Abstract
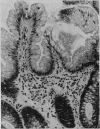
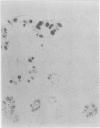
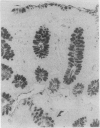
To test the suggestion that an inherited defect in colonic mucus rendering it susceptible to degradation by bacterial enzymes may be an important factor in the aetiology of ulcerative colitis, 650 colonoscopic and rectal biopsy specimens from 166 patients with colitis were stained by mild periodic acid Schiff (mPAS), which shows sialic acid that is deficient in O-acetyl substituents. There was an excess of mPAS positive sialic acid in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis, but the increased expression was patchy and coincided with a morphological change in the form of epithelial hyperplasia (metaplasia). Hyperplasia was more common in the rectum and in women and was associated with, and presumably secondary to, active inflammation. It is concluded that variation in the structure of sialic acid is acquired and is therefore unlikely to be implicated in the aetiology of ulcerative colitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper H. S. Peanut lectin-binding sites in large bowel carcinoma. Lab Invest. 1982 Oct;47(4):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culling C. F., Reid P. E., Clay M. G., Dunn W. L. The histochemical demonstration of O-acylated sialic acid in gastrointestinal mucins. Their association with the potassium hydroxide-periodic acid-schiff effect. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Aug;22(8):826–831. doi: 10.1177/22.8.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culling C. F., Reid P. E., Dunn W. L. A histochemical comparison of the O-acylated sialic acids of the epithelial mucins in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and normal controls. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;32(12):1272–1277. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.12.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass J. R., England J., Miller K. Value of mucin histochemistry in follow up surveillance of patients with long standing ulcerative colitis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):393–398. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. E., Culling C. F., Dunn W. L., Ramey C. W., Clay M. G. Chemical and histochemical studies of normal and diseased human gastrointestinal tract. I. A comparison between histologically normal colon, colonic tumours, ulcerative colitis and diverticular disease of the colon. Histochem J. 1984 Mar;16(3):235–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01003608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. M., Black R. R., Gallimore R., Savage A. Histochemical demonstration of desialation and desulphation of normal and inflammatory bowel disease rectal mucus by faecal extracts. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1312–1318. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara K., Jass J. R. Colorectal goblet cell sialomucin heterogeneity: its relation to malignant disease. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Oct;39(10):1088–1095. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.10.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]