Abstract
The association between the concentration of different plasma lipoproteins and plasma factor VII (F VII) was analysed by isolating plasma very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL), and high density lipoprotein (HDL) lipoproteins and assessing their in vitro interaction with F VII by immunoenzyme assay using peroxidase labelled anti-factor VII immunoglobulins to determine whether F VII coagulant activity is prognostic for cardiovascular mortality. F VII bound to triglyceride rich lipoproteins, the fixation being stronger on chylomicrons and VLDL fractions than on LDL fractions. In our experiments HDL did not bind to F VII. The fixation of coagulation factor X (FX) tested by the same method is comparable with that of F VII. The nature of this fixation seemed to arise from hydrophobic interaction as calcium was not necessary and the use of Tween 20 inhibited the interaction. The binding of factors VII and X was increased when lipids were previously treated by phospholipase C and the interaction seemed to be completely dependent on the lipid part of the lipoproteins. Hyrophobic fixation is a possible mechanism of interaction of plasma lipoproteins and F VII and X, and it may be of importance in the covariance of triglyceride concentrations and the activity of vitamin K dependent coagulation factors.
Full text
PDF
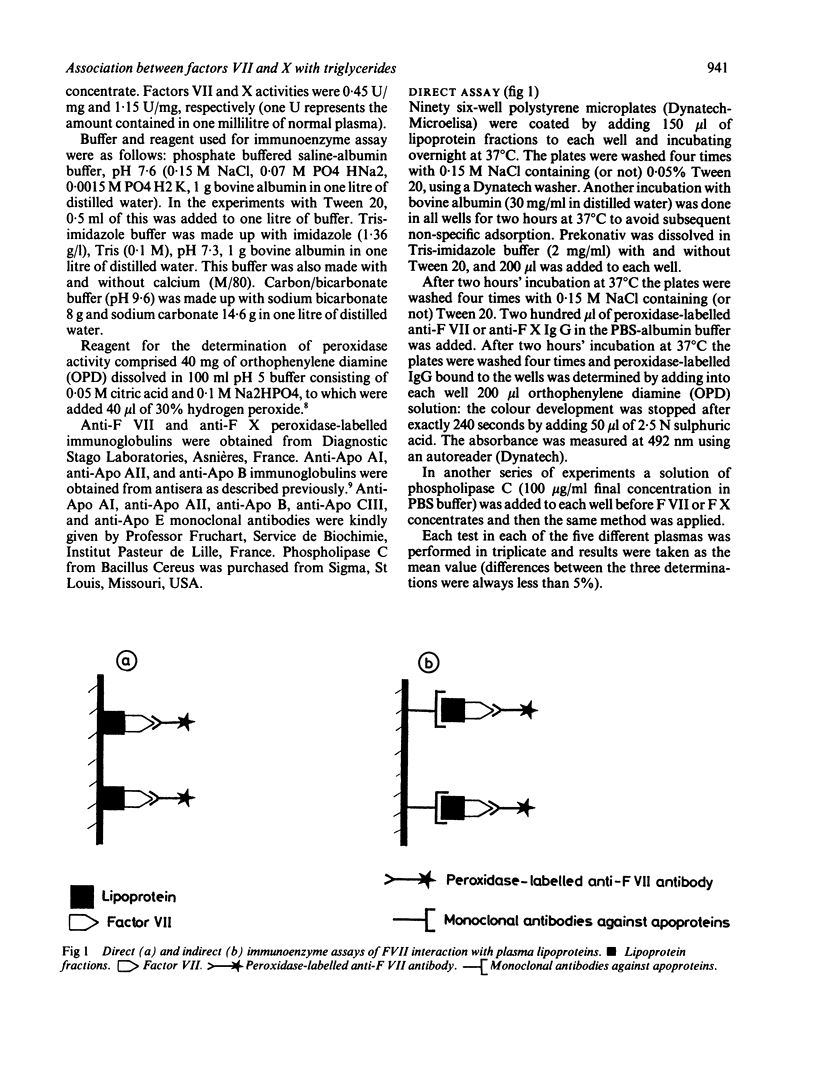
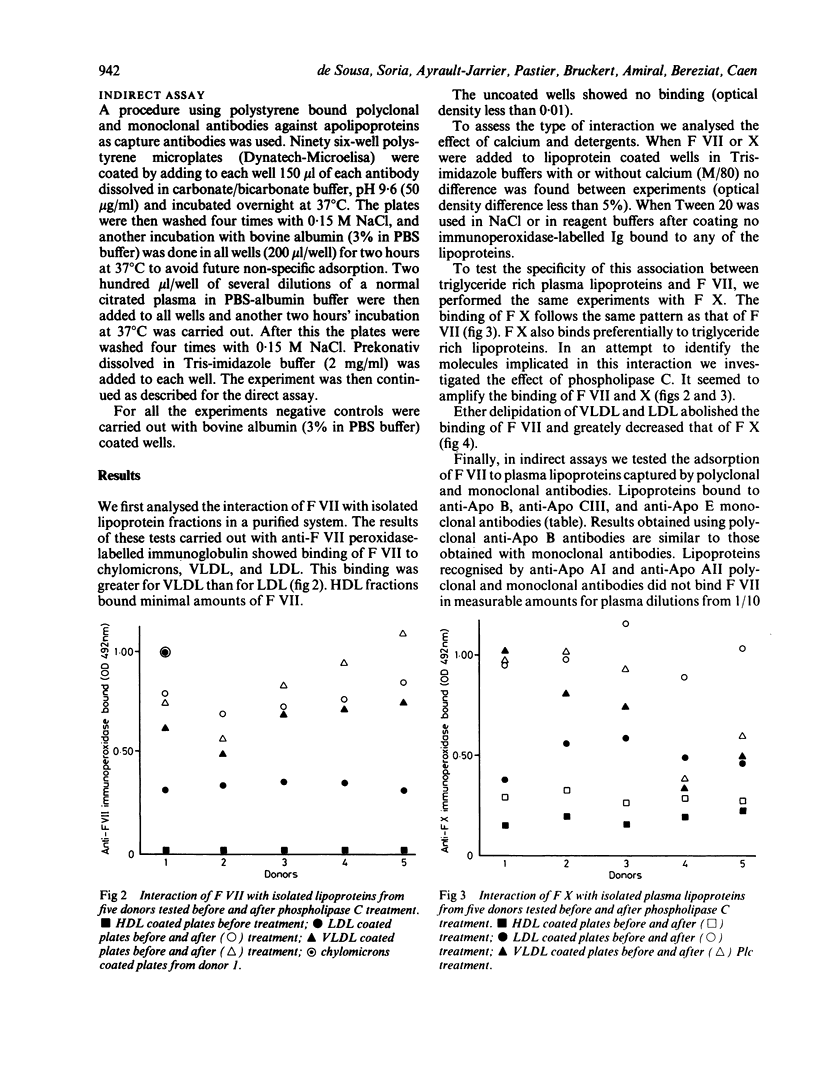
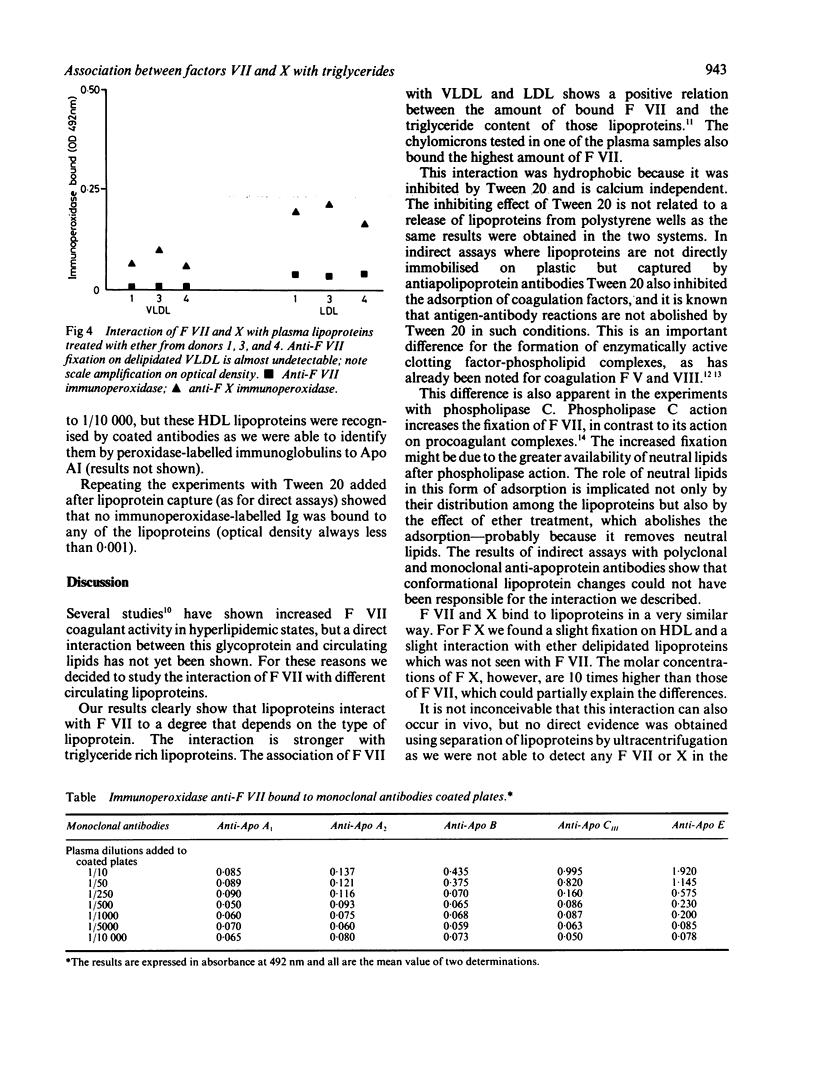

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constantino M., Merskey C., Kudzma D. J., Zucker M. B. Increased activity of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in human hyperlipoproteinaemia - association with cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Aug 31;38(2):465–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalaker K., Hjermann I., Prydz H. A novel form of factor VII in plasma from men at risk for cardiovascular disease. Br J Haematol. 1985 Oct;61(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin P., Antoine J. M., Pointel J. P., Louis J., Debry G. Métabolisme des lipoprotéines. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1983 Jan-Mar;44(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetland O., Janson T. L., Johnsen B. In vitro effect of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus on tissue thromboplastin from different species. Thromb Res. 1982 Oct 1;28(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. J., Hemker H. C. Studies on blood coagulation factor V. I. The interaction of salts of fatty acids and coagulation factors. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Dec 31;22(3):417–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitrot B., Lastra G., Ayrault-Jarrier M., Polonovski J. Mise en évidence de plusieurs antigènes dans la fraction LDL des lipoprotéines sériques humaines. Biochimie. 1972;54(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J., Martin J. C., Webster J., Wilkes H., Miller N. E., Wilkinson W. H., Meade T. W. Association between dietary fat intake and plasma factor VII coagulant activity--a predictor of cardiovascular mortality. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Jun;60(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S., Goldstein S., Pastier D., Theron L., Berthelier M., Ayrault-Jarrier M., Dubarry M., Rebourcet R., Pau B. Monoclonal antibodies to low density lipoprotein used for the study of low- and very-low-density lipoproteins, in "ELISA" and immunoprecipitation technics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):704–711. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarabin P. Y., Bara L., Samama M., Orssaud G. Further evidence that activated factor VII is related to plasma lipids. Br J Haematol. 1985 Sep;61(1):186–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb04076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson H. C., Mann J. I., Meade T. W., Chakrabarti R., Stirling Y., Woolf L. Hypertriglyceridaemia and hypercoagulability. Lancet. 1983 Apr 9;1(8328):786–790. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91849-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G., Kuijpers L., Kacaki J., Schuurs A. Solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Oct;29(10):873–879. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.10.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


