Abstract
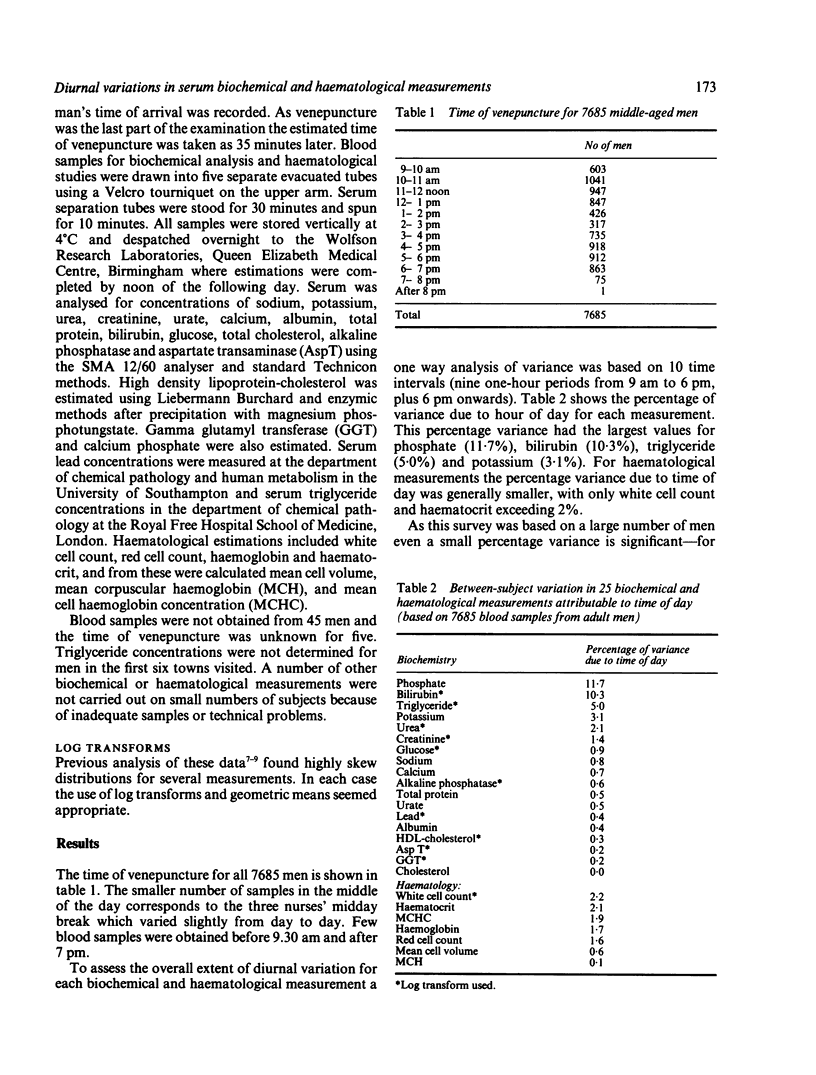
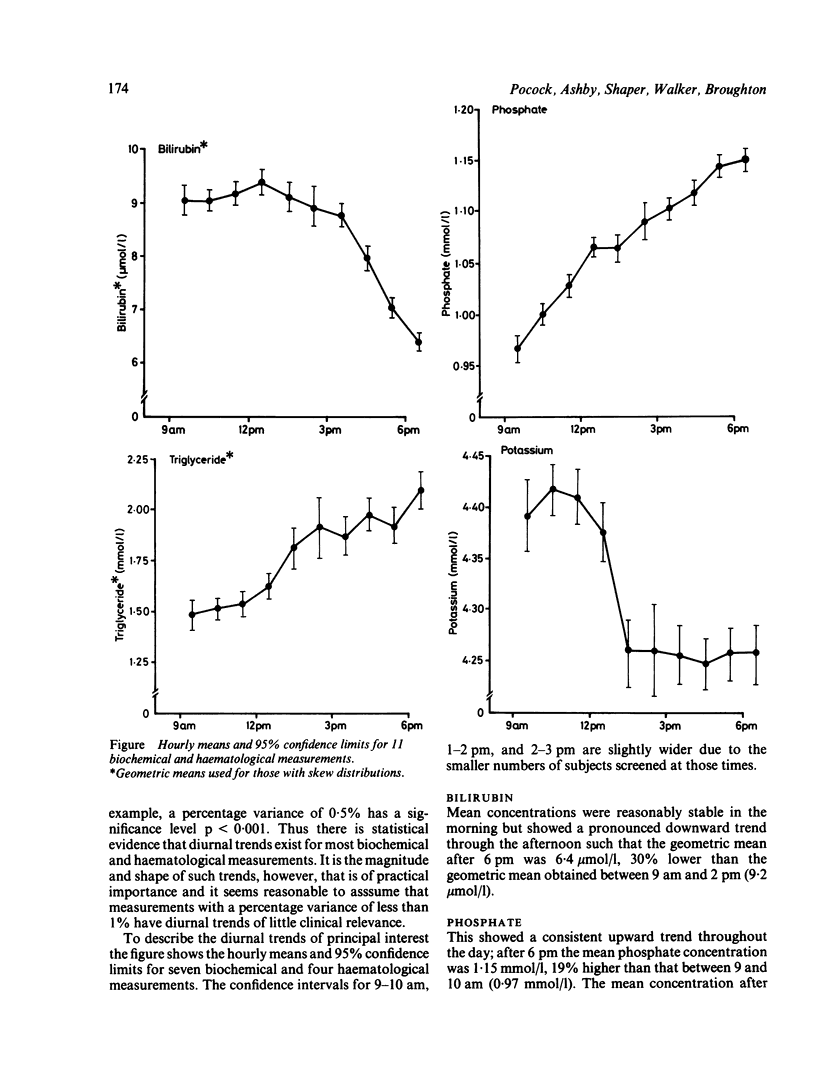
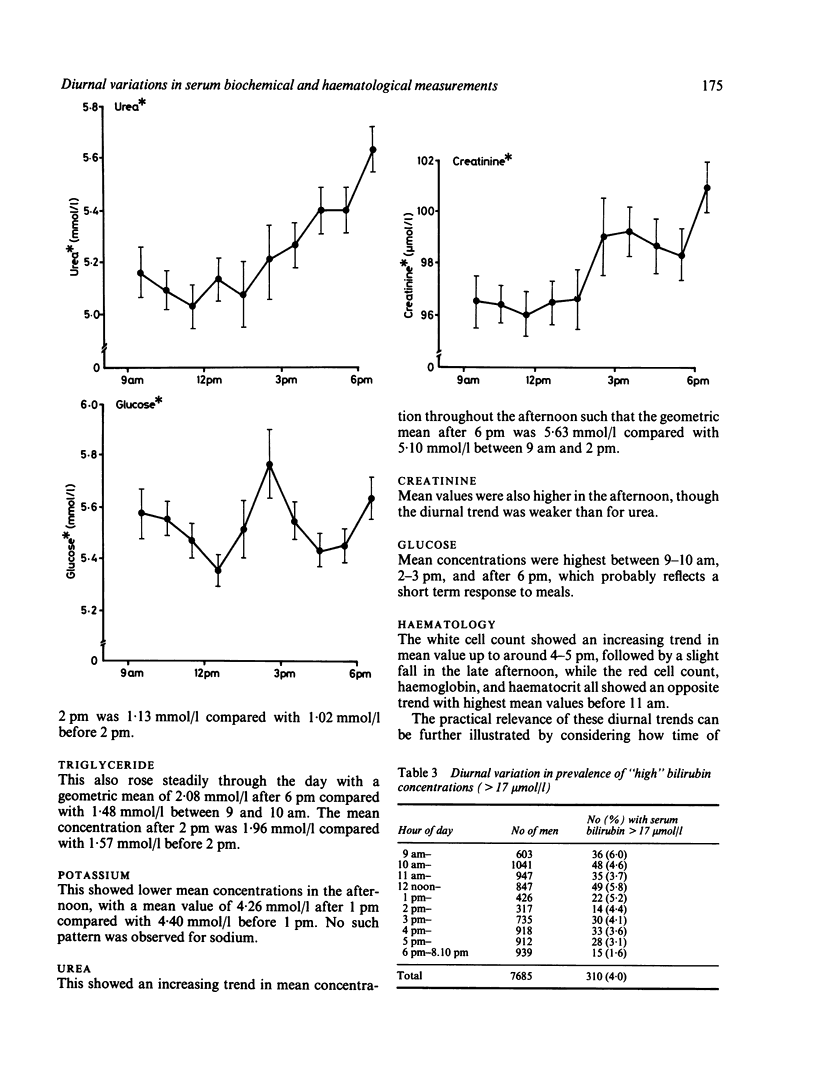
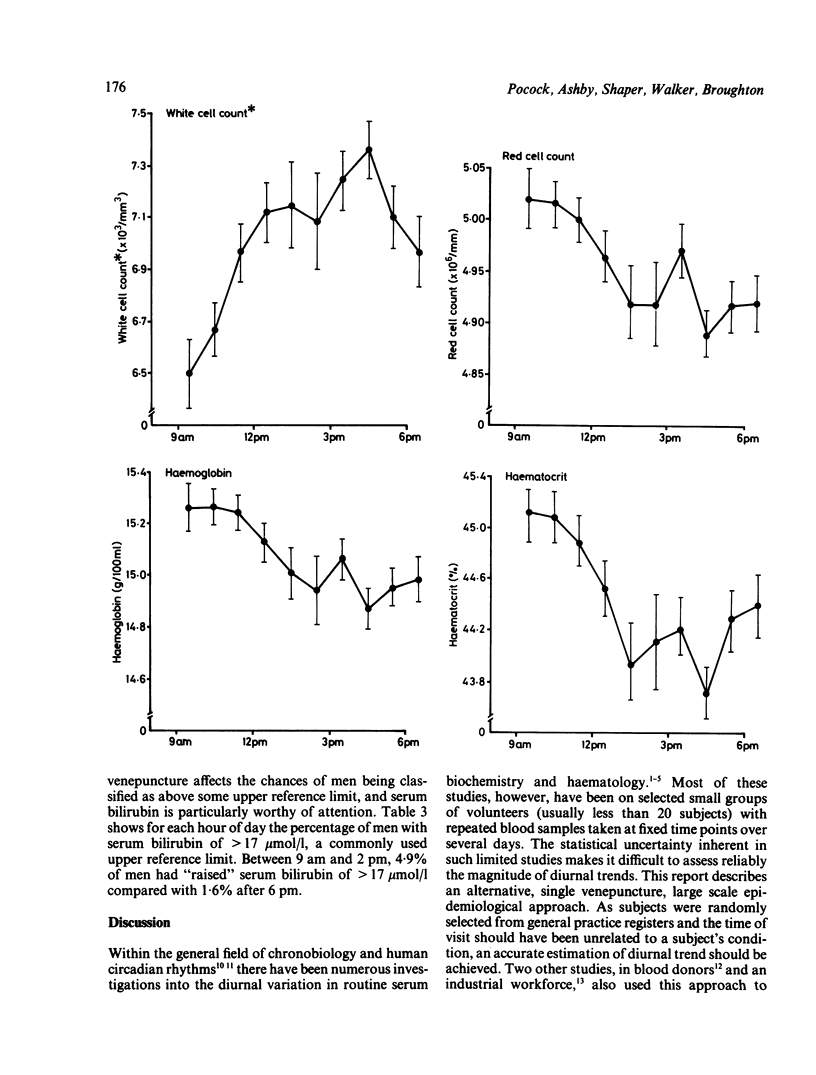
Twenty five biochemical and haematological measurements were determined on nonfasting blood and serum samples collected between 9 am and 7 pm from a representative group of 7685 British middle-aged men. Most measurements showed significant diurnal variations, but only for bilirubin, phosphate, and triglyceride did time of day account for more than 5% of the between subject variance. Serum bilirubin concentrations showed a pronounced downward trend in the afternoon, the mean value after 6 pm being 30% lower than the mean value in the morning. Mean serum triglyceride and phosphate concentrations increased steadily through the day. Mean concentrations of potassium, haemoglobin, and haematocrit and red cell count were higher in the morning, while urea and creatinine concentrations and white cell count had higher means in the afternoon. Glucose showed a pattern consistent with short term response to meals. The effects of these diurnal trends on routine use of biochemical tests needs careful consideration, and a greater understanding of their biological mechanisms is required.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett P. V. Hyperbilirubinemia of fasting. JAMA. 1971 Sep 6;217(10):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton P. M., Holder R., Ashby D. Long-term trends in biochemical data obtained from two population surveys. Ann Clin Biochem. 1986 Jul;23(Pt 4):474–486. doi: 10.1177/000456328602300416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLAIN A. C., TURNER F. M., WILLIAMS E. K. The evaluation of white-cell counting in radiation protection. Br J Radiol. 1952 Apr;25(292):169–176. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-25-292-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlow D. A., Church J. F., Clayton B. E. Haematological and biochemical parameters in an industrial workforce. Ann Clin Biochem. 1983 Nov;20(Pt 6):341–348. doi: 10.1177/000456328302000603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUO P. T., CARSON J. C. Dietary fats and the diurnal serum triglyceride levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 Aug;38(8):1384–1393. doi: 10.1172/JCI103914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz M. E., Rosen J. F., Mizruchi M. Circadian variations in serum zinc (Zn) concentrations: correlation with blood ionized calcium, serum total calcium and phosphate in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Apr;41(4):689–696. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.4.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz M., Rotkin L., Rosen J. F. Circadian rhythms of blood minerals in humans. Science. 1981 Aug 7;213(4508):672–674. doi: 10.1126/science.7256269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson K., Healy M. J., Flynn F. V., Piper K. A., Garcia-Webb P. The effect of age, sex and other factors on blood chemistry in health. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 15;84(3):373–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N. Human circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jan;46(1):128–171. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison B., Shenkin A., McLelland A., Robertson D. A., Barrowman M., Graham S., Wuga G., Cunningham K. J. Intra-individual variation in commonly analyzed serum constituents. Clin Chem. 1979 Oct;25(10):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Pocock S. J., Ashby D., Walker M., Whitehead T. P. Biochemical and haematological response to alcohol intake. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(Pt 1):50–61. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Pocock S. J., Walker M., Cohen N. M., Wale C. J., Thomson A. G. British Regional Heart Study: cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged men in 24 towns. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jul 18;283(6285):179–186. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6285.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Pocock S. J., Walker M., Phillips A. N., Whitehead T. P., Macfarlane P. W. Risk factors for ischaemic heart disease: the prospective phase of the British Regional Heart Study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1985 Sep;39(3):197–209. doi: 10.1136/jech.39.3.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statland B. E., Winkel P., Bokelund H. Factors contributing to intra-individual variation of serum constituents. 1. Within-day variation of serum constituents in healthy subjects. Clin Chem. 1973 Dec;19(12):1374–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi C. G. Circadian challenges in "quality control". Biochemical rhythms and spacial phenomena. Hum Pathol. 1973 Jun;4(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(73)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelle D. S., Cramp D. G., Patel I., Walker M., Marr J. W., Shaper A. G. Total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and triglycerides after a standardized high-fat meal. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr. 1982;36(6):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touitou Y., Touitou C., Bogdan A., Reinberg A., Auzeby A., Beck H., Guillet P. Differences between young and elderly subjects in seasonal and circadian variations of total plasma proteins and blood volume as reflected by hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythrocyte counts. Clin Chem. 1986 May;32(5):801–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel P., Statland B. E., Bokelund H. The effects of time of venipuncture on variation of serum constituents. Consideration of within-day and day-to-day changes in a group of healthy young men. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Oct;64(4):433–447. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


