Abstract
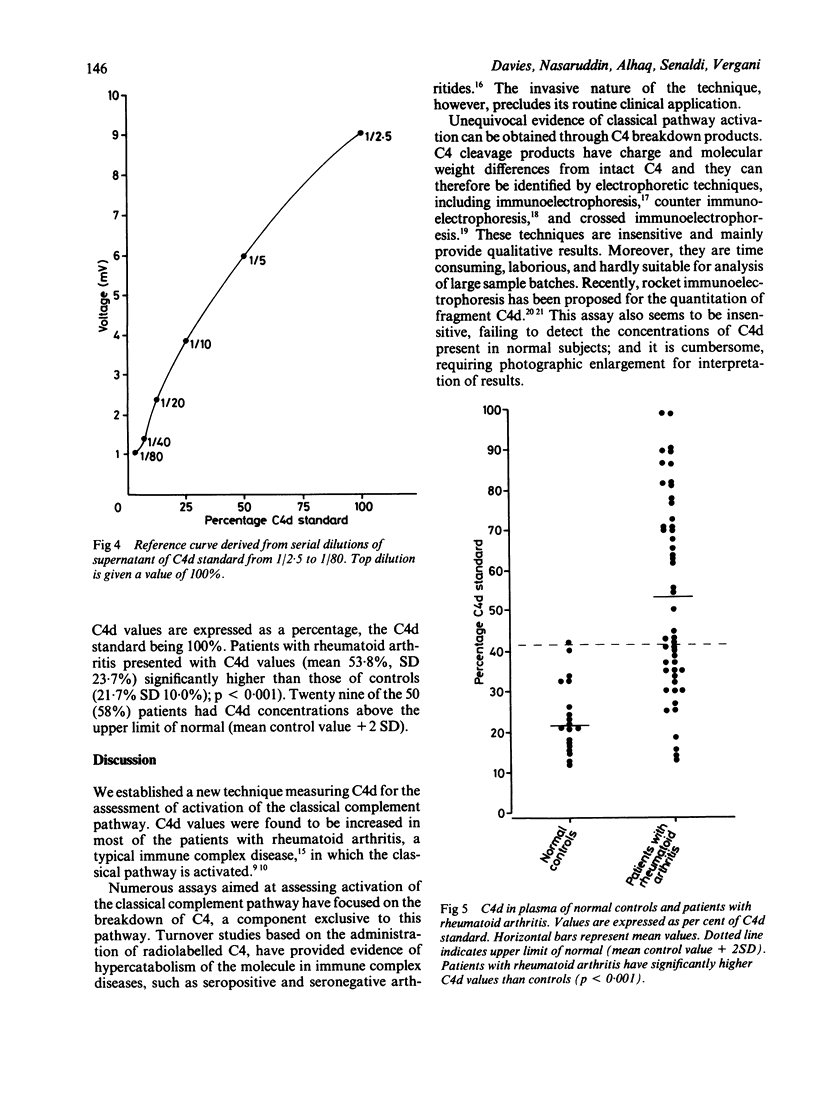
A new laser nephelometric technique that measures C4d for the assessment of the activation of the classical complement pathway was developed. C4d was isolated from other larger C4 related molecules at a final concentration of polyethylene glycol of 12% and then quantitated by laser nephelometry using a commercially available antiserum, which reacts with C4d determinants. C4d standard (100%) was produced by exhaustive activation of the classical pathway in pooled normal human serum using heat aggregated human immunoglobulin. Serial dilutions of the standard provided a reference curve against which clinical samples were read. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis showed significantly higher C4d values (mean 53.8%) than controls (21.7%; p less than 0.001). The technique proved accurate, rapid, and suitable for the routine laboratory evaluation of complement activation through the classical pathway, and it may be useful in the management of those conditions in which complement activation has a pathogenic role.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyave C. M., Tan E. M. Detection of complement activation by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE). J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cleavage of the fourth component of human complement (C4) by C1 esterase: isolation and characteristics of the low molecular weight product. Immunochemistry. 1970 Feb;7(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffone G. J., Savory J., Hermans J. Evaluation of kinetic light scattering as an approach to the measurement of specific proteins with the centrifugal analyzer. II. Theoretical considerations. Clin Chem. 1975 Nov;21(12):1735–1746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielder A. H., Walport M. J., Batchelor J. R., Rynes R. I., Black C. M., Dodi I. A., Hughes G. R. Family study of the major histocompatibility complex in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: importance of null alleles of C4A and C4B in determining disease susceptibility. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):425–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom H., Curd J. G., Kaplan R. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Vaughan J. H. Activation of the fourth component of complement (C4): assessment by rocket immunoelectrophoresis and correlation with the metabolism of C4. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2780–2785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsche J. F., Tucker E. S., 3rd, Sugimoto S., Vaughan J. H., Curd J. G. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis of C4 and C4d. A simple sensitive method for detecting complement activation in plasma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Nov;76(5):679–684. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.5.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Shiraishi S., Stroud R. M., Lambert P. H. Detection and quantitation in plasma and synovial fluid of a fragment of human C4 with alpha mobility generated during the activation of the complement system. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Gigli I., Austen K. F. The complement system of man. 4. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 28;287(13):642–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209282871306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi S., Stroud R. M. Cleavage products of C4b produced by enzymes in human serum. Immunochemistry. 1975 Dec;12(12):935–939. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm A. G., Laurell A. B. Conversion of the fourth complement component studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):515–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valet G., Cooper N. R. Isolation and characterization of the proenzyme form of the C1s subunit of the first complement component. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):339–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Bevis L., Nasaruddin B. A., Mieli-Vergani G., Tee D. E. Clinical application of a new nephelometric technique to measure complement activation. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;36(7):793–797. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.7.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D. Complement. Diabet Med. 1986 Jul-Aug;3(4):306–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O., Goodman M. G., Morgan E. L., Hugli T. E. Regulation of immune response by components of the complement cascade and their activated fragments. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(2-3):173–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00205872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whicher J. T. The value of complement assays in clinical chemistry. Clin Chem. 1978 Jan;24(1):7–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid synovitis. An extravascular immune complex disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):297–305. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



