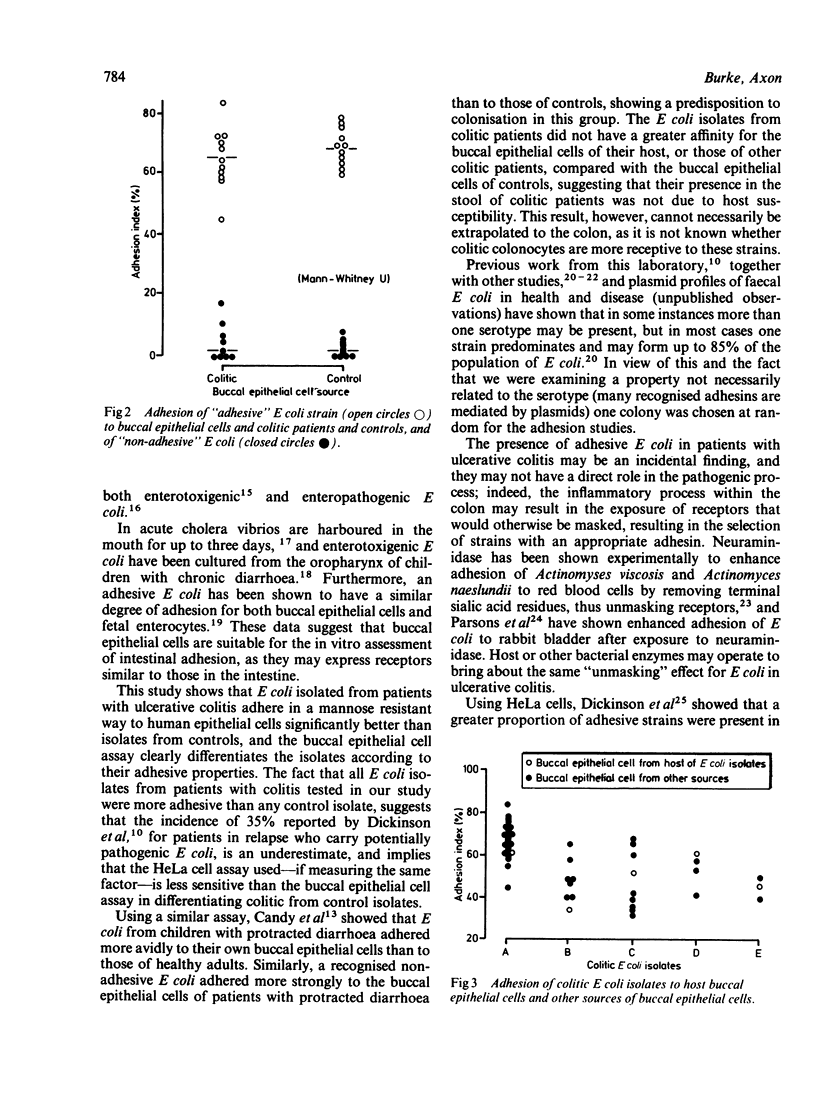
A quantitative assessment of the mannose resistant, adhesive property of Escherichia coli from patients with ulcerative colitis and from controls was made using a buccal epithelial cell adhesion assay, which also permitted assessment of adhesion to cells from other host sources. E coli from patients with ulcerative colitis adhered to buccal epithelial cells to a greater extent than those obtained from controls (p less than 0.0001), but did not show an increased affinity for the buccal epithelial cell of their host, compared with those obtained from other sources. The mannose resistant adhesive property of E coli raises the possibility that it has a role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bettelheim K. A., Faiers M., Shooter R. A. Serotypes of Escherichia coli in normal stools. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1223–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARR A. A., BARTTER F. C. Effect of angiotensin II on adrenal ascorbic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Oct;111:210–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candy D. C., Leung T. S., Marshall W. C., Harries J. T. Increased adhesion of Escherichia coli to mucosal cells from infants with protracted diarrhoea: a possible factor in the pathogenesis of bacterial overgrowth and diarrhoea. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):538–541. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candy D. C., Leung T. S., Phillips A. D., Harries J. T., Marshall W. C. Models for studying the adhesion of enterobacteria to the mucosa of the human intestinal tract. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:72–93. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candy D. C. The role of mucosal adhesion in the pathogenesis of Escherichia coli induced diarrhoea. J Trop Pediatr. 1980 Jun;26(3):75–79. doi: 10.1093/tropej/26.3.75-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe D. N., Richardson J. M., Rowe B., Anderson C. M. Bacterial microflora of the upper gastrointestinal tract in infants with protracted diarrhoea. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Apr;49(4):270–277. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.4.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M. A quantitative comparison of the faecal flora of patients with ulcerative colitis and that of normal persons. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):439–444. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M., Ewins S. P., Hywel-Jones J., Lennard-Jones J. E. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli carried in different phases of ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):143–146. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R. J., Varian S. A., Axon A. T., Cooke E. M. Increased incidence of faecal coliforms with in vitro adhesive and invasive properties in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1980 Sep;21(9):787–792. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.9.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Fillery E. D., Chan K. H., Grove D. A. Sialidase-enhanced lectin-like mechanism for Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.335-343.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R., Brigham K. L., Neogy K. N. Intestinal microflora in Asiatic cholera. II. The small bowel. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):38–45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Plaut A. G., Weinstein L., Patterson J. F., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. V. Fecal microbial ecology in ulcerative colitis and regional enteritis: relationship to severity of disease and chemotherapy. Gastroenterology. 1968 Apr;54(4):575–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J. Escherichia coli diarrhoea. J Infect. 1983 Nov;7(3):177–192. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(83)96953-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayappa H. G., Goodnow R. A., Geary S. J. Role of Escherichia coli type 1 pilus in colonization of porcine ileum and its protective nature as a vaccine antigen in controlling colibacillosis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):350–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.350-354.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Arabi Y., Dimock F., Burdon D. W., Allan R. N., Alexander-Williams J. Influence of inflammatory bowel disease on intestinal microflora. Gut. 1978 Dec;19(12):1099–1104. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.12.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. L., Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W., Brinton C. C., To C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrheal disease by vaccinating dams with purified 987 or K99 pili: protection correlates with pilus homology of vaccine and challenge. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.771-777.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Bartlett J. G. Bacteriological studies of experimental ulcerative colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):258–265. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. I. Transmission of the determinant of the K88 antigen and influence on the transfer of chromosomal markers. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.69-75.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. L., Shrom S. H., Hanno P. M., Mulholland S. G. Bladder surface mucin. Examination of possible mechanisms for its antibacterial effect. Invest Urol. 1978 Nov;16(3):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Hammarström S., Lagercrantz R., Campbell D. Autoantibodies to colon in rats and human ulcerative colitis: cross reactivity with Escherichia coli O:14 antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):975–980. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. J., Wilmot A. J. Ulcerative post-dysenteric colitis. Gut. 1966 Oct;7(5):438–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART G. T. Post-dysenteric colitis. Br Med J. 1950 Feb 18;1(4650):405–409. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4650.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite T. K., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Evans D. J., Jr Role of Escherichia coli colonisation factor antigen in acute diarrhoea. Lancet. 1978 Jul 22;2(8082):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91921-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer J., König W., Hacker J., Goebel W. Bacterial adherence and hemolysin production from Escherichia coli induces histamine and leukotriene release from various cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):271–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.271-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. M., Acres S. D., Sadowski P. L., Springer J. A., Bray B., Raybould T. J., Muscoplat C. C. Protection of calves against fatal enteric colibacillosis by orally administered Escherichia coli K99-specific monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):653–658. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.653-658.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Faris A., Lindahl M., Hjertén S., Agerup B. A new principle for prevention of diarrhoea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) possessing colonization factor antigen (CFA/I). Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(2):129–132. doi: 10.3109/inf.1981.13.issue-2.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Stuart C. A. Antigenic Relationships of Escherichia coli Isolated from One Individual. J Bacteriol. 1943 Feb;45(2):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.2.121-126.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Sedgwick M. I., Evans N., Turner P. J., George R. H., McNeish A. S. Adherence of an enteropathogenic strain of Escherichia coli to human intestinal mucosa is mediated by a colicinogenic conjugative plasmid. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):393–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.393-402.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wiel-Korstanje J. A., Winkler K. C. The faecal flora in ulcerative colitis. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):491–501. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


