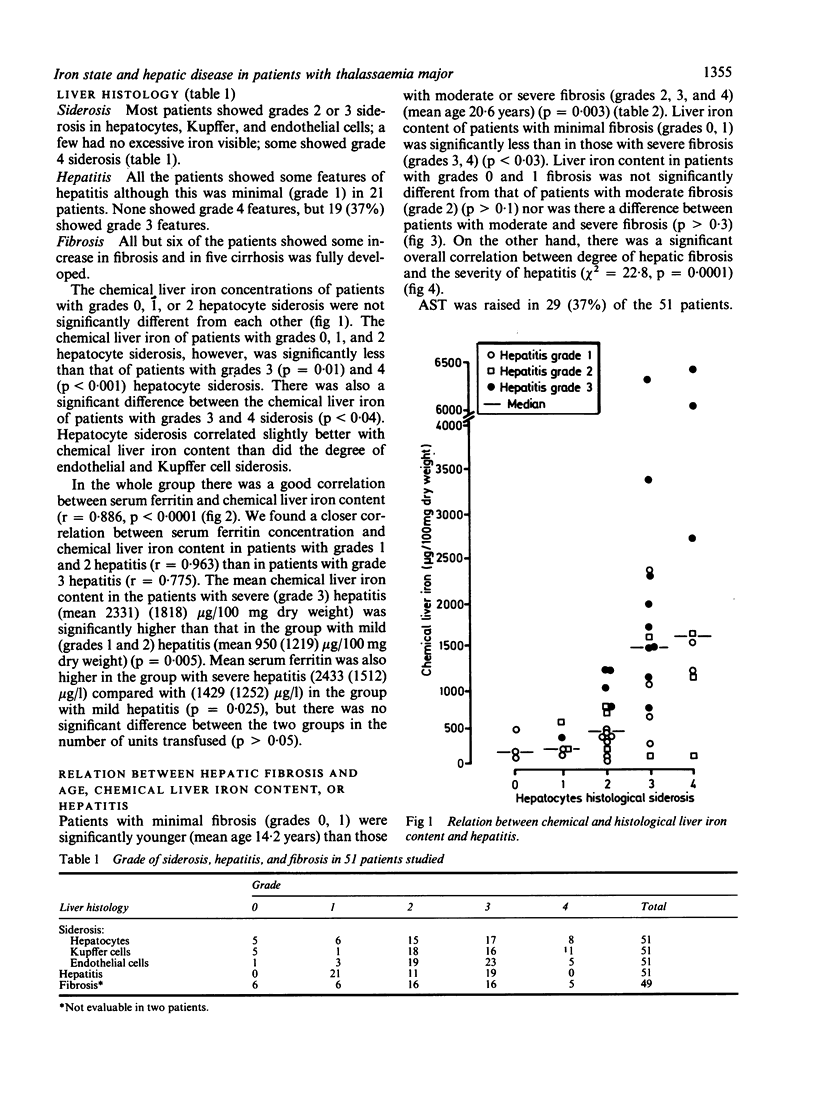
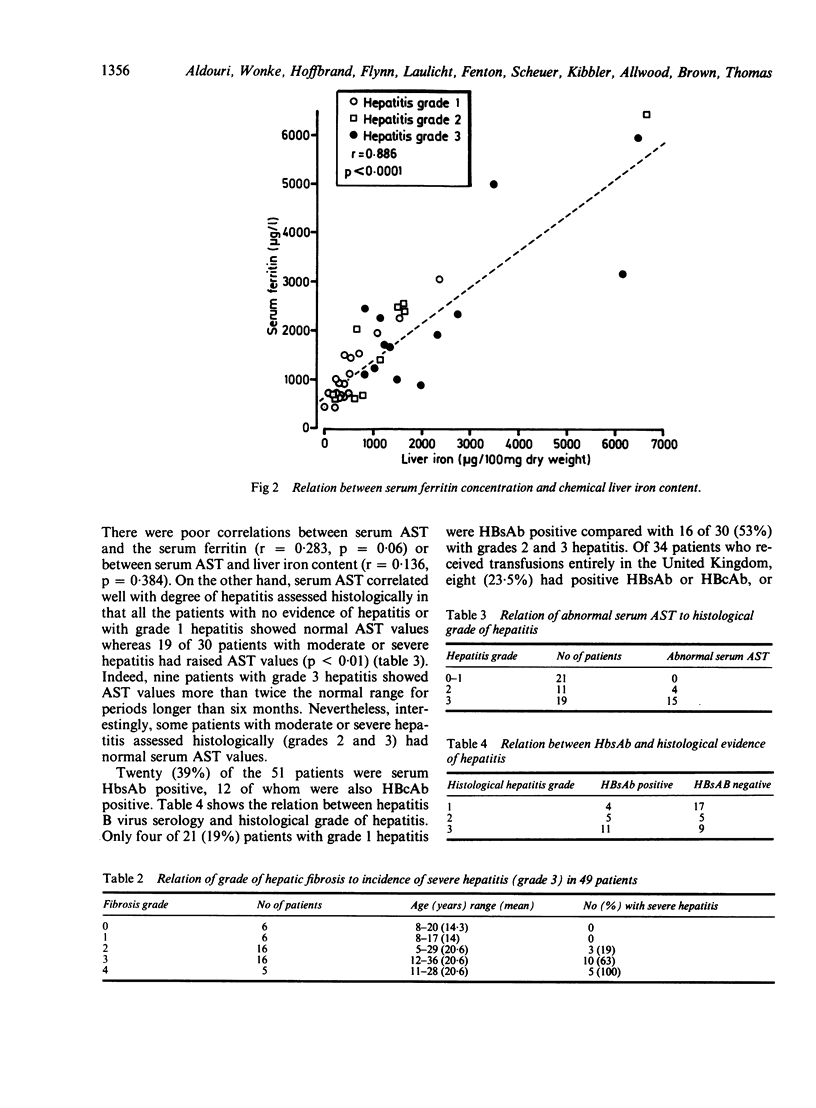
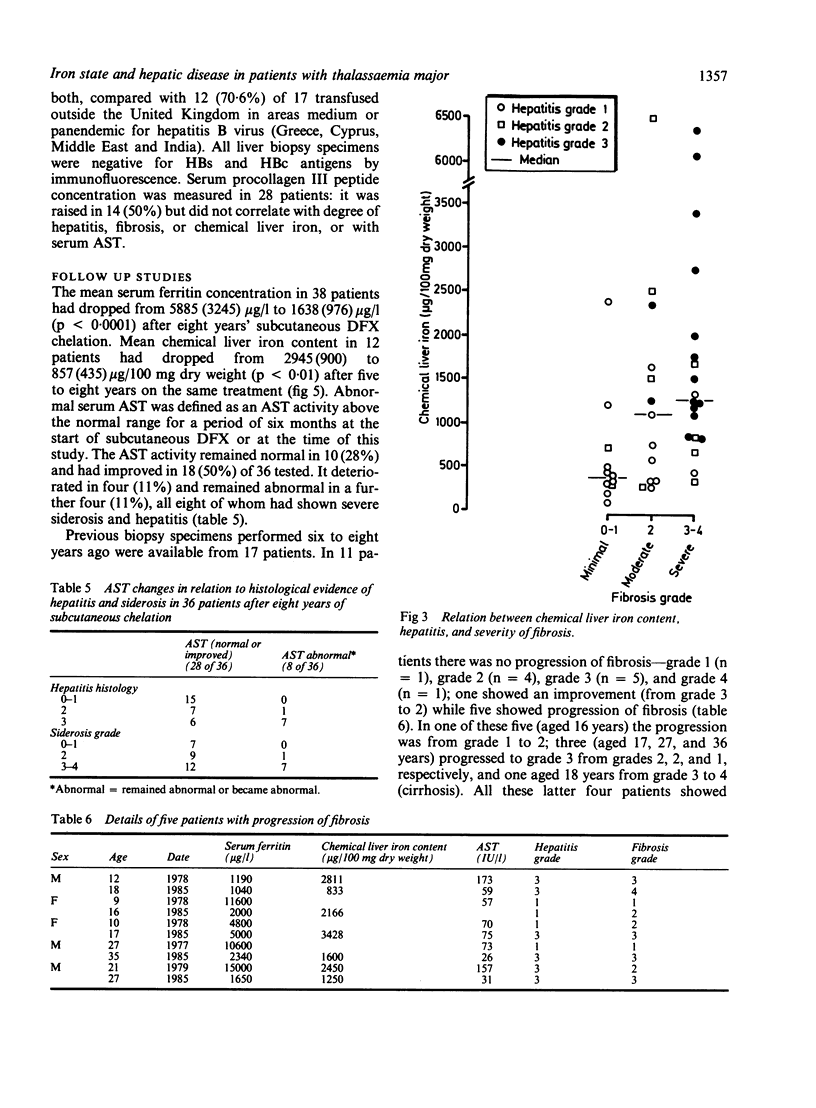
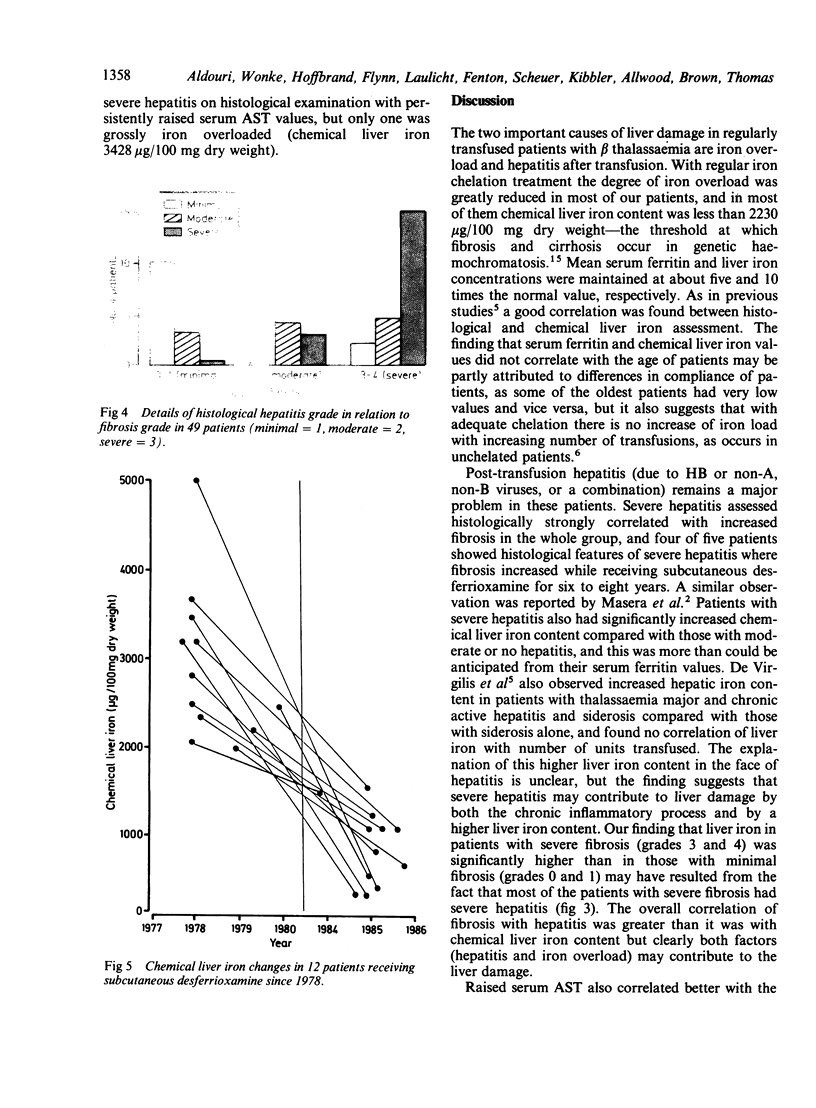
Abstract
Liver biopsies were performed on 51 regularly transfused patients with beta thalassaemia, age range 5-36 (mean 18.6) years, who had received regular subcutaneous desferrioxamine (DFX) treatment for periods between one and eight years (40 for eight years). The biopsy specimens were examined by light microscopy and immunofluorescence for hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens (HBsAg and HBcAg), and the iron content was determined chemically. The results were compared with serum ferritin concentration and aspartate transaminase (AST) activity and with hepatitis B virus serology. Biopsy specimens, in which chemical liver iron had been determined in 12, were also available from 17 patients. Mean serum ferritin (+/- SD) had fallen from 5885 (3245) micrograms/l to 1638 (976) micrograms/l in 36 patients after eight years' chelation, while mean (+/- SD) liver iron concentration had fallen from 2945 (900) micrograms/100 mg dry weight to 857 (435) micrograms/100 mg dry weight in 12 of them. All biopsy specimens examined were negative for HBs and HBc antigens. The presence of histological features of hepatitis was associated with increased liver iron content, increased fibrosis, and with progression of fibrosis between the two biopsies. Procollagen III peptide was assayed in 28 patients but did not correlate with the degree of hepatitis, fibrosis, or with chemical liver iron content. We conclude that with regular subcutaneous DFX, mean concentrations of serum ferritin and liver iron are maintained in these patients at about five and 10 times the normal value, respectively, and that progression of liver damage is more likely to be due to viral hepatitis, presumably related to the parenterally transmitted non-A, non-B agents than to iron overload.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison G. M., Beamish M. R., Hales C. N., Hodgkins M., Jacobs A., Llewellin P. An immunoradiometric assay for ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Apr;25(4):326–329. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.4.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M., Flynn D. M., Letsky E. A., Risdon R. A. Long-term chelation therapy in thalassaemia major: effect on liver iron concentration, liver histology, and clinical progress. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 6;2(5909):16–20. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5909.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M., Sherlock S. Measurement of liver-iron concentration in needle-biopsy specimens. Lancet. 1971 Jan 16;1(7690):100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90838-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Martin M., Schwartz E. Depletion of excessive liver iron stores with desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1984 Oct;58(2):369–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb06096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Virgiliis S., Cornacchia G., Sanna G., Argiolu F., Galanello R., Fiorelli G., Rais M., Cossu P., Bertolino F., Cao A. Chronic liver disease in transfusion-dependent thalassemia: liver iron quantitation and distribution. Acta Haematol. 1981;65(1):32–39. doi: 10.1159/000207146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Virgiliis S., Cossu P., Sanna G., Frau F., Loi E., Lobrano R., Nucaro A., Toccafondi C., Cornacchia G., Loi A. Iron chelation in transfusion-dependent thalassemia with chronic hepatitis. Acta Haematol. 1982;67(1):49–56. doi: 10.1159/000207024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall A. H., Meek F. L., Waters J. A., Miescher G. C., Janossy G., Thomas H. C. A rapid one-step radiometric assay for hepatitis B surface antigen utilizing monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jul 30;52(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffbrand A. V., Gorman A., Laulicht M., Garidi M., Economidou J., Georgipoulou P., Hussain M. A., Flynn D. M. Improvement in iron status and liver function in patients with transfusional iron overload with long-term subcutaneous desferrioxamine. Lancet. 1979 May 5;1(8123):947–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91721-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean G., Terzoli S., Mauri R., Borghetti L., Di Palma A., Piga A., Magliano M., Melevendi M., Cattaneo M. Cirrhosis associated with multiple transfusions in thalassaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jan;59(1):67–70. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masera G., Jean G., Gazzola G., Novakova M. Role of chronic hepatitis in development of thalassaemic liver disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Sep;51(9):680–685. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.9.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroni G. A., Piacentini G., Terzoli S., Jean G., Masera G. Hepatitis B or non-A, non-B virus infection in multitransfused thalassaemic patients. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Dec;59(12):1127–1130. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.12.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propper R. D., Cooper B., Rufo R. R., Nienhuis A. W., Anderson W. F., Bunn H. F., Rosenthal A., Nathan D. G. Continuous subcutaenous administration of deferoxamine in patients with iron overload. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 25;297(8):418–423. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708252970804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risdon R. A., Barry M., Flynn D. M. Transfusional iron overload: the relationship between tissue iron concentration and hepatic fibrosis in thalassaemia. J Pathol. 1975 Jun;116(2):83–95. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


