Abstract
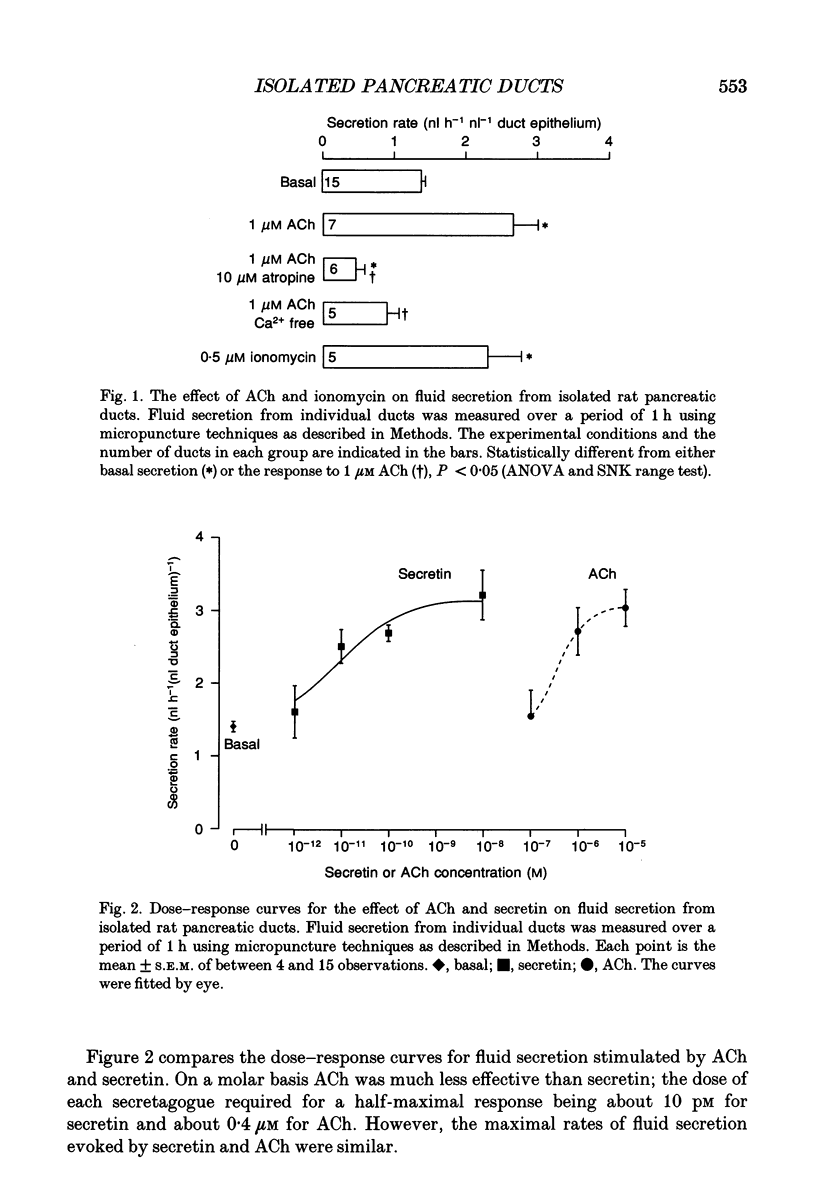
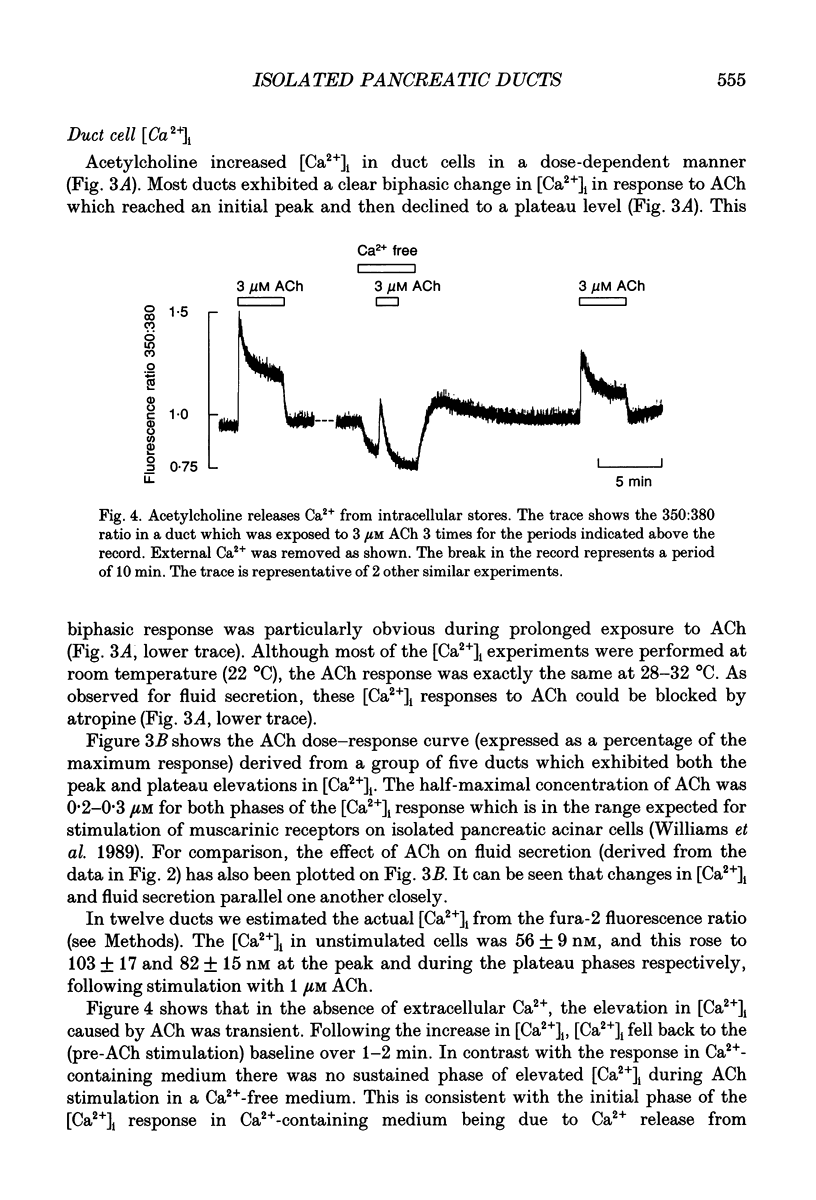
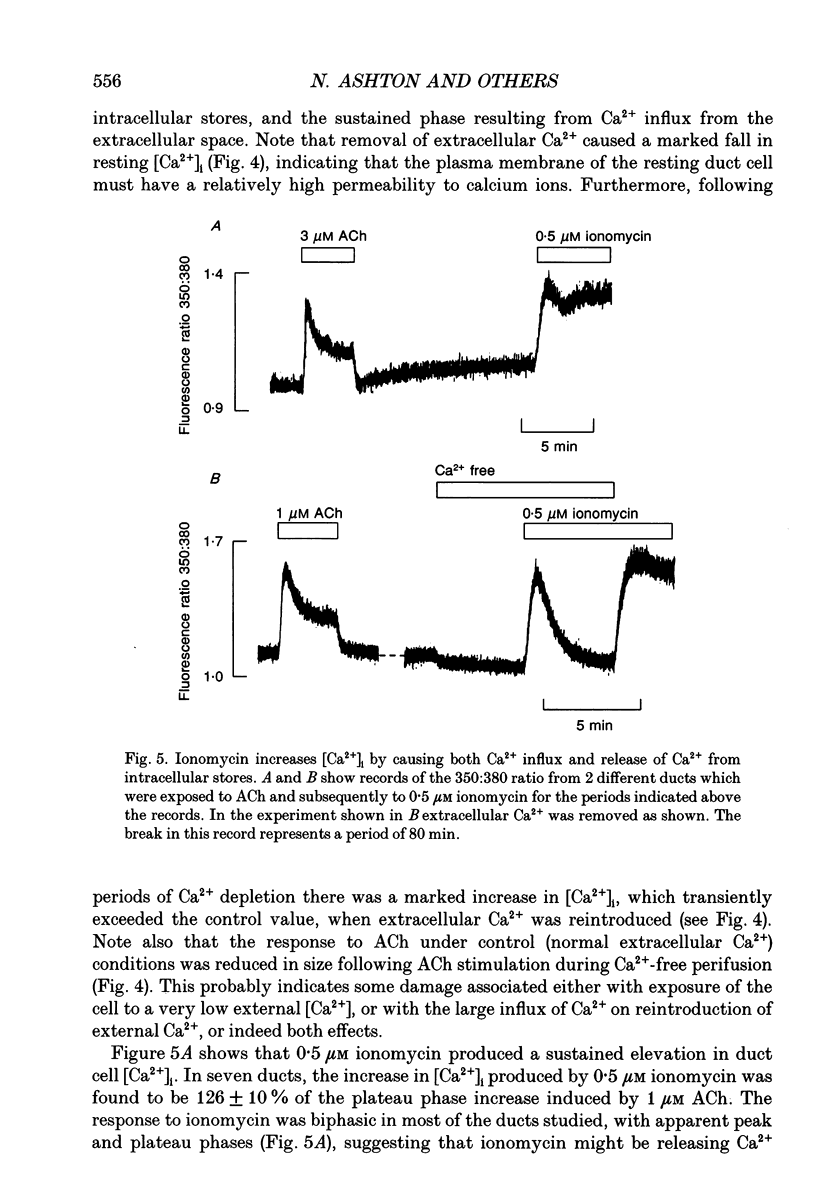
1. We have studied the effects of acetylcholine (ACh) on fluid secretion and intracellular messengers in interlobular ducts isolated from the rat pancreas and maintained in short-term tissue culture. 2. Ductal fluid secretion was measured using micropuncture techniques. Intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) and cyclic AMP concentrations were measured in single ducts using fura-2 microspectrofluorimetry and radioimmunoassay techniques respectively. Changes in the levels of these intracellular messengers were correlated with fluid secretion. 3. ACh stimulated ductal fluid secretion. The dose required for a half-maximal response was about 0.4 microM and maximal secretion was achieved with 10 microM ACh. These effects of ACh were blocked by atropine and by removal of extracellular Ca2+. 4. ACh was about four orders of magnitude less potent as an activator of ductal fluid transport than the hormone secretin; however, the maximal rates of fluid secretion evoked by these two agonists were similar. 5. ACh caused a dose-dependent rise in duct cell [Ca2+]i, but had no effect on cyclic AMP. In contrast, secretin increased duct cell cyclic AMP, but had no effect on [Ca2+]i. 6. The [Ca2+]i response evoked by ACh resulted from both mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ stores and influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular space. 7. The Ca2+ ionophore, ionomycin, mimicked the effect of ACh on ductal [Ca2+]i and fluid secretion. 8. We conclude that ACh stimulates fluid secretion from rat pancreatic duct cells by activating a 'Ca2+ pathway' which is distinct from the well documented 'cyclic AMP pathway' utilized by secretin.
Full text
PDF



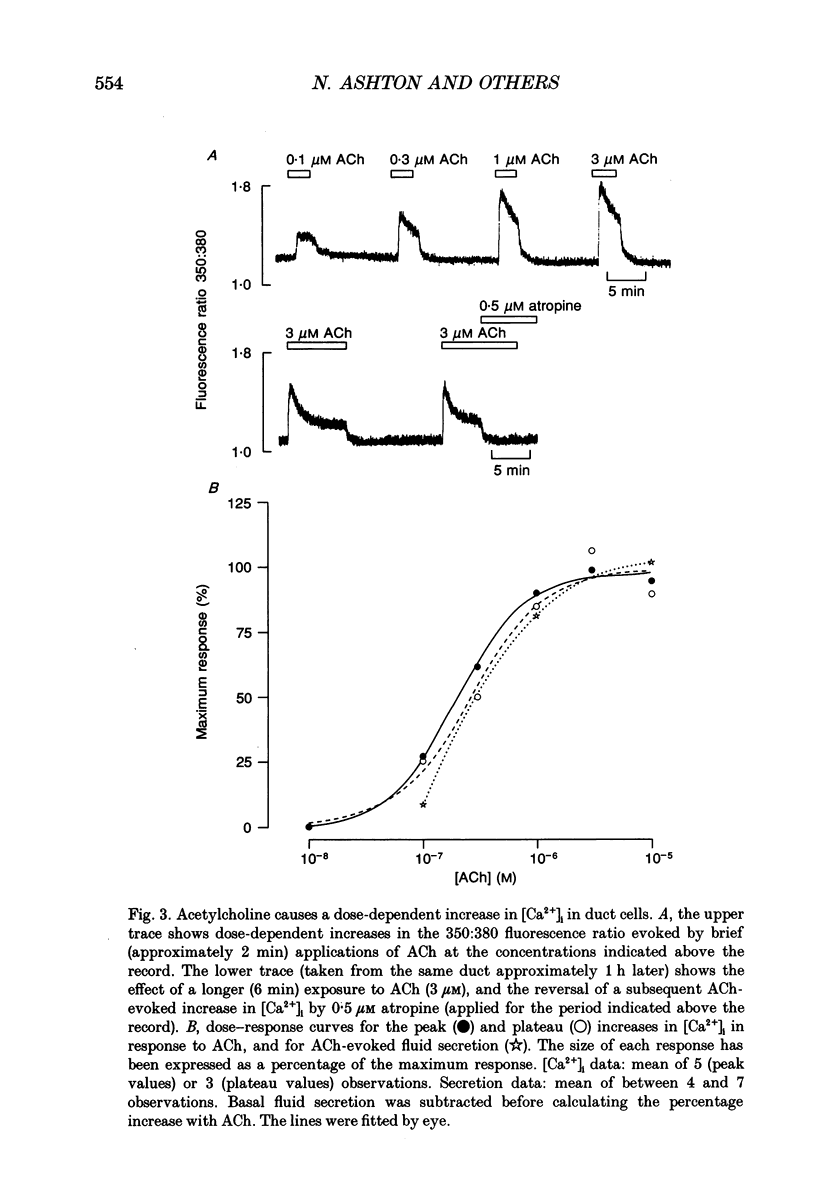






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argent B. E., Arkle S., Cullen M. J., Green R. Morphological, biochemical and secretory studies on rat pancreatic ducts maintained in tissue culture. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Oct;71(4):633–648. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp003023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkle S., Lee C. M., Cullen M. J., Argent B. E. Isolation of ducts from the pancreas of copper-deficient rats. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Apr;71(2):249–265. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton N., Argent B. E., Green R. Characteristics of fluid secretion from isolated rat pancreatic ducts stimulated with secretin and bombesin. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:533–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton N., Argent B. E., Green R. Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide, bombesin and substance P on fluid secretion by isolated rat pancreatic ducts. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:471–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher F. R., Putney J. W., Jr Regulation of parotid gland function by cyclic nucleotides and calcium. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:215–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Montégut M., Mistaoui M., Butlen D., Morel F. Atrial natriuretic peptide effects on cGMP and cAMP contents in microdissected glomeruli and segments of the rat and rabbit nephrons. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):366–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00581130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chariot J., Rozé C., de la Tour J., Souchard M., Vaille C. Modulation of stimulated pancreatic secretion by sympathomimetic amines in the rat. Pharmacology. 1983;26(6):313–323. doi: 10.1159/000137817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Pancreatic acinar cells: measurement of membrane potential and miniature depolarization potentials. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Robberecht P., De Neef P., Lammens M., Christophe J. In vitro action of bombesin and bombesin-like peptides on amylase secretion, calcium efflux, and adenylate cyclase activity in the rat pancreas: a comparison with other secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):891–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI108542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta Y., Hashimoto K., Washizaki M. beta-Adrenoceptor stimulation of exocrine secretion from the rat pancreas. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):25–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fölsch U. R., Fischer H., Söling H. D., Creutzfeldt W. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones and carbamylcholine on cAMP accumulation in isolated pancreatic duct fragments from the rat. Digestion. 1980;20(4):277–292. doi: 10.1159/000198449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwell J. R. The effects of cholecystokinin-pancreozymin, acetylcholine and secretin on the membrane potentials of mouse pancreatic cells in vitro. Pflugers Arch. 1975;353(2):159–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00599876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habara Y. Influences of ionic environments on ACh-induced secretory responses in isolated perfused pancreas of rats. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(4):561–574. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingard J. M., Young J. A. beta-Adrenergic control of exocrine secretion by perfused rat pancreas in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):G690–G696. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.5.G690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden M. E., Sarras M. P., Jr The pancreatic ductal system of the rat: cell diversity, ultrastructure, and innervation. Pancreas. 1989;4(4):472–485. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198908000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak I., Greger R. Electrophysiological study of transport systems in isolated perfused pancreatic ducts: properties of the basolateral membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):58–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00581647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Ueda N. Pancreatic acinar cells: effect of acetylcholine, pancreozymin, gastrin and secretin on membrane potential and resistance in vivo and in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):461–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Ueda N. Secretion of fluid and amylase in the perfused rat pancreas. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):819–835. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell W. A., Young J. A. Secretion of electrolytes by the pancreas of the anaestetized rat. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):379–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Kasper H. Effect of acetylcholine, gastrin, and glucagon alone and in combination with secretin and cholecystokinin on the secretion of the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1981;179(3):239–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01851621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuenkel E. L., Hootman S. R. Secretagogue effects on intracellular calcium in pancreatic duct cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Aug;416(6):652–658. doi: 10.1007/BF00370610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. V., Sorenson R. L., Kaung H. C. Immunocytochemical localization of insulin-immunoreactive cells in the pancreatic ducts of rats treated with trypsin inhibitor. Diabetologia. 1985 Oct;28(10):781–785. doi: 10.1007/BF00265028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


