Abstract
1. In order to examine the sensitivity to local anaesthetics of afferent neural feedback from working muscle during dynamic exercise, sixteen subjects cycled for 12 min before and after epidural anaesthesia using 1% lidocaine. The presence of afferent neural blockade was verified by elimination of the blood pressure response to a cold pressor test, laser-induced evoked potentials and increases in pain detection and tolerance thresholds of the foot. Conversely, epidural anaesthesia had no effect on these variables in the unblocked skin areas or on electrically evoked potentials in blocked or unblocked skin. 2. During dynamic exercise, heart rate increased as did mean arterial pressure and cardiac output. Mean arterial pressure remained at the exercise level during post-exercise ischaemia, but heart rate and cardiac output decreased while total peripheral resistance increased. Epidural anaesthesia did not significantly affect these variables during rest, dynamic exercise, post-exercise ischaemia or recovery. 3. The results of this study show that, in order to affect blood pressure during dynamic exercise, epidural anaesthesia must block the pressor response to post-exercise ischaemia. The implication of these data is that complete or almost complete block of group III and/or group IV muscle afferents is necessary to inhibit the pressor response to dynamic exercise in man.
Full text
PDF




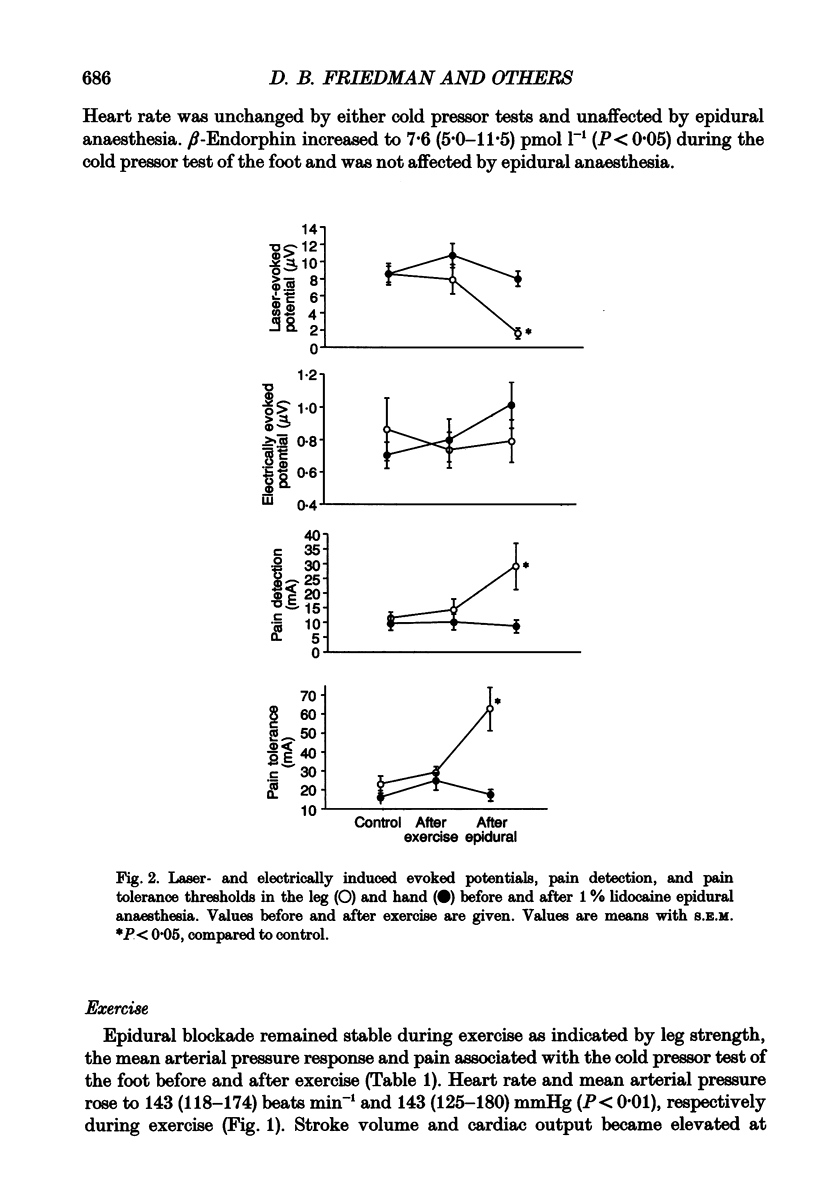
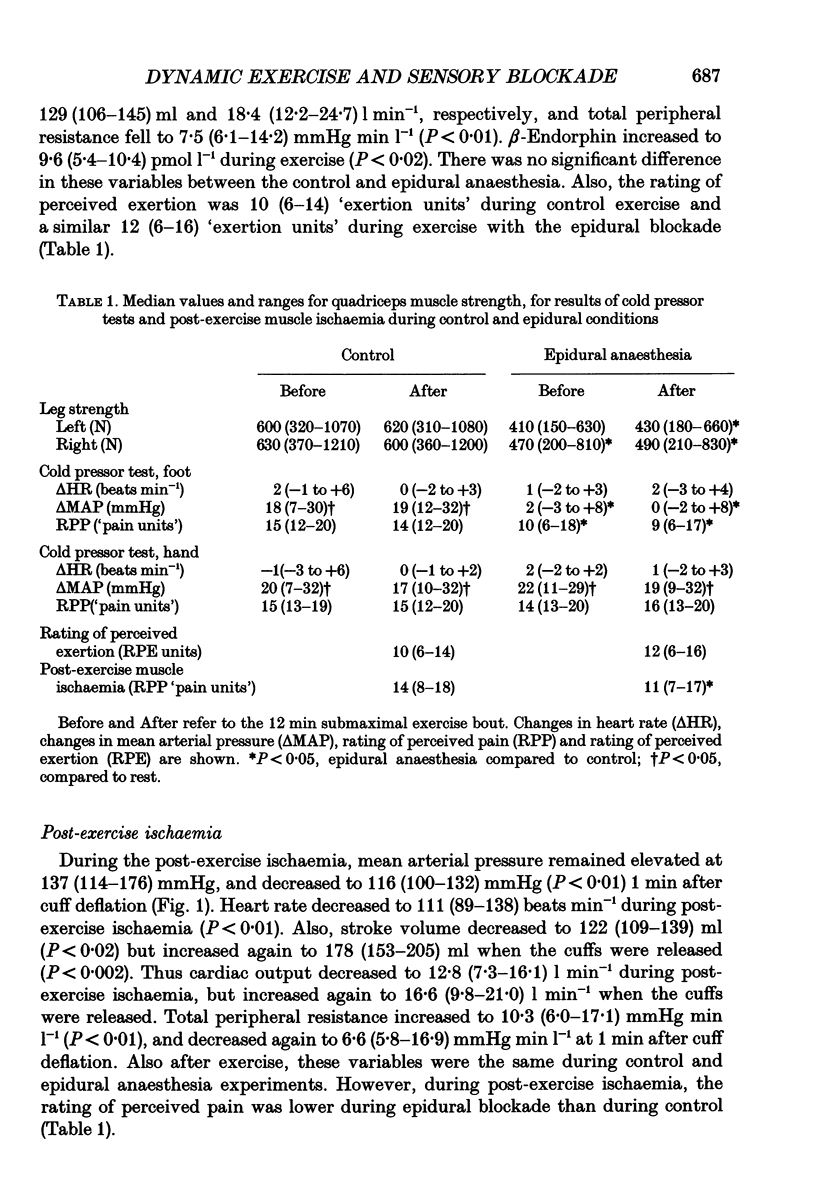




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Smirk F. H. Observations in man upon a blood pressure raising reflex arising from the voluntary muscles. J Physiol. 1937 Jun 3;89(4):372–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendt-Nielsen L., Anker-Møller E., Bjerring P., Spangsberg N. Hypoalgesia following intrathecal morphine: a segmental dependent effect. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1991 Jul;35(5):402–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1991.tb03318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. W., Fahrenkrug J., Jensen K., Dahlstrøm G., Ekman R. Plasma beta-endorphin during clinical and experimental ischaemic pain. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;47(8):751–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonde-Petersen F., Rowell L. B., Murray R. G., Blomqvist G. G., White R., Karlsson E., Campbell W., Mitchell J. H. Role of cardiac output in the pressor responses to graded muscle ischemia in man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Oct;45(4):574–580. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1970;2(2):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennum J., Arendt-Nielsen L., Secher N. H., Jensen T. S., Bjerring P. Quantitative sensory examination in human epidural anaesthesia and analgesia: effects of lidocaine. Pain. 1992 Oct;51(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90005-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennum J., Jensen T. S. Relationship between vertex potentials and magnitude of pre-pain and pain sensations evoked by electrical skin stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 May;82(5):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(92)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale G., Pecorini M., Cuzzoni G., de Nicola P. Beta-endorphin and cold pressor test in the aged. Gerontology. 1985;31(2):101–105. doi: 10.1159/000212687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E., Kiley J. P., Waldrop T. G. Stimulation by central command of locomotion, respiration and circulation during exercise. Respir Physiol. 1985 Mar;59(3):313–337. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(85)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes A., Galbo H., Kjaer M., Mitchell J. H., Secher N. H., Thomas S. N. Cardiovascular and ventilatory responses to dynamic exercise during epidural anaesthesia in man. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:281–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund P. R., Rowell L. B., Murphy T. M., Hobbs S. F., Butler S. H. Blockade of the pressor response to muscle ischemia by sensory nerve block in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):H433–H439. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.4.H433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. B., Jensen F. B., Mitchell J. H., Secher N. H. Heart rate and arterial blood pressure at the onset of static exercise in man with complete neural blockade. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:543–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Kjaer M., Secher N. H. Cardiovascular, ventilatory and catecholamine responses to maximal dynamic exercise in partially curarized man. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:557–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajduczok G., Hade J. S., Mark A. L., Williams J. L., Felder R. B. Central command increases sympathetic nerve activity during spontaneous locomotion in cats. Circ Res. 1991 Jul;69(1):66–75. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes J. A., De Cort S. C., Evans P. J., Guz A. Central command influences cardiorespiratory response to dynamic exercise in humans with unilateral weakness. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:551–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer M., Secher N. H., Bach F. W., Galbo H., Reeves D. R., Jr, Mitchell J. H. Hormonal, metabolic, and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in humans: influence of epidural anesthesia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):E214–E220. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.2.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer M., Secher N. H., Bach F. W., Sheikh S., Galbo H. Hormonal and metabolic responses to exercise in humans: effect of sensory nervous blockade. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):E95–101. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.1.E95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausen K., Secher N. H., Clausen J. P., Hartling O., Trap-Jensen J. Central and regional circulatory adaptations to one-leg training. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):976–983. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund C., Selmar P., Hansen O. B., Hjortsø N. C., Kehlet H. Effect of epidural bupivacaine on somatosensory evoked potentials after dermatomal stimulation. Anesth Analg. 1987 Jan;66(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnin P. A., Stewart J. A., Myers S., von Ramm O., Kisslo J. A. Combined doppler and phased-array echocardiographic estimation of cardiac output. Circulation. 1981 Feb;63(2):388–392. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.63.2.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. H., Reeves D. R., Jr, Rogers H. B., Secher N. H. Epidural anaesthesia and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in man. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:13–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moret V., Forster A., Laverrière M. C., Lambert H., Gaillard R. C., Bourgeois P., Haynal A., Gemperle M., Buchser E. Mechanism of analgesia induced by hypnosis and acupuncture: is there a difference? Pain. 1991 May;45(2):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90178-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowell L. B., Hermansen L., Blackmon J. R. Human cardiovascular and respiratory responses to graded muscle ischemia. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Nov;41(5 Pt 1):693–701. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals D. R., Victor R. G. Regulation of muscle sympathetic nerve activity during exercise in humans. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1991;19:313–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange S., Secher N. H., Pawelczyk J. A., Karpakka J., Christensen N. J., Mitchell J. H., Saltin B. Neural control of cardiovascular responses and of ventilation during dynamic exercise in man. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:693–704. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldrop T. G., Henderson M. C., Iwamoto G. A., Mitchell J. H. Regional blood flow responses to stimulation of the subthalamic locomotor region. Respir Physiol. 1986 Apr;64(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(86)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. B., Wall P. T., Matsukawa K., Mitchell J. H. Multiplicity of the afferent pathways mediating the exercise pressor reflex. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 25;539(2):316–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91636-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


