Full text
PDF

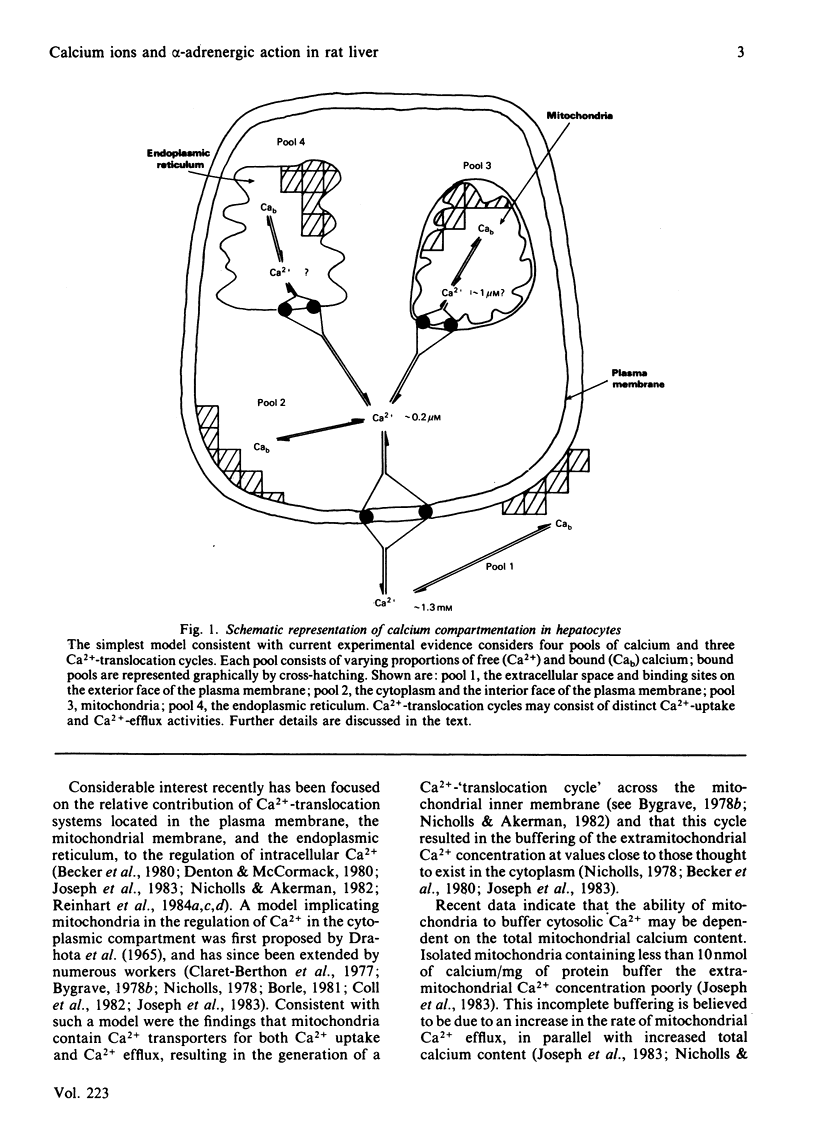




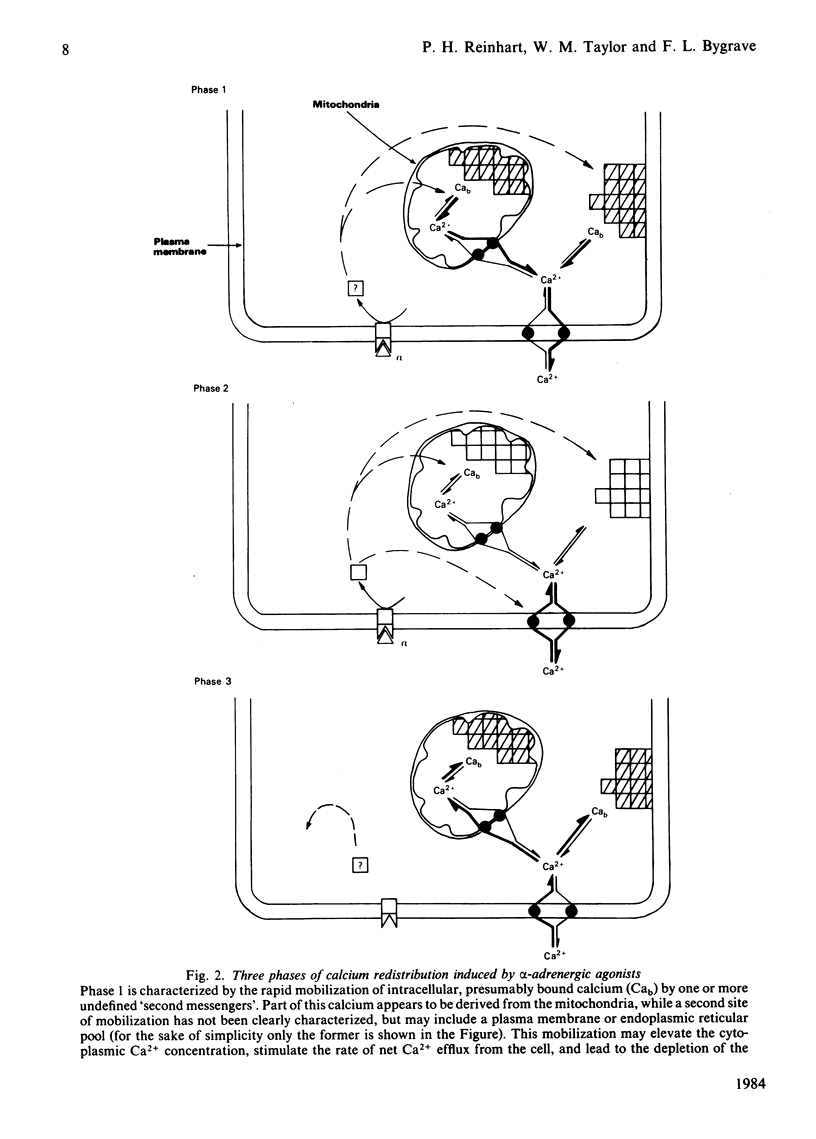


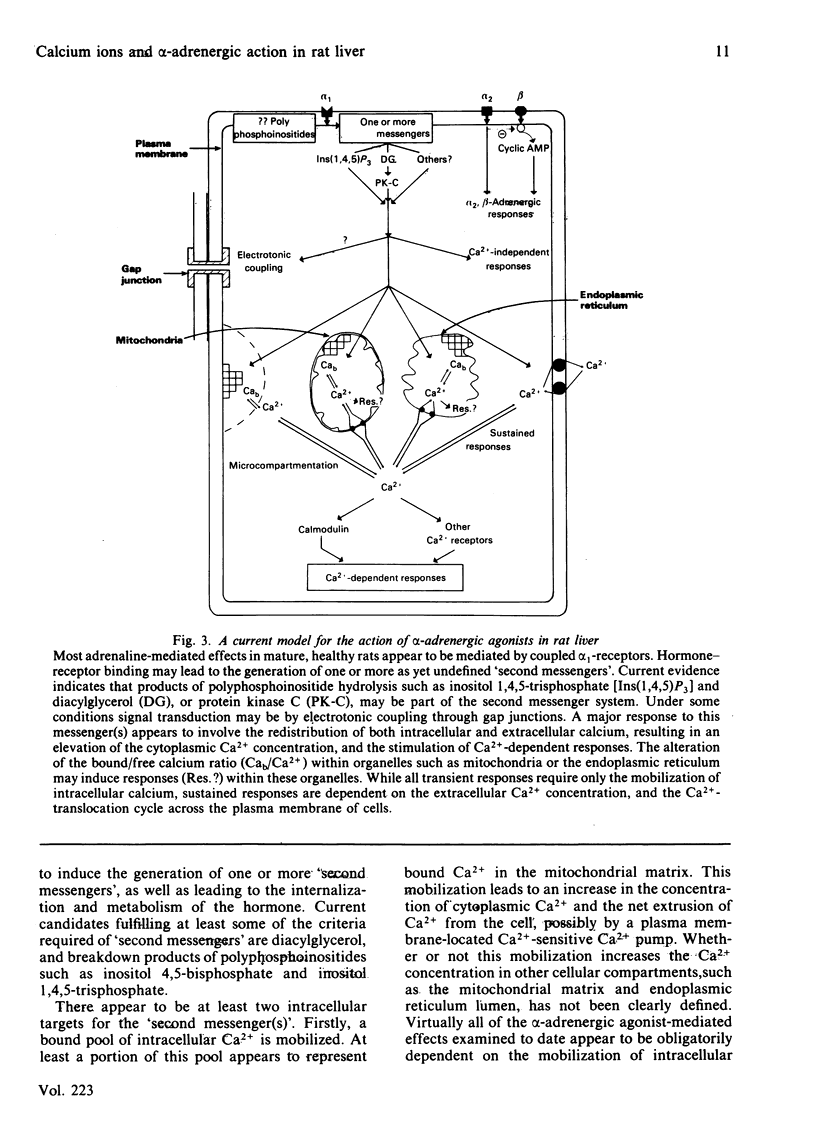


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Guellaen G., Hanoune J. Adrenergic receptor of the alpha 1-subtype mediates the activation of the glycogen phosphorylase in normal rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 15;29(4):643–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Althaus-Salzmann M., Carafoli E., Jakob A. Ca2+, K+ redistributions and alpha-adrenergic activation of glycogenolysis in perfused rat livers. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F. D., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Studies on role of calcium in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. F., Chen J. L., Yip B. P., Lardy H. A. Evidence for mitochondrial localization of the hormone-responsive pool of Ca2+ in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8117–8120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barritt G. J., Parker J. C., Wadsworth J. C. A kinetic analysis of the effects of adrenaline on calcium distribution in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:29–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G. L., Fiskum G., Lehninger A. L. Regulation of free Ca2+ by liver mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9009–9012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and calcium signaling. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthon B., Poggioli J., Capiod T., Claret M. Effect of the alpha-agonist noradrenaline on total and 45Ca2+ movements in mitochondria of rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):177–180. doi: 10.1042/bj2000177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Dehaye J. P., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. The role of mitochondrial calcium release in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6945–6950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Hughes B. P., Shuman E. A., Exton J. H. alpha-Adrenergic activation of phosphorylase in liver cells involves mobilization of intracellular calcium without influx of extracellular calcium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):190–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Control, Modulation, and regulation of cell calcium. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;90:13–153. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Methods for assessing hormone effects on calcium fluxes in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:513–573. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L. Mitochondria and the control of intracellular calcium. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1978 Feb;53(1):43–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1978.tb00992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Berthon B., Exton J. H. Changes in free cytosolic Ca2+ in hepatocytes following alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation. Studies on Quin-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8769–8773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret-Berthon B., Claret M., Mazet J. L. Fluxes and distribution of calcium in rat liver cells: kinetic analysis and identification of pools. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):529–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll K. E., Joseph S. K., Corkey B. E., Williamson J. R. Determination of the matrix free Ca2+ concentration and kinetics of Ca2+ efflux in liver and heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8696–8704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAHOTA Z., CARAFOLI E., ROSSI C. S., GAMBLE R. L., LEHNINGER A. L. THE STEADY STATE MAINTENANCE OF ACCUMULATED CA++ IN RAT LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2712–2720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wulf H., Keppens S. Proceedings: Is calcium the second messenger in liver for cyclic AMP-independent glycogenolytic hormones? Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Feb;84(1):159–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehaye J. P., Blackmore P. F., Venter J. C., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. alpha-Adrenergic activation of phosphorylase by immobilized epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3905–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G., Edgell N. J. Role of calcium ions in the regulation of intramitochondrial metabolism. Effects of Na+, Mg2+ and ruthenium red on the Ca2+-stimulated oxidation of oxoglutarate and on pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in intact rat heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):107–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1900107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. On the role of the calcium transport cycle in heart and other mammalian mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Refai M. F., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Evidence for two alpha-adrenergic binding sites in liver plasma membranes. Studies with [3H]epinephrine and [3H]dihydroergocryptine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4375–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Molecular mechanisms involved in alpha-adrenergic responses. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Sep;23(3):233–264. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foden S., Randle P. J. Calcium metabolism in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):615–625. doi: 10.1042/bj1700615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geynet P., Ferry N., Borsodi A., Hanoune J. Two distinct alpha1-adrenergic receptor sites in rat liver: differential binding of (--)-[3H]dihydroergocryptine. Effects of guanine nucleotides and proteolysis; implications for a two-site model of alpha-receptor regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 15;30(12):1665–1675. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. M., Hess H. J., Homcy C. J. Solubilization and purification of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor using a novel affinity resin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2186–2190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guellaen G., Aggerbeck M., Hanoune J. Characterization and solubilization of the alpha-adrenoreceptor of rat liver plasma membranes labeled with [3H]phenoxybenzamine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10761–10768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford R. G., Castro F. Effects of micromolar concentrations of free calcium ions on the reduction of heart mitochondrial NAD(P) by 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1980525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford R. G., Castro F. Intramitochondrial and extramitochondrial free calcium ion concentrations of suspensions of heart mitochondria with very low, plausibly physiological, contents of total calcium. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Dec;14(5-6):361–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00743064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford R. G. Effect of micromolar concentrations of free Ca2+ ions on pyruvate dehydrogenase interconversion in intact rat heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):721–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1940721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Kilpatrick D. M., Lefkowitz R. J., Tolbert M. E., Gilman H., Fain J. N. Agonist versus antagonist binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob A., Diem S. Metabolic responses of perfused rat livers to alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists, glucagon and cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Stimulus-response coupling at alpha-adrenergic receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):673–688. doi: 10.1042/bst0060673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Coll K. E., Cooper R. H., Marks J. S., Williamson J. R. Mechanisms underlying calcium homeostasis in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):731–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Steinberg D. Stimulation of rat liver phosphorylase kinase by micromolar concentrations of Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Kugai N., Tada R., Kojima I., Abe K., Ogata E. Sources of calcium mobilized by alpha-adrenergic stimulation in perfused rat liver. Horm Metab Res. 1982 Mar;14(3):133–138. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Kan W. H., Greguski R., Venter J. C. Selective affinity labeling and molecular characterization of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptors with [3H]phenoxybenzamine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Tsien R. Y., Miner C., Bookchin R. M. Physiological [Ca2+]i level and pump-leak turnover in intact red cells measured using an incorporated Ca chelator. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):478–481. doi: 10.1038/298478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra R., Olson M. S. The effects of chlorotetracycline on calcium movements in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madeira V. M. A rapid and ultrasensitive method to measure Ca++ movements across biological membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):870–876. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. A comparative study of the regulation of Ca2+ of the activities of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex and NAD+-isocitrate dehydrogenase from a variety of sources. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):619–624. doi: 10.1042/bj1960619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Role of calcium ions in the regulation of intramitochondrial metabolism. Properties of the Ca2+-sensitive dehydrogenases within intact uncoupled mitochondria from the white and brown adipose tissue of the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):95–105. doi: 10.1042/bj1900095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Coll K., Rich T. L., Williamson J. R. Hormonal effects on calcium homeostasis in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6600–6608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in the brain. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):583–588. doi: 10.1038/305583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The regulation of extramitochondrial free calcium ion concentration by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):463–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1760463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Akerman K. Mitochondrial calcium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 1;683(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Berthon B., Claret M. Calcium movements in in situ mitochondria following activation of alpha-adrenergic receptors in rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Arslan P., Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Anti-immunoglobulin, cytoplasmic free calcium, and capping in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. myo-Inositol uptake and metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11315–11322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. A procedure for the rapid preparation of mitochondria from rat liver. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):731–735. doi: 10.1042/bj2040731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. Binding and uptake of [3H]adrenaline by perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):765–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2180765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. Calcium ion fluxes induced by the action of alpha-adrenergic agonists in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):619–630. doi: 10.1042/bj2080619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. Studies on alpha-adrenergic-induced respiration and glycogenolysis in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1906–1912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. The contribution of both extracellular and intracellular calcium to the action of alpha-adrenergic agonists in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):35–42. doi: 10.1042/bj2200035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. The effect of ionophore A23187 on calcium ion fluxes and alpha-adrenergic-agonist action in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):405–412. doi: 10.1042/bj2140405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in hepatocytes by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2770–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytka J., Bilinski T., Labbe-Bois R. Modified uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity in a yeast mutant which mimics porphyria cutanea tarda. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):405–413. doi: 10.1042/bj2180405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Matsumura S., Okimura Y., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Liver glycogen phosphorylase kinase. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6631–6637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Kirk C. J. Determination of mitochondrial calcium content in hepatocytes by a rapid cellular-fractionation technique. Alpha-adrenergic agonists do not mobilize mitochondrial Ca2+. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):383–389. doi: 10.1042/bj2190383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Cohen P. T., Cohen P., Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. The role of calmodulin in the structure and regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazu T., Amakawa A. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in liver by the autonomic nervous system. VI. Possible mechanism of phosphorylase activation by the splanchnic nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H., Graf P., Estrela J. M. Hepatic calcium efflux during cytochrome P-450-dependent drug oxidations at the endoplasmic reticulum in intact liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3358–3362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Taube H. D., Browski E. Presynaptic receptor systems in catacholamingergic transmission. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Feb 15;26(4):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano T., Shiota M., Khono H., Shimada M., Oshino N. Effects of calcium ions on the activation of gluconeogenesis by norepinephrine in perfused rat liver. J Biochem. 1980 Feb;87(2):465–472. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano T., Suda K., Shimada M., Oshino N. Biochemical and ultrastructural evaluation of isolated rat liver systems perfused with a hemoglobin-free medium. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):995–1007. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kawahara Y., Minakuchi R., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Mori T., Yu B., Kaibuchi K., Nishizuka Y. Calcium and phosphatidylinositol turnover as signalling for transmembrane control of protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:301–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. M., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Bygrave F. L. Stable changes to calcium fluxes in mitochondria isolated from rat livers perfused with alpha-adrenergic agonists and with glucagon. Biochem J. 1980 May 15;188(2):443–450. doi: 10.1042/bj1880443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. M., Reinhart P. H., Bygrave F. L. On the role of calcium in the mechanism of action of alpha-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;21(1):125–141. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. M., Reinhart P. H., Bygrave F. L. Stimulation by alpha-adrenergic agonists of Ca2+ fluxes, mitochondrial oxidation and gluconeogenesis in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):555–565. doi: 10.1042/bj2120555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., White A. C., Aspry K., Cutts J., Fain J. N. Stimulation by vasopressin and alpha-catecholamines of phosphatidylinositol formation in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1938–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rossum G. D. Net movements of calcium and magnesium in slices of rat liver. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):18–32. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. X., Millikin D. M., Schlender K. K., Reimann E. M. Stimulation of phosphorylase b kinase by the calcium-dependent regulator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5036–5042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting J. A., Barritt G. J. On the mechanism by which hormones induce the release of Ca2+ from mitochondria in the liver cell. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):121–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2060121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton P. D., Rodrigues L. M., Hems D. A. Influence of extracellular calcium ions on hormonal stimulation of glycogen breakdown in hepatocyte suspensions [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):992–994. doi: 10.1042/bst0050992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J. Calcium ions: their ligands and their functions. Biochem Soc Symp. 1974;(39):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Cooper R. H., Hoek J. B. Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):243–295. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Hue L., Hers H. G. Hormonal and ionic control of the glycogenolytic cascade in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):135–142. doi: 10.1042/bj1620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


