Abstract
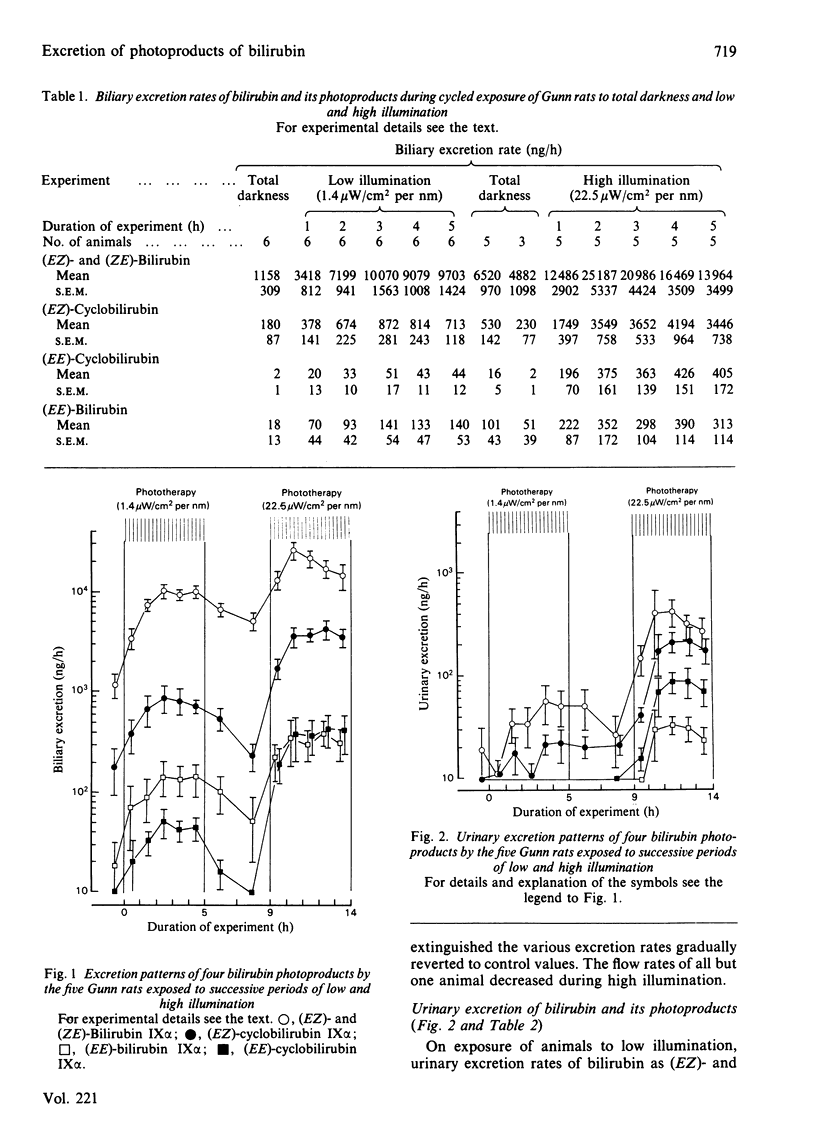
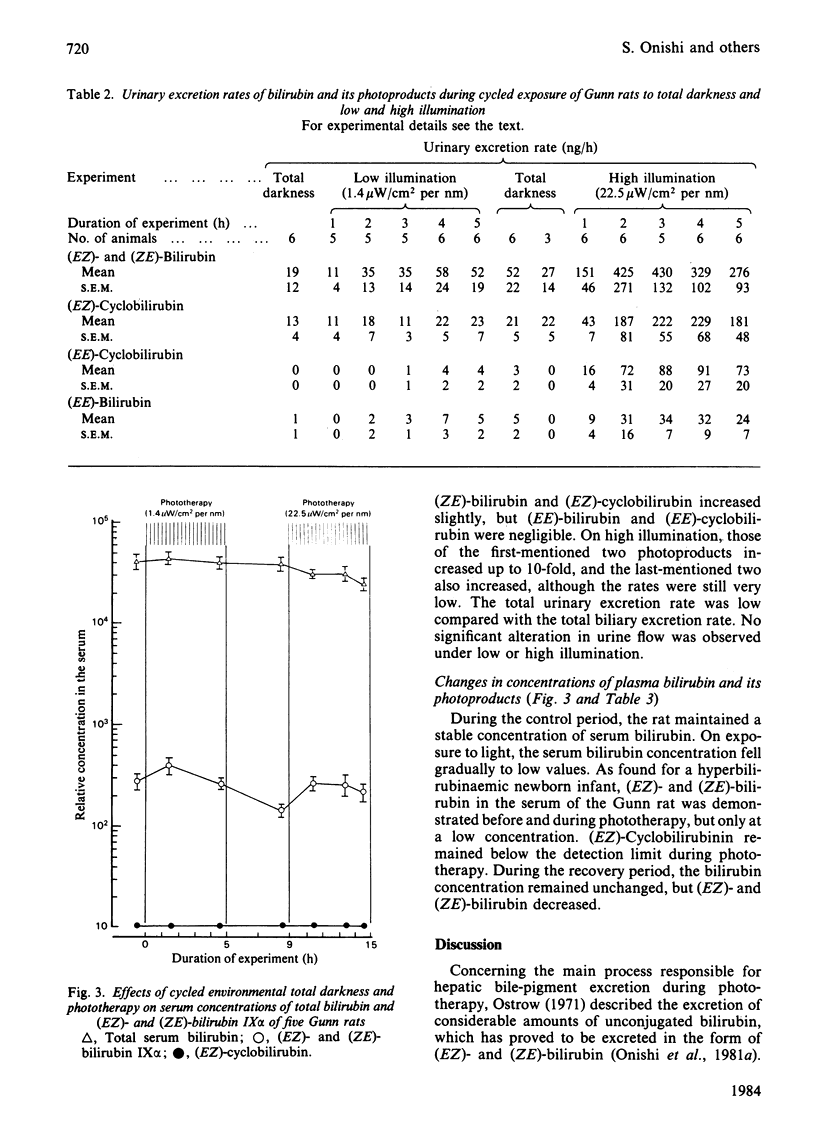
On cycled exposure of Gunn rats to total darkness and low and high illumination, biliary excretion rates of (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin and (EZ)-cyclobilirubin increased up to approx. 10-fold from the mean basal values of 1.2 and 0.2 microgram/h to the mean maximum values of 25.2 and 4.2 micrograms/h respectively, and at the same time those of (EE)-bilirubin and (EE)-cyclobilirubin also increased, but at very much lower rates than those of the first-mentioned two. During the low illumination only (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin and (EZ)-cyclobilirubin appeared in the urine; during the high illumination (EE)-bilirubin and (EE)-cyclobilirubin also appeared, showing a similar excretion pattern to that observed in the bile, but the total urinary excretion rates were lower than the total biliary excretion rates. The serum bilirubin concentrations fell gradually to lower values, accompanied by an increment in (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin, but (EZ)-cyclobilirubin was not detected. It is concluded that during phototherapy the predominant pathway for the removal of bilirubin from the body in the Gunn rat is by biliary excretion of the geometric photoisomers (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin, derived from Z----E isomerization, and the structural photoisomer (EZ)-cyclobilirubin, formed from intramolecular endo-vinyl cyclization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. K., McDonagh A. F. Phototherapy for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: efficacy, mechanism and toxicity. Adv Pediatr. 1980;27:341–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER R. J., PERRYMAN P. W., RICHARDS D. H. Influence of light on the hyperbilirubinaemia of infants. Lancet. 1958 May 24;1(7030):1094–1097. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91849-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe K., Itoh S., Onishi S., Yamakawa T., Ogino T., Yokoyama T. Kinetic study of photochemical and thermal conversion of bilirubin IX alpha and its photoproducts. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):695–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2090695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R., SCHMID R. Intestinal absorption of bile pigments. I. The enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI104766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund H. T., Jacobsen J. Influence of phototherapy on unconjugated bilirubin in duodenal bile of newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 Nov;61(6):693–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb15968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F. The role of singlet oxygen in bilirubin photo-oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep 17;44(6):1306–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Isobe K., Itoh S., Kawade N., Sugiyama S. Demonstration of a geometric isomer of bilirubin-IX alpha in the serum of a hyperbilirubinaemic newborn infant and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):533–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1900533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Itoh S., Kawade N., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. The separation of configurational isomers of bilirubin by high pressure liquid chromatography and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):890–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91911-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Kawade N., Itoh S., Isobe K., Sugiyama S., Hashimoto T., Narita H. Kinetics of biliary excretion of the main two bilirubin photoproducts after injection into Gunn rats. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):107–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1980107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Kawade N., Itoh S., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of anaerobic photoproducts of bilirubin-IX alpha in vitro and its comparison with photoproducts in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):527–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1900527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Miura I., Isobe K., Itoh S., Ogino T., Yokoyama T., Yamakawa T. Structure and thermal interconversion of cyclobilirubin IX alpha. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj2180667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. D. Photocatabolism of labeled bilirubin in the congenitally jaundiced (Gunn) rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):707–718. doi: 10.1172/JCI106541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Vicker N., Gray C. H., Bonnett R. Concerning the structure of photobilirubin II. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):179–188. doi: 10.1042/bj2010179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


