Abstract
Malaria continues to pose a health challenge globally, and its elimination has remained a major topic of public health discussions. A key factor in eliminating malaria is the early and accurate detection of the parasite, especially in asymptomatic individuals, and so the importance of enhanced diagnostic methods cannot be overemphasized. This paper reviewed the advances in malaria diagnostic tools and detection methods over recent years. The use of these advanced diagnostics in lower and lower-middle-income countries as compared to advanced economies has been highlighted. Scientific databases such as Google Scholar, PUBMED, and Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI), among others, were reviewed. The findings suggest important advancements in malaria detection, ranging from the use of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) and molecular-based technologies to advanced non-invasive detection methods and computerized technologies. Molecular tests, RDTs, and computerized tests were also seen to be in use in resource-limited settings. In all, only twenty-one out of a total of eighty (26%) low and lower-middle-income countries showed evidence of the use of modern malaria diagnostic methods. It is imperative for governments and other agencies to direct efforts toward malaria research to upscale progress towards malaria elimination globally, especially in endemic regions, which usually happen to be resource-limited regions.
Keywords: malaria, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), diagnostic methods
1. Introduction
Malaria elimination has been a focal topic of public health discussions for the past decade or more. Despite being a tropically endemic parasitic infection, the impact of malaria is far reaching and remains a global health concern. The 2023 World Health Organization (WHO) report states that malaria cases rose to an estimated 249 million in 2022, with an increase of 5 million more cases from the year 2021 [1]. Although relentless efforts are being made and strategies put in place, much more is required to free our globe of the parasitic infection, particularly in indigenous malaria-endemic countries such as a number of sub-Saharan African countries where most cases occur [2].
Central to eliminating malaria is early, accurate detection, quantification, and differentiation of the parasitic infection, especially among asymptomatic persons. Asymptomatic plasmodium-infected individuals represent a major threat to malaria elimination worldwide as they do not show signs of clinical disease yet serve as parasite reservoirs and significantly contribute to the spread of the infection [3]. Notably, the majority of these asymptomatic infections are missed by conventional diagnostic techniques. As a result, the need for reliable, sensitive, and specific diagnostic or detection methods arises, which would also be useful for monitoring any decline in malaria transmission [4].
Technologies for malaria diagnosis have advanced in recent years; however, certain factors, such as the lack of laboratory infrastructure, operational costs, electricity requirements, and special operation expertise, have impeded the implementation of these advanced techniques in the vast majority of malaria endemic areas. This is especially the case when it comes to molecular testing, as these tests can be particularly expensive in addition to other challenges not only for malaria but for other infectious diseases [5]. The WHO describes microscopy (thin and thick film) as the primary method of detection [6]. Though microscopy is extensively used, it is unable to adequately detect low parasitemia, which is essential for effective treatment and subsequent elimination of the parasitic infection [7]. In addition, it is a laborious process requiring much expertise and experience for accurate diagnosis [4,8]. Other concerns have been the invasive approach of this technique, where blood samples are collected after a painful pierce of a needle, and yet an accurate diagnosis unassuredly relies solely on the discretion of the laboratory scientist. In several developing countries, there is inadequate expertise, equipment, and supplies required for accurate detection; as such, there are greater risks of contamination and false diagnosis [9]. Furthermore, it becomes more unreliable and difficult to distinguish low level infections as transmissions decline; hence, there is a need for alternative approaches to detection as elimination is being considered [4].
Can there be a faster, more specific, and more sensitive method of detecting malaria that can easily be implemented in resource-limited areas? The question remains among scientists globally. Can malaria be eliminated and many more lives saved by the emergence of technologies that offer early detection and differentiation of very minimal malarial infections? Does mankind stand a chance of advancement towards needle-free malaria detection, point-of-care devices, and personalized malaria medicine? For lower and lower-middle-income countries, which total 26 and 54, respectively (Table 1), according to the World Bank, will there be access to such effective diagnostic tools [10]? It is worthy of note that 11 of these countries, all in sub-Saharan Africa, bear 70% of the global malaria burden, according to the 2023 WHO report [1] (Table 1). The above-mentioned questions are but a few that remain on the minds of scientists and thus drive research.
Table 1.
Countries classified by World Bank as low or lower-middle-income economies in 2024 [1,10]. The table lists all resource-limited countries divided into low (top portion) and lower-middle (bottom portion) income countries, with special emphasis placed on the 11 countries (right portion) that together bear 70% of the global malaria burden.
| LOW AND LOWER-MIDDLE INCOME COUNTRIES | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70% GLOBAL MALARIA BURDEN | |||||||||
| LOW-INCOME COUNTRIES | Afghanistan | Burundi | Central African Republic | Chad | Eritrea | Ethiopia | Gambia | Burkina Faso | Congo, Dem. Rep |
| Guinea-Bissau | Korea, Dem. People’s Rep | Liberia | Madagascar | Malawi | Rwanda | Sierra Leone | Mali | Mozambique | |
| Somalia | South Sudan | Sudan | Syrian Arab Republic | Togo | Yemen, Rep | Niger | Uganda | ||
| LOWER-MIDDLE INCOME COUNTRIES | Angola | Algeria | Bangladesh | Benin | Bhutan | Bolivia | Cabo Verde | Cameroon | Ghana |
| Cambodia | Comoros | Congo, Rep. | Côte d’Ivoire | Djibouti | Egypt, Arab Rep. | Eswatini | India | Nigeria | |
| Guinea | Haiti | Honduras | Jordan | Iran, Islamic Rep | Kenya | Kiribati | Tanzania | ||
| Kyrgyz Republic | Lao PDR | Lebanon | Lesotho | Mauritania | Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | Mongolia | |||
| Morocco | Myanmar | Nepal | Nicaragua | Pakistan | Papua New Guinea | Philippines | |||
| Samoa | São Tomé and Principe | Senegal | Solomon Islands | Sri Lanka | Tajikistan | Timor-Leste | |||
| Tunisia | Ukraine | Uzbekistan | Vanuatu | Vietnam | Zambia | Zimbabwe | |||
Subsequently, there are several techniques that have been developed over the years to address some of the challenges with the gold standard technique. Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are fast and reliable. Malaria RDTs do not require skilled personnel or constant electricity, but relative to malaria microscopy, they are expensive, have a short shelf life, and only give qualitative results [11]. Other diagnostic techniques, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA), microarrays, aptamer-based biosensors, genomic sequencing, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), nested PCR, real-time PCR, and quantitative nucleic sequence-based amplification, are usually reserved for research and surveillance purposes. These techniques have higher sensitivity and specificity for malaria diagnosis relative to microscopy and RDTs. Notwithstanding, some of them are more laborious and expensive to deploy in resource-limited areas.
This systematic review looks at traditional and modern techniques in light of their main advantages and disadvantages, as well as the countries where they have been used, with emphasis placed on lower and lower-middle-income countries. Also, emphasis would be placed on molecular-based techniques and how common they are in resource-limited settings, which usually happen to be endemic to malaria.
2. Materials and Methods
In conducting this systematic review, an accurate and authentic outcome was ensured by adherence to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. The review was registered in the open science framework database (https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/DV6Z3 (accessed on 28 June 2024)). Relevant details needed were obtained from articles published in journals and from databases up to 2022 since the search was done in early 2023. Key search phrases used for the search included “malaria detection methods”, “emerging technologies in malaria”, “recent advances in malaria detection or diagnosis”, “emerging methods in malaria diagnosis”, “traditional methods of malaria detection”, “Point of care devices for malaria detection”, “Non-invasive or needle-free malaria detection”, and “personalized malaria medicine”. Numerous articles were obtained from databases, journals, and other publishing sites, including Google Scholar, PUBMED, and MDPI databases.
From the databases, a total of 327 were identified. After the searches, the publications were sorted out to remove duplicates, and 20 publications were removed. The records were further screened to remove all incomplete, unpublished articles, and ineligible publications. With articles published in recent years under consideration, all accessible publications were considerable options, leaving out articles from journals that needed to be purchased, were restricted, or there was not a PDF version of the complete paper readily available.
Upon abstract screening, articles were selected based on the following general criteria: a traditional or modern method of malaria detection or diagnosis was investigated. A total of 276 articles were obtained, uploaded into Mendeley Reference Manager and Endnote, and carefully reviewed for full text eligibility and results presentation.
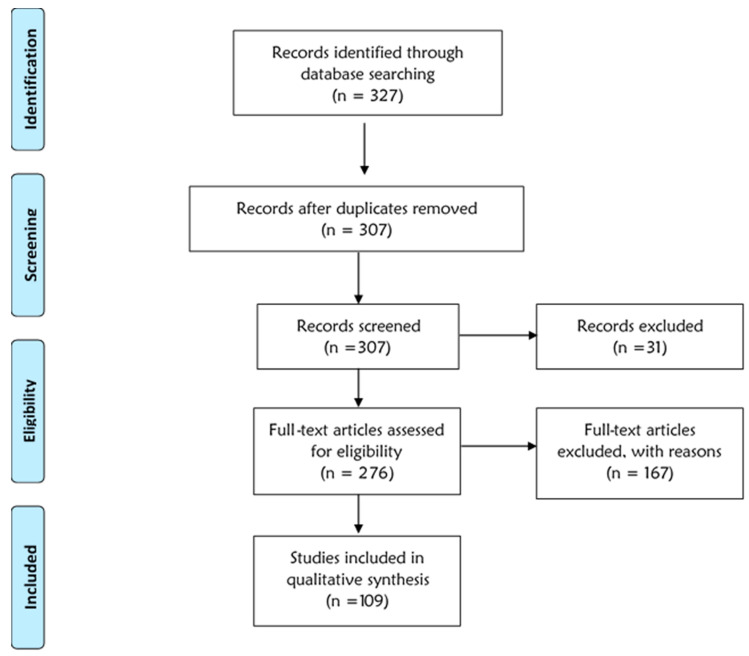
Of these articles, some investigated traditional methods, while most investigated various modern methods. Some articles were also found useful as they investigated or reviewed “emerging technologies in malaria detection” or “advances in malaria detection”, among others, and thus were used in the other parts of the review writing. After a comprehensive document screening, 167 were later removed as it was found that they did not suit the review criteria, leaving 109 to be reviewed. These articles were removed for reasons including the papers being published earlier than 2014 (for those to be analyzed), they did not specifically investigate diagnostic tools for malaria, the article obtained was not the published version, and the research scope and contents were not clear or did not focus on a possible malaria detection method. In several instances, multiple malaria detection methods were identified in a single publication; thus, the number of developed methods identified exceeded the number of publications used. Figure 1 below shows the sorting-out process.
Figure 1.
A PRISMA flow diagram showing the method of article selection.
3. Results
3.1. Traditional Methods Used for Malaria Detection
Table 2 below shows a summary of traditionally used methods of malaria detection, elaborating on their approach as well as the pros and cons of using these methods for diagnosis. Though there has been the development of new and innovative methods of detection over the years, microscopy, using thick and thin blood films coupled with Giemsa staining, remains the gold standard for the diagnosis of malaria parasitic infections [8,12].
Table 2.
Traditional methods used for malaria detection.
| Traditional Methods | Specimen Used | Summary of Procedure | Invasive/Non-Invasive | Advantages | Disadvantages | Refer-ences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin film microscopy | Blood | Thin blood smears are prepared and stained using Giemsa stain. Thin smears are examined with a 100× oil immersion objective. | Invasive | Reliable in the identification of four human plasmodium species and their various stages | Limited by quality of blood smears as well as availability of skilled microscopists. Lack of sensitivity where non-falciparum or mixed infections exist. |
[8,13,14,15,16,17,18] |
| Thick film microscopy | Blood | Thick blood smears are prepared and stained using Giemsa stain. Thin smears are examined with a 100× oil immersion objective. | Invasive | Reliable in the detection of four human plasmodium species | Limited by quality of blood smears as well as availability of skilled microscopists. | [8,13,14,15,16,17,18] |
| Morphology-based diagnosis | Blood | Optical images from Giemsa-stained infected blood are measured using Olysia and Scanning Probe Image Processor software based on morphology of red blood cells. | Invasive | Faster prediction of malaria cases | Expertise needed | [19] |
| Centrifuged buffy coat smear examination (CBCS) | Blood | Centrifugation of buffy coat is done prior to Giemsa staining and microscopic examination | Invasive | Specificity is similar to conventional method but sensitivity a bit better than conventional method | Limited by availability of skilled microscopists | [20] |
3.2. Modern Methods Used for Malaria Detection
The quest to effectively treat malaria while gravitating towards its elimination has driven the development of various tools and assays for the diagnosis of malaria (4). Table 3 and Table 4 contain recently developed methods used in the diagnosis of malaria and where they have been used. These diagnostic approaches vary greatly, ranging from biosensors and molecular assays down to computerized algorithms and automated analyzers, which have been developed or used over recent years, no earlier than 2014. The advantages and limitations of each diagnostic method are considered, as well as the summarized procedure by which it is conducted.
Table 3.
Modern (PCR/LAMP-based) methods used for malaria detection and evidence of use in developed countries.
| Modern Methods | Specimen Used | Description | Invasive/Non-Invasive | Point of Care/Molecular/Other | Advantages | Disadvantages | Developed Countries | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct conventional PCR | Blood | With plasmodium cytochrome oxidase III gene (COX-III) as target, direct conventional PCR is conducted on bloodspot samples. Results are visualized on a gel. | Invasive | Molecular | High Sensitivity; faster than nested; does not require DNA isolation | Requires much expertise and expensive | USA | [21] |
| Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | Blood | Using different primer pairs to run 2 sequential amplification reactions. Plasmodium genomic DNA extracted from dried blood spots | Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity and specificity | Time consuming, expensive, requires much expertise | Thailand, USA, Brazil, United Kingdom, Austria | [13,16,18,21,22,23,24,25] |
| Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) | Blood, Serum | DNA extracted from blood and serum samples are analyzed using the ddPCR method, which is based on water–oil emulsion droplet technology | Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity using blood samples | Low sensitivity using serum samples; expensive | Italy, Thailand |
[26,27] |
| Photo- Induced Electron transfer PCR (PET-PCR) | Blood | Total DNA is extracted from dried blood spots and PCR performed using photo-induced electron transfer fluorogenic primers | Invasive | Molecular | High sen-sitivity for parasite identification and characterization. | Requires much expertise and is expensive | USA | [15] |
| Fluoresen-ce reson-ance energy transfer (FRET) real time PCR | Blood | Real-time PCR utilizing FRET whereby fluorophores are brought in close proximity after hybridization is performed on DNA extracted from lyophilized blood samples targeting the 18S rRNA gene | Invasive | Molecular | High sensit-ivity, and allows for simultaneous quantitative and species-specific detection |
This specific protocol could not differentiate between P. vivax and P. knowlesi; expensive | United Kingdom, Austria | [22] |
| SYBR Green Real-Time PCR-RFLP Assay | Blood | Real-time PCR using sybr green dye that binds to all double-stranded DNA followed by restriction fragment polymorphism to differentiate species | Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity | Meltcurve required in PCR since Sybr green alone can be non-specific; expensive | Sweden | [28] |
| Hair qPCR | Head hairs | Hairs without roots are taken from patients and qPCR assay conducted | Non-invasive | molecular | Requires no special trans-port/storage conditions for samples | Sensitivity lower than when blood samples are used | Spain | [29] |
| Insulated Isothermal PCR (iiPCR) | Blood | PCR is performed in a portable device using an assay based on the Rayleigh–Bénard convection method | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | Portable, easy and fast operation; direct interpretation | Not as sensitive as qPCR | Malaysia | [30] |
| Lab Chip Real Time PCR (LRP) | Blood | DNA is extracted from collected blood samples and a portable LRP device is used to detect malarial parasites based on lab-on-chip technology | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | High sensitivity and specificity. Fast and cost effective | Risk of false negatives higher than traditional real-time PCR | Korea | [31] |
| Pv-mt Cox PCR | Blood | DNA is extracted from collected blood samples and qPCR with mitochondrial gene target is carried out | Invasive | Molecular | More sensitive in the detection of P. vivax | Expensive | Brazil | [32] |
| PvLAP5 and Pvs25qRT-PCR assays | Blood | Extracted RNA is subjected to quantitative reverse transcription PCR | Invasive | Molecular | Suitable assay for the determination of human transmission reservoir | Expensive | Panama | [33] |
| Other Quantita-tive PCR (qPCR) | Blood | Real-time PCR performed using primers targeting different regions and SYBR green or probe-based technology on DNA extracted from whole blood | Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity and rapid | Extreme caution needed to prevent contamination; expensive | France, Canada, USA Columbia Germany, Brazil, China, Malaysia |
[34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44] |
| Dry LAMP system (CZC-LAMP) | Blood | Blood samples are analyzed directly without extraction using the assay made up of dried reagents | Invasive | Point of care/molecular | High sensitivity and specificity; no need for prior extraction | Not widely available | [45] | |
| Particle Diffusometry (PD)-LAMP | Blood | PD, which senses images, is combined with LAMP on a smartphone-enabled device to detect low levels of parasitemia | Invasive | Point of care/molecular | Sensitivitities higher than RDTs and similar to qPCR |
Sensitivity slightly lower than nested PCR | USA | [46] |
| LAMP and MinION™ nanopore sequencer | Blood | Primers targeting the 18S–rRNA gene of all five human Plasmodium species are generated and samples subjected to LAMP. Min-ION™ nanopore sequencer is used on amplicons to identify Plasmodium spp. | Invasive | Molecular | Highly sensitive, and simple | Expensive | Japan | [47] |
| Other Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), | Blood | Extracted DNA is subjected to loop-mediated isothermal amplification with a variety of detection methods | Invasive | Point of care/molecular | Simple, low cost; can be used in resource-limited settings and point-of-care settings | Some cannot quantify par-asite density; some are insensitive towards low parasitemia and mixed infections | France, Korea, Thailand Italy, Brazil Spain, Mala-ysia, Japan, Peru, USA |
[26,34,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] |
Table 4.
Modern (non-PCR/non-LAMP-based) methods used for malaria detection and evidence of use in developed countries.
| Modern Methods | Specimen Used | Description | Invasive/Non-Invasive | Point of Care/Molecular/Other | Advantages | Disadvantages | Developed Countries | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaria SD Bioline RDT kit | Urine, Saliva, Blood | Using immuno-chromatography to detect PfhRP2 and PLDH following manufacturer’s instructions | Non-invasive/Invasive | Point of care | Effective for non-invasive detection of malaria; low cost | Low sensitivity | [64] | |
| Other (RDTs) | Blood | Immunochromatography/ according to manufacturer’s instructions |
Invasive | Point of care | Suitable for point of care in hard-to-access areas; low cost | Low sensit-ivity for some kits; poor identification of non-falciparum infections for some brands | Indonesia Australia, USA |
[14,15,17,18,65,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| Computeri-zed/digital deep mach-ine learnin-g approach | Blood | Machine learning models are used to detect malaria parasites in blood smears. Some can be integrated into smartphone detection apps | Invasive | Other | Accurate/ reliable |
For some, results are affected by quality of smears | USA, Taiwan, China, Turkey | [72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81] |
| Spectros-copy | Blood | Blood samples are analyzed using spectroscopy | Invasive | Other | Highly effective for identifying infected cell | Only qualitative results obtained | Thailand, China, Australia |
[82,83,84] |
| Portable Optical Diagnostic System (PODS) |
Blood | Works by differential optical spectroscopy. The change in optical power before and after a magnet is applied, is monitored in order to determine β-hematin concentration in whole blood | Invasive | Point of care | Portable; low cost; useful for low resource settings; high sensitivity |
Not widely available | USA | [85] |
| Ultra bright SERS nanorattles | Blood | DNA detection method that uses sandwich hybridization of magnetic bead, target sequence, and ultrabright SERS nanorattle are employed | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | Sensitive; can be automated and added to portable devi-ces for POC diagnosis; can identify SNPs hence, discri-minate betw-een wild-type and mutant parasites | Not widely available | USA | [86] |
| Automated Microscopy/Digital Analysis | Blood | Comprises a fluorescent dye staining or Giemsa staining and an automated microscopy platform and digital analysis | Invasive | Other | Rapid diagn-osis and par-asite density monitoring. High sens- itivity, linear-ity, and precision | Not widely available | Korea, Finland, Sweden | [87,88,89] |
| Flow cytometry | Blood | Parasites are detected and quantified in blood by use of analyzers utilizing flow cytometry technology | Invasive | Molecular | Rapid and high sensiti-vity; useful for mass screening | May not be able to distinguish plasmodium species | Netherlands, France, USA, South Africa, Japan |
[90,91,92,93,94] |
| Thin-Film Optical Filters | Blood | A thin film optical device is used based on optical reflectance spectrophotometry, for the parasite detection through haemozoin quantification | Invasive | Point of care | High sensitivity | High transmittance regions outside target wavelength | Portugal | [95] |
| Rotating cr- ystal magn-eto optical detection (RMOD) method | Blood | RMOD works by detection of the periodic modulation of light transmission. This is induced by hemozoin crystals which co-rotates with a rotating magnetic field | Invasive | Other | Higher sensitivity and accuracy than light microscopy | Sensitivity is poorer than PCR methods | Thailand, Hungary |
[96,97,98] |
| Hemozin-Based Malaria diagnostic device (GazelleTM) | Blood | Using magneto-optical technology, the device detects hemozoin produced by Plasmodium | Invasive | Other | Sensitivities comparable to light micr-oscopy; faster than micros-copy; portab-le; can run on battery power | Unable to distinguish between species | [16] | |
| Hemozoin-generated vapor nanobubbles | Blood vessel (transdermal) | Hemozoin generates a transient vapor nanobubble around hemozoin in response to a short and safe laser pulse. The acoustic signals of these nanobubbles that are malaria specific enable detection | Non-invasive | Point of care | Non-invasive; rapid |
Not widely available | USA | [99] |
| Electroche-mical immunosensor | Blood | Egg yolk IgY antibodies against Plasmodium vivax lactate dehydrogenase antigen are immobilized on a gold electrode surface followed by differential pulse voltammetry and contact angle measurements are made. | Invasive | Point of care | High Sensitivity for malaria caused by P. vivax | Only malaria caused by P. vivax can be detected | Brazil | [100] |
| Simplified ELISA)/PfHRP 2 ELISA | Blood | Modified ElISA was performed on blood samples. | Invasive | Point of care | High sensitivity, portable and low cost | Not widely available | Spain UK Denmark |
[101,102] |
| Multiple-xed ELISA based assay | Blood | Multiplexed ELISA-based (either planar-based array or magnetic bead-based platforms) technologies are used for malaria detection | Invasive | Molecular | Can detect malaria spe-cies mutants; have high throughput potential | Not widely available | USA | [103] |
| Dye-Cou-pledApt-amer-Capt-ured Enzy-me-Cataly-zed assay | Blood | Aptamer- and enzyme-based method is used to detect malaria infection in blood. Method can be used on instrument or instrument free platform | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | Low cost; useful for resource-limited and point-of-care settings. | Not widely available | [104] | |
| Recombinase-Aided Amplificat-ion with Lateral Flow Dip-stick Assay (RAA-LFD) |
Blood | A combination of recombinase-aided amplification lasting for 15 min at 37 degrees and lateral flow dipstick is used to detect plasmodium species in blood | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | Highly sensitive, specific, low cost, convenient for on-site screening and low resource settings. |
Not widely available | China | [105] |
| Portable image-based Cytometer | Blood | P. falciparum-infected blood cells are identified and counted from Giemsa-stained smears using the image based portable cytometer. | Invasive | Other | Simple to operate; low cost |
Not widely available | Singapore | [106] |
| Two-stage sample-to-answer sy-stem based on nucleic acid ampl-ification approach | Blood | It combines the dimethyl adipimidate (DMA)/thin film sample processing (DTS) technique and the Mach–Zehnder interferometer isothermal solid-phase DNA amplification (MZI-IDA) technique to detect infection in blood |
Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity, rapid | Not widely available | Singapore, Korea |
[107] |
| Fluorescen-ce In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Assays | Blood | Detects and localizes specific malaria nucleic acid sequences by hybridizing with complementary sequences that are labeled with fluorescent probes | Invasive | Molecular | High sensitivity | Skilled expertise required. | USA | [108,109] |
| NMR-based hemozoin detection | Blood | Detection is based on the ability to recognize the paramagnetic susceptibility of malaria hemozoin crystals | Invasive | Molecular/point of care | High sensitivity and rapid | Not widely available | Australia, Singapore, USA | [110,111,112] |
| Multi-omics | Varies | Integrating data from different omic methods | Invasive/non-invasive | Other | Comprehen-sive underst-anding of the infection | Requires skilled experitise | Austria USA Columbia |
[113,114,115,116] |
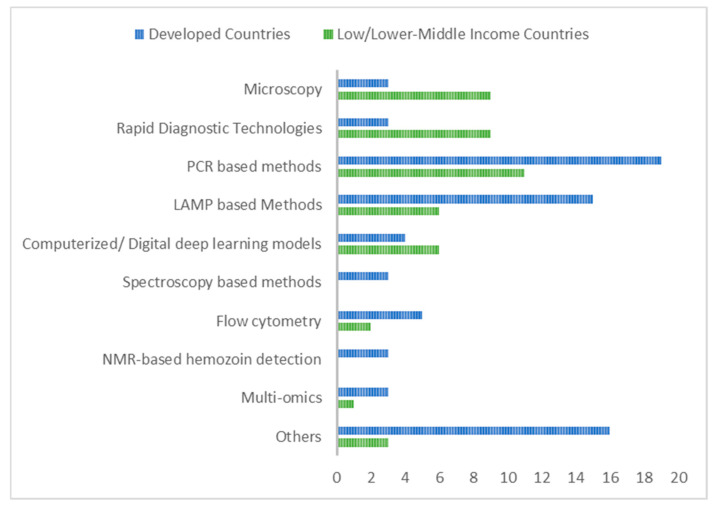
Table 5 analyzes evidence of the use of some recently developed detection tools in lower and lower-middle-income countries where there are often resource limitations. The test types that featured most frequently in publications were PCR techniques (eleven), followed by RDT tests (nine), then LAMP techniques and computerized/digital deep machine learning approaches (six each). In all, twenty-one countries had publications featuring modern malaria diagnostic methods.
Table 5.
Evidence of use of modern methods of malaria detection in low and lower-middle-income countries.
| Modern Method | Resource-Limited Countries | References |
|---|---|---|
| Malaria rapid test kit (SD Bioline RDT kit) using urine and saliva samples | Ghana | [64] |
| Other rapid diagnostic tests | Nigeria, Senegal, Kenya, Benin, Pakistan, Burkina Faso | [14,15,17,18,65,66,68,69] |
| Nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Pakistan, Nigeria, Myanmar, Honduras, India | [13,16,18,23,25] |
| Hair qPCR | Rwanda | [29] |
| Other quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) | Bangladesh, Eritrea, Tanzania D.R. Congo, Sierra Leone, Cambodia |
[35,36,37,38,40] |
| Dry LAMP system (CZC-LAMP | Zambia | [45] |
| Other loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), | India, Tanzania, Senegal, Ghana | [48,56,57,58,59] |
| Computerized/digital deep machine learning approach | Nigeria, Uganda, Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Zambia, | [59,75,77,78,79,80] |
| The rotating-crystal magneto-optical detection (RMOD) method | Papua New Guinea | [96] |
| Hemozin-based malaria diagnostic device (GazelleTM) | Honduras | [16] |
| Flow cytometry | Burkina Faso, India | [90,93] |
| Dye-coupled aptamer-captured enzyme-catalyzed assay | India | [104] |
| Multi-omics | India | [114] |
In Figure 2, the various methods of malaria detection reported from the identified studies have been represented graphically, indicating which diagnostic trends are being largely investigated, used more, or have gained much research interest. The chart represents malaria diagnostic developments investigated from 2014 until 2022. PCR-based methods and LAMP-based methods were the most prevalent methods.
Figure 2.
Frequencies of malaria detection/diagnosis methods in reviewed publications.
4. Discussion
Critical to achieving effective control, treatment, and subsequent elimination of malaria is the timely detection of the parasitic infection. In the face of this threatening infection, continuous progress and innovative research are required, which leads to the development of new tools that will be useful in the fight against malaria [117]. This article reviewed the recent developments in malaria diagnostic methods and their potential for point-of-care and personalized malaria care, with special emphasis on the use of these methods in economically challenged countries.
The findings from this review suggest great advancement recently in malaria diagnostics. Research efforts by many scientists around the globe have progressed from developing improved malaria microscopy techniques into enhanced and more accurate molecular, immunological, computerized, digital methods of detection, automated analyzers, and point-of-care devices. Studies suggest that the influence of the old age infection on global health outcomes has urged on the design of more efficient diagnostics, with efforts directed at the development of point-of-care devices useful for resource-limited areas [7]. For an active drive towards the elimination of malaria, an early detection approach capable of revealing low levels of the parasitic infection is imperative [3].
As observed in Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5, the outcome of this review indicates that recent malaria detection methods actively being used or investigated include traditional methods, molecular techniques with polymerase chain reaction (PCR), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-based assays, and machine learning/computerized techniques (that exploit the physical and/or biological properties of Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes to enhance malaria diagnosis), among others. Figure 2 shows the frequencies of detection methods as identified from various articles published over the last decade. Several other technologies and chemical assays are also being designed to tackle the malaria burden. RDTs were among the commonly used or researched modern methods in resource-limited settings, as seen in Table 5 and Figure 2. This is not surprising since they are relatively low cost and easy to use.
Studies confirm PCR-based techniques as having widespread use globally as they are highly sensitive and capable of detecting very low parasitemia levels [3,22,35]. Polymerase chain reaction basically makes use of DNA extracted from whole blood or other samples. The process continues with denaturation, amplification, and elongation steps, after which the sensitivity and specificity of the assay can be assessed [35]. It is proposed that the PCR method, under equal reaction parameters, can diagnose all five species of the plasmodium parasitic infection [35]. Our findings reveal that a wide range of PCR assays have been developed or used over the past decade, which are less laborious and provide much faster and more accurate results [22]. Furthermore, PCR-based assays are widely preferred due to several reasons, including simultaneous species-specific detection and quantification, higher sensitivity, higher specificity, less time consuming, easy to use, and capable of diagnosing subclinical infections [13,18,22,23,41,42].
Though PCR is an effective approach to malaria detection, it is limited by the requirement of costly laboratory facilities and expertise and thus less beneficial to resource-limited areas and at the point of care [3]. Despite that, quite a number of studies in resource-limited settings, including some African countries, utilized PCR-based techniques, as shown in Table 5 and Figure 2 [13,16,18,23,25,29,35,36,37,38,40]. Other advanced PCR techniques, such as lab chip real-time PCR (LRP) and hair qPCR, were found to be suitable alternatives for point-of-care or resource-limited settings, though no evidence was found of the former currently being used or researched in lower or lower-middle-income countries [29,31]. Gómez-Luque et al. proposed that due to limitations observed, more research is required to affirm the use of the hair qPCR as an efficient technique for malaria detection [29]. The one advantage the hair qPCR has over other PCR types is the use of non-invasive samples. LRP, however, being highly sensitive, specific, and less expensive will be beneficial for diagnosis and control in malaria-endemic countries [31].
LAMP-based assays have also dominated research on malaria diagnostics. As seen in Table 3, studies have shown the development or use of various LAMP assays, which are effective malaria diagnostics [118]. Rei Yan et al. reviewed LAMP assays and found them easy to use in regions where there is limited access to clinical expertise and molecular biology equipment. Modified LAMP based assays such as multiplex LAMP with dipstick DNA chromatography, high throughput LAMP, 18S rRNA LAMP, mediated LAMP combined with lateral flow detection (LFD), etc., are highly sensitive, easy to use, consistent, convenient, cost effective, and useful in point-of-care situations [55,56,58,59], thus enabling an approach towards personalized healthcare. Table 5 provides evidence of the development and use of LAMP techniques in lower and lower-middle-income countries, including countries in sub-Saharan Africa where malaria is endemic [45,48,56,57,58,59].
Other molecular methods worthy of note as they double as point-of-care or easy-to-use methods include nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based hemozoin detection, ultra-bright SERS nanorattles, recombinase-aided amplification with lateral flow dipstick assay, and dye-coupled aptamer-captured enzyme-catalyzed assay [86,104,105,110,111,112]. Though the latter two could be used in resource-limited settings due to their low cost, the study found only a dye-coupled aptamer-captured enzyme-catalyzed assay used in India [104]. Veiga and Peng identified nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based hemozoin detection as having the potential of enabling personalized malaria medicine (that is, malaria treatment tailored to individual characteristics) with needleless diagnosis foresighted [119]. This technology may offer the detection of phenotypic variants, which are observable variations in characteristics among parasites of the same species as a result of genetic diversity, host–parasite interactions, or environmental factors, among others [120,121]. For example, there are drug-resistant variants, those with surface antigen variations, and variants with different clinical presentations, among others [121,122,123]. The ability to detect such variants would increase diagnostic accuracy and be considerably useful against parasite drug resistance. Acquiring these time- and patient-specific phenotypic identifiers is a basic step to personalized malaria medicine as variants continually rise [119]. The one advantage that phenotypic variant determination using NMR technology may have over nucleic acid amplification-based methods for genomic profiling is the extremely fast turnaround time for some of the devices [110]. Unfortunately, there was no evidence of such methods being used in lower and lower-middle-income countries as per the studied published data in the research articles reviewed.
Furthermore, a number of other technologies have emerged capable of point-of-care diagnosis. Unlike the traditional microscopy and commonly used RDTs, some of these methods were found to be highly sensitive, non-invasive as far as sample collection was concerned, and cost effective, even though there was no evidence that cost-effective ones were necessarily being used in economically challenged settings [85,95,99,100,101,102]. In addition to these, Aggarwal et al. classify omics-based diagnostics as another important category to malaria diagnosis and elimination [124]. Multi-omics combines genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, phenomics, and transcriptomics in the investigation of biomarkers optimal for disease diagnosis and treatment. Though each omics has individual limitations, collectively, multi-omics can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of malaria infections, which can lead to more effective treatments [124]. In this review, the only struggling economy we found using multi-omics was India. No African nation was indicated.
5. Conclusions
Given the literature reviewed, there is adequate evidence to suggest that malaria detection or diagnosis will progress significantly in the next decade and beyond towards needleless detection. This advancement will however require increased, detailed, and specified research into the various molecular identifiers and phenotypic variant characteristics of malaria infection while enhancing the accuracy, precision, and specificity of the modernized point-of-care diagnostic tools. With this in view, precedence is duly set for the use of personalized medicine in the treatment of malaria infections. Notwithstanding, the traditional thin and thick film microscopy and RDTs will continue to play an important role in the accurate detection of malaria infections, especially in resource-limited areas where there is less access to modernized diagnostic tools and little research into advanced malaria detection methods. It is, however, encouraging to see that PCR-based and LAMP-based tests were seen being utilized in these areas, including African countries. However, other modern molecular/point-of-care tests were not being utilized in sub-Saharan Africa. Findings of this study show that approximately a quarter (26%) of a total of eighty countries in low and lower-middle-income settings employ state-of-the-art methods for malaria diagnostics. This underscores the need for governments, non-governmental organizations, and funding bodies to intensify efforts towards malaria diagnostics and research in the fight against malaria.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.Y.; methodology, A.K.Y., J.O. and J.E.C.; software, A.K.Y. and J.O.; validation, A.K.Y., J.O., J.E.C., N.I.N.-T., E.O., I.K.Y., A.A.K.-K., G.A., I.A.-B. and D.A.P.; formal analysis, A.K.Y. and J.O.; investigation, A.K.Y., J.O. and J.E.C.; resources, A.K.Y., J.O., J.E.C., N.I.N.-T., E.O., I.K.Y., A.A.K.-K., G.A., I.A.-B. and D.A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.Y., J.O. and J.E.C.; writing—review and editing, A.K.Y., J.O., J.E.C., N.I.N.-T., E.O., I.K.Y., A.A.K.-K., G.A., I.A.-B. and D.A.P.; funding acquisition, A.K.Y., N.I.N.-T., E.O., I.K.Y., A.A.K.-K., G.A., I.A.-B. and D.A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This review work received no external funding.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.WHO World Malaria Report. 2023. [(accessed on 19 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240086173.
- 2.Tetteh-Quarcoo P.B., Dayie N.T., Adutwum-Ofosu K.K., Ahenkorah J., Afutu E., Amponsah S.K., Abdul-Rahman M., Kretchy J.-P., Ocloo J.Y., Nii-Trebi N.I. Unravelling the perspectives of day and night traders in selected markets within a sub-saharan african city with a malaria knowledge, attitude and practice survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:3468. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zheng Z., Cheng Z. Advances in molecular diagnosis of malaria. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2017;80:155–192. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2016.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.malERA Consultative Group on Diagnoses and Diagnostics A research agenda for malaria eradication: Diagnoses and diagnostics. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1000396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yalley A.K., Ahiatrogah S., Kafintu-Kwashie A.A., Amegatcher G., Prah D., Botwe A.K., Adusei-Poku M.A., Obodai E., Nii-Trebi N.I. A systematic review on suitability of molecular techniques for diagnosis and research into infectious diseases of concern in resource-limited settings. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022;44:4367–4385. doi: 10.3390/cimb44100300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.WHO Global Malaria Program. 2024. [(accessed on 10 June 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/case-management/diagnosis/microscopy.
- 7.Krampa F.D., Aniweh Y., Awandare G.A., Kanyong P. Recent progress in the development of diagnostic tests for malaria. Diagnostics. 2017;7:54. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics7030054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Singh K., Bharti P.K., Devi N.C., Ahmed N., Sharma A. Plasmodium malariae Detected by Microscopy in the International Bordering Area of Mizoram, a Northeastern State of India. Diagnostics. 2022;12:2015. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12082015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Edwards H. Tales from the bench: Laboratory diagnosis of malaria. Trop. Dr. 2011;41:106–107. doi: 10.1258/td.2010.100199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Worldbank World Bank Country and Lending Groups. 2024. [(accessed on 13 May 2024)]. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups.
- 11.Azikiwe C.C., Ifezulike C., Siminialayi I., Amazu L.U., Enye J., Nwakwunite O. A comparative laboratory diagnosis of malaria: Microscopy versus rapid diagnostic test kits. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012;2:307–310. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60029-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iqbal J., Hira P.R., Al-Ali F., Khalid N., Sher A. Modified Giemsa staining for rapid diagnosis of malaria infection. Med. Princ. Pract. 2003;12:156–159. doi: 10.1159/000070751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nadeem M.F., Khattak A.A., Yaqoob A., Awan U.A., Zeeshan N. Assessment of Microscopic detection of Malaria with Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction in War-torn Federally Administered Tribal Areas of Pakistan. Acta Parasitol. 2021;66:1186–1192. doi: 10.1007/s11686-021-00374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Awosolu O.B., Yahaya Z.S., Farah Haziqah M.T. Efficacy of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (Pfhrp 2) rapid diagnostic test (RDT) and microscopy in the detection of falciparum malaria among symptomatic patients in Akure, Nigeria. Trop. Biomed. 2022;39:144–149. doi: 10.47665/tb.39.1.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Badiane A., Thwing J., Williamson J., Rogier E., Diallo M.A., Ndiaye D. Sensitivity and specificity for malaria classification of febrile persons by rapid diagnostic test, microscopy, parasite DNA, histidine-rich protein 2, and IgG: Dakar, Senegal 2015. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022;121:92–97. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.04.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fontecha G., Escobar D., Ortiz B., Pinto A., Serrano D., Valdivia H.O. Field Evaluation of a Hemozoin-Based Malaria Diagnostic Device in Puerto Lempira, Honduras. Diagnostics. 2022;12:1206. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ahmad A., Soni P., Kumar L., Singh M.P., Verma A.K., Sharma A., Das A., Bharti P.K. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction, microscopy, and rapid diagnostic test in malaria detection in a high burden state (Odisha) of India. Pathog. Glob. Health. 2021;115:267–272. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2021.1893484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ugah U.I., Alo M.N., Owolabi J.O., Okata-Nwali O.D.G., Ekejindu I.M., Ibeh N., Elom M.O. Evaluation of the utility value of three diagnostic methods in the detection of malaria parasites in endemic area. Malar. J. 2017;16:189. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1838-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karimi A., Navidbakhsh M., Haghi A.M., Faghihi S. A morphology-based method for the diagnosis of red blood cells parasitized by Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2014;46:368–375. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2014.880186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mohanty S., Sharma R., Deb M. Usefulness of a centrifuged buffy coat smear examination for diagnosis of malaria. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2015;33:63–67. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.148380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Echeverry D.F., Deason N.A., Davidson J., Makuru V., Xiao H., Niedbalski J., Kern M., Russell T.L., Burkot T.R., Collins F.H., et al. Human malaria diagnosis using a single-step direct-PCR based on the Plasmodium cytochrome oxidase III gene. Malar. J. 2016;15:128. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1185-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schneider R., Lamien-Meda A., Auer H., Wiedermann-Schmidt U., Chiodini P.L., Walochnik J. Validation of a novel FRET real-time PCR assay for simultaneous quantitative detection and discrimination of human Plasmodium parasites. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0252887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ranjan P., Ghoshal U. Utility of nested polymerase chain reaction over the microscopy and immuno-chromatographic test in the detection of Plasmodium species and their clinical spectrum. Parasitol. Res. 2016;115:3375–3385. doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Freitas D.R.C.d., Gomes L.T., Fontes C.J.F., Tauil P.L., Pang L.W., Duarte E.C. Sensitivity of nested-PCR for Plasmodium detection in pooled whole blood samples and its usefulness to blood donor screening in endemic areas. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2014;50:242–246. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2014.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li P., Zhao Z., Wang Y., Xing H., Parker D.M., Yang Z., Baum E., Li W., Sattabongkot J., Sirichaisinthop J., et al. Nested PCR detection of malaria directly using blood filter paper samples from epidemiological surveys. Malar. J. 2014;13:175. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pomari E., Silva R., Moro L., Marca G.L., Perandin F., Verra F., Bisoffi Z., Piubelli C. Droplet digital PCR for the detection of Plasmodium falciparum DNA in whole blood and serum: A comparative analysis with other molecular methods. Pathogens. 2020;9:478. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9060478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Srisutham S., Saralamba N., Malleret B., Rénia L., Dondorp A.M., Imwong M. Four human Plasmodium species quantification using droplet digital PCR. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0175771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xu W., Morris U., Aydin-Schmidt B., Msellem M.I., Shakely D., Petzold M., Björkman A., Mårtensson A. SYBR green real-time PCR-RFLP assay targeting the Plasmodium cytochrome B gene—A highly sensitive molecular tool for malaria parasite detection and species determination. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0120210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gómez-Luque A., Parejo J.C., Clavijo-Chamorro M.Z., López-Espuela F., Munyaruguru F., Lorenzo S.B., Monroy I., Gómez-Nieto L.C. Method for malaria diagnosis based on extractions of samples using non-invasive techniques: An opportunity for the nursing clinical practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;17:5551. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chua K.H., Lee P.C., Chai H.C. Development of insulated isothermal PCR for rapid on-site malaria detection. Malar. J. 2016;15:134. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1183-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim J., Lim D.H., Mihn D.-C., Nam J., Jang W.S., Lim C.S. Clinical usefulness of labchip real-time PCR using lab-on-a-chip technology for diagnosing malaria. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021;59:77. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2021.59.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barbosa L.R., da Silva E.L., de Almeida A.C., Salazar Y.E., Siqueira A.M., Alecrim M.d.G.C., Vieira J.L.F., Bassat Q., de Lacerda M.V., Monteiro W.M. An Ultra-Sensitive Technique: Using Pv-mtCOX1 qPCR to Detect Early Recurrences of Plasmodium vivax in Patients in the Brazilian Amazon. Pathogens. 2020;10:19. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10010019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Obaldía N., Barahona I., Lasso J., Avila M., Quijada M., Nuñez M., Marti M. Comparison of PvLAP5 and Pvs25 qRT-PCR assays for the detection of Plasmodium vivax gametocytes in field samples preserved at ambient temperature from remote malaria endemic regions of Panama. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022;16:e0010327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bouzayene A., Zaffaroullah R., Bailly J., Ciceron L., Sarrasin V., Cojean S., Argy N., Houzé S., Joste V., Angoulvant A., et al. Evaluation of two commercial kits and two laboratory-developed qPCR assays compared to LAMP for molecular diagnosis of malaria. Malar. J. 2022;21:204. doi: 10.1186/s12936-022-04219-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sazed S.A., Kibria M.G., Alam M.S. An optimized real-time qpcr method for the effective detection of human malaria infections. Diagnostics. 2021;11:736. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grignard L., Nolder D., Sepúlveda N., Berhane A., Mihreteab S., Kaaya R., Phelan J., Moser K., van Schalkwyk D.A., Campino S., et al. A novel multiplex qPCR assay for detection of Plasmodium falciparum with histidine-rich protein 2 and 3 (pfhrp2 and pfhrp3) deletions in polyclonal infections. EBioMedicine. 2020;55:102757. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aimeé K.K., Lengu T.B., Nsibu C.N., Umesumbu S.E., Ngoyi D.M., Chen T. Molecular detection and species identification of Plasmodium spp. infection in adults in the Democratic Republic of Congo: A populationbased study. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0242713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Canier L., Khim N., Kim S., Eam R., Khean C., Loch K., Ken M., Pannus P., Bosman P., Stassijns J., et al. Malaria PCR detection in Cambodian low-transmission settings: Dried blood spots versus venous blood samples. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015;92:573–577. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Phuong M., Lau R., Ralevski F., Boggild A.K. Sequence-based optimization of a quantitative real-time PCR assay for detection of Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014;52:1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03477-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Leski T.A., Taitt C.R., Swaray A.G., Bangura U., Reynolds N.D., Holtz A., Yasuda C., Lahai J., Lamin J.M., Baio V., et al. Use of real-time multiplex PCR, malaria rapid diagnostic test and microscopy to investigate the prevalence of Plasmodium species among febrile hospital patients in Sierra Leone. Malar. J. 2020;19:84. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03163-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Murillo E., Muskus C., Agudelo L.A., Vélez I.D., Ruiz-Lopez F. A new high-resolution melting analysis for the detection and identification of Plasmodium in human and Anopheles vectors of malaria. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36515-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Amaral L.C., Robortella D.R., Guimarães L.F.F., Limongi J.E., Fontes C.J.F., Pereira D.B., De Brito C.F.A., Kano F.S., De Sousa T.N., Carvalho L.H. Ribosomal and non-ribosomal PCR targets for the detection of low-density and mixed malaria infections. Malar. J. 2019;18:154. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2781-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Frickmann H., Wegner C., Ruben S., Behrens C., Kollenda H., Hinz R., Rojak S., Schwarz N.G., Hagen R.M., Tannich E. Evaluation of the multiplex real-time PCR assays RealStar malaria S&T PCR kit 1.0 and FTD malaria differentiation for the differentiation of Plasmodium species in clinical samples. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019;31:101442. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2019.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lee P.C., Chong E.T.J., Anderios F., Lim Y.A.L., Chew C.H., Chua K.H. Molecular detection of human Plasmodium species in Sabah using PlasmoNex™ multiplex PCR and hydrolysis probes real-time PCR. Malar. J. 2015;14:28. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0542-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hayashida K., Kajino K., Simukoko H., Simuunza M., Ndebe J., Chota A., Namangala B., Sugimoto C. Direct detection of falciparum and non-falciparum malaria DNA from a drop of blood with high sensitivity by the dried-LAMP system. Parasites Vectors. 2017;10:26. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1949-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Colbert A.J., Co K., Lima-Cooper G., Lee D.H., Clayton K.N., Wereley S.T., John C.C., Linnes J.C., Kinzer-Ursem T.L. Towards the use of a smartphone imaging-based tool for point-of-care detection of asymptomatic low-density malaria parasitaemia. Malar. J. 2021;20:380. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03894-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Imai K., Tarumoto N., Misawa K., Runtuwene L.R., Sakai J., Hayashida K., Eshita Y., Maeda R., Tuda J., Murakami T., et al. A novel diagnostic method for malaria using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and MinION™ nanopore sequencer. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017;17:621. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2718-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Azam M., Upmanyu K., Gupta R., Sruthy K.S., Matlani M., Savargaonkar D., Singh R. Development of two-tube loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for differential diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax and its comparison with loopamp™ malaria. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1689. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jang W.S., Lim D.H., Choe Y., Jee H., Moon K.C., Kim C., Choi M., Park I.S., Lim C.S. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for diagnosis of Plasmodium spp., Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1950. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11111950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mohon A.N., Getie S., Jahan N., Alam M.S., Pillai D.R. Ultrasensitive loop mediated isothermal amplification (US-LAMP) to detect malaria for elimination. Malar. J. 2019;18:350. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2979-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Viana G.M.R., Silva-Flannery L., Barbosa D.R.L., Lucchi N., do Valle S.C.N., Farias S., Barbalho N., Marchesini P., Rossi J.C.N., Udhayakumar V., et al. Field evaluation of a real time loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay (RealAmp) for malaria diagnosis in Cruzeiro do Sul, Acre, Brazil. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0200492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cuadros J., Martin Ramírez A., González I.J., Ding X.C., Perez Tanoira R., Rojo-Marcos G., Gómez-Herruz P., Rubio J.M. LAMP kit for diagnosis of non-falciparum malaria in Plasmodium ovale infected patients. Malar. J. 2017;16:20. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1669-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lau Y.L., Lai M.Y., Fong M.Y., Jelip J., Mahmud R. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for identification of five human Plasmodium species in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016;94:336–339. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Patel J.C., Lucchi N.W., Srivastava P., Lin J.T., Sug-Aram R., Aruncharus S., Bharti P.K., Shukla M.M., Congpuong K., Satimai W., et al. Field evaluation of a real-time fluorescence loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay, realamp, for the diagnosis of Malaria in Thailand and India. J. Infect. Dis. 2014;210:1180–1187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Moonga L.C., Hayashida K., Kawai N., Nakao R., Sugimoto C., Namangala B., Yamagishi J. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for simultaneous detection of spotted fever group rickettsiae and malaria parasites by dipstick DNA chromatography. Diagnostics. 2020;10:897. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Aydin-Schmidt B., Morris U., Ding X.C., Jovel I., Msellem M.I., Bergman D., Islam A., Ali A.S., Polley S., Gonzalez I.J., et al. Field evaluation of a high throughput loop mediated isothermal amplification test for the detection of asymptomatic Plasmodium infections in Zanzibar. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0169037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lucchi N.W., Gaye M., Diallo M.A., Goldman I.F., Ljolje D., Deme A.B., Badiane A., Ndiaye Y.D., Barnwell J.W., Udhayakumar V., et al. Evaluation of the Illumigene Malaria LAMP: A Robust Molecular Diagnostic Tool for Malaria Parasites. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:36808. doi: 10.1038/srep36808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sharma S., Kumar S., Ahmed M.Z., Bhardwaj N., Singh J., Kumari S., Savargaonkar D., Anvikar A.R., Das J. Advanced multiplex loop mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP) combined with lateral flow detection (LFD) for rapid detection of two prevalent malaria species in india and melting curve analysis. Diagnostics. 2022;12:32. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Aninagyei E., Boakye A.A., Tettey C.O., Ntiri K.A., Ofori S.O., Tetteh C.D., Aphour T.T., Rufai T. Utilization of 18s ribosomal RNA LAMP for detecting Plasmodium falciparum in microscopy and rapid diagnostic test negative patients. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0275052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lai M.Y., Ooi C.H., Jaimin J.J., Lau Y.L. Evaluation of WarmStart colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for diagnosis of Malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020;102:1370–1372. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Barazorda K.A., Salas C.J., Braga G., Ricopa L., Ampuero J.S., Siles C., Sanchez J.F., Montano S., Lizewski S.E., Joya C.A., et al. Validation study of Boil & Spin Malachite Green Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (B&S MG-LAMP) versus microscopy for malaria detection in the Peruvian Amazon. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0258722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Vincent J.P., Komaki-Yasuda K., Iwagami M., Kawai S., Kano S. Combination of PURE-DNA extraction and LAMP-DNA amplification methods for accurate malaria diagnosis on dried blood spots 11 Medical and Health Sciences 1108 Medical Microbiology. Malar. J. 2018;17:373. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2527-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cordray M.S., Richards-Kortum R.R. A paper and plastic device for the combined isothermal amplification and lateral flow detection of Plasmodium DNA. Malar. J. 2015;14:472. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0995-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Aninagyei E., Abraham J., Atiiga P., Antwi S.D., Bamfo S., Acheampong D.O. Evaluating the potential of using urine and saliva specimens for malaria diagnosis in suspected patients in Ghana. Malar. J. 2020;19:349. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03427-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Turnbull L.B., Ayodo G., Knight V., John C.C., McHenry M.S., Tran T.M. Evaluation of an ultrasensitive HRP2–based rapid diagnostic test for detection of asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia among children in western Kenya. Malar. J. 2022;21:337. doi: 10.1186/s12936-022-04351-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Briand V., Cottrell G., Tuike Ndam N., Martiáñez-Vendrell X., Vianou B., Mama A., Kouwaye B., Houzé S., Bailly J., Gbaguidi E., et al. Prevalence and clinical impact of malaria infections detected with a highly sensitive HRP2 rapid diagnostic test in Beninese pregnant women. Malar. J. 2020;19:188. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03261-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wardhani P., Butarbutar T.V., Adiatmaja C.O., Betaubun A.M., Hamidah N., Aryati. Performance comparison of two malaria rapid diagnostic test with real time polymerase chain reaction and gold standard of microscopy detection method. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020;12:8731. doi: 10.4081/idr.2020.8731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Naeem M.A., Ahmed S., Khan S.A. Detection of asymptomatic carriers of malaria in Kohat district of Pakistan. Malar. J. 2018;17:44. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2191-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Maltha J., Guiraud I., Lompo P., Kaboré B., Gillet P., Van Geet C., Tinto H., Jacobs J. Accuracy of PfHRP2 versus Pf-pLDH antigen detection by malaria rapid diagnostic tests in hospitalized children in a seasonal hyperendemic malaria transmission area in Burkina Faso. Malar. J. 2014;13:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fedele P.L., Wheeler M., Lemoh C., Chunilal S. Immunochromatographic antigen testing alone is sufficient to identify asymptomatic refugees at risk of severe malaria presenting to a single health service in Victoria. Pathology. 2014;46:551–554. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kim J., Cao X.E., Finkelstein J.L., Cárdenas W.B., Erickson D., Mehta S. A two-colour multiplexed lateral flow immunoassay system to differentially detect human malaria species on a single test line. Malar. J. 2019;18:313. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2957-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Abubakar A., Ajuji M., Yahya I.U. Deepfmd: Computational analysis for malaria detection in blood-smear images using deep-learning features. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021;4:82. doi: 10.3390/asi4040082. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kassim Y.M., Palaniappan K., Yang F., Poostchi M., Palaniappan N., Maude R.J., Antani S., Jaeger S. Clustering-Based Dual Deep Learning Architecture for Detecting Red Blood Cells in Malaria Diagnostic Smears. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021;25:1735–1746. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3034863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sriporn K., Tsai C.F., Tsai C.E., Wang P. Analyzing malaria disease using effective deep learning approach. Diagnostics. 2020;10:744. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Nakasi R., Mwebaze E., Zawedde A. Mobile-aware deep learning algorithms for malaria parasites and white blood cells localization in thick blood smears. Algorithms. 2021;14:17. doi: 10.3390/a14010017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Yang F., Poostchi M., Yu H., Zhou Z., Silamut K., Yu J., Maude R.J., Jaeger S., Antani S. Deep Learning for Smartphone-Based Malaria Parasite Detection in Thick Blood Smears. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020;24:1427–1438. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2939121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Manescu P., Shaw M.J., Elmi M., Neary-Zajiczek L., Claveau R., Pawar V., Kokkinos I., Oyinloye G., Bendkowski C., Oladejo O.A., et al. Expert-level automated malaria diagnosis on routine blood films with deep neural networks. Am. J. Hematol. 2020;95:883–891. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Islam M.R., Nahiduzzaman M., Goni M.O.F., Sayeed A., Anower M.S., Ahsan M., Haider J. Explainable Transformer-Based Deep Learning Model for the Detection of Malaria Parasites from Blood Cell Images. Sensors. 2022;22:4358. doi: 10.3390/s22124358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Abdurahman F., Fante K.A., Aliy M. Malaria parasite detection in thick blood smear microscopic images using modified YOLOV3 and YOLOV4 models. BMC Bioinform. 2021;22:112. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04036-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chibuta S., Acar A.C. Real-time Malaria Parasite Screening in Thick Blood Smears for Low-Resource Setting. J. Digit. Imaging. 2020;33:763–775. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00284-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ashraf S., Khalid A., de Vos A.L., Feng Y., Rohrbach P., Hasan T. Malaria Detection Accelerated: Combing a High-Throughput NanoZoomer Platform with a ParasiteMacro Algorithm. Pathogens. 2022;11:1182. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kongklad G., Chitaree R., Taechalertpaisarn T., Panvisavas N., Nuntawong N. Discriminant Analysis PCA-LDA Assisted Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Direct Identification of Malaria-Infected Red Blood Cells. Methods Protoc. 2022;5:49. doi: 10.3390/mps5030049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wang W., Dong R.L., Gu D., He J.A., Yi P., Kong S.K., Ho H.P., Loo J.F.C., Wang W., Wang Q. Antibody-free rapid diagnosis of malaria in whole blood with surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy using Nanostructured Gold Substrate. Adv. Med. Sci. 2020;65:86–92. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2019.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Heraud P., Chatchawal P., Wongwattanakul M., Tippayawat P., Doerig C., Jearanaikoon P., Perez-Guaita D., Wood B.R. Infrared spectroscopy coupled to cloud-based data management as a tool to diagnose malaria: A pilot study in a malaria-endemic country. Malar. J. 2019;18:348. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2945-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.McBirney S.E., Chen D., Scholtz A., Ameri H., Armani A.M. Rapid Diagnostic for Point-of-Care Malaria Screening. ACS Sens. 2018;3:1264–1270. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.8b00269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ngo H.T., Gandra N., Fales A.M., Taylor S.M., Vo-Dinh T. Sensitive DNA detection and SNP discrimination using ultrabright SERS nanorattles and magnetic beads for malaria diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016;81:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yoon J., Jang W.S., Nam J., Mihn D.C., Lim C.S. An automated microscopic Malaria parasite detection system using digital image analysis. Diagnostics. 2021;11:527. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kim J.D., Nam K.M., Park C.Y., Kim Y.S., Song H.J. Automatic detection of malaria parasite in blood images using two parameters. Technol. Health Care. 2015;24:S33–S39. doi: 10.3233/THC-151049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Linder N., Turkki R., Walliander M., Mårtensson A., Diwan V., Rahtu E., Pietikäinen M., Lundin M., Lundin J. A malaria diagnostic tool based on computer vision screening and visualization of Plasmodium falciparum candidate areas in digitized blood smears. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e104855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Post A., Kaboré B., Reuling I.J., Bognini J., Van Der Heijden W., Diallo S., Lompo P., Kam B., Herssens N., Lanke K., et al. The XN-30 hematology analyzer for rapid sensitive detection of malaria: A diagnostic accuracy study. BMC Med. 2019;17:103. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1334-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Dumas C., Bienvenu A.L., Girard S., Picot S., Debize G., Durand B. Automated Plasmodium detection by the Sysmex XN hematology analyzer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018;71:594–599. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2017-204878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Racsa L.D., Gander R.M., Southern P.M., McElvania TeKippe E., Doern C., Luu H.S. Detection of intracellular parasites by use of the CellaVision DM96 analyzer during routine screening of peripheral blood smears. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015;53:167–171. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01783-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Pillay E., Khodaiji S., Bezuidenhout B.C., Litshie M., Coetzer T.L. Evaluation of automated malaria diagnosis using the Sysmex XN-30 analyser in a clinical setting. Malar. J. 2019;18:15. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2655-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Hashimoto M., Yokota K., Kajimoto K., Matsumoto M., Tatsumi A., Yamamoto K., Hyodo T., Matsushita K., Minakawa N., Mita T., et al. Quantitative detection of Plasmodium falciparum using, luna-fl, a fluorescent cell counter. Microorganisms. 2020;8:1356. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Costa M.S., Baptista V., Ferreira G.M., Lima D., Minas G., Veiga M.I., Catarino S.O. Multilayer thin-film optical filters for reflectance-based malaria diagnostics. Micromachines. 2021;12:890. doi: 10.3390/mi12080890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Orbán Á., Longley R.J., Sripoorote P., Maneechai N., Nguitragool W., Butykai Á., Mueller I., Sattabongkot J., Karl S., Kézsmárki I. Sensitive detection of Plasmodium vivax malaria by the rotating-crystal magneto-optical method in Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:18547. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97532-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Pukáncsik M., Molnár P., Orbán Á., Butykai Á., Marton L., Kézsmárki I., Vértessy B.G., Kamil M., Abraham A., Aly A.S.I. Highly sensitive and rapid characterization of the development of synchronized blood stage malaria parasites via magneto-optical hemozoin quantification. Biomolecules. 2019;9:579. doi: 10.3390/biom9100579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Orbán Á., Butykai Á., Molnár A., Pröhle Z., Fülöp G., Zelles T., Forsyth W., Hill D., Müller I., Schofield L., et al. Evaluation of a novel magneto-optical method for the detection of malaria parasites. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e96981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lukianova-Hleb E.Y., Campbell K.M., Constantinou P.E., Braam J., Olson J.S., Ware R.E., Sullivan D.J., Lapotko D.O. Hemozoin-generated vapor nanobubbles for transdermal reagent- and needle-free detection of malaria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:900–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316253111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Gandarilla A.M.D., Glória J.C., Barcelay Y.R., Mariuba L.A.M., Brito W.R. Electrochemical immunosensor for detection of Plasmodium vivax lactate dehydrogenase. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2022;117:e220085. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760220085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.de la Serna E., Arias-Alpízar K., Borgheti-Cardoso L.N., Sanchez-Cano A., Sulleiro E., Zarzuela F., Bosch-Nicolau P., Salvador F., Molina I., Ramírez M., et al. Detection of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in 1 h using a simplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2021;1152:338254. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hemben A., Ashley J., Tothill I.E. Development of an Immunosensor for Pf HRP 2 as a biomarker for malaria detection. Biosensors. 2017;7:28. doi: 10.3390/bios7030028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Jang I.K., Jiménez A., Rashid A., Barney R., Golden A., Ding X.C., Domingo G.J., Mayor A. Comparison of two malaria multiplex immunoassays that enable quantification of malaria antigens. Malar. J. 2022;21:176. doi: 10.1186/s12936-022-04203-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Singh N.K., Jain P., Das S., Goswami P. Dye coupled aptamer-captured enzyme catalyzed reaction for detection of pan malaria and p. Falciparum species in laboratory settings and instrument-free paper-based platform. Anal. Chem. 2019;91:4213–4221. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Lin H., Zhao S., Liu Y., Shao L., Ye Y., Jiang N., Yang K. Rapid Visual Detection of Plasmodium Using Recombinase-Aided Amplification With Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022;12:922146. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.922146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Yang D., Subramanian G., Duan J., Gao S., Bai L., Chandramohanadas R., Ai Y. A portable image-based cytometer for rapid malaria detection and quantification. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0179161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Liu Q., Nam J., Kim S., Lim C.T., Park M.K., Shin Y. Two-stage sample-to-answer system based on nucleic acid amplification approach for detection of malaria parasites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016;82:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.03.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Shah J., Mark O., Weltman H., Barcelo N., Lo W., Wronska D., Kakkilaya S., Rao A., Bhat S.T., Sinha R., et al. Fluorescence In Situ hybridization (FISH) assays for diagnosing malaria in endemic areas. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0136726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Shah J., Poruri A., Mark O., Khadilka U., Mohring F., Moon R.W., Ramasamy R. A dual colour fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay for identifying the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi with a potential application for the specific diagnosis of knowlesi malaria in peripheral-level laboratories of Southeast Asia. Parasites Vectors. 2017;10:342. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2273-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Peng W.K., Kong T.F., Ng C.S., Chen L., Huang Y., Bhagat A.A.S., Nguyen N.-T., Preiser P.R., Han J. Micromagnetic resonance relaxometry for rapid label-free malaria diagnosis. Nat. Med. 2014;20:1069–1073. doi: 10.1038/nm.3622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Thamarath S.S., Xiong A., Lin P.-H., Preiser P.R., Han J. Enhancing the sensitivity of micro magnetic resonance relaxometry detection of low parasitemia Plasmodium falciparum in human blood. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:2555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38805-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Fook Kong T., Ye W., Peng W.K., Wei Hou H., Marcos, Preiser P.R., Nguyen N.-T., Han J. Enhancing malaria diagnosis through microfluidic cell enrichment and magnetic resonance relaxometry detection. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:11425. doi: 10.1038/srep11425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Tomescu O.A., Mattanovich D., Thallinger G.G. Integrative omics analysis. A study based on Plasmodium falciparum mRNA and protein data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014;8:S4. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-S2-S4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Awasthi G., Tyagi S., Kumar V., Patel S.K., Rojh D., Sakrappanavar V., Kochar S.K., Talukdar A., Samanta B., Das A. A proteogenomic analysis of haptoglobin in malaria. PROTEOMICS–Clin. Appl. 2018;12:1700077. doi: 10.1002/prca.201700077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Lindner S.E., Swearingen K.E., Shears M.J., Walker M.P., Vrana E.N., Hart K.J., Minns A.M., Sinnis P., Moritz R.L., Kappe S.H. Transcriptomics and proteomics reveal two waves of translational repression during the maturation of malaria parasite sporozoites. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:4964. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12936-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gardinassi L.G., Arévalo-Herrera M., Herrera S., Cordy R.J., Tran V., Smith M.R., Johnson M.S., Chacko B., Liu K.H., Darley-Usmar V.M. Integrative metabolomics and transcriptomics signatures of clinical tolerance to Plasmodium vivax reveal activation of innate cell immunity and T cell signaling. Redox Biol. 2018;17:158–170. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Commonwealth The Commonwealth Malaria Report. 2022. [(accessed on 15 June 2024)]. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/commonwealth-malaria-report-2022.
- 118.Yan S.L.R., Wakasuqui F., Wrenger C. Point-of-care tests for malaria: Speeding up the diagnostics at the bedside and challenges in malaria cases detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020;98:115122. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Veiga M.I., Peng W.K. Rapid phenotyping towards personalized malaria medicine. Malar. J. 2020;19:68. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-3149-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Su X.-Z., Zhang C., Joy D.A. Host-malaria parasite interactions and impacts on mutual evolution. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020;10:587933. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.587933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Laishram D.D., Sutton P.L., Nanda N., Sharma V.L., Sobti R.C., Carlton J.M., Joshi H. The complexities of malaria disease manifestations with a focus on asymptomatic malaria. Malar. J. 2012;11:29. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Leski T.A., Taitt C.R., Colston S.M., Bangura U., Holtz A., Yasuda C.Y., Reynolds N.D., Lahai J., Lamin J.M., Baio V. Prevalence of malaria resistance-associated mutations in Plasmodium falciparum circulating in 2017–2018, Bo, Sierra Leone. Front. Microbiol. 2022;13:1059695. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1059695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Bull P.C., Berriman M., Kyes S., Quail M.A., Hall N., Kortok M.M., Marsh K., Newbold C.I. Plasmodium falciparum variant surface antigen expression patterns during malaria. PLoS Pathog. 2005;1:e26. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Aggarwal S., Peng W.K., Srivastava S. Multi-omics advancements towards Plasmodium vivax malaria diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2021;11:2222. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.