Abstract
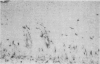
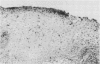
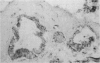
Cervical biopsy samples from 67 patients who had various grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or who showed evidence, in the form of koilocytosis, of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection of the uterine cervix, and from 10 women with normal cervices were examined. Cryostat sections from the biopsy samples were stained using monoclonal antibodies to T6, a Langerhans' cell marker, and to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigens (HLA-DP, DQ, and DR). Epithelial Langerhans' cells were reduced in number and showed changed morphology and distribution in koilocytic lesions and in all grades of CIN (p less than 0.01) except CIN I. HLA-DR expression by Langerhans' cells was significantly increased in koilocytic lesions and in CIN grades I and II (p less than 0.05); HLA-DQ expression was significantly increased in all grades of CIN (p less than 0.05) with the increase being most pronounced in CIN I (p less than 0.01). Columnar epithelium expressed MHC class II antigens in all samples tested and squamous epithelium in four of 29 cases of CIN III. These findings support the view that there is a localised disturbance of immune function in both neoplastic cervical epithelium and that infected with papillomavirus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. W., MacCuish A. C., Loudon N. B., Jordan J., Irvine W. J. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte transformation and circulating autoantibodies in women taking oral contraceptives. Lancet. 1974 May 11;1(7863):898–900. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman B., Duncan M. R., Smith B., Ziboh V. A., Palladino M. Interferon enhancement of HLA-DR antigen expression on epidermal Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jan;84(1):54–58. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C. H., Butler E. B., Fox H. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jan;35(1):1–13. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. M., McVittie E., Guy K., Gawkrodger D. J., Hunter J. A. MHC class II antigen expression in normal human epidermis. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):223–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardonnet Y., Viac J., Thivolet J. Langerhans cells in human warts. Br J Dermatol. 1986 Dec;115(6):669–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb06647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield E. J., Evans B. A. Effect of local infection and oral contraception on immunoglobulin levels in cervical mucus. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):215–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.215-221.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. F., Meanwell C. A., Maitland N. J., Blackledge G., Scully C., Jordan J. A. Human papillomavirus type-16 homologous DNA in normal human ectocervix. Lancet. 1986 Jul 19;2(8499):157–158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Cordier G., Schmitt D., Faure M., Laquoi C., Thivolet J. Quantitative evaluation of two distinct cell populations expressing HLA-DR antigens in normal human epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Jul;111(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher S. Histopathology of papilloma virus infection of the cervix uteri: the history, taxonomy, nomenclature and reporting of koilocytic dysplasias. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;36(6):616–624. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.6.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi S., La Vecchia C., Talamini R. Oral contraceptives and cervical neoplasia: pooled information from retrospective and prospective epidemiologic studies. Tumori. 1986 Feb 28;72(1):21–30. doi: 10.1177/030089168607200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonwa T. A., Picker L. J., Raff H. V., Goyert S. M., Silver J., Stobo J. D. Antigen-presenting capabilities of human monocytes correlates with their expression of HLA-DS, an Ia determinant distinct from HLA-DR. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):706–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy K., Van Heyningen V., Cohen B. B., Deane D. L., Steel C. M. Differential expression and serologically distinct subpopulations of human Ia antigens detected with monoclonal antibodies to Ia alpha and beta chains. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Nov;12(11):942–948. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrist T. J., Muhlbauer J. E., Murphy G. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Bhan A. K. T6 is superior to Ia (HLA-DR) as a marker for Langerhans cells and indeterminate cells in normal epidermis: a monoclonal antibody study. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Feb;80(2):100–103. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A. Expression of HLA-DR (Ia like) antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in human dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):93–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle J. P., Muller H. K. Quantitative assessment of Langerhans' cells in human cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and wart virus infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Mar;154(3):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90592-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J. K., Beckmann A. M., Kiviat N. B. Methods for diagnosing papillomavirus infection. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;120:86–103. doi: 10.1002/9780470513309.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. H., Gatter K. C., Sykes G., Casemore V., Mason D. Y. Langerhans' cells in human cervical epithelium: effects of wart virus infection and intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 May;90(5):412–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1983.tb08936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Sato S., Harrist T. J., Mihm M. C., Jr Characterization of Langerhans cells by the use of monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):465–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete C., Jaraquemada D., Fainboim L., Karr R., Hui K., Awad J., Bagnara M., Festenstein H. Genetic and functional relationship of the HLA-DR and HLA-DQ antigens. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(1):97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00372246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete C., Jaraquemada D., Hui K., Awad J., Okoye R., Festenstein H. Different functions and associations of HLA-DR and HLA-DQ(DC) antigens shown by serological, cellular and DNA assays. Tissue Antigens. 1985 Mar;25(3):130–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1985.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez G., Ball E. J., Myers L. K., Stastny P. Allostimulating cells in man. Quantitative variation in the expression of HLA-DR and HLA-DQ molecules influences T-cell activation. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(1):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00430597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G. P., Shaw S., Ziegler A., Müller C., Wernet P. Differential inhibition of HLA-D- or SB-directed secondary lymphoproliferative responses with monoclonal antibodies detecting human Ia-like determinants. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1070–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehamberger H., Stingl L. A., Pogantsch S., Steiner G., Wolff K., Stingl G. Epidermal cell-induced generation of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses against alloantigens or TNP-modified syngeneic cells: requirement for Ia-positive Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Sep;81(3):208–211. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12517984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper J. M. Oral contraceptives and cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1985 Sep;22(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(85)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabibzadeh S. S., Bettica A., Gerber M. A. Variable expression of Ia antigens in human endometrium and in chronic endometritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;86(2):153–160. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tay S. K., Jenkins D., Maddox P., Campion M., Singer A. Subpopulations of Langerhans' cells in cervical neoplasia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987 Jan;94(1):10–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1987.tb02244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tay S. K., Jenkins D., Maddox P., Singer A. Lymphocyte phenotypes in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and human papillomavirus infection. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987 Jan;94(1):16–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1987.tb02245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thivolet J., Viac J., Staquet M. J. Cell-mediated immunity in wart infection. Int J Dermatol. 1982 Mar;21(2):94–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1982.tb00510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Janossy G., Chilosi M., Pritchard J., Pincott J. R. Combined immunological and histochemical analysis of skin and lymph node lesions in histiocytosis X. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Mar;35(3):327–337. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toon P. G., Arrand J. R., Wilson L. P., Sharp D. S. Human papillomavirus infection of the uterine cervix of women without cytological signs of neoplasia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 15;293(6557):1261–1264. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6557.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., DeMars R., Trowbridge I. S., Bach F. H. Detection of a novel human class II HLA antigen. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):358–361. doi: 10.1038/304358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong M. C., Blanken R., Nanninga J., Van Voorst Vader P. C., Poppema S. Defined in situ enumeration of T6 and HLA-DR expressing epidermal Langerhans cells: morphologic and methodologic aspects. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):698–702. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]