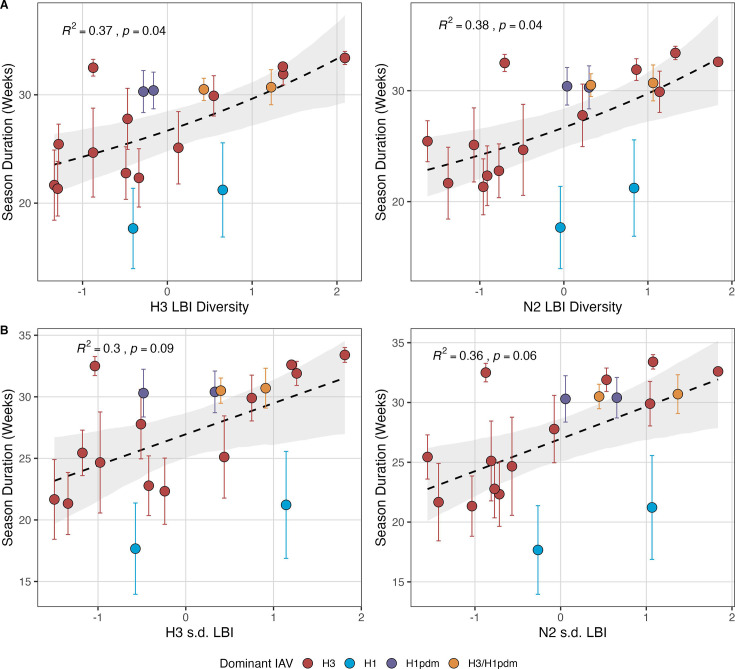
Figure 5. Influenza A(H3N2) seasonal duration increases with the diversity of hemagglutinin (H3) and neuraminidase (N2) clade growth rates in each season.
Seasonal diversity of clade growth rates is measured as the (A) Shannon diversity or (B) standard deviation (s.d.) of H3 and N2 local branching index (LBI) values of viruses circulating in each season. LBI values are scaled to aid in direct comparisons of different LBI diversity metrics. Point color indicates the dominant influenza A subtype based on CDC influenza season summary reports (red: A(H3N2), blue: A(H1N1), purple: A(H1N1)pdm09, orange: A(H3N2)/A(H1N1)pdm09 co-dominant), and vertical bars are 95% confidence intervals of regional estimates (pre-2009 seasons: 9 regions; post-2009 seasons: 10 regions). Mean seasonal duration was fit as a function of H3 or N2 LBI diversity using Gaussian GLMs (inverse link) with 1000 bootstrap resamples. In each plot, the black dashed line represents the mean regression fit, and the gray shaded band shows the 95% confidence interval, based on 1000 bootstrap resamples. The R2 and associated p-value from the mean regression fit are in the top left section of each plot.