Abstract
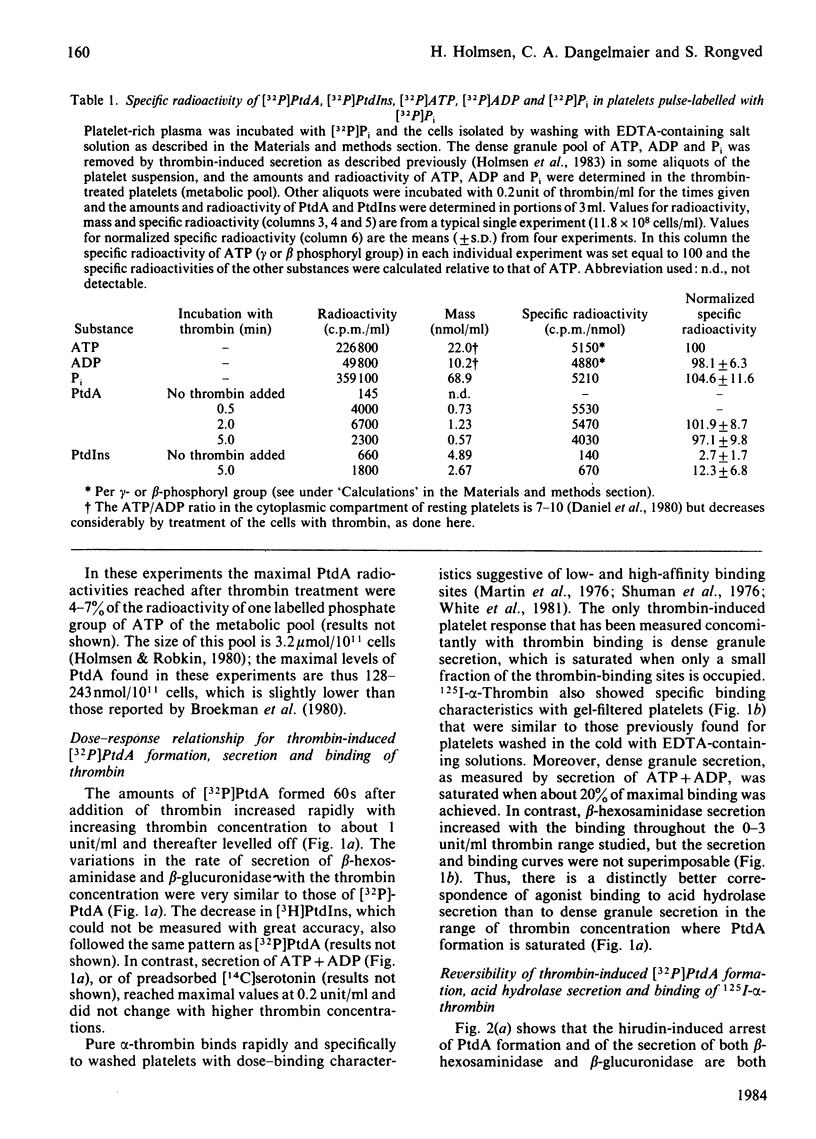
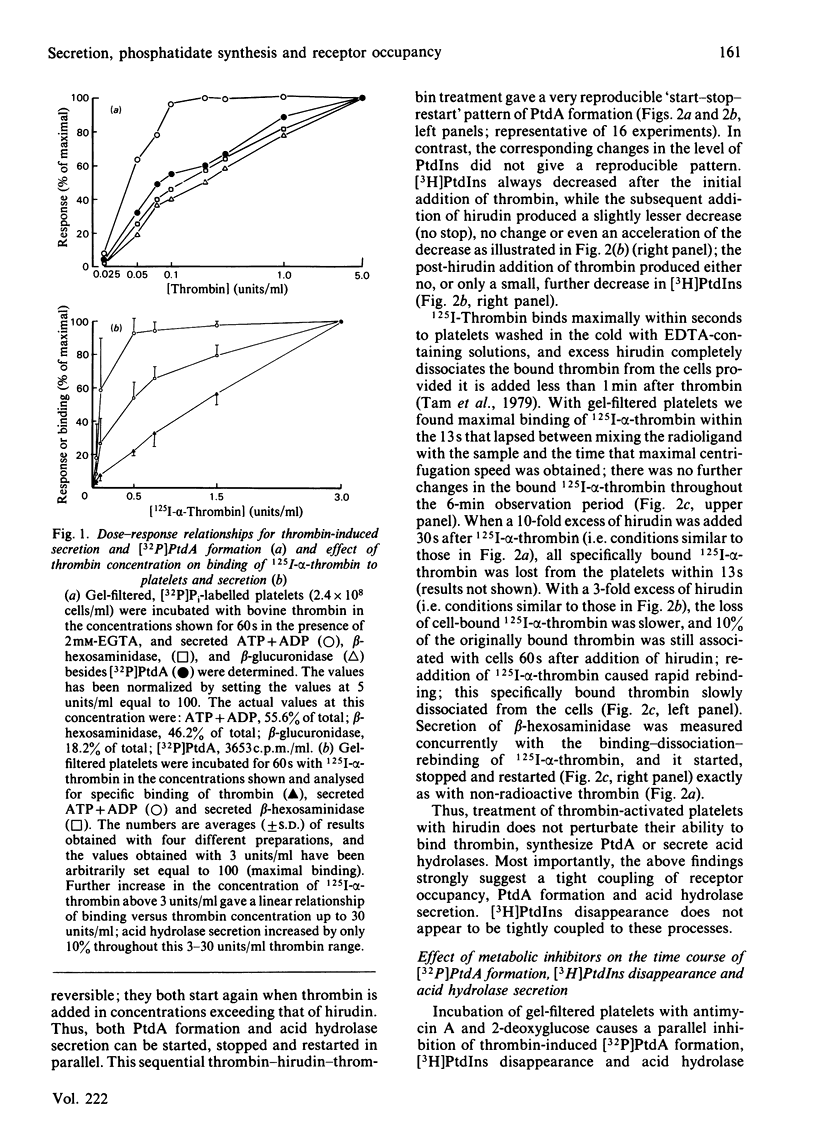
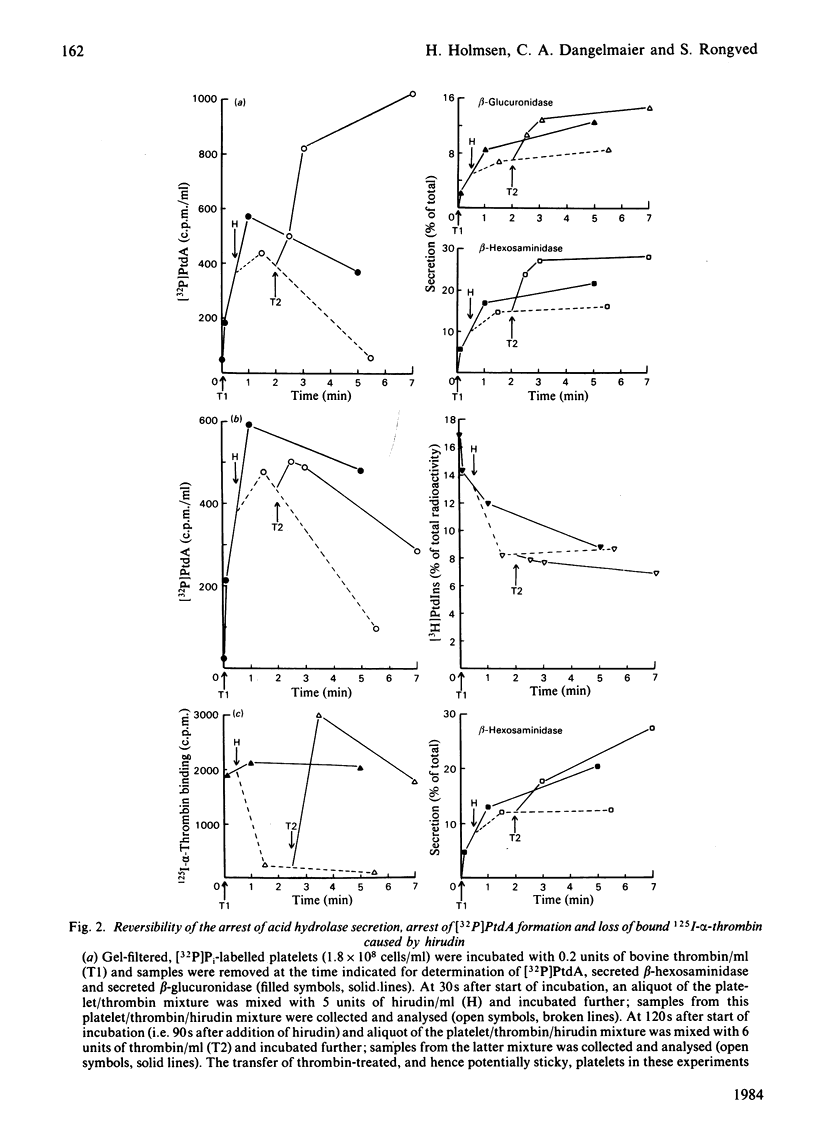
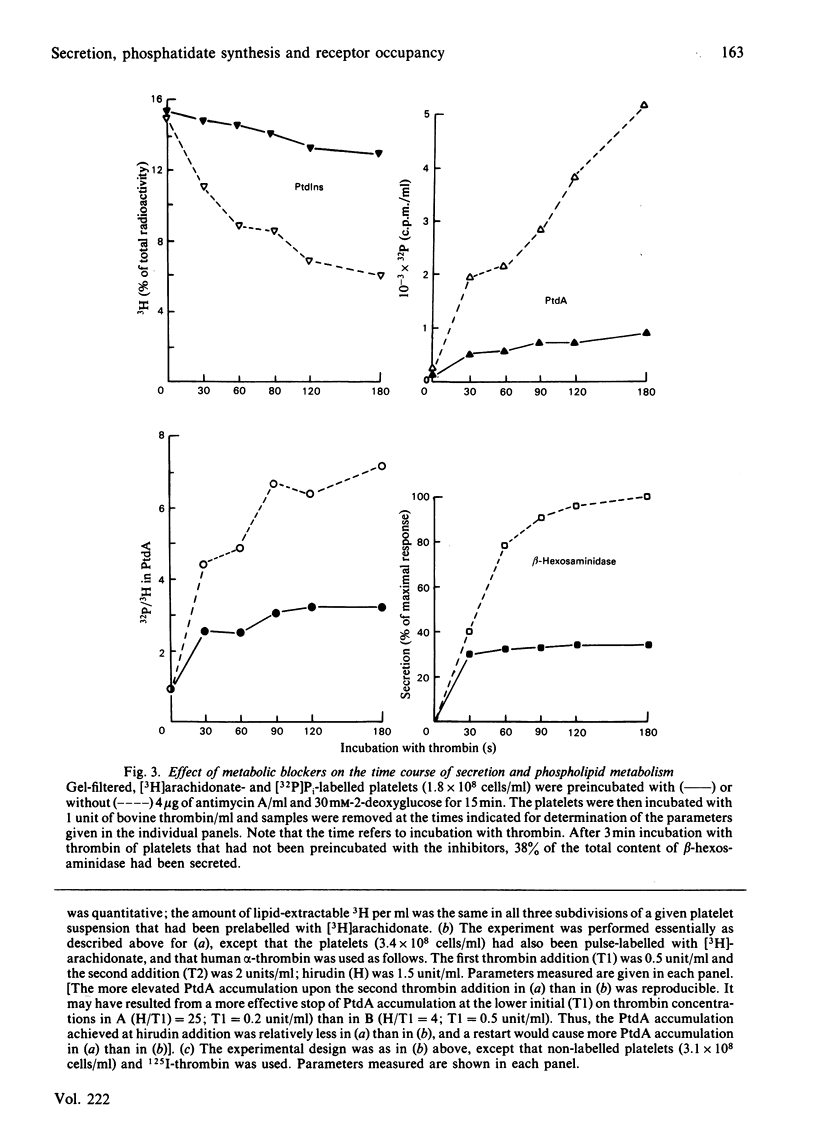
Human platelets incubated with [32P]Pi and [3H]arachidonate were transferred to a Pi-free Tyrode's solution by gel filtration. The labile phosphoryl groups of ATP and ADP as well as Pi in the metabolic pool of these platelets had equal specific radioactivity which was identical to that of[32P]phosphatidate formed during treatment of the cells with thrombin for 5 min. Therefore, the 32P radioactivity of phosphatidate was a true, relative measure for its mass. The thrombin-induced formation of[32P]-phosphatidate had the same time course and dose-response relationships as the concurrent secretion of acid hydrolases. 125I-alpha-Thrombin bound maximally to the platelets within 13s and was rapidly dissociated from the cells by hirudin; readdition of excess 125I-alpha-thrombin caused rapid rebinding of radioligand. This binding-dissociation-rebinding sequence was paralleled by a concerted start-stop-restart of phosphatidate formation and acid hydrolase secretion. [3H]Phosphatidylinositol disappearance was initiated upon binding but little affected by thrombin dissociation and rebinding. ATP deprivation caused similar changes in the time courses for [32P]-phosphatidate formation and acid hydrolase secretion which were different from those of [3H]phosphatidylinositol disappearance. The metabolic stress did not alter the magnitude (15%) of the initial decrease in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bis[32P]phosphate, but did abolish the subsequent increase of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bis[32P]-phosphate in the thrombin-treated platelets. It is concluded that in thrombin-treated platelets (1) phosphatidate synthesis, but not phosphatidylinositol disappearance, is tightly coupled to receptor occupancy and acid hydrolase secretion in platelets, (2) successive phosphorylations to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is unlikely to be the main mechanism for phosphatidylinositol disappearance, and (3) only a small fraction (15%) of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is susceptible to hydrolysis.
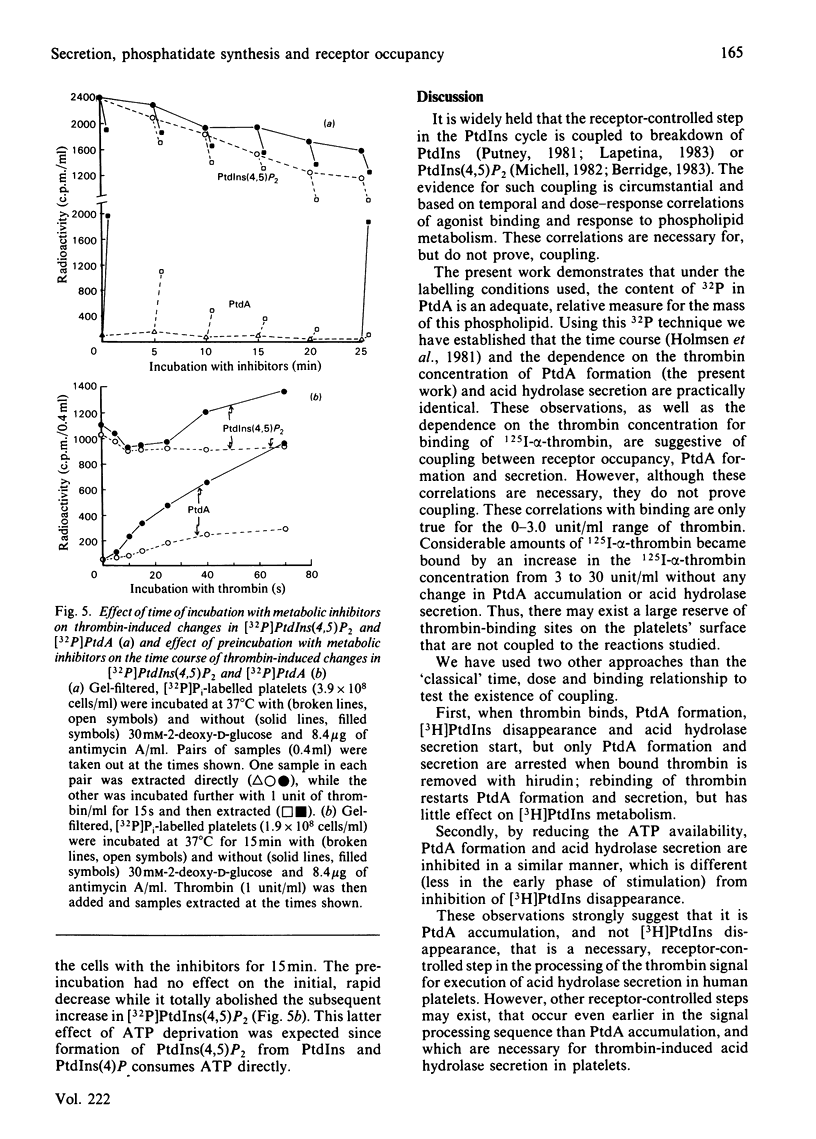
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akkerman J. W., Doucet-De Bruïne M. H., Gorter G., De Graaf S., Holme S., Lips J. P., Numeuer A., Over J., Starkenburg A. E., Trieschnigg A. C. Evaluation of platelet tests for measurement of cell integrity. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Feb 28;39(1):146–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 activity specific for phosphatidic acid. A possible mechanism for the production of arachidonic acid in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5399–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Platelet-activating factor stimulates metabolism of phosphoinositides in horse platelets: possible relationship to Ca2+ mobilization during stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):965–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets. Changes in phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid, and lysophospholipids. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):275–283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Rubert M. Diglyceride kinase in human platelets. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):466–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. Phosphatidate phosphatase in human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Oct;82(4):663–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J. L., Murphy D. L. Platelet 5-HT uptake and release stopped rapidly by formaldehyde. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):407–408. doi: 10.1038/255407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangelmaier C. A., Holmsen H. Determination of acid hydrolases in human platelets. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Molish I. R., Holmsen H. Radioactive labeling of the adenine nucleotide pool of cells as a method to distinguish among intracellular compartments. Studies on human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 15;632(3):444–453. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Hadjian R. A. Effects of the calmodulin antagonist trifluoperazine on stimulus-induced calcium mobilization, aggregation, secretion, and protein phosphorylation in platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):422–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Diglyceride kinase and other path ways for phosphatidic acid synthesis in the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 12;67:470–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91852-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Scrutton M. C., Wallis R. B. Responses of rabbit platelets to adrenaline induced by other agonists. 1981 Feb 15-Mar 1Thromb Res. 21(4-5):413–424. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser G., Eichberg J. Identification of cytidine diphosphate-diglyceride in the pineal gland of the rat and its accumulation in the presence of DL-propranolol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H. Biochemistry of the platelet release reaction. Ciba Found Symp. 1975;35:175–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470720172.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Akkerman J. W. Determination of levels of glycolytic intermediates and nucleotides in platelets by pulse-labeling with [32P]orthophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Holmsen H. K. Thrombin-induced platelet responses differ in requirement for receptor occupancy. Evidence for tight coupling of occupancy and compartmentalized phosphatidic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9393–9396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Day H. J., Setkowsky C. A. Secretory mechanisms. Behaviour of adenine nucleotides during the platelet release reaction induced by adenosine diphosphate and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):67–82. doi: 10.1042/bj1290067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Kaplan K. L., Dangelmaier C. A. Differential energy requirements for platelet responses. A simultaneous study of aggregation, three secretory processes, arachidonate liberation, phosphatidylinositol breakdown and phosphatidate production. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):9–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2080009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Robkin L. Effects of antimycin A and 2-deoxyglucose on energy metabolism in washed human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;42(5):1460–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky Dangelmaier C. A. Adenine nucleotide metabolism of blood platelets. X. Formaldehyde stops centrifugation-induced secretion after A23187-stimulation and causes breakdown of metabolic ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):46–61. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Storm E., Day H. J. Determination of ATP and ADP in blood platelets: a modification of the firefly luciferase assay for plasma. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. The rapid polyphosphoinositide metabolism may be a triggering event for thrombin-mediated stimulation of human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Nozawa Y. The rapid PI-turnover is not coupled with the aggregation in A23187-activated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):236–243. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Schrama L. H., Gispen W. H. Calcium-dependent turnover of brain polyphosphoinositides in vitro after prelabelling in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Hallam T. J., Scrutton M. C. Agonist selectivity and second messenger concentration in Ca2+-mediated secretion. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):256–257. doi: 10.1038/296256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lages B., Scrutton M. C., Holmsen H. Studies on gel-filtered human platelets: isolation and characterization in a medium containing no added Ca2+, Mg2+, or K+. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):811–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The initial action of thrombin on platelets. Conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidic acid preceding the production of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5037–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Metabolism of inositides and the activation of platelets. Life Sci. 1983 May 2;32(18):2069–2082. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32P-content of phosphatidic acid and the phosphoinositides of rabbit platelets during aggregation induced by collagen or thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1974 Feb;26(2):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Haldar J., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32 p-labelling of platelet phospholipids in response to ADP. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):571–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. M., Wasiewski W. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Detwiler T. C. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to platelets. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4886–4893. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Platelet activating factor (PAF-acether) promotes an early degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate in rabbit platelets. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Is phosphatidylinositol really out of the calcium gate? Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):492–493. doi: 10.1038/296492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERINGER R. A., KUNNES R. S. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF PHOSPHATIDIC ACID AND LYSOPHOSPHATIDIC ACID BY GLYCERIDE PHOSPHOKINASE PATHWAYS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2833–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B. P., Plantavid M., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Are polyphosphoinositides involved in platelet activation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):660–667. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Recent hypotheses regarding the phosphatidylinositol effect. Life Sci. 1981 Sep 21;29(12):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Weiss S. J., Van De Walle C. M., Haddas R. A. Is phosphatidic acid a calcium ionophore under neurohumoral control? Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):345–347. doi: 10.1038/284345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Smith S. W., Tsien R. Y. Cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human platelets: Ca2+ thresholds and Ca-independent activation for shape-change and secretion. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D. M., Honeyman T. W. Proposed mechanism of cholinergic action in smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):344–345. doi: 10.1038/284344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C., Anderson P., Goodman E., Dunham P., Weissmann G. Phosphatidate and oxidized fatty acids are calcium ionophores. Studies employing arsenazo III in liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Tollefsen D. M., Majerus P. W. The binding of human and bovine thrombin to human platelets. Blood. 1976 Jan;47(1):43–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somermeyer M. G., Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Characterization of Ca2+ transport in rat renal brush-border membranes and its modulation by phosphatidic acid. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):37–46. doi: 10.1042/bj2140037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Detwiler T. C. Dissociation of thrombin from platelets by hirudin. Evidence for receptor processing. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8723–8725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walenga R., Vanderhoek J. Y., Feinstein M. B. Serine esterase inhibitors block stimulus-induced mobilization of arachidonic acid and phosphatidylinositide-specific phospholipase C activity in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6024–6027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. C., Lundblad R. L., Griffith M. J. Structure-function relations in platelet-thrombin reactions. Inhibition of platelet-thrombin interactions by lysine modification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1763–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Swart C. A., Nijmeyer B., Roelofs J. M., Sixma J. J. Kinetics of intravenously administered heparin in normal humans. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1251–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


