Abstract
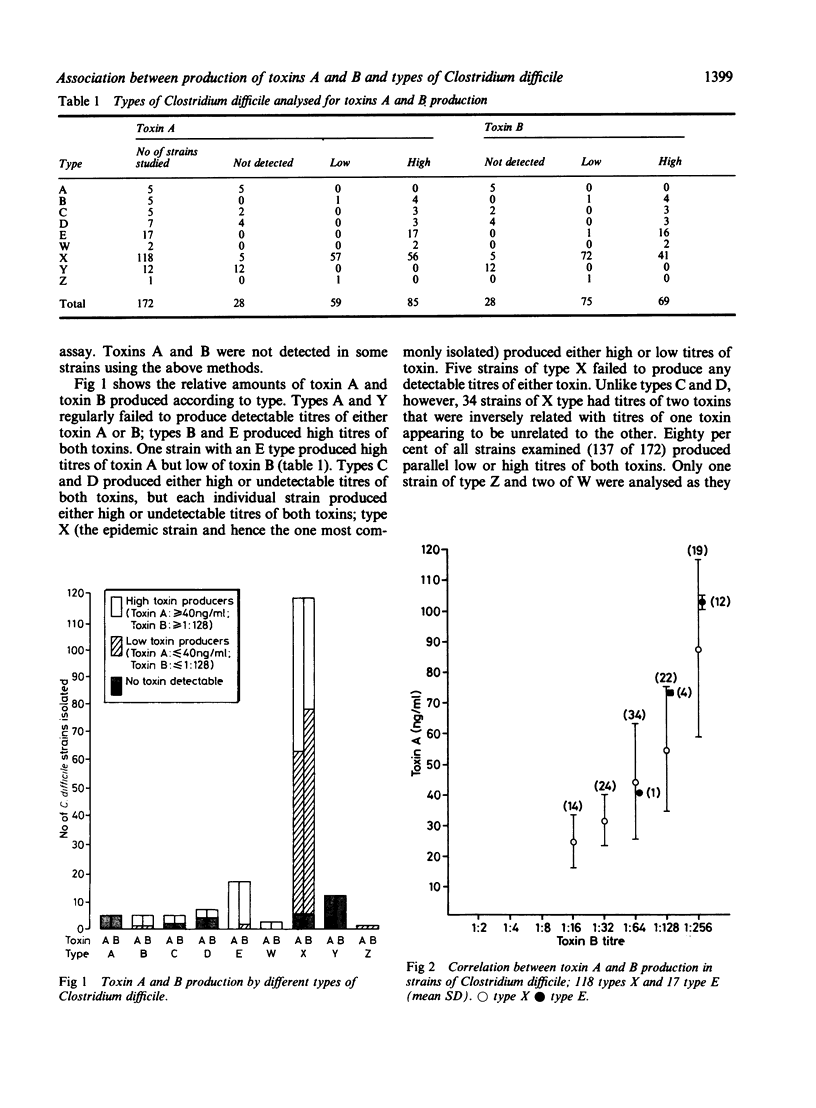
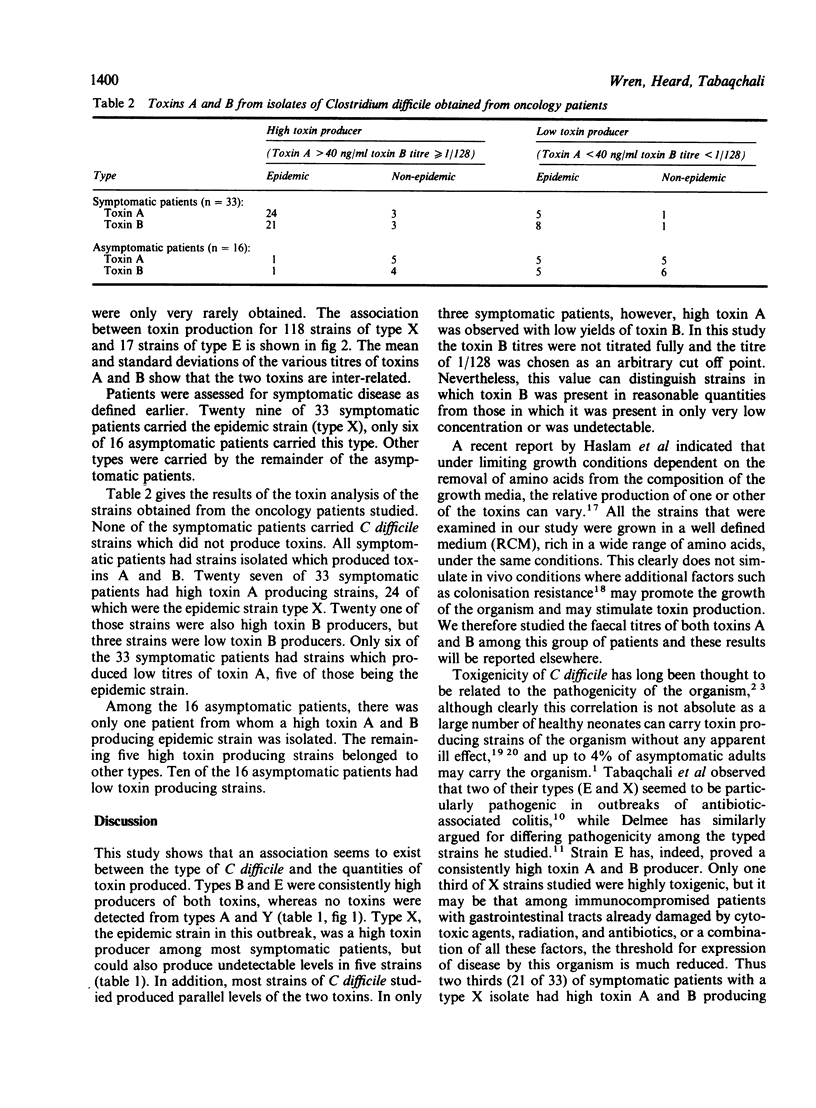
One hundred and seventy two strains of Clostridium difficile isolated from 62 patients with antibiotic associated diarrhoea or pseudomembranous colitis were analysed for the production of toxins A and B and typed using 35S-methionine labelling followed by sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). There was a correlation between production of toxins A and B and the type of C difficile. One hundred and forty four of 172 strains were either high or low producers of both toxins. Toxins were not detected in 28 of 172 strains. Types A and Y were consistently non-toxin producers; types B and E were high toxin producers. Type X, the epidemic strain, showed variable toxin production. Symptoms of 49 patients with haematological malignant pathology who were part of a documented outbreak of antibiotic associated diarrhoea, were analysed in relation to toxin production and type of the clinical strains isolated. In general, there was a correlation between symptoms of antibiotic associated diarrhoea, the type of C difficile, and its potential for producing toxins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Onderdonk A. B., Cisneros R. L., Kasper D. L. Clindamycin-associated colitis due to a toxin-producing species of Clostridium in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):701–705. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello S. P., Barclay F. E. An in-vitro model of colonisation resistance to Clostridium difficile infection. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):299–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmee M., Homel M., Wauters G. Serogrouping of Clostridium difficile strains by slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):323–327. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.323-327.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam S. C., Ketley J. M., Mitchell T. J., Stephen J., Burdon D. W., Candy D. C. Growth of Clostridium difficile and production of toxins A and B in complex and defined media. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):293–297. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard S. R., O'Farrell S., Holland D., Crook S., Barnett M. J., Tabaqchali S. The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile with use of a typing scheme: nosocomial acquisition and cross-infection among immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):159–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai P. S., Ngeow Y. F., Puthucheary S. D., Wang C. W. Comparison of two methods for bacteriocin typing of Serratia marcescens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.1-6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B. Pseudomembranous colitis: Presence of clostridial toxin. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1312–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby J. M., Wilkins T. D. Production of antitoxins to two toxins of Clostridium difficile and immunological comparison of the toxins by cross-neutralization studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):374–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.374-376.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Lockwood D. E., Richardson S. H., Wilkins T. D. Biological activities of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1147–1150. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1147-1150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Holland D., O'Farrell S., Silman R. Typing scheme for Clostridium difficile: its application in clinical and epidemiological studies. Lancet. 1984 Apr 28;1(8383):935–938. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., O'Farrell S., Holland D., Silman R. Method for the typing of Clostridium difficile based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of [35S]methionine-labeled proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):197–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.197-198.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Laughon B. E., Yolken R., Bo-Linn P., Moench T., Ryder R. W., Bartlett J. G. Serum antibody response to toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):93–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Willey S., Bartlett J. G. Isolation rates and toxigenic potential of Clostridium difficile isolates from various patient populations. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüst J., Sullivan N. M., Hardegger U., Wilkins T. D. Investigation of an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis by various typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


