In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published.
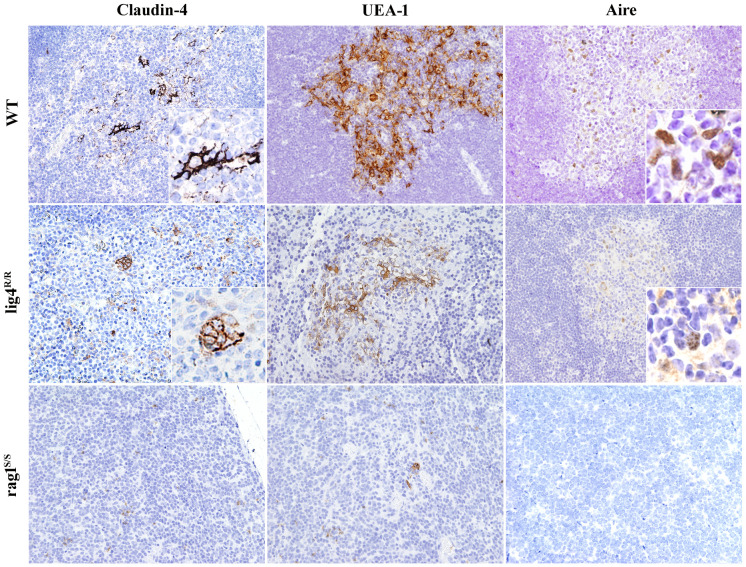
Figure 5.
Maturation of medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) in wild-type (WT), Lig4 R/R, and Rag1 S/S mice. Mature mTECs from WT mice express claudin-4 (Cld4), Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1 (UEA-1) and Aire (upper panels). Insets highlight fully mature mTECs showing immunoreactivity (IR) for Cld4 and the characteristic granular dot-like Aire positivity in the nuclei. Thymuses from Lig4 R/R mice show residual presence of mTECs that reach full maturation with positivity for UEA-1, Cld4, and Aire expression (middle panels). Loss of corticomedullary demarcation (CMD) with impaired maturation of mTECs was observed in the thymuses from the Rag1 S/S mice in which only rare UEA-1 IR cells but no mature Cld4+ and Aire+ cells were found (lower panels). IR staining: brown. All panels are from 20× original magnification; insets are from 40× original magnification. One representative example of five mice analyzed per each strain.
“The insets within the right upper and middle panels showing a higher magnification of the AIRE immunostaining have been corrected. In the original panels, there was a mistake in placing the original insets from a higher magnification image.”
The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.