Abstract
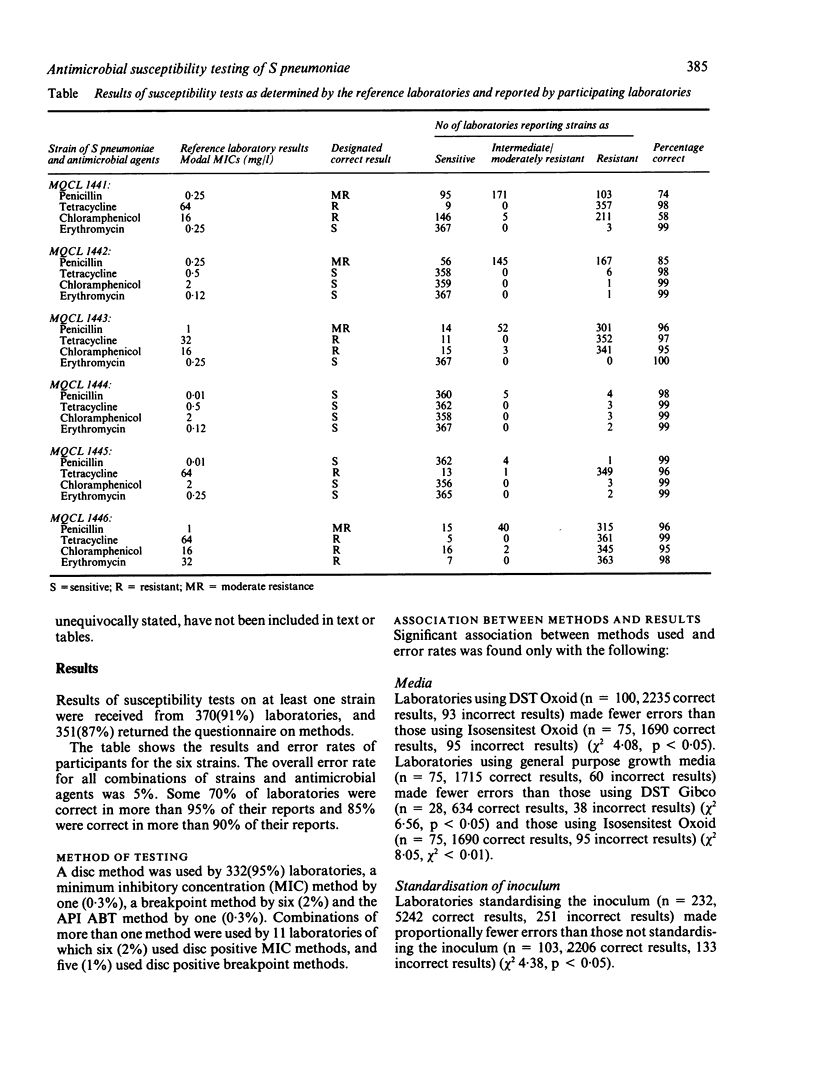
Six strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae were distributed to 405 United Kingdom laboratories who were asked to test the susceptibility of the strains to penicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol and erythromycin and to provide details of methodology to test the standards of susceptibility testing. High error rates were seen only in failure to detect moderate resistance to penicillin (12%) and resistance to chloramphenicol (16%). Increased error rates were associated with several methods or practices. These included the use of certain culture media; failure to standardise the inoculum; inoculation by loop rather than by swab; failure to use control organisms; failure to measure zone sizes; the use of discs containing a high content of penicillin to test susceptibility to penicillin, and the use of high content discs for testing erythromycin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Gaspar M. N., Robins-Browne R. M., Koornhof H. J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of pneumococci. 2. Determination of optimal disc diffusion test for detection of penicillin G resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jan;6(1):53–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., Brown D. F. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: a trial organised as part of the United Kingdom national external quality assessment scheme for microbiology. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):97–102. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., Brown D. F., Phua T. J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae: trial organised as part of United Kingdom national external quality assessment scheme for microbiology. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Sep;39(9):1006–1012. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.9.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., De Mello J. V., Gardner P. S. The United Kingdom national microbiological quality assessment scheme. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jan;35(1):82–93. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Hill B. C., Thornsberry C. Screening pneumococci for penicillin resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.749-752.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. Antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):254–266. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


