Abstract
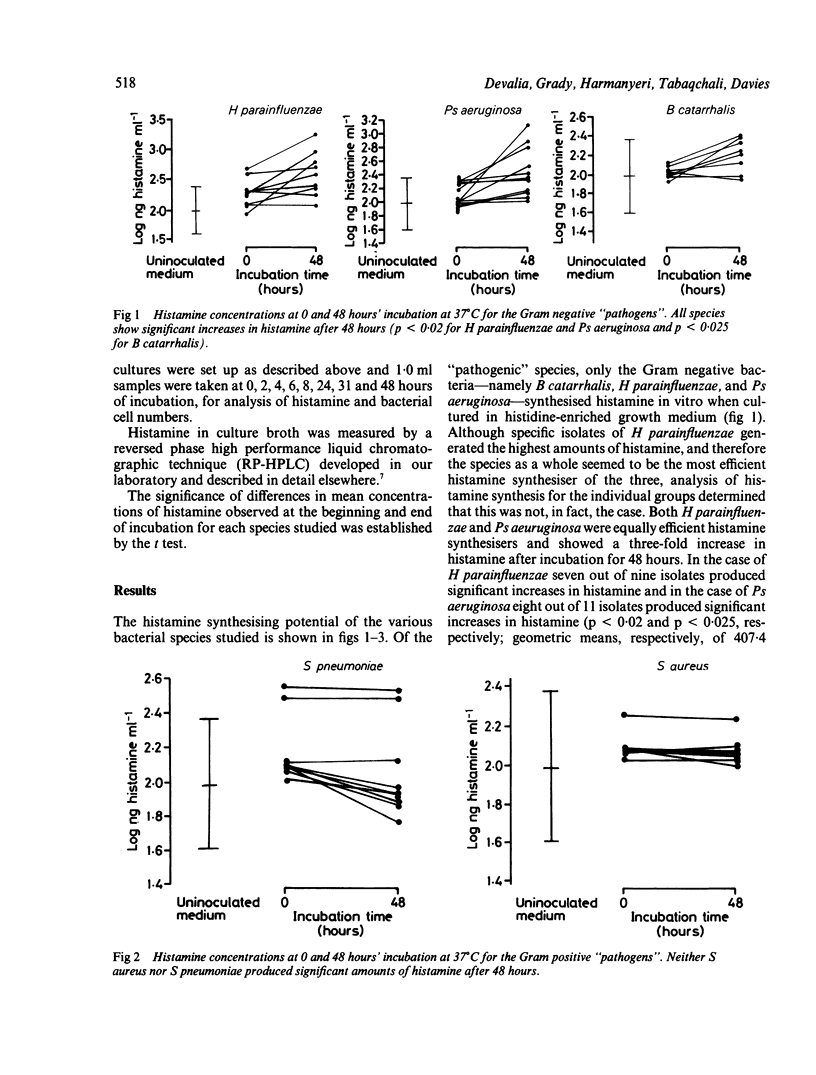
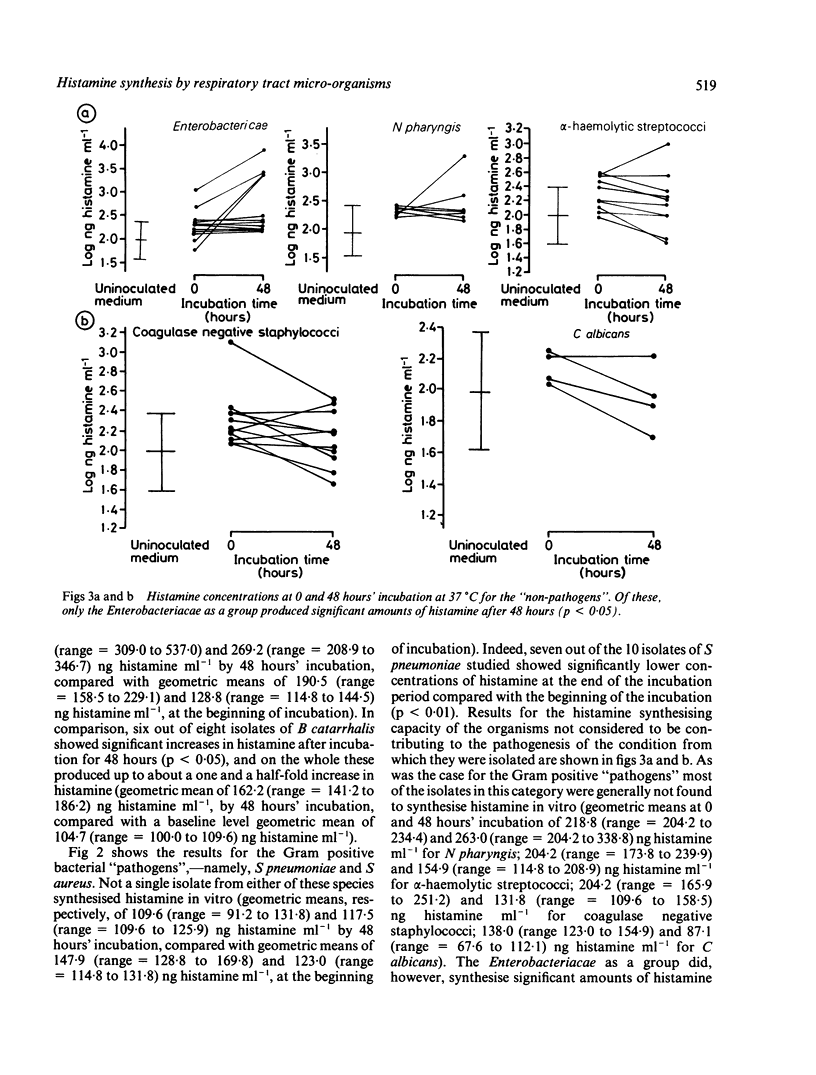
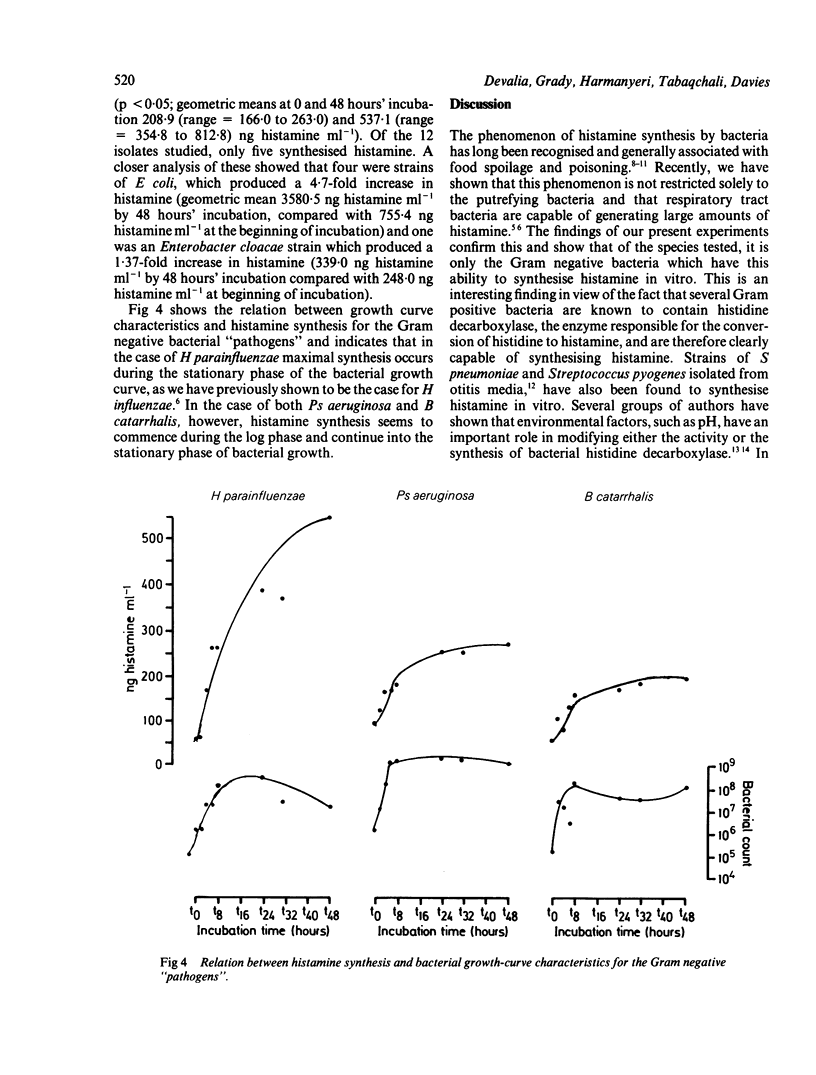
Five bacterial species considered to be potential pathogens in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, and pneumonia--Branhamella catarrhalis, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae--were evaluated for their potential to synthesise histamine in vitro. Bacterial species commonly isolated from infected sputum but generally not considered to be pathogenic--Enterobacteriacae, Neisseria pharyngis, coagulase negative staphylococci, alpha-haemolytic streptococci, and Candida albicans--were similarly studied. Of the "pathogens", the Gram negative species B catarrhalis, H parainfluenzae and Ps aeruginosa synthesised clinically important amounts of histamine; this was not the case for the Gram positive species S aureus and S pneumoniae. Of the "non-pathogenic" species, only the Enterobacteriacae, as a group, were found to synthesise clinically important amounts of histamine. These results show that some Gram negative bacteria, associated with acute exacerbations in respiratory infections, produce histamine and possibly other inflammatory mediators, which may contribute to their pathogenecity in the lower respiratory tract in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold S. H., Brown W. D. Histamine (?) toxicity from fish products. Adv Food Res. 1978;24:113–154. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2628(08)60157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Horáková Z., Severs W. B. Bacterial histidine decarboxylase in rat stomach. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul 15;11(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Ranga V., Paré P. D., Inoue S., Moroz L. A., Hogg J. C. Effect of histamine and methacholine on guinea pig tracheal permeability to HRP. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Dec;45(6):939–948. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.6.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. H., Pui A. Histamine content of sputum from patients with asthma and chronic bronchitis. Clin Allergy. 1982 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1982.tb03122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Norn S., Pao G. J., Holgate S. T. Non-IgE-dependent bacteria-induced histamine release from human lung and tonsillar mast cells. Clin Allergy. 1987 Jul;17(4):341–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1987.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devalia J. L., Sheinman B. D., Davies R. J. Highly sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic technique for the simultaneous measurement of histamine, 1-methylhistamine and other biogenic amines. J Chromatogr. 1985 Oct 11;343(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84610-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Stephens D. S., Mulks M. H., Cooper M. D., Bricker J. V., Mirra S. S., Wright A. Pathogenesis of IgA1 protease-producing and -nonproducing Haemophilus influenzae in human nasopharyngeal organ cultures. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):752–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. J., Hobbs G., Murray C. K., Cruickshank J. G., Young S. E. Scombrotoxic fish poisoning: features of the first 50 incidents to be reported in Britain (1976-9). Br Med J. 1980 Jul 5;281(6232):71–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ieniştea C. Bacterial production and destruction of histamine in foods, and food poisoning caused by histamine. Nahrung. 1971;15(1):109–113. doi: 10.1002/food.19710150115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. A., Heino M., Laitinen A., Kava T., Haahtela T. Damage of the airway epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):599–606. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Federman M. J. Gram-negative bacillary pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):425–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodley I., Zhong N. S., Morgan D. J., Davies R. J. A comparison of the available methods for the measurement of histamine in sputum. Clin Allergy. 1984 Mar;14(2):153–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1984.tb02647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. K., Hobbs G., Gilbert R. J. Scombrotoxin and scombrotoxin-like poisoning from canned fish. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):215–220. doi: 10.1017/s002217240007008x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P. A., Snell E. E. Prohistidine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus 30a. A new type of zymogen. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):365–371. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees P. J., Shelton D., Chan T. B., Eiser N., Clark T. J., Maisey M. N. Effects of histamine on lung permeability in normal and asthmatic subjects. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):603–606. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley H. C., Brogan T. D. Variation in the composition of sputum in chronic chest diseases. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Dec;49(6):625–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinman B. D., Devalia J. L., Crook S. J., Davies R. J. De novo generation of histamine in sputum and the effect of antibiotics. Agents Actions. 1986 Mar;17(5-6):449–453. doi: 10.1007/BF01965512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinman B. D., Devalia J. L., Davies R. J., Crook S. J., Tabaqchali S. Synthesis of histamine by Haemophilus influenzae. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 29;292(6524):857–858. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6524.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull L. S., Turnbull L. W., Leitch A. G., Crofton J. W., Kay A. B. Mediators of immediate-type hypersensitivity in sputum from patients with chronic bronchitis and asthma. Lancet. 1977 Sep 10;2(8037):526–529. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90664-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderslice P., Copeland W. C., Robertus J. D. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of wild type and a mutant histidine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus 30a. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15186–15191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. V., Slater J. E., Kaliner M. A. Histamine and asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1165–1176. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga D. H., Frank H. A. Histamine-producing bacteria in decomposing skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):447–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.447-452.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


