Abstract
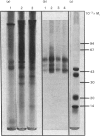
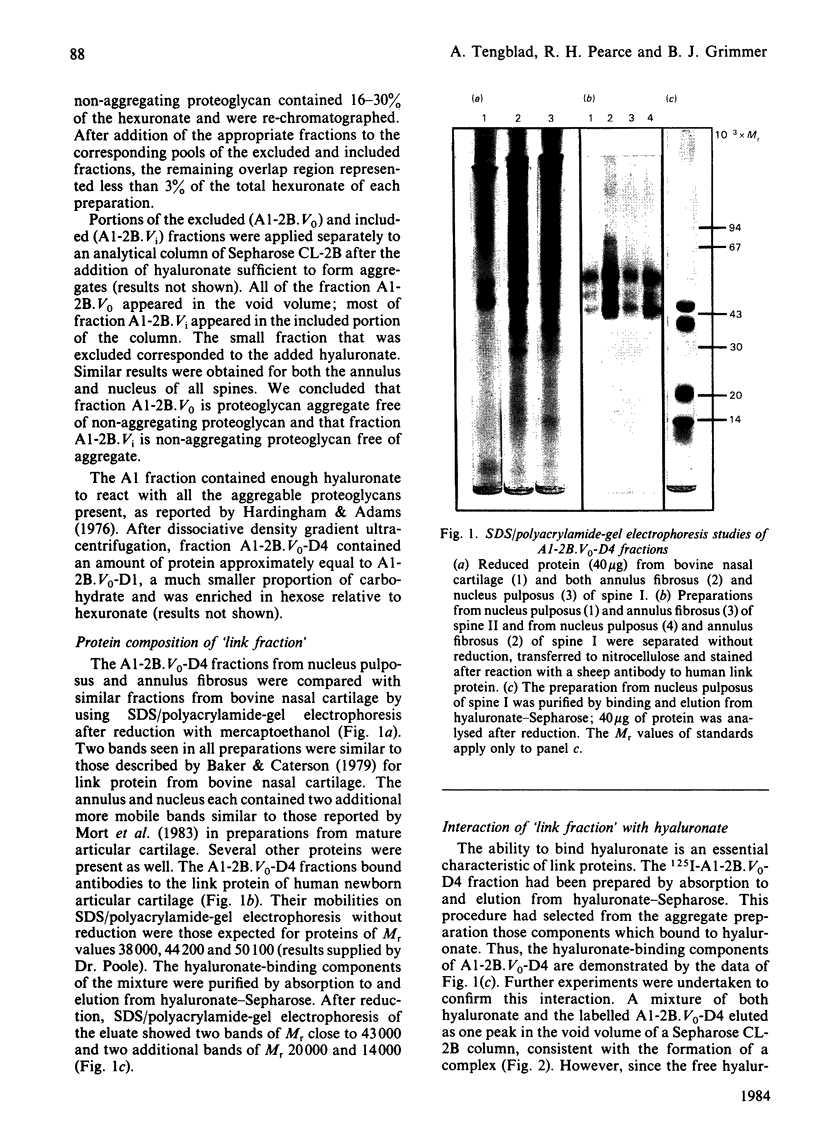
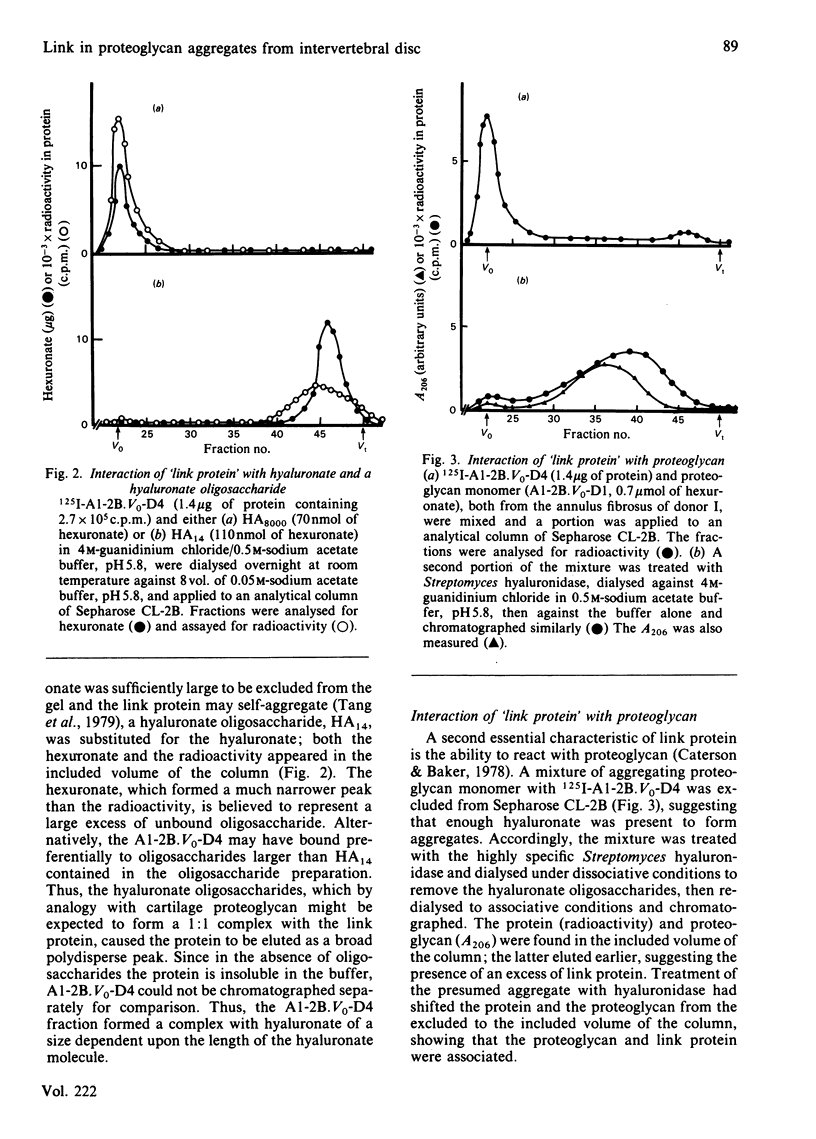
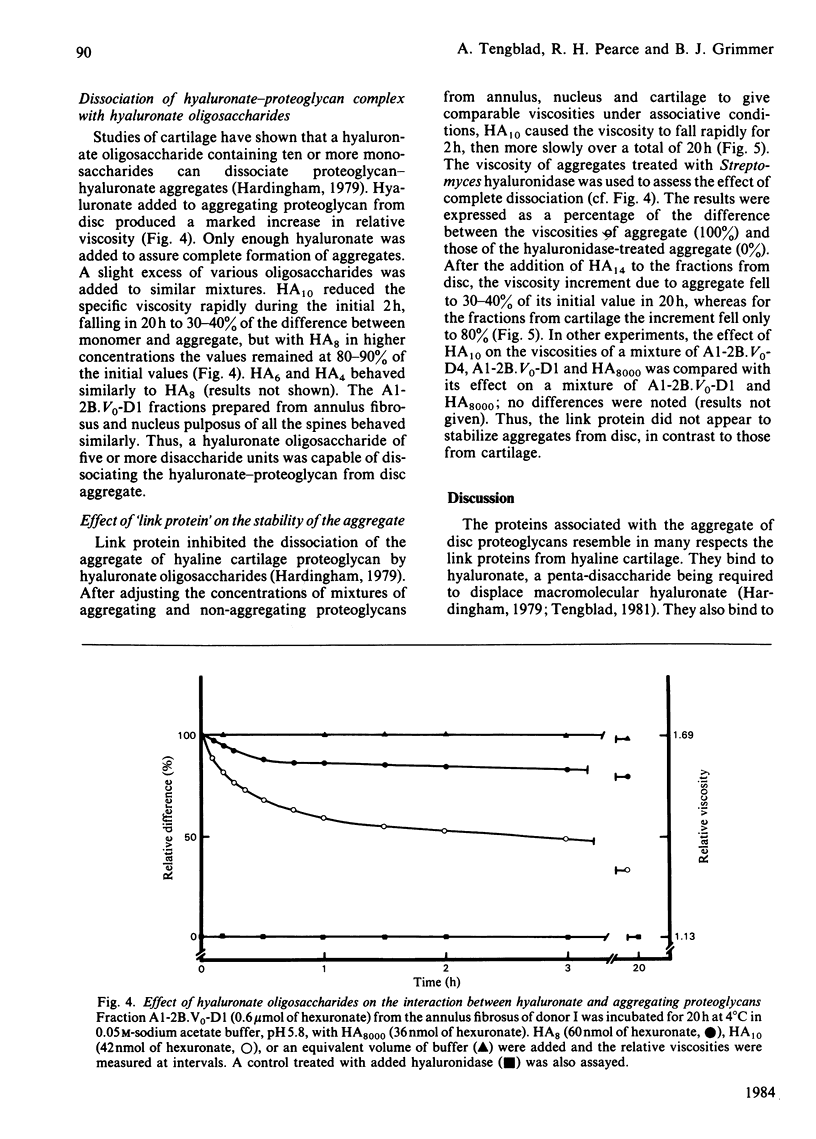
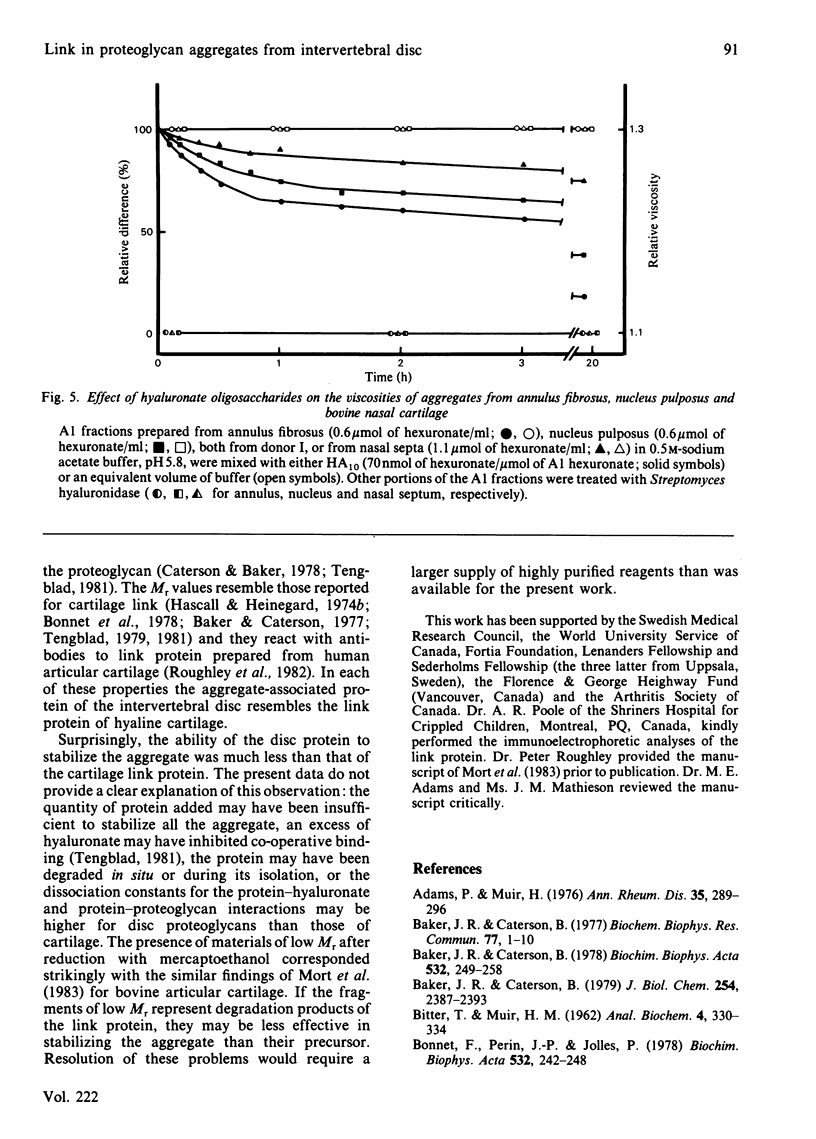
Proteoglycan aggregates free of non-aggregating proteoglycan have been prepared from the annuli fibrosi and nuclei pulposi of intervertebral discs of three human lumbar spines by extraction with 4M-guanidinium chloride, associative density gradient centrifugation, and chromatography on Sepharose CL-2B. The aggregate (A1-2B.V0) was subjected to dissociative density-gradient ultracentrifugation. Three proteins of Mr 38 900, 44 200 and 50 100 found in the fraction of low buoyant density (A1-2B.V0-D4) reacted with antibodies to link protein from newborn human articular cartilage. After reduction with mercaptoethanol, two proteins of Mr 43 000 and two of Mr 20 000 and 14 000 were seen. The A1-2B.V0-D4 fraction, labelled with 125I, coeluted with both hyaluronate and a hyaluronate oligosaccharide (HA14) on a Sepharose CL-2B column. HA10 and HA14 reduced the viscosity of A1 fractions; HA4, HA6 and HA8 did not. HA14 decreased the viscosity of disc proteoglycans less than it did that of bovine cartilage proteoglycans. Thus, although a link protein was present in human intervertebral disc, it stabilized proteoglycan aggregates less well than did the link protein from bovine nasal cartilage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P., Muir H. Qualitative changes with age of proteoglycans of human lumbar discs. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):289–296. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Caterson B. The isolation and characterization of the link proteins from proteoglycan aggregates of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2387–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Caterson B. The isolation of "link proteins" from bovine nasal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90579-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J., Caterson B. The purification and cyanogen bromide cleavage of the 'link proteins' from cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Périn J. P., Jollès P. Isolation and chemical characterization of two distinct "link proteins" from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90578-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. The interaction of link proteins with proteoglycan monomers in the absence of hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emes J. H., Pearce R. H. The proteoglycans of the human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1450549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L., Chisholm P. L., Rice P. A. Experimental models of bacterial arthritis: a microbiologic and histopathologic characterization of the arthritis after the intraarticular injections of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Staphylococcus aureus, group A streptococci, and Escherichia coli. J Rheumatol. 1983 Feb;10(1):5–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Adams P. A method for the determination of hyaluronate in the presence of other glycosaminoglycans and its application to human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 1;159(1):143–147. doi: 10.1042/bj1590143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. Proteoglycans: their structure, interactions and molecular organization in cartilage. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Dec;9(6):489–497. doi: 10.1042/bst0090489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Wright P. L. Macromolecular composition of an amoeba plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):439–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIN T. OSTEOARTHRITIS IN LUMBAR SYNOVIAL JOINTS. A MORPHOLOGIC STUDY. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1964:SUPPL 73–8112. doi: 10.3109/ort.1964.35.suppl-73.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons G., Eisenstein S. M., Sweet M. B. Biochemical changes in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90476-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. Age-related changes in the structure of proteoglycan link proteins present in normal human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2140269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce R. H., Grimmer B. J. The chemical constitution of the proteoglycan of human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):753–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1570753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Ewins R. J., Revell P. A., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the intervertebral disc. Homology of structure with laryngeal proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1790561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L. H., Rosenberg L., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Properties of a soluble form of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10523–10531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A. A comparative study of the binding of cartilage link protein and the hyaluronate-binding region of the cartilage proteoglycan to hyaluronate-substituted Sepharose gel. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):297–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1990297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A. Affinity chromatography on immobilized hyaluronate and its application to the isolation of hyaluronate binding properties from cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 19;578(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]