Abstract
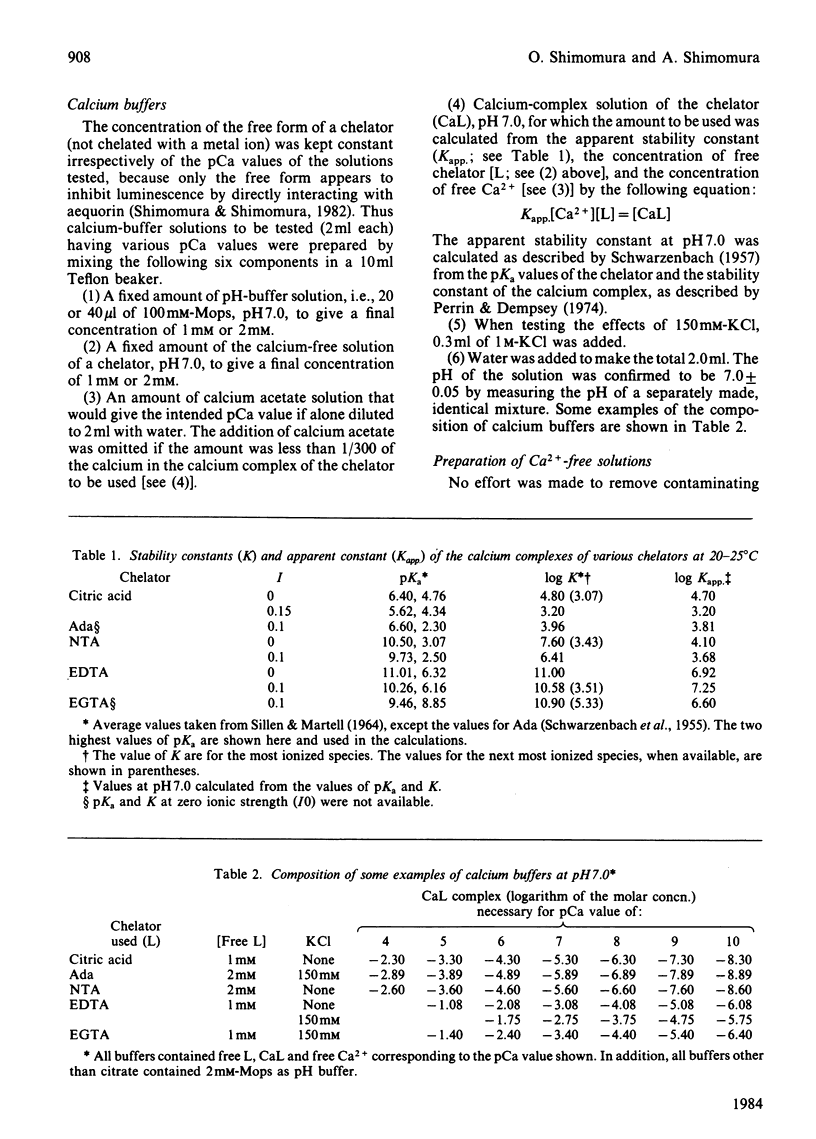
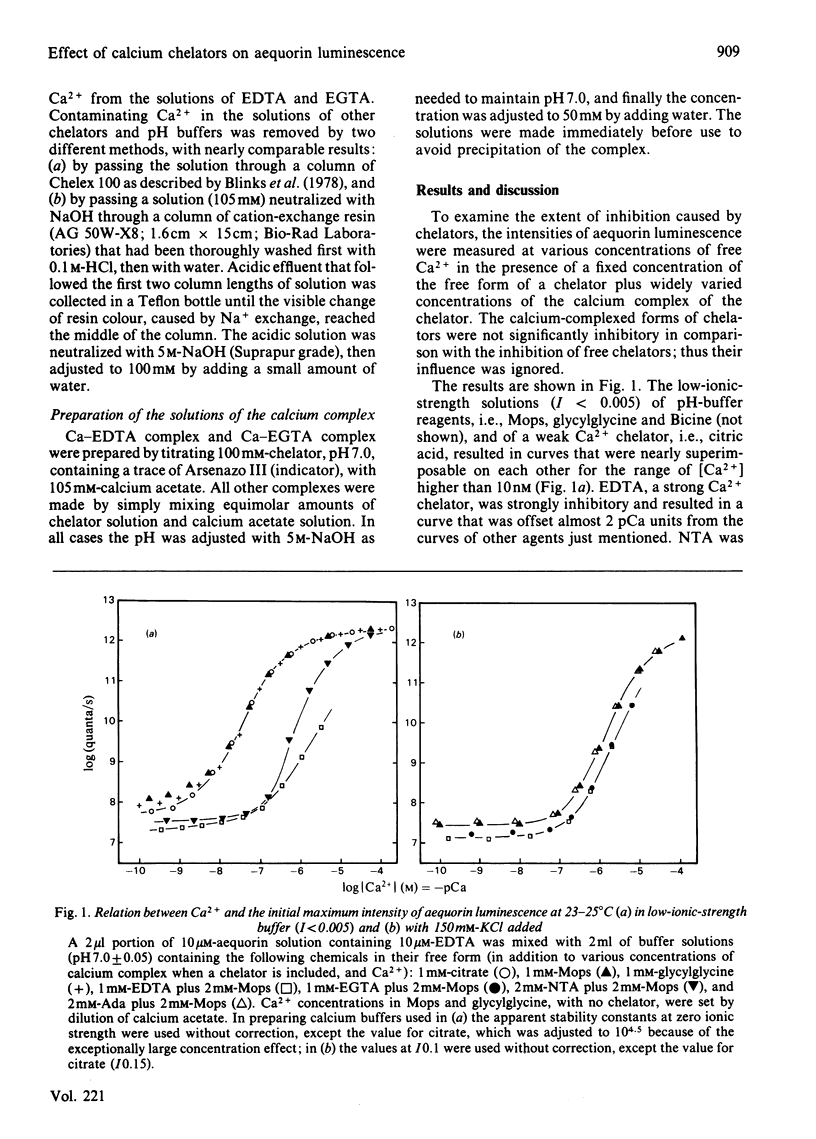
The luminescence of aequorin, a useful tool for studying intracellular Ca2+, was recently found to be inhibited by the free EDTA and EGTA that are present in calcium buffers. In the present study we have examined the effect of the free forms of various chelators in the calibration of [Ca2+] with aequorin. Free EDTA and EGTA in low-ionic-strength solutions strongly inhibited the Ca2+-triggered luminescence of aequorin, causing large errors in the calibration of [Ca2+] (approx. 2 pCa units), whereas in solutions containing 150mM-KCl, errors were relatively small (0.2-0.3 pCa units). Citric acid in low-ionic-strength solutions and [(carbamoylmethyl)imino]diacetic acid in high-ionic-strength solutions showed no inhibition and did not cause detectable error in the calibration of [Ca2+], indicating that they are better chelators than EDTA and EGTA for use with aequorin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G., Allen D. G. Photoproteins as biological calcium indicators. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Mar;28(1):1–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMOMURA O., JOHNSON F. H., SAIGA Y. Extraction, purification and properties of aequorin, a bioluminescent protein from the luminous hydromedusan, Aequorea. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:223–239. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Johnson F. H., Kohama Y. Reactions involved in bioluminescence systems of limpet (Latia neritoides) and luminous bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2086–2089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Shimomura A. EDTA-binding and acylation of the Ca2+-sensitive photoprotein aequorin. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


