Abstract
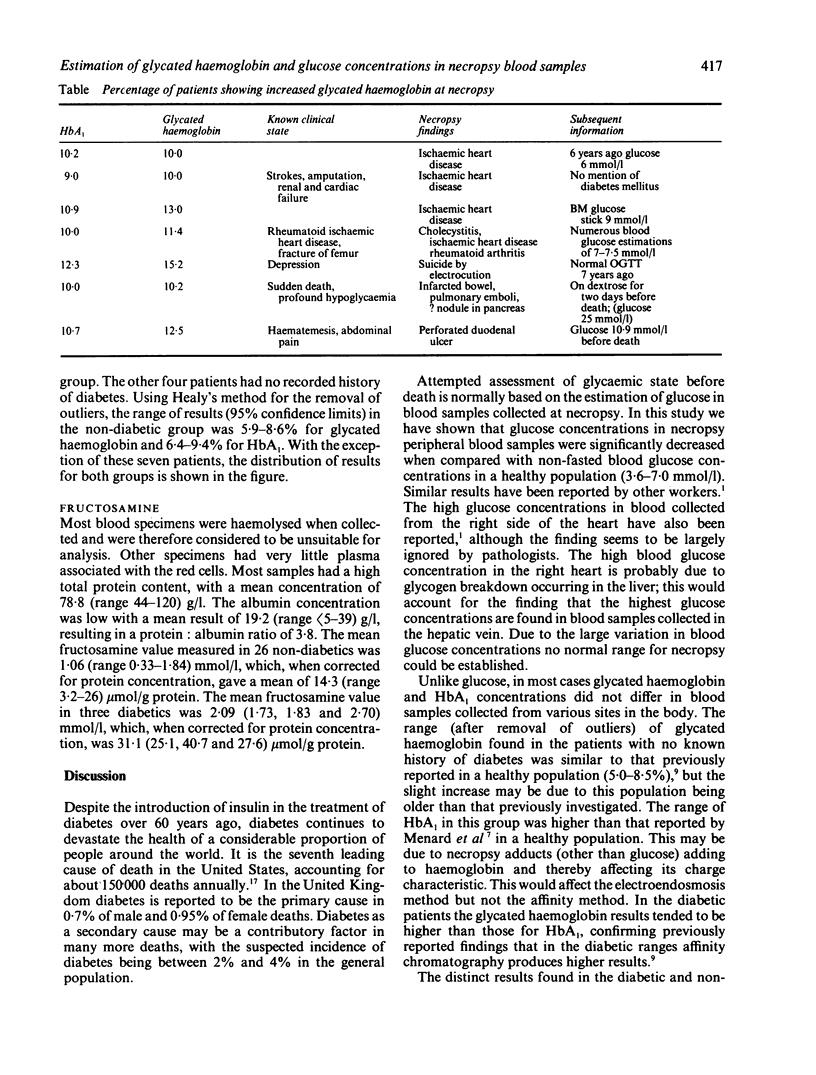
Glycated haemoglobin and glycated protein (fructosamine) and blood glucose concentrations were measured in blood samples collected from 75 patients at necropsy. Estimation of blood glucose was a poor indicator of glycaemia before death. Measurement of glycated haemoglobin by affinity chromatography distinguished non-diabetic patients from diabetic patients. The distinction was not as clear cut when HbA1 was estimated using electroendosmosis. Seven patients, who at necropsy had no known history of diabetes, had glycated haemoglobin concentrations in the diabetic range. Two of these patients were found to be diabetic, and diabetes had been suspected at some time in another three patients. It is concluded that measurement of glycated haemoglobin or HbA1, in necropsy specimens is a valuable tool for assessing glycaemic control in known diabetic patients, and may be useful in diagnosing previously unsuspected diabetes.
Full text
PDF
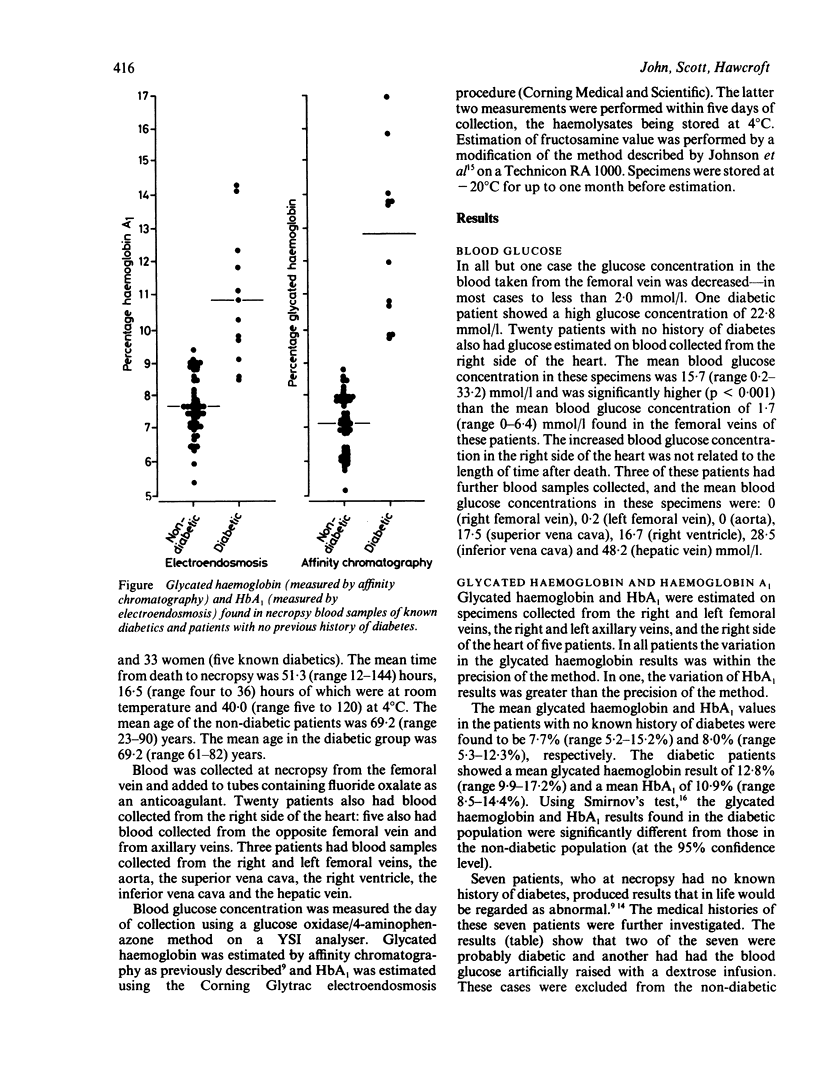

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albutt E. C., Nattrass M., Northam B. E. Glucose tolerance test and glycosylated haemoglobin measurement for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus--an assessment of the criteria of the WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus 1980. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(Pt 1):67–73. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Gallop P. M. Structure of hemoglobin AIc: nature of the N-terminal beta chain blocking group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 11;32(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher B. J., Welch S. G., Beer M. S. Glycosylated haemoglobins in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and for the assessment of chronic hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia. 1981 Jul;21(1):34–36. doi: 10.1007/BF03216220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. M., Cook J. G., Sheldon J., Rutherford S. M., Gould B. J. Glycosylated hemoglobins and glycosylated plasma proteins in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 1984 Mar-Apr;7(2):147–150. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John W. G., Albutt E. C., Handley G., Richardson R. W. Affinity chromatography method for the measurement of glycosylated haemoglobin: comparison with two methods in routine use. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Jan 31;136(2-3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John W. G., Richardson R. W. Glycosylated haemoglobin levels in patients referred for oral glucose tolerance tests. Diabet Med. 1986 Jan;3(1):46–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. N., Metcalf P. A., Baker J. R. Fructosamine: a new approach to the estimation of serum glycosylprotein. An index of diabetic control. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Blobstein S. H., Cerami A. Structure of carbohydrate of hemoglobin AIc. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2992–2997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester E., Frazer A. D., Shepherd C. A., Woodroffe F. J. Glycosylated haemoglobin as an alternative to the glucose tolerance test for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(Pt 1):74–78. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard L., Dempsey M. E., Blankstein L. A., Aleyassine H., Wacks M., Soeldner J. S. Quantitiative determination of glycosylated hemoglobin A1 by agar gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1980 Oct;26(11):1598–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahbar S. An abnormal hemoglobin in red cells of diabetics. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Oct;22(2):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickland M. H., Perkins C. M., Wales J. K. The Measurement of Haemoglobin A1c by isoelectric focussing in diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1982 May;22(5):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00253573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


