Abstract
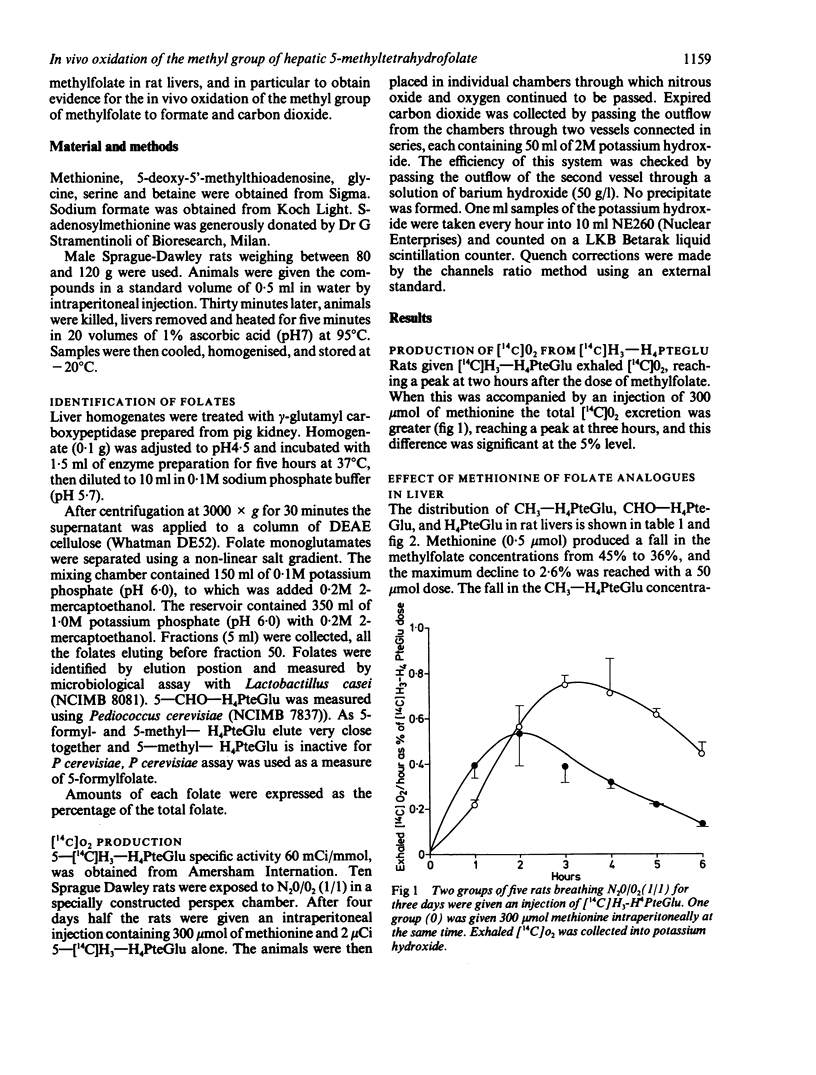
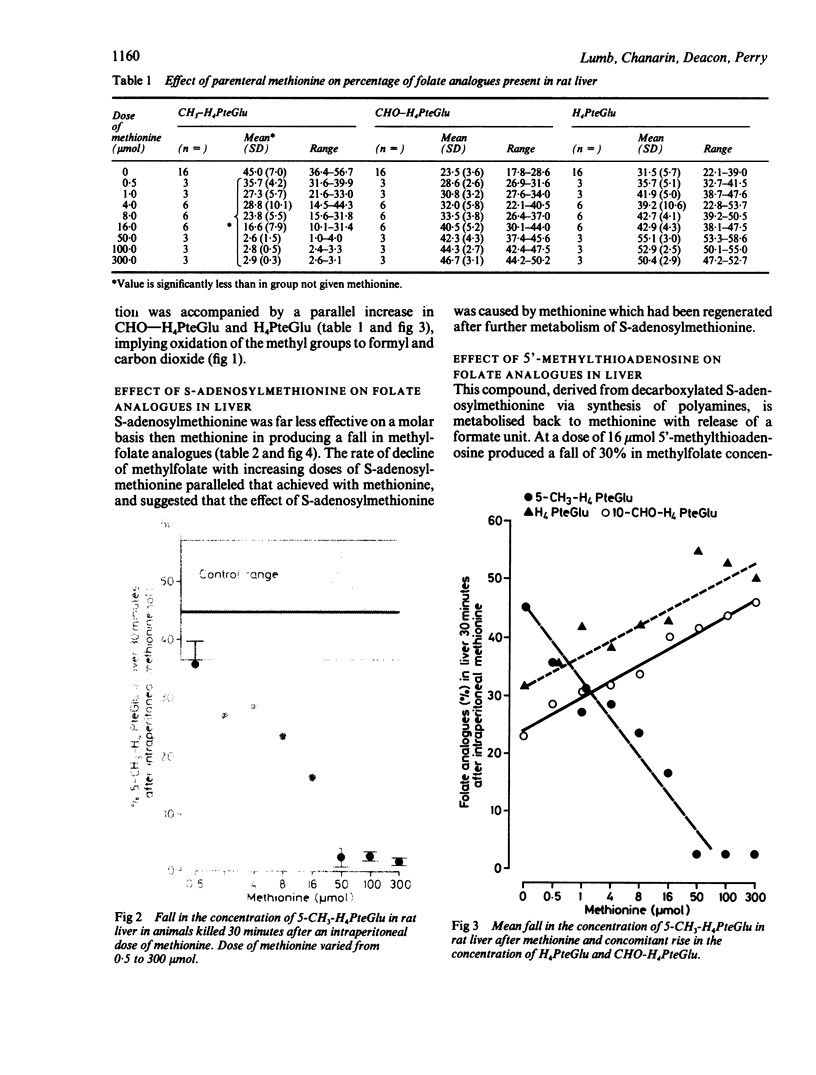
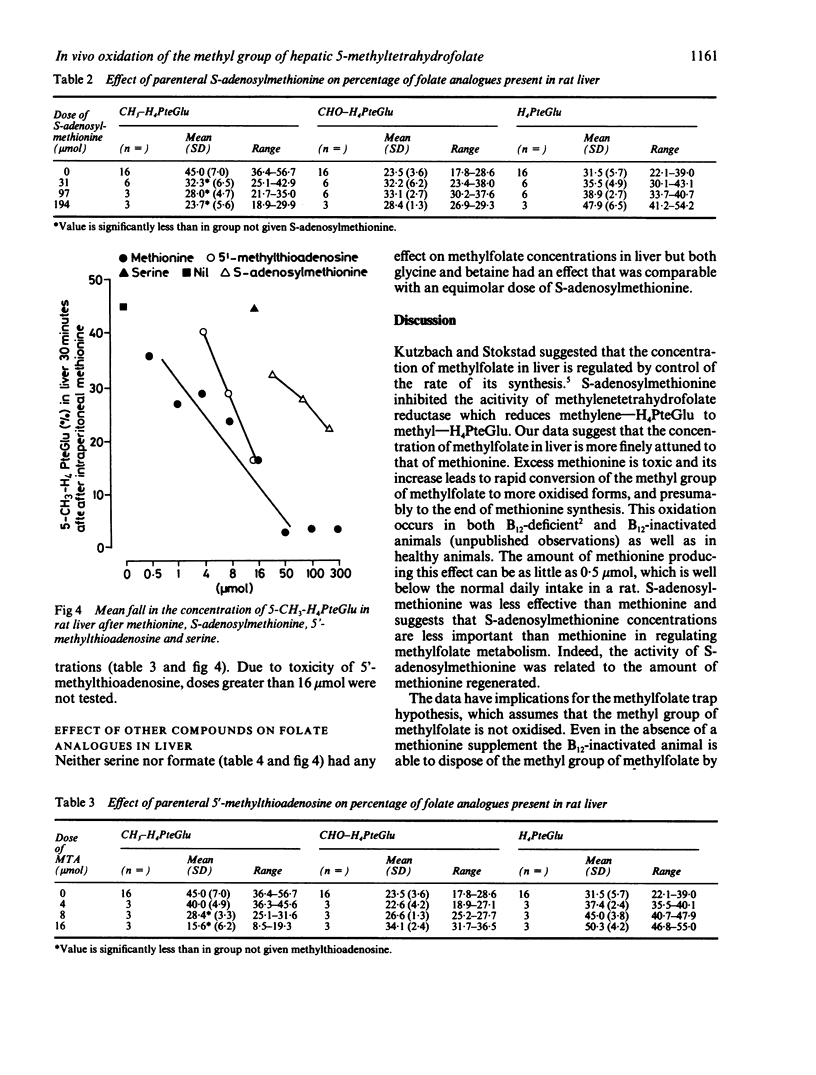
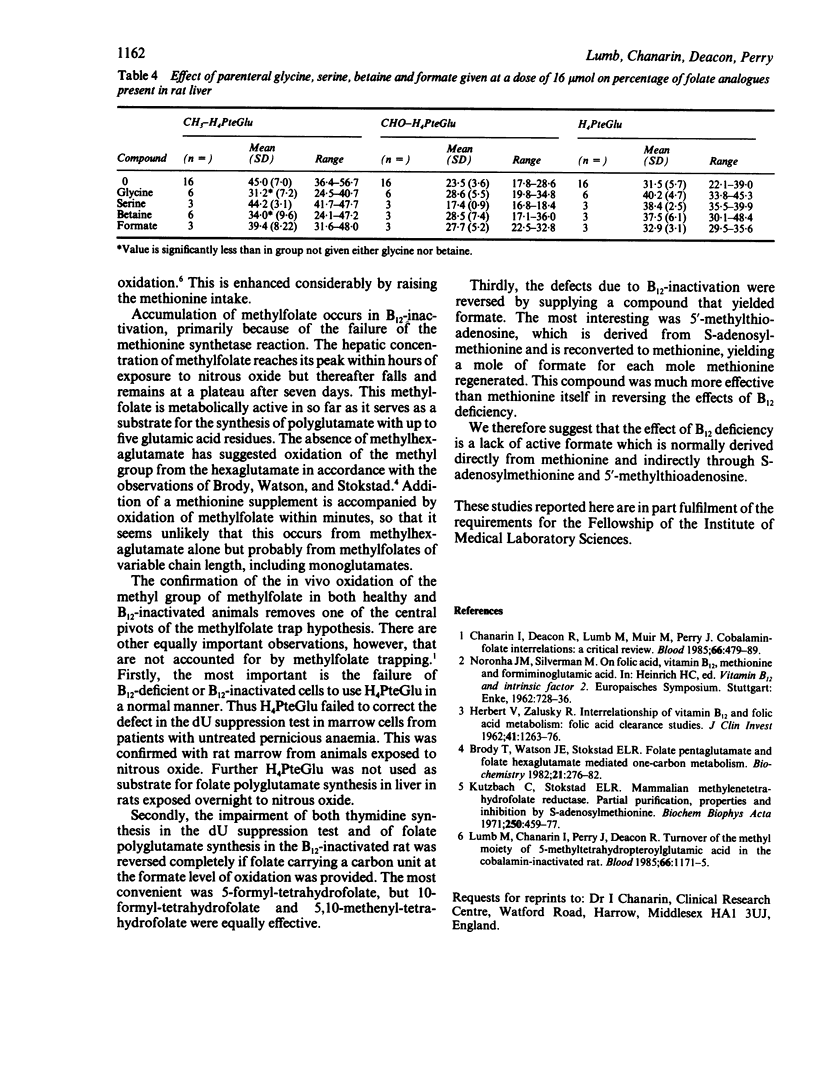
Methionine given parenterally to rats caused rapid disappearance of methyltetrahydrofolate from the liver and a corresponding rise in tetrahydrofolate and formyl-tetrahydrofolate concentrations. When [14C]H3--H4folate was given, methionine caused an increased [14C]0(2) excretion, indicating that oxidation of the methyl group had occurred. Methionine was more effective than S-adenosylmethionine at causing oxidation, but serine was ineffective. The lowest dose of methionine to produce an effect was 0.5 mumol, which is less than the daily dietary intake in a rat. The data suggest that the concentration of methylfolate in rat livers is controlled by the concentrations of methionine.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody T., Watson J. E., Stokstad E. L. Folate pentaglutamate and folate hexaglutamate mediated one-carbon metabolism. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):276–282. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanarin I., Deacon R., Lumb M., Muir M., Perry J. Cobalamin-folate interrelations: a critical review. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):479–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., ZALUSKY R. Interrelations of vitamin B12 and folic acid metabolism: folic acid clearance studies. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jun;41:1263–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI104589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Allen R. W., Baldassare J. Alternate sources and substitutes for therapeutic blood components. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutzbach C., Stokstad E. L. Mammalian methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Partial purification, properties, and inhibition by S-adenosylmethionine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 15;250(3):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


