Abstract
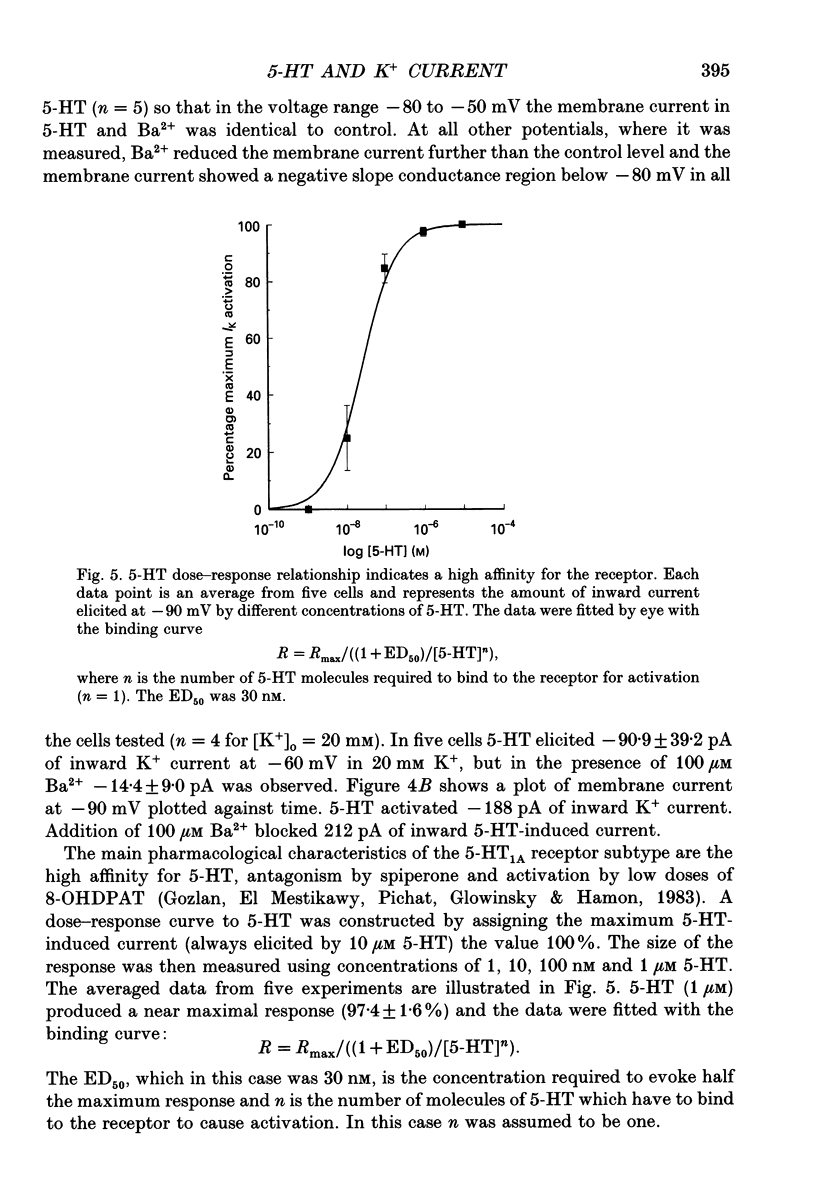
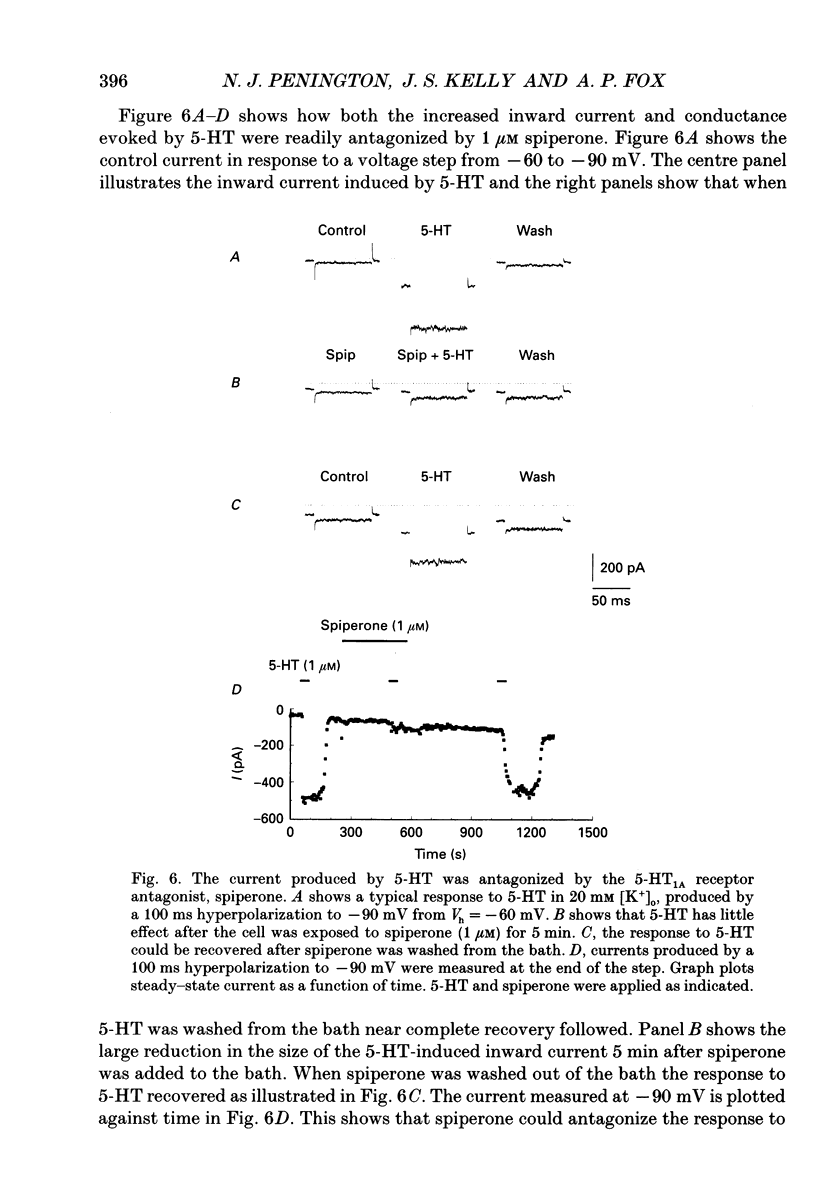
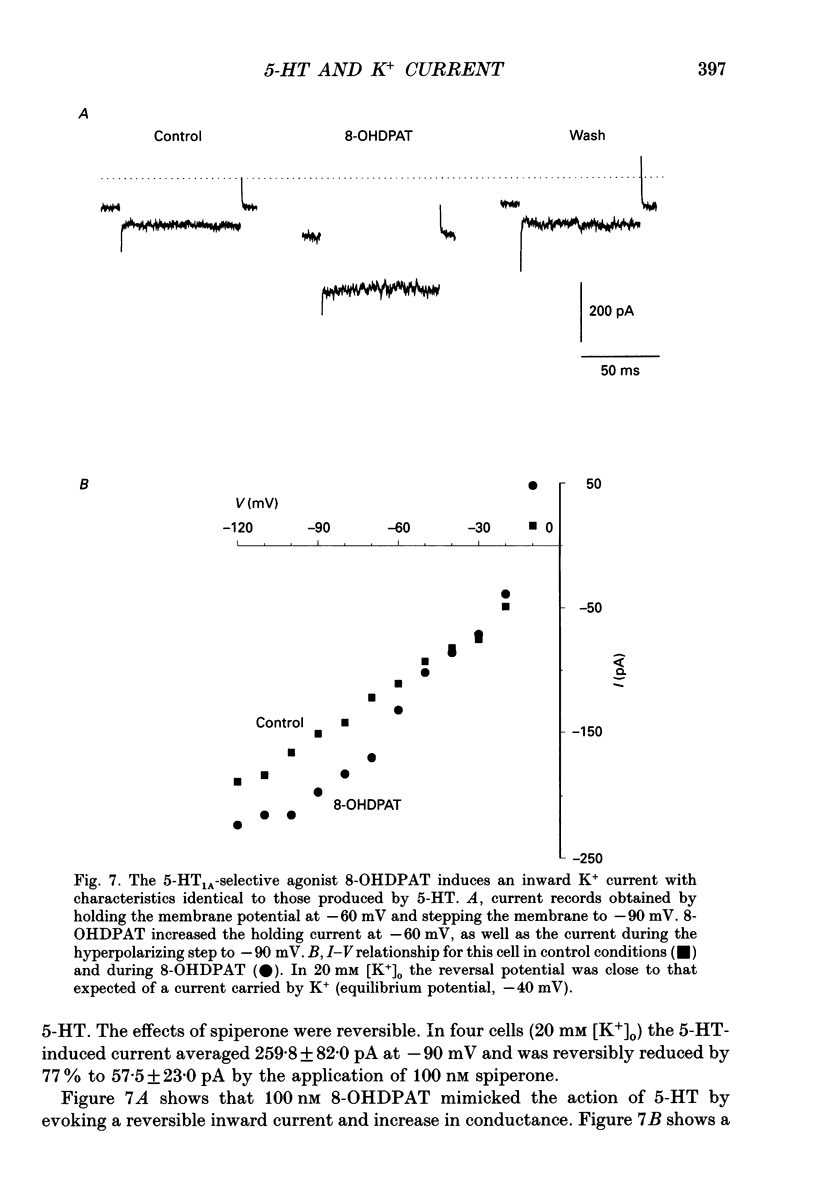
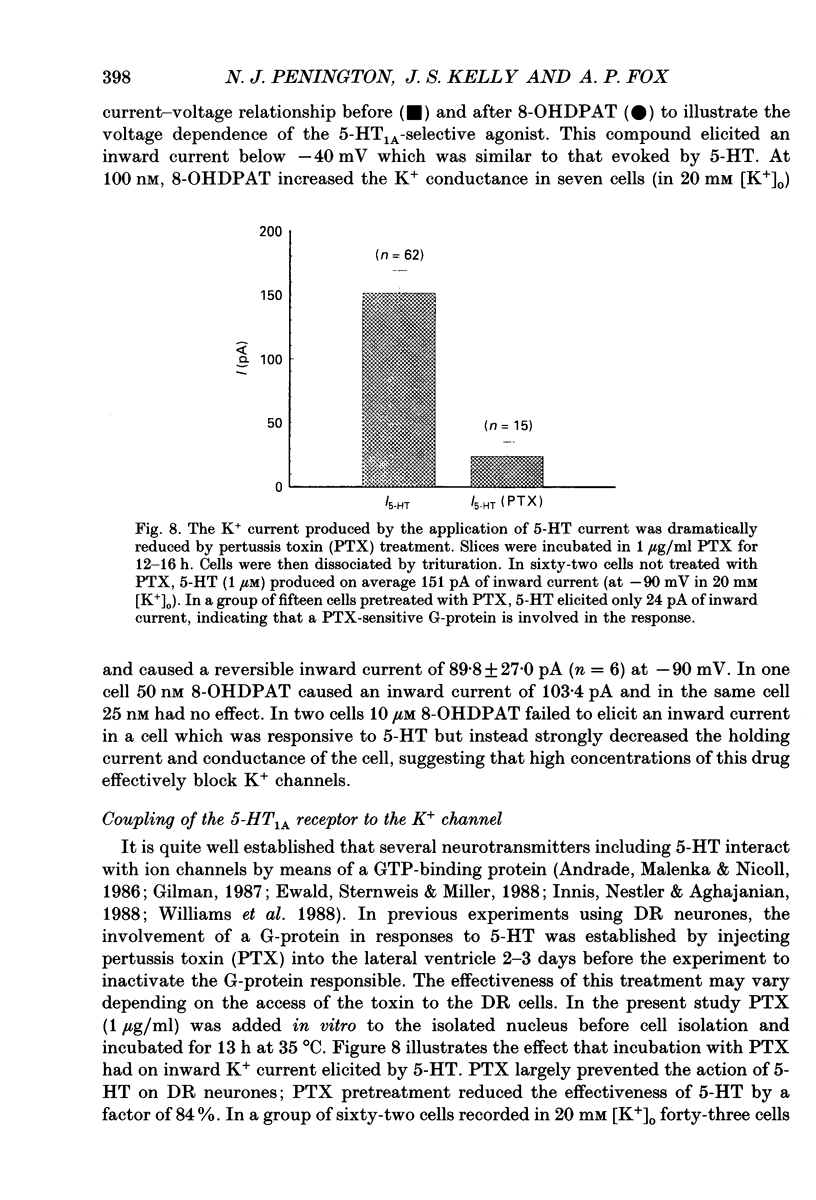
1. An inwardly rectifying K+ current activated by serotonin (5-HT) was recorded from acutely isolated adult dorsal raphe (DR) neurones using the whole-cell recording mode of the patch clamp technique. 2. The 5-HT-induced K+ current (I5-HT) was only visible at an [K+]0 > 5 mM and it was observed in 69% of the cells. 3. The reversal potential for I5-HT was close to the potassium equilibrium potential and was shifted by 51 mV per 10-fold change in [K+]0 indicating that I5-HT was carried predominantly by K+. The chord conductance of I5-HT at -90 mV was proportional to the external [K+] raised to a fractional power. 4. A dose-response relationship revealed that I5-HT was activated with an ED50 of 30 nM. Ba2+ (0.1 mM) blocked I5-HT completely. Spiperone reversibly antagonized the response to 5-HT and 8-OHDPAT (8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin) mimicked the response indicating that the receptor activated was of the 5-HT1A subtype. 5. The response to 5-HT was largely prevented by in vitro pretreatment of the cells with pertussis toxin (PTX) indicating the involvement of a PTX-sensitive G-protein in the transduction mechanism. 6. cAMP and lipoxygenase metabolites, both implicated in the modulation of similar currents in other preparations, were found not to alter the effectiveness of 5-HT. 7. Glibenclamide and tolbutamide, blockers of the ATP-regulated K+ channel, did not reduce the effect of 5-HT in DR neurones. 8. These results show that in acutely isolated adult DR neurones 5-HT activates an inwardly rectifying K+ current and this involves a PTX-sensitive G-protein in the transduction pathway which may interact with the K+ channel directly.
Full text
PDF


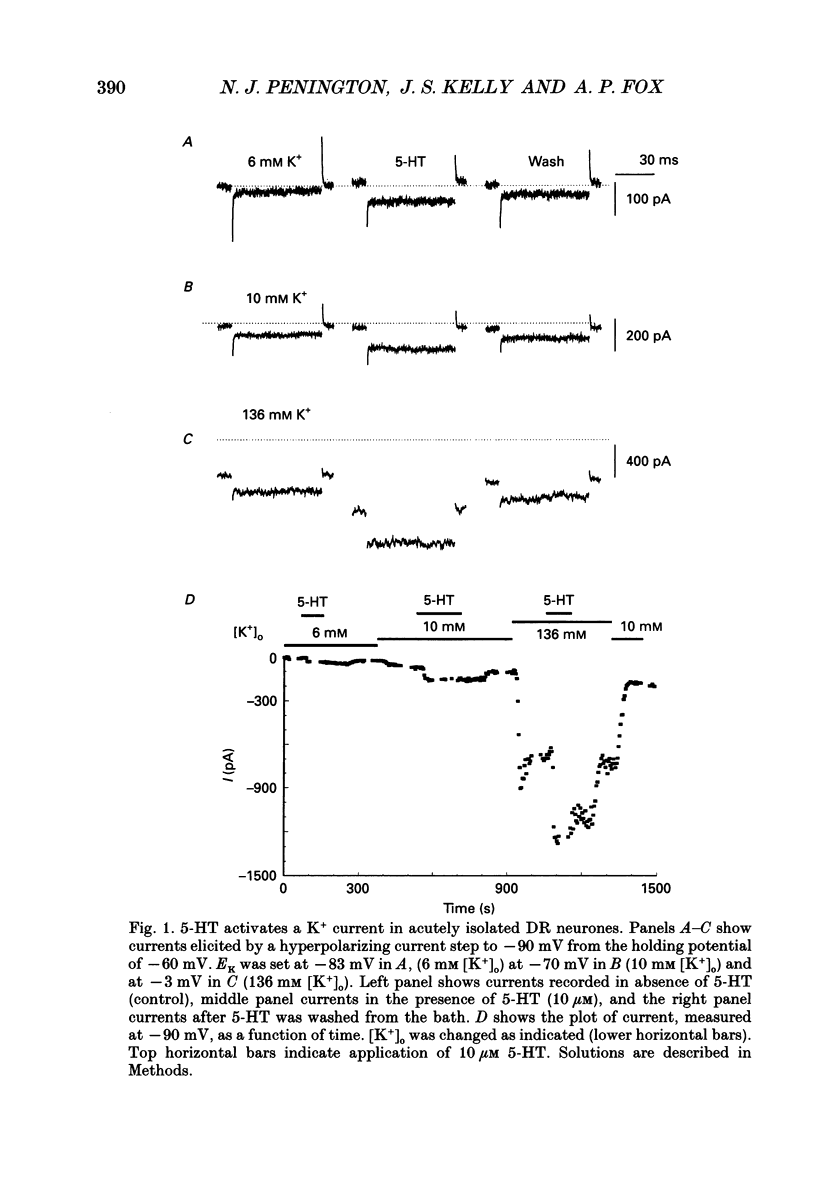
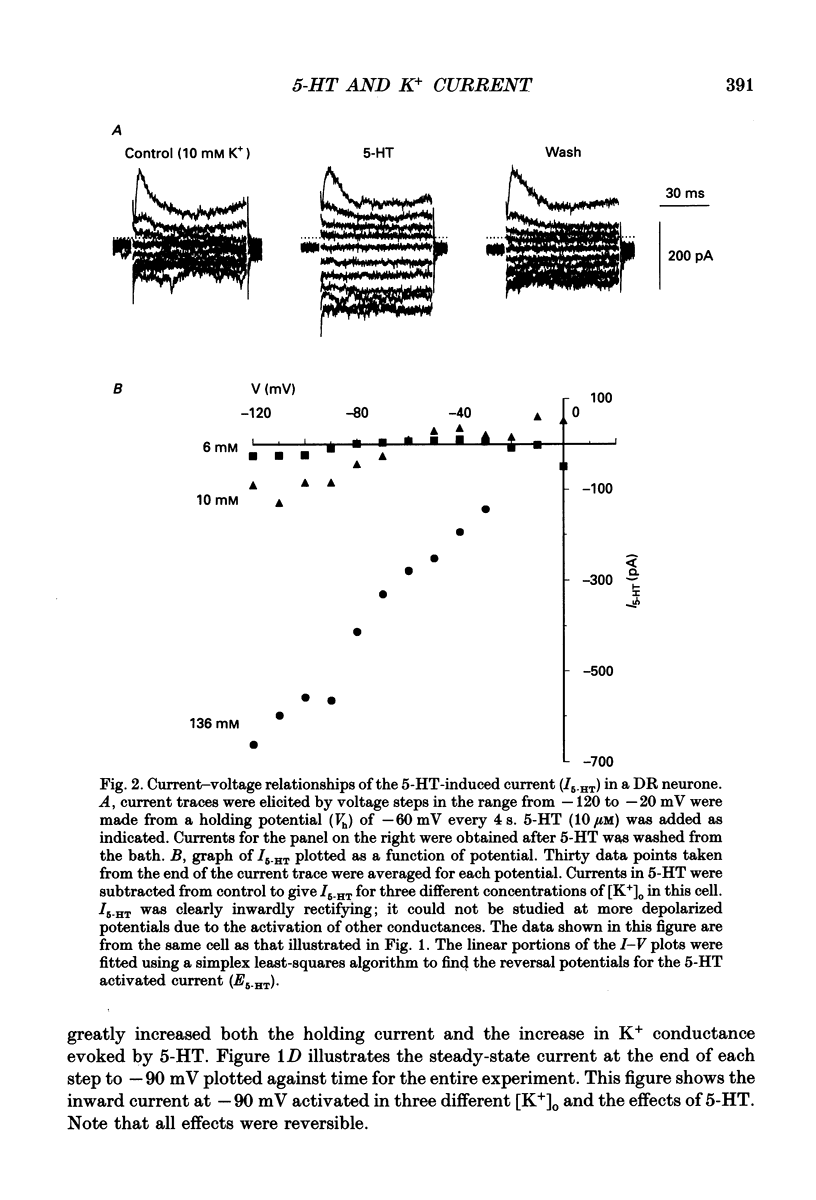
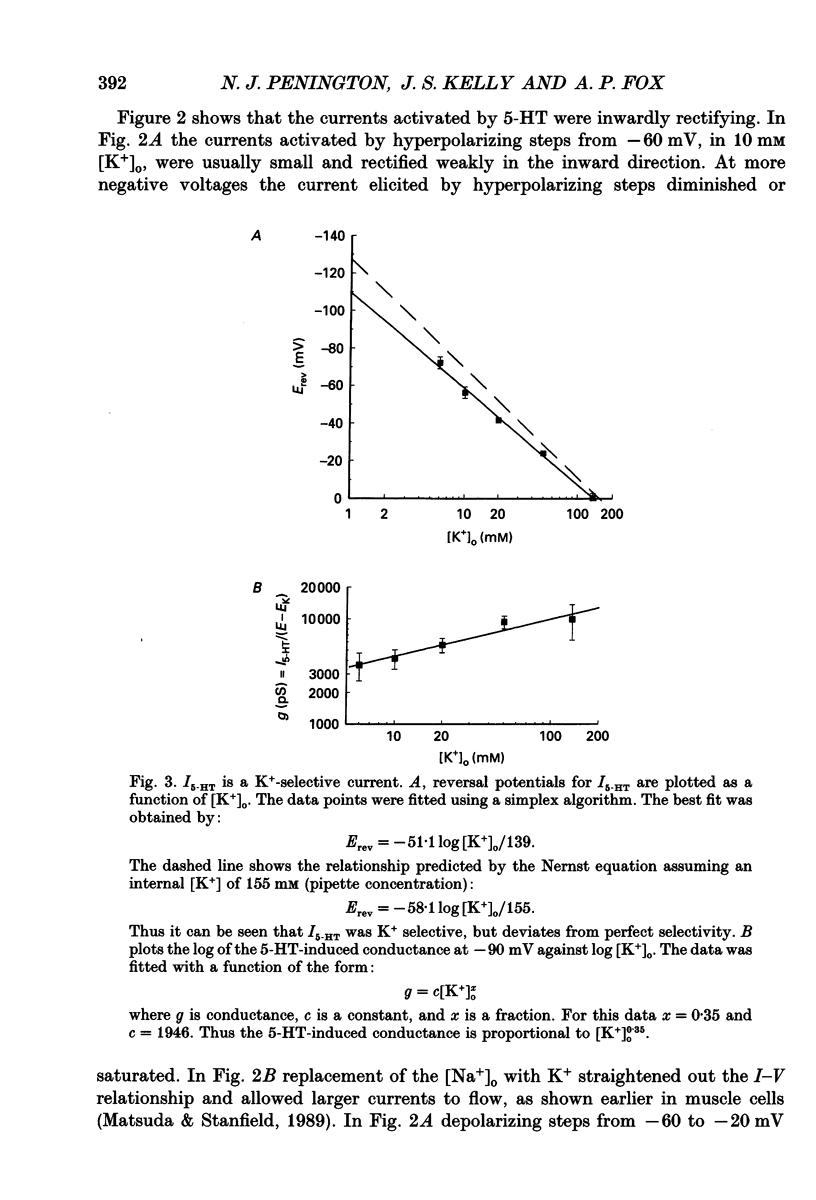

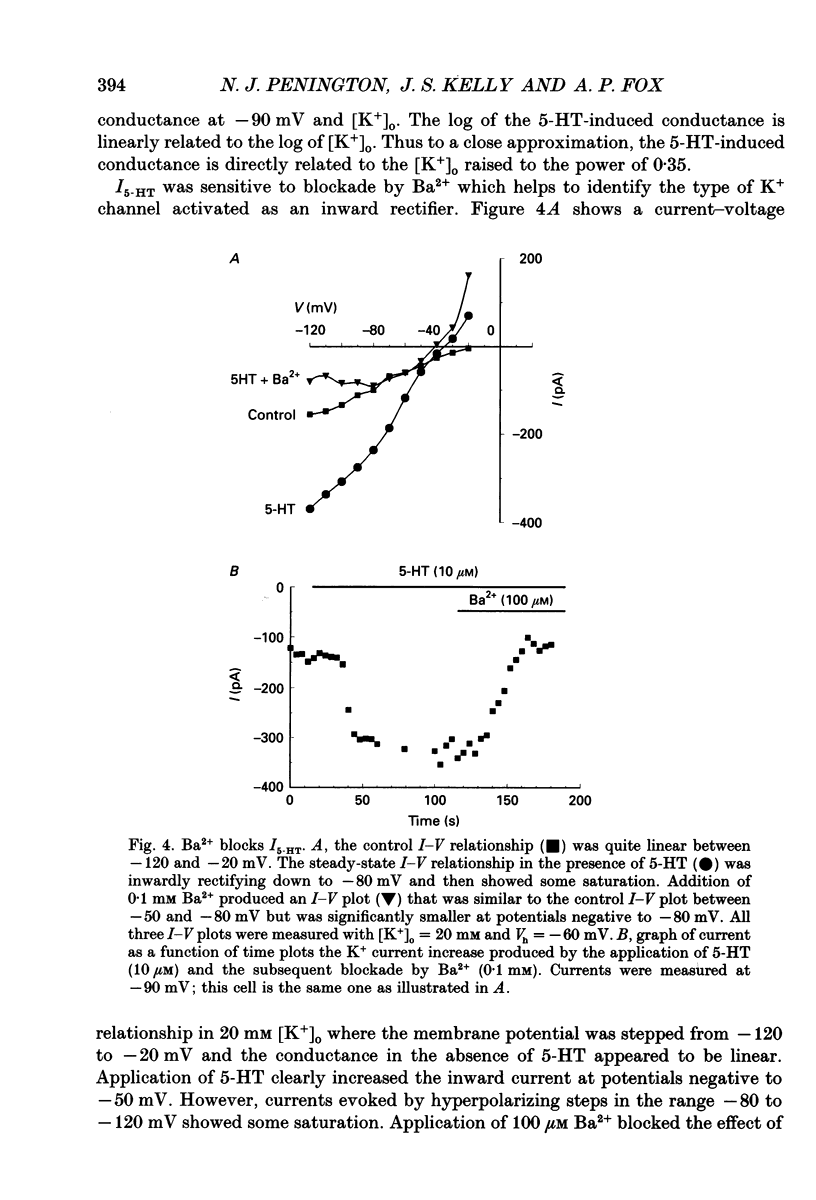






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K., Lakoski J. M. Hyperpolarization of serotonergic neurons by serotonin and LSD: studies in brain slices showing increased K+ conductance. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 2;305(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Aghajanian G. K. Opiate- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor-induced hyperpolarizations of locus ceruleus neurons in brain slices: reversal by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate analogues. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2359–2364. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02359.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Galvan M. Fast inward-rectifying current accounts for anomalous rectification in olfactory cortex neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:153–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A receptors which inhibit cAMP production in hippocampal and cortical neurons in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;33(2):178–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald D. A., Sternweis P. C., Miller R. J. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go-induced coupling of neuropeptide Y receptors to Ca2+ channels in sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3633–3637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozlan H., El Mestikawy S., Pichat L., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Identification of presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors using a new ligand: 3H-PAT. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):140–142. doi: 10.1038/305140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ozawa S., Sand O. Voltage clamp analysis of two inward current mechanisms in the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):617–644. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Nestler E. J., Aghajanian G. K. Evidence for G protein mediation of serotonin- and GABAB-induced hyperpolarization of rat dorsal raphe neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 30;459(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Lewis D. L., Graziadei L., Neer E. J., Bar-Sagi D., Clapham D. E. G-protein beta gamma-subunits activate the cardiac muscarinic K+-channel via phospholipase A2. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):557–560. doi: 10.1038/337557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Ito H., Sugimoto T., Shimizu T., Miki I., Ui M. Arachidonic acid metabolites as intracellular modulators of the G protein-gated cardiac K+ channel. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):555–557. doi: 10.1038/337555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan E. S., Kramer R. H. Neuropeptide modulation of single calcium and potassium channels detected with a new patch clamp configuration. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):545–547. doi: 10.1038/348545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Matsuura H., Noma A. Triple-barrel structure of inwardly rectifying K+ channels revealed by Cs+ and Rb+ block in guinea-pig heart cells. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:139–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Stanfield P. R. Single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in cultured muscle cells from rat and mouse. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:111–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. E., Krnjević K. Some measurements of extracellular potassium activity in the mammalian central nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;50(0):129–143. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9023-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Z., Colmers W. F., Williams J. T. 5-HT-mediated synaptic potentials in the dorsal raphe nucleus: interactions with excitatory amino acid and GABA neurotransmission. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Aug;62(2):481–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington N. J., Kelly J. S., Fox A. P. A study of the mechanism of Ca2+ current inhibition produced by serotonin in rat dorsal raphe neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3594–3609. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington N. J., Kelly J. S., Fox A. P. Unitary properties of potassium channels activated by 5-HT in acutely isolated rat dorsal raphe neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:407–426. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington N. J., Kelly J. S. Serotonin receptor activation reduces calcium current in an acutely dissociated adult central neuron. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):751–758. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90201-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Volterra A., Dale N., Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Belardetti F. Lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid as second messengers for presynaptic inhibition of Aplysia sensory cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):38–43. doi: 10.1038/328038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeper J., Hainsworth A. H., Ashcroft F. M. Tolbutamide reverses membrane hyperpolarisation induced by activation of D2 receptors and GABAB receptors in isolated substantia nigra neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):473–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00370758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Trube G. Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:641–657. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Smith P. A., Zidichouski J. A. Effects of muscarine and adrenaline on neurones from Rana pipiens sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:471–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo Constantino, Cholley Béatrice, El Mestikawy Salah, Gozlan Henri, Hamon Michel. Direct Immunohistochemical Evidence of the Existence of 5-HT1A Autoreceptors on Serotoninergic Neurons in the Midbrain Raphe Nuclei. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(12):1144–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trulson M. E., Jacobs B. L. Raphe unit activity in freely moving cats: correlation with level of behavioral arousal. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 9;163(1):135–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A. Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Aghajanian G. K. Antidromically identified serotonergic neurons in the rat midbrain raphe: evidence for collateral inhibition. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90719-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Colmers W. F., Pan Z. Z. Voltage- and ligand-activated inwardly rectifying currents in dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3499–3506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Higashi H. 5-Hydroxytryptamine mediates inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat dorsal raphe neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 7;53(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidichouski J. A., Kehoe M. P., Wong K., Smith P. A. Elevation of intracellular cyclic AMP concentration fails to inhibit adrenaline-induced hyperpolarization in amphibian sympathetic neurons. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;96(4):779–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


