Abstract
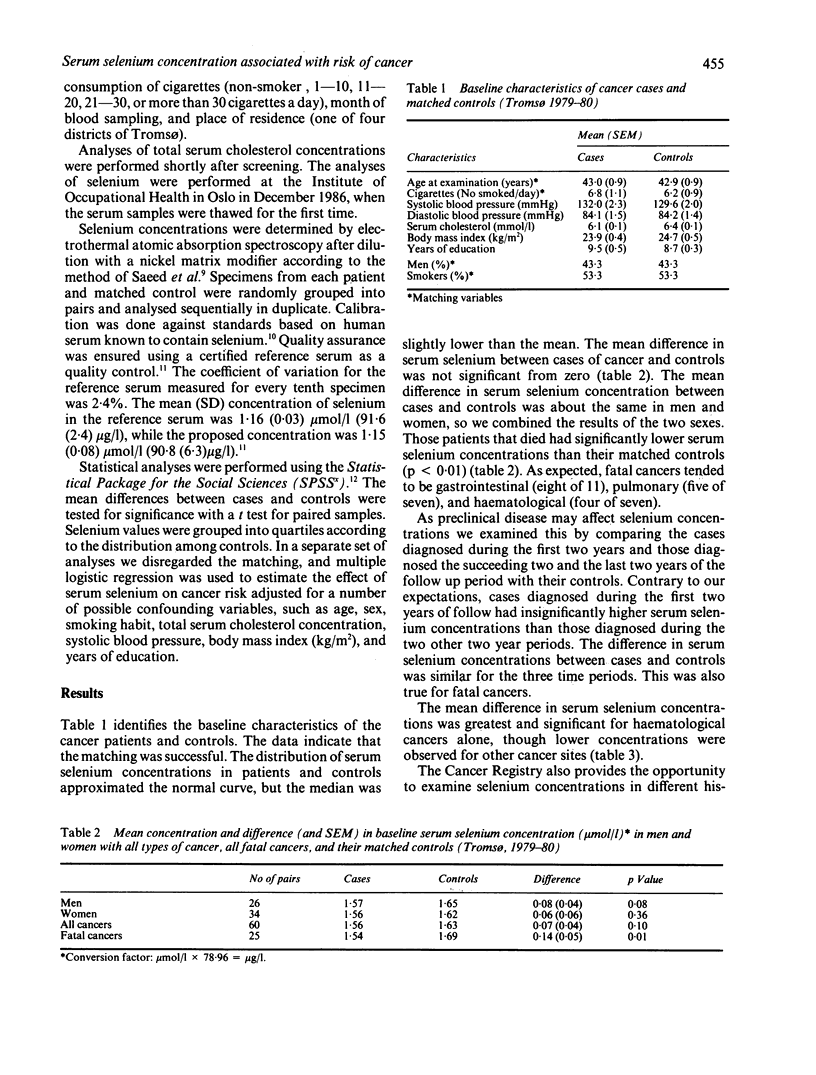
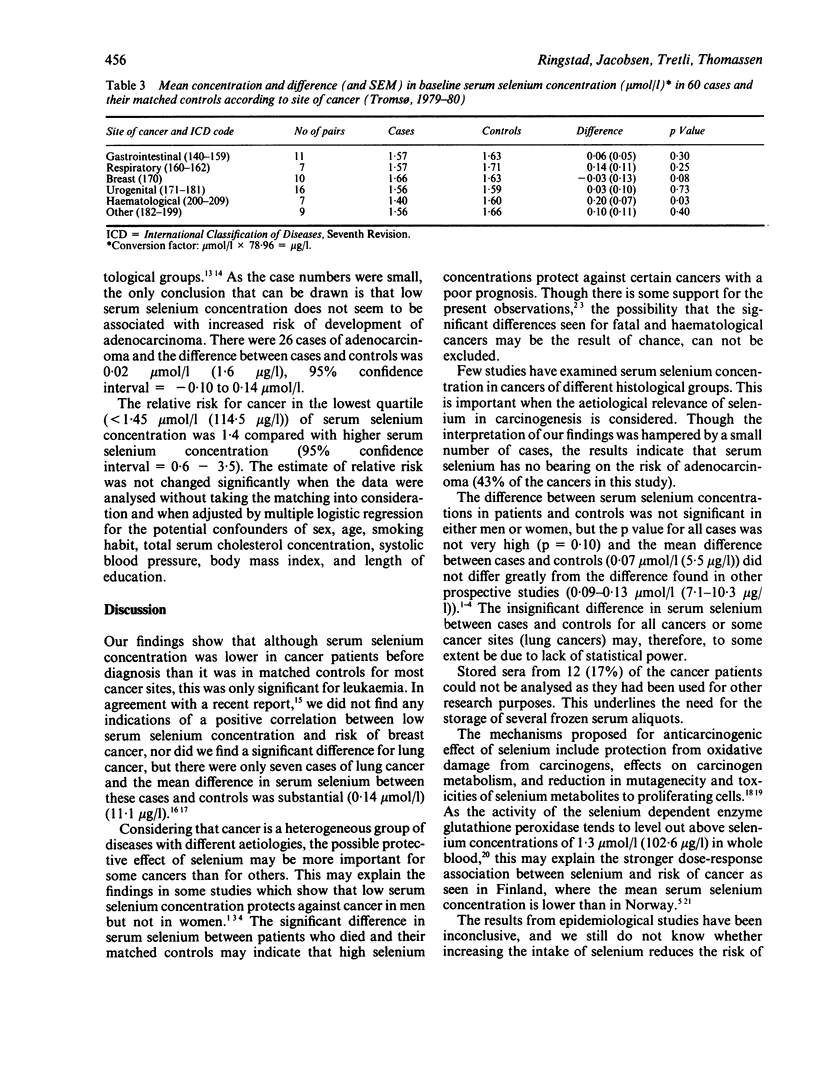
The association between serum selenium concentration and risk of cancer was studied in a nested case control study. Case control pairs came from a population of 9364 people examined in 1979. During the six year follow up, 60 men and women aged between 20-54 at the time of blood sampling, who had been free of malignant disease, developed cancer. The mean serum selenium concentration of 1.56 mumol/l (123.2 micrograms/l) in patients was not significantly different from that in controls (1.63 mumol/l (128.7 micrograms/l]. The difference in mean selenium concentration was largest and most significant for haematological malignancies alone. The difference in selenium concentrations in cases of fatal cancer compared with controls was significant (p less than 0.01). The risk of developing adenocarcinomas does not seem to be influenced by serum selenium concentration.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjartveit K., Foss O. P., Gjervig T., Lund-Larsen P. G. The cardiovascular disease study in Norwegian counties. Background and organization. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1979;634:1–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combs G. F., Jr, Clark L. C. Can dietary selenium modify cancer risk? Nutr Rev. 1985 Nov;43(11):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1985.tb02392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok F. J., de Bruijn A. M., Hofman A., Vermeeren R., Valkenburg H. A. Is serum selenium a risk factor for cancer in men only? Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jan;125(1):12–16. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes M. S., Comstock G. W., Vuilleumier J. P., Helsing K. J., Rider A. A., Brookmeyer R. Serum beta-carotene, vitamins A and E, selenium, and the risk of lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 13;315(20):1250–1254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611133152003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Verreault R. Erythrocyte selenium and breast cancer risk. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 May;125(5):917–919. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Heilbrun L. K., Morris J. S., Stemmermann G. N. Serum selenium and the risk of cancer, by specific sites: case-control analysis of prospective data. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Jul;79(1):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringstad J., Jacobsen B. K., Thomassen Y. The Tromsø Heart Study: relationships between the concentration of selenium in serum and risk factors for coronary heart disease. J Trace Elem Electrolytes Health Dis. 1987 Sep;1(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J. T., Alfthan G., Huttunen J. K., Puska P. Association between serum selenium and the risk of cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Sep;120(3):342–349. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J. T., Salonen R., Lappeteläinen R., Mäenpä P. H., Alfthan G., Puska P. Risk of cancer in relation to serum concentrations of selenium and vitamins A and E: matched case-control analysis of prospective data. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 9;290(6466):417–420. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6466.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelle D. S., Arnesen E., Førde O. H. The Tromsø heart study. Does coffee raise serum cholesterol? N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1454–1457. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelle D. S., Føorde O. H., Try K., Lehmann E. H. The Tromsøo heart study. Methods and main results of the cross-sectional study. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200(1-2):107–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. D., Rea H. M., Doesburg V. M., Robinson M. F. Selenium concentrations and glutathione peroxidase activities in whole blood of New Zealand residents. Br J Nutr. 1977 May;37(3):457–460. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernie L. N. Selenium in carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;738(4):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(83)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermarck T., Raunu P., Kirjarinta M., Lappalainen L. Selenium content of whole blood and serum in adults and children of different ages from different parts of Finland. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1977 Apr;40(4):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


