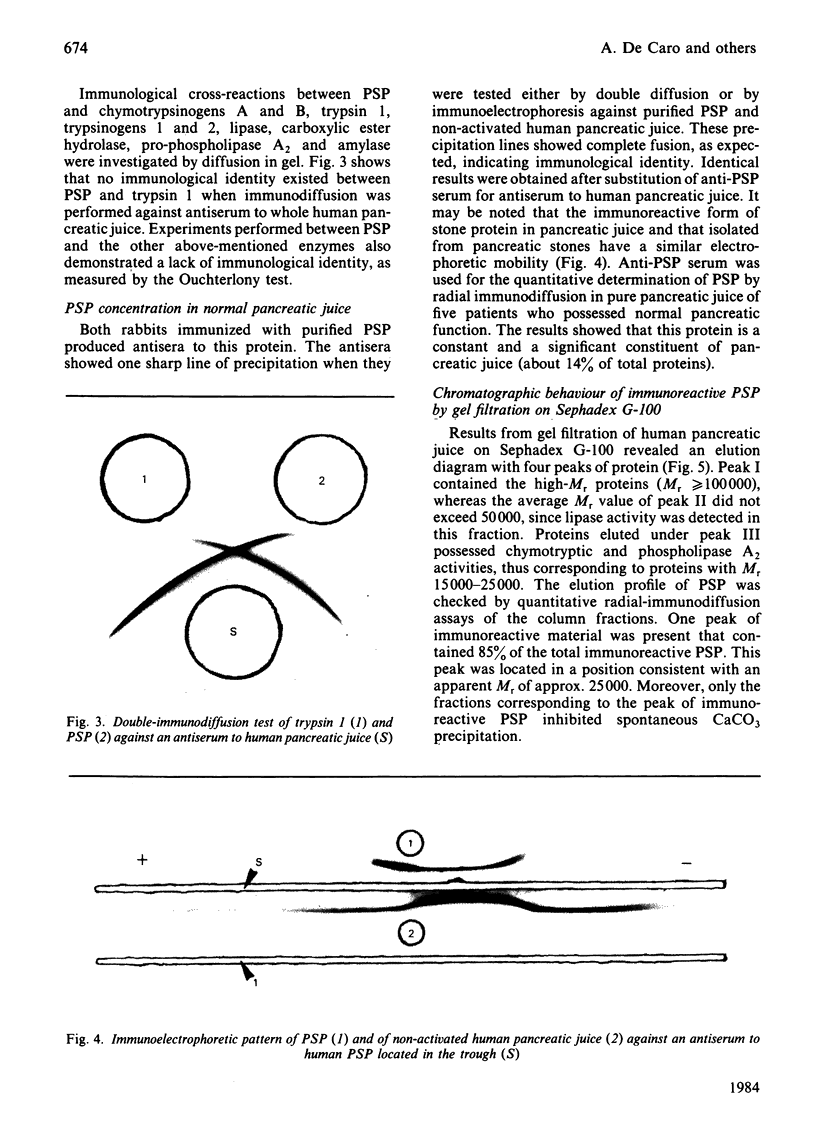
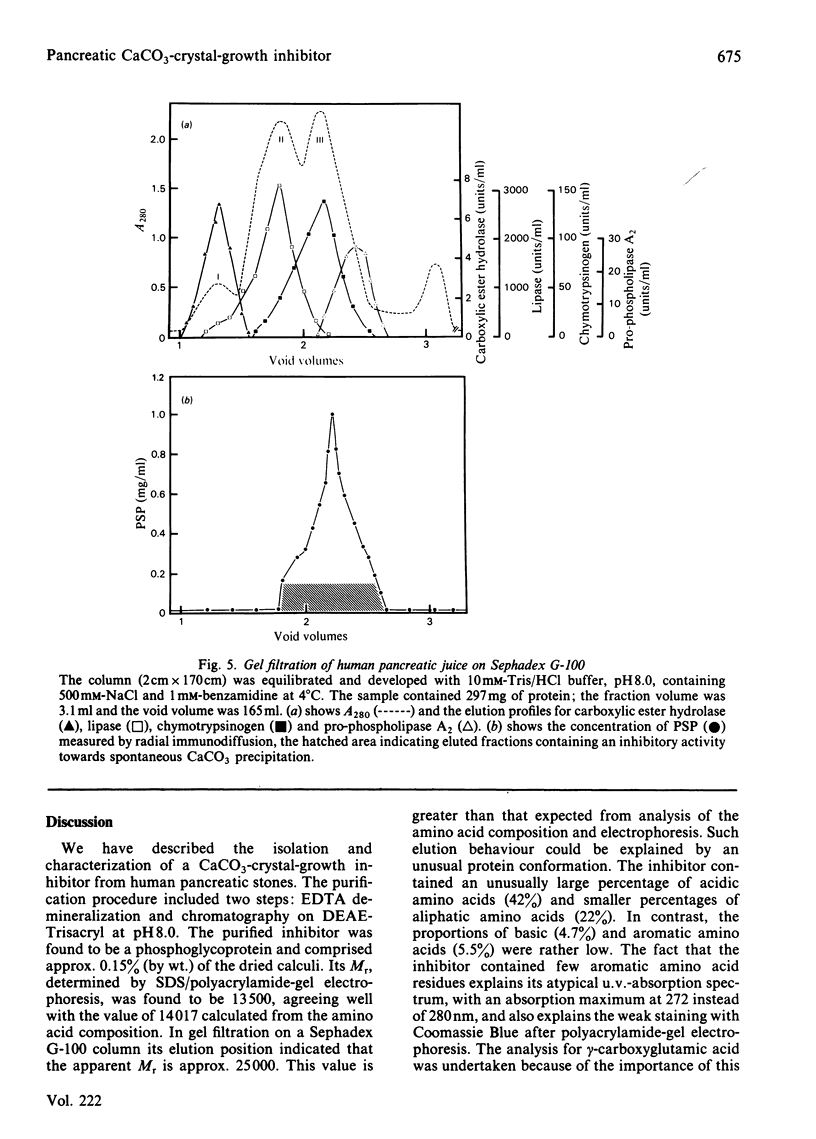
Abstract
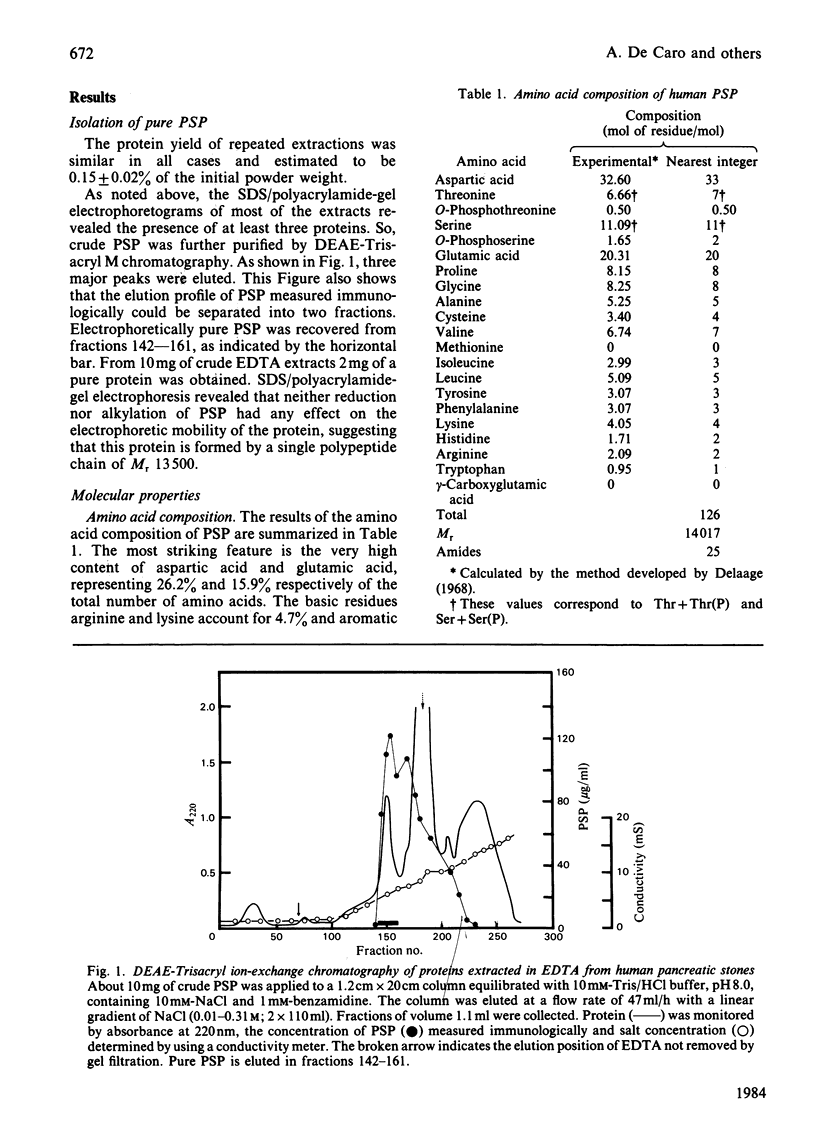
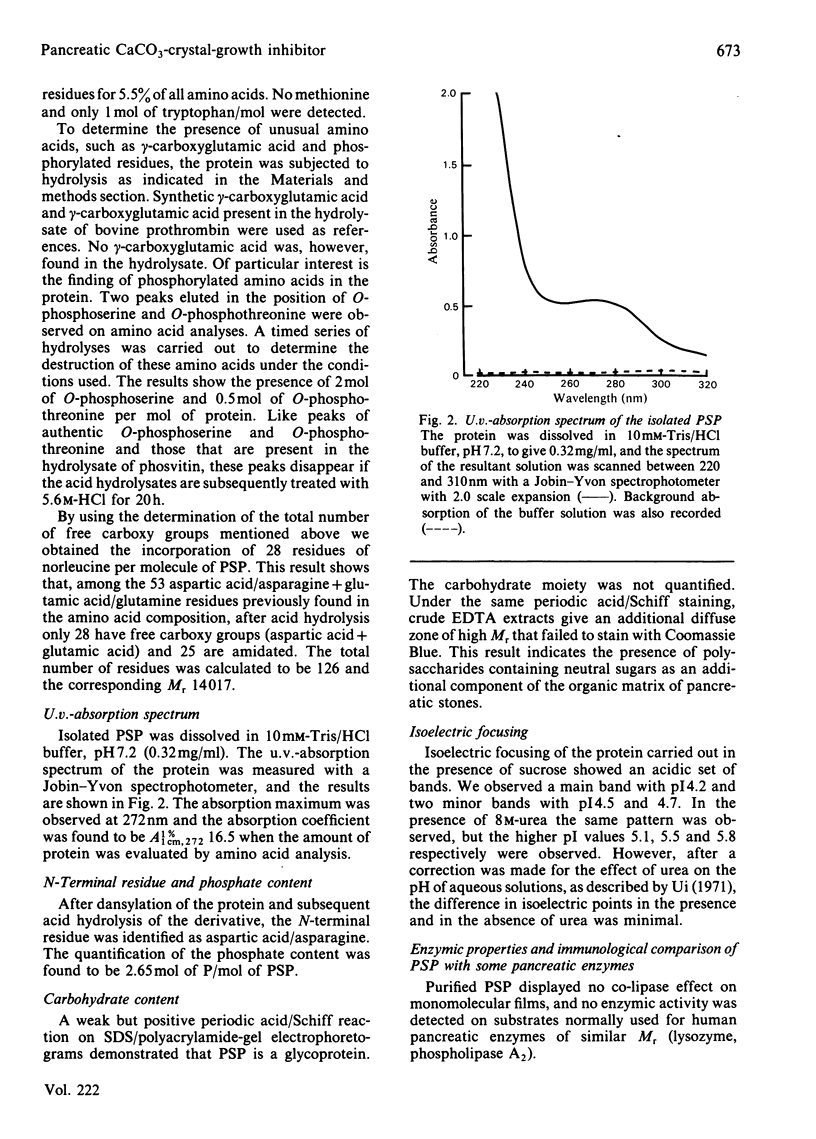
A CaCO3-crystal-growth inhibitor was isolated from human pancreatic stones by using EDTA demineralization, followed by DEAE-Trisacryl chromatography. The isolated inhibitor was found to be a phosphoglycoprotein with Mr 14017 and having an unusual chemical composition. It is characterized by a high (42%) acidic amino acid content, but lacks methionine and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. The protein contains 2.65 mol of P/mol of protein, as phosphoserine (2 mol) and phosphothreonine (0.5 mol). Isoelectric focusing of the protein yields one major band corresponding to an isoelectric point of 4.2. Immunochemical quantification of the crystal-growth inhibitor in pure pancreatic juice reveals that it constitutes 14% of the normal exocrine secretion. Our findings demonstrate that this is a novel secretory protein, which has no enzymic activity and which maintains pancreatic juice in a supersaturated state with respect to CaCO3.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amic J., Hauton J. C., Lafont H., Montet J. C., Teissier N. Une méthode sensible d'analyse semi-automatique des phospholipides particulièrement adaptée à l'analyse des collections de fractions. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1969 Dec 18;51(9):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonmarchand G., Rivault O., Moirot E., Leroy J. Embolie graisseuse grave après traumatisme minime. Nouv Presse Med. 1981 Dec 26;10(47):3851–3852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borman A. H., de Jong E. W., Huizinga M., Kok D. J., Westbroek P., Bosch L. The role in CaCO3 crystallization of an acid Ca2+-binding polysaccharide associated with coccoliths of Emiliania huxleyi. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):179–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente F., Ribeiro T., Colomb E., Figarella C., Sarles H. Comparaison des protéines de sucs pancréatiques humains normaux et pathologiques. Dosage des protéines sériques et mise en evidence d'une protéine particulière dans la pancréatite chronique calcifiante. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):456–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Solal L., Lian J. B., Kossiva D., Glimcher M. J. The identification of O-phosphothreonine in the soluble non-collagenous phosphoproteins of bone matrix. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caro A., Figarella C., Amic J., Michel R., Guy O. Human pancreatic lipase: a glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 22;490(2):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caro A., Figarella C., Guy O. The two human chymotrypsinogens. Purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caro A., Multigner L., Vérine H. Identification of two major proteins of bovine pancreatic stones as immunoreactive forms of trypsinogens. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 1;205(3):543–549. doi: 10.1042/bj2050543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaage M. Sur la recherche du poids moléculaire le plus cohérent avec l'analyse des acides aminés d'une protéine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 3;168(3):573–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figarella C., Clemente F., Guy O. On zymogens of human pancreatic juice. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(5):351–353. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grataroli R., De Caro A., Guy O., Amic J., Figarella C. Isolation and properties of prophospholipase A2 from human pancreatic juice. Biochimie. 1981 Aug-Sep;63(8-9):677–684. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy O., Lombardo D., Bartelt D. C., Amic J., Figarella C. Two human trypsinogens. Purification, molecular properties, and N-terminal sequences. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1669–1675. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V. Quantitative determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in proteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 15;80(1):212–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Prien E. L., Jr, Glimcher M. J., Gallop P. M. The presence of protein-bound gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in calcium-containing renal calculi. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1151–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI108739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo D., Fauvel J., Guy O. Studies on the substrate specificity of a carboxyl ester hydrolase from human pancreatic juice. I. Action on carboxyl esters, glycerides and phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 11;611(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo D., Guy O., Figarella C. Purification and characterization of a carboxyl ester hydrolase from human pancreatic juice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 10;527(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo D. Modification of the essential amino acids of human pancreatic carboxylic-ester hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 4;700(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Multigner L., De Caro A., Lombardo D., Campese D., Sarles H. Pancreatic stone protein, a phosphoprotein which inhibits calcium carbonate precipitation from human pancreatic juice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Abram V., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T., Coe F. L. Purification and characterization of the principal inhibitor of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal growth in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12594–12600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The mode of action of vitamin K. Isolation of a peptide containing the vitamin K-dependent portion of prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3366–3370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F. A modified technique of immunoelectrophoresis facilitating the identification of specific precipitin arcs. J Immunol. 1960 Jan;84:93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F. Phosphoproteins in the parotid saliva from the subhuman primate Macaca fascicularis. Isolation and characterization of a proline-rich phosphoglycoprotein and the complete covalent structure of a proline-rich phosphopeptide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9271–9282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietsch J., Pattus F., Desnuelle P., Verger R. Further studies of mode of action of lipolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4313–4318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahel J., Sarles H. Modifications of pure human pancreatic juice induced by chronic alcohol consumption. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Dec;24(12):897–905. doi: 10.1007/BF01311942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles H. Chronic calcifying pancreatitis--chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):604–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger D. H., Hay D. I. Complete covalent structure of statherin, a tyrosine-rich acidic peptide which inhibits calcium phosphate precipitation from human parotid saliva. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1689–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui N. Isoelectric points and conformation of proteins. I. Effect of urea on the behavior of some proteins in isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):567–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R., De Haas G. H. Enzyme reactions in a membrane model. 1. A new technique to study enzyme reactions in monolayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1973 Feb;10(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(73)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler A. P., George J. W., Evans C. A. Control of calcium carbonate nucleation and crystal growth by soluble matrx of oyster shell. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1397–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4501.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M., Iacobucci G. A., Myers D. V. 5-Methyltryptophan: an internal strandard for tryptophan determination by ion-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1976 Feb;70(2):470–478. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Bennick A. The primary structure of a salivary calcium-binding proline-rich phosphoprotein (protein C), a possible precursor of a related salivary protein A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5943–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]