Abstract
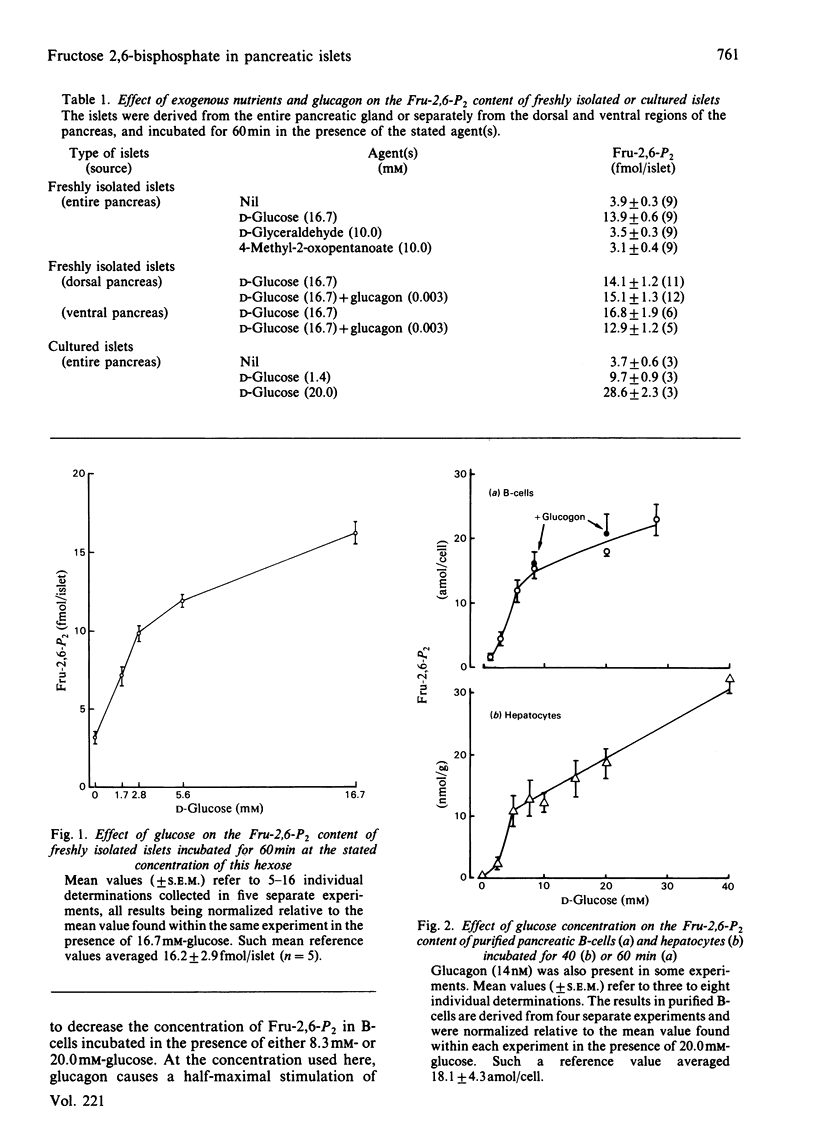
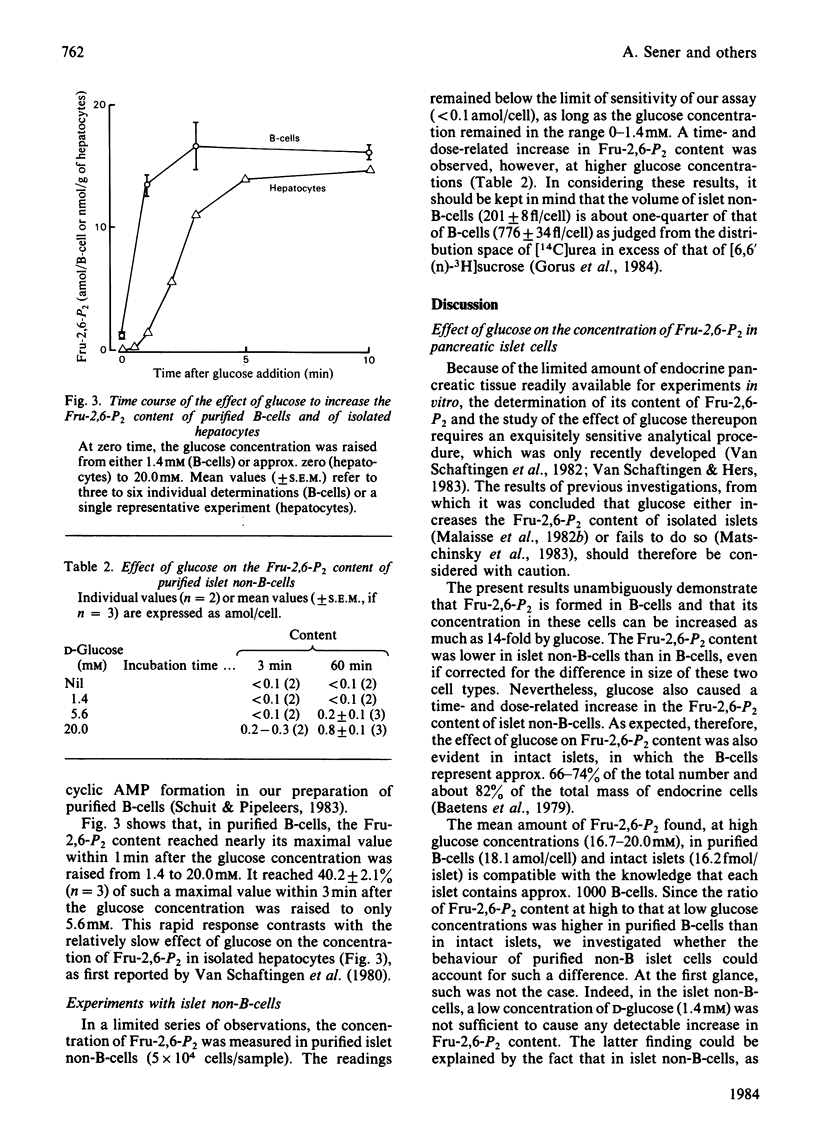
Glucose caused a sustained and dose-related increase in the fructose 2,6-bisphosphate content of isolated pancreatic islets, as well as of purified pancreatic B-cells. With isolated B-cells, the glucose saturation curve was sigmoidal and superimposable on that obtained with hepatocytes isolated from unfed rats. However, the response to glucose was notably faster in purified B-cells than in isolated hepatocytes. In contrast again with the situation prevailing in the liver, glucagon failed to decrease significantly the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in either islets or purified B-cells. It is proposed that, in the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, an early increase in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate formation may, by causing activation of 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase, allow glycolysis to keep pace with the rate of glucose phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartrons R., Hue L., Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Hormonal control of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate concentration in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):829–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2140829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorus F. K., Malaisse W. J., Pipeleers D. G. Differences in glucose handling by pancreatic A- and B-cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1196–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Hue L. Gluconeogenesis and related aspects of glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:617–653. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate 2 years after its discovery. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2060001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L. Role of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the stimulation of glycolysis by anoxia in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 15;206(2):359–365. doi: 10.1042/bj2060359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohen E., Kohen C., Thorell B., Mintz D. H., Rabinovitch A. Intercellular communication in pancreatic islet monolayer cultures: a microfluorometric study. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):862–865. doi: 10.1126/science.35828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Carpinelli A. R., Sener A. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Timing of early metabolic, ionic, and secretory events. Metabolism. 1981 May;30(5):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. Glucose-induced accumulation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate in pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1982 Jan;31(1):90–93. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. Presence of fructose-6-phosphate,2-kinase in pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80977-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. The glycolytic cascade in pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1982 Jul;23(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00257721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Hutton J. C. Insulin release: the fuel hypothesis. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F. [Insulin secretion by isolated islets of Langerhans. Effects of pancreatic and intestinal hormones]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1968 Oct;5 (Suppl 1):64–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Burch P. T., Berner D. K., Najafi H., Vogin A. P., Matschinsky F. M. Chromatographic resolution and kinetic characterization of glucokinase from islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Howell S. L. The mode of action of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in mammalian islets of Langerhans. Preparation and properties of islet-cell protein phosphokinase. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):551–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1290551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens D., Ravazzola M., Stefan Y., Malaisse-Lagae F. Pancreatic polypeptide and glucagon : non-random distribution in pancreatic islets. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1811–1815. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse-Lagae F., Ravazzola M., Rouiller D., Renold A. E., Perrelet A., Unger R. A morphological basis for intercellular communication between alpha- and beta-cells in the endocrine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1066–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI108154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A. A method for the purification of single A, B and D cells and for the isolation of coupled cells from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00257436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D., in't Veld P. I., Maes E., Van De Winkel M. Glucose-induced insulin release depends on functional cooperation between islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7322–7325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtle J. R., Kipnis D. M. An adrenergic receptor mechanism for the control of cyclic 3'5' adenosine monophosphate synthesis in tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):797–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Winkel M., Pipeleers D. Autofluorescence-activated cell sorting of pancreatic islet cells: purification of insulin-containing B-cells according to glucose-induced changes in cellular redox state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Control of the fructose-6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate cycle in isolated hepatocytes by glucose and glucagon. Role of a low-molecular-weight stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):887–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1920887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Winkle M., Maes E., Pipeleers D. Islet cell analysis and purification by light scatter and autofluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


