Abstract
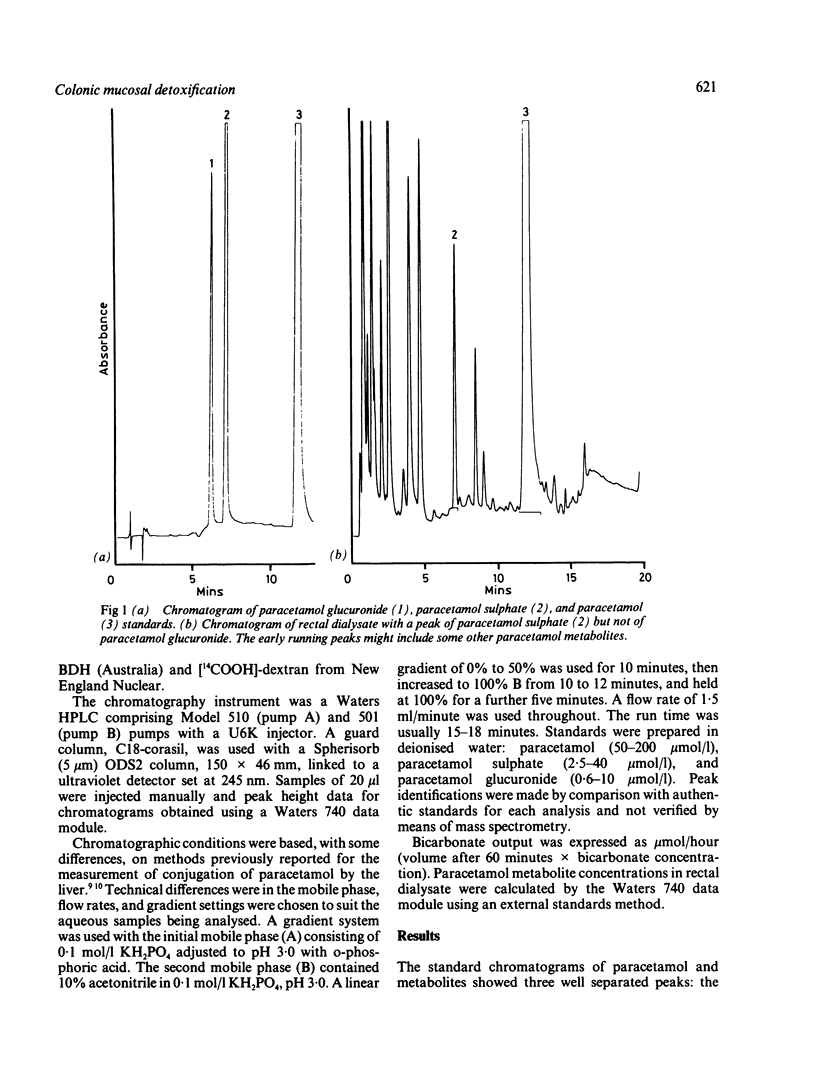
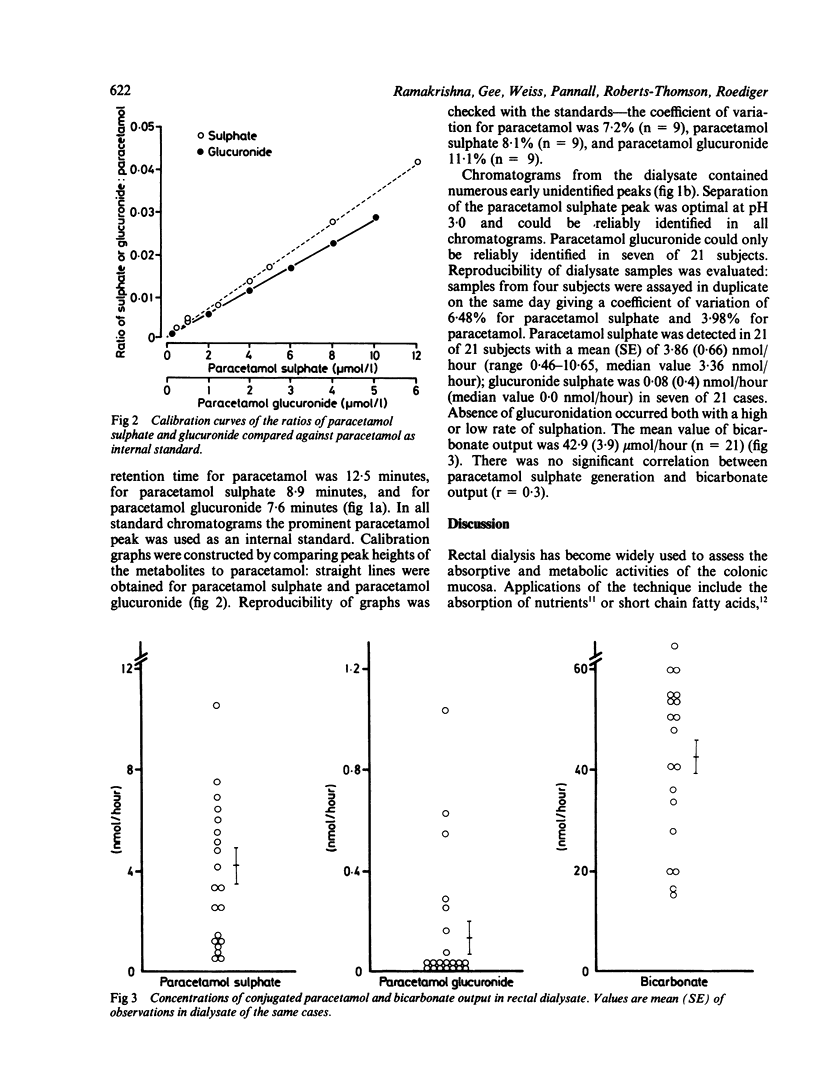
Conjugation of phenol by the colonic mucosa was assessed in vivo using dialysis tubing containing 1.5 ml of 1 mmol/l acetaminophen (paracetamol) and 10 mmol/l butyrate. These were allowed to equilibrate in the rectum for one hour. The glucuronidated and sulphated conjugates of acetaminophen were measured by high pressure liquid chromatography and bicarbonate concentrations by gas analysis. In 21 subjects without colonic disease sulphate conjugation was observed in all cases, with a mean (SE) of 3.86 (0.66) nmol/hour, while glucuronide conjugation was found in seven of 21 cases. Mean (SE) bicarbonate output of 42.9 (3.9) mumol/hour (n = 21) indicated healthy colonic mucosal metabolism and phenolic sulphation in dialysate and agreed with published sulphation rates obtained with cultured cells of colonic epithelium. Acetaminophen sulphation suggests that the colonic mucosa has an important role in the conjugation of phenols, and the method reported here would be useful in assessing the detoxification capacity of the colonic mucosa in diseases of the rectal mucosa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen G. M., Grafstrom R. C., Gibby E. M., Smith L., Autrup H., Harris C. C. Metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene and 1-naphthol in cultured human tumorous and nontumorous colon. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):1312–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffeth L. K., Rosen G. M., Rauckman E. J. Effects of model traumatic injury on hepatic drug metabolism in the rat. V. Sulfation and acetylation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1985 Jul-Aug;13(4):398–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackford A. W., Mayhew J. W., Goldin B. R. An isolated perfused model for the study of colonic metabolism and transport. J Surg Res. 1988 Jan;44(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(88)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE N., CARO L., OTERO VILARDEBO L. R., GODMAN G. C. ON THE SITE OF SULFATION IN COLONIC GOBLET CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:339–351. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil N. I., Cummings J. H., James W. P. Short chain fatty acid absorption by the human large intestine. Gut. 1978 Sep;19(9):819–822. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.9.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldéus P. Paracetamol metabolism and toxicity in isolated hepatocytes from rat and mouse. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(24):2859–2863. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASTERNAK C. A., KENT P. W. Biosynthesis of intestinal mucins. 2. Incorporation of [35S] sulphate by guinea-pig colon in vitro. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):452–457. doi: 10.1042/bj0680452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASTERNAK C. A. The synthesis of 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate by mouse tissue: sulfate activation in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:438–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. M., Miller J. J., Olavesen A. H., Curtis C. G. Liver as major organ of phenol detoxication? Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):234–235. doi: 10.1038/252234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampton D. S., Sladen G. E., Youlten L. J. Rectal mucosal prostaglandin E2 release and its relation to disease activity, electrical potential difference, and treatment in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1980 Jul;21(7):591–596. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.7.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk M., Locher M. 1-Naphthol conjugation in isolated cells from liver, jejunum, ileum, colon and kidney of the guinea pig. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 1;34(5):697–701. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sund R. B., Lauterbach F. Drug metabolism and metabolite transport in the small and large intestine: experiments with 1-naphthol and phenolphthalein by luminal and contraluminal administration in the isolated guinea pig mucosa. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1986 Jan;58(1):74–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1986.tb00073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey N. A., Orlando R. C., Schreiner V. J., Powell D. W. Cytoprotective effect of sulfate ions in acid-exposed rabbit esophagus. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):G866–G869. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.6.G866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., METCALFE-GIBSON A., MORRISON R. B., NG S. T., HOWARD A. V. IN VIVO DIALYSIS OF FAECES AS A METHOD OF STOOL ANALYSIS. I. TECHNIQUE AND RESULTS IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. Clin Sci. 1965 Apr;28:357–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



