Abstract
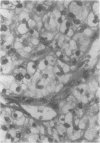
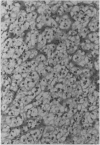
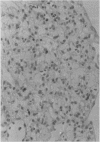
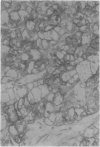
The potential role of immunohistochemistry in making the distinction between primary cerebellar haemangioblastoma and metastatic renal carcinoma was investigated by examining the reaction pattern of 10 cerebellar haemangioblastomas (seven women, three men, aged 20-40 years) and 10 primary renal carcinomas (six men, four women, aged 49-82 years) to a panel of epithelial, glial, and neural/neuroendocrine antisera. The tumour cell membranes of the renal carcinomas stained strongly with epithelial membrane antigen (EMA); membrane staining was totally absent in the haemangioblastomas. Strong neurone specific enolase (NSE) and S100 staining were also seen in haemangioblastomas but were more variable than EMA staining in renal carcinomas. It is concluded that a panel of antisera is required to distinguish between histologically similar areas in primary haemangioblastomas and metastatic renal carcinomas, and that while complementing conventional histological techniques, new problems of interpretation result which must be taken into account.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew S. M., Gradwell E. Immunoperoxidase labelled antibody staining in differential diagnosis of central nervous system haemangioblastomas and central nervous system metastases of renal carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):917–919. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deck J. H., Rubinstein L. J. Glial fibrillary acidic protein in stromal cells of some capillary hemangioblastomas: significance and possible implications of an immunoperoxidase study. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(3):173–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00687739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. I., White C. L., 3rd, Mendelsohn G. Factor VIII related antigen and glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the differential diagnosis of central nervous system hemangioblastomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Mar;81(3):285–292. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S., Symes C. E. The distribution of cytokeratin antigens in the kidney and in renal tumours. Histopathology. 1987 Feb;11(2):157–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAAC F., SCHOEN I., WALKER P. An unusual case of Lindau's disease; cystic disease of the kidneys and pancreas with renal and cerebellar tumors. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1956 May;75(5):912–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail S. M., Jasani B., Cole G. Histogenesis of haemangioblastomas: an immunocytochemical and ultrastructural study in a case of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Apr;38(4):417–421. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.4.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELMON K. L., ROSEN S. W. LINDAU'S DISEASE. REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND STUDY OF A LARGE KINDRED. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:595–617. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. M., Krajewski A. S., Dewar A. E. Immunohistochemical staining of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with monoclonal antibodies specific for the leucocyte common antigen. J Pathol. 1985 Aug;146(4):345–353. doi: 10.1002/path.1711460408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]