Abstract
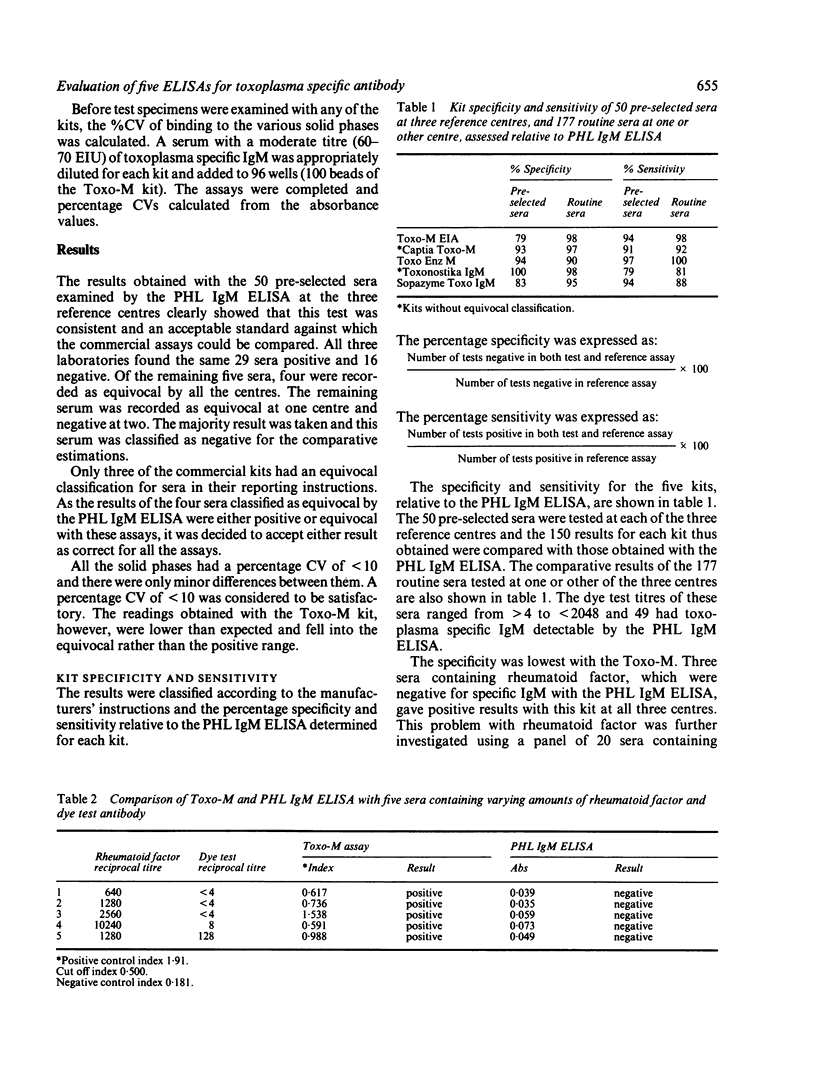
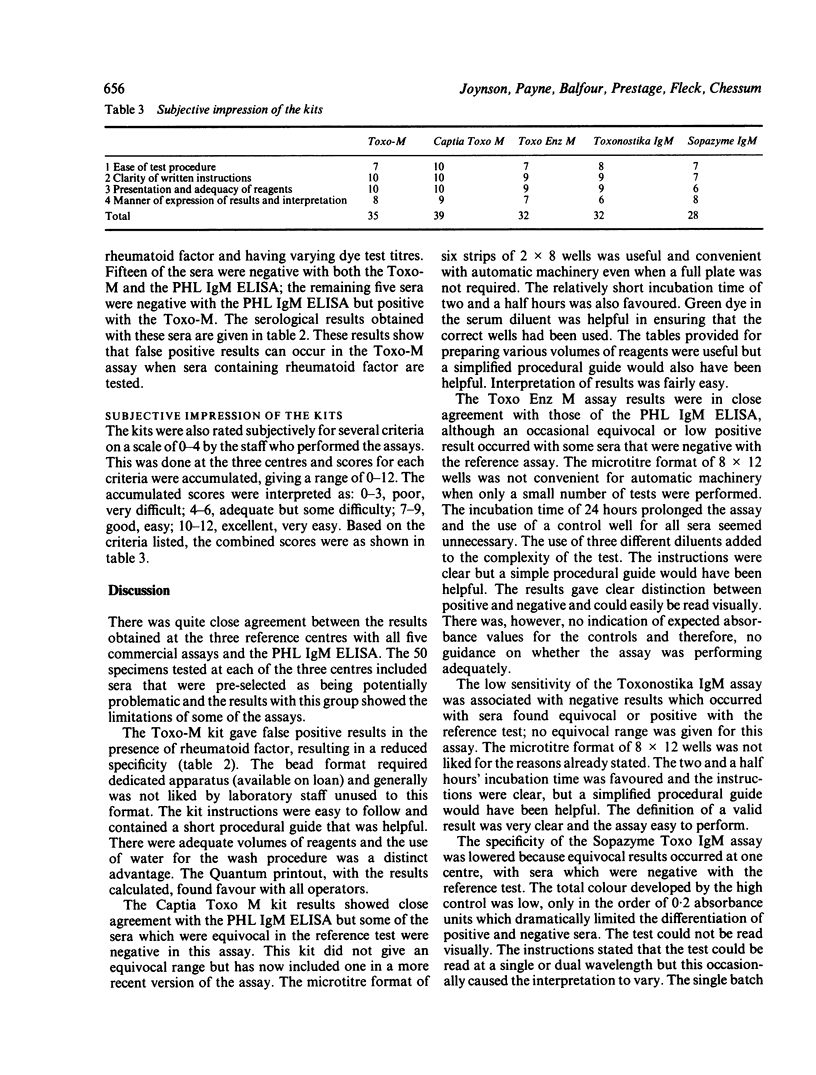
Five commercially available enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits for the detection of specific IgM against Toxoplasma gondii were evaluated in a three centre study and results compared with those of the Public Health Laboratory Service ELISA for Toxoplasma IgM (PHL IgM ELISA). Fifty selected sera were tested by all the methods (Toxo-M, Captia Toxo-M EIA, Toxo Enz M EIA, Toxonostika IgM EIA, Sopazyme Toxo IgM EIA) at the three reference centres in England and Wales and 177 routine sera by all the methods in one or other of the centres. Ten of the 50 selected sera contained autoimmune antibodies but no specific IgM and 29 had toxoplasma specific IgM detectable by the PHL IgM ELISA. The kits were assessed for their specificity and sensitivity compared with the PHL IgM ELISA, and the percentage coefficient of variation for binding to the solid phases was determined. They were also rated subjectively by the staff performing the assays and an overall impression of each kit was gained by allocating scores of several criteria. There was quite close agreement among the results obtained with all five commercial assays and the PHL IgM ELISA, although some of the sera pre-selected as being potentially problematic showed the limitations of some of the assays.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Herbrink P., van Loon A. M., Rotmans J. P., van Knapen F., van Dijk W. C. Interlaboratory evaluation of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunoblotting for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.100-105.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R. A., Joynson D. H., Balfour A. H., Harford J. P., Fleck D. G., Mythen M., Saunders R. J. Public Health Laboratory Service enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for detecting Toxoplasma specific IgM antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):276–281. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



