Abstract
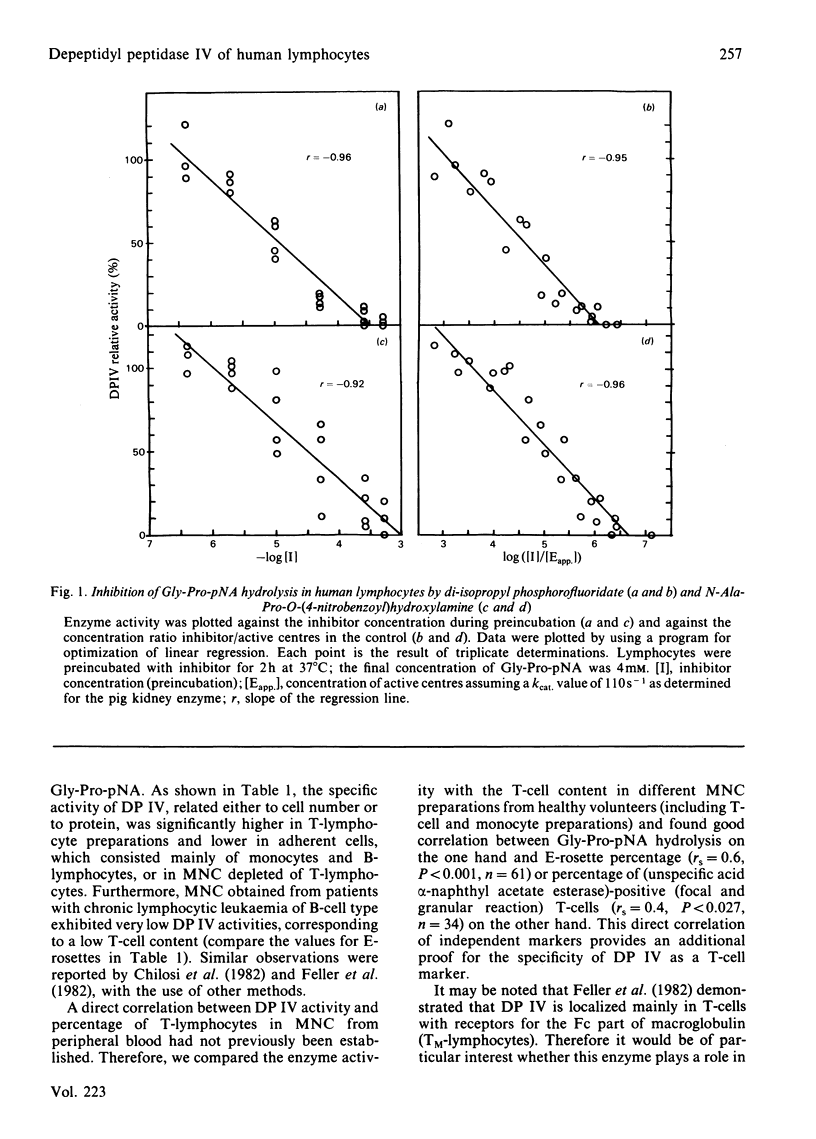
Glycylproline p-nitroanilide is hydrolysed in lymphocytes from human blood exclusively by dipeptidyl peptidase IV. This was demonstrated by specific inhibition with N-alanylprolyl-O-(4-nitrobenzoyl)hydroxylamine and di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate and by studying the membrane localization of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and determining specific dipeptidyl peptidase II activity. Additional evidence that dipeptidyl peptidase IV is a marker for T-lymphocytes, obtained from determinations of biochemical activity on intact lymphocyte preparations and correlation studies with other T-cell markers, is also presented.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chilosi M., Pizzolo G., Menestrina F., Iannucci A. M., Bonetti F., Fiore-Donati L. Dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV (DAP-IV) histochemistry on normal and pathologic lymphoid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;77(6):714–719. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.6.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J. Biogenesis of plasma membrane glycoproteins. Purification and properties of two rat liver plasma membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5807–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller A. C. Cytochemical reactivity of T mu lymphocytes in human lymphatic tissue for dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV. Histochem J. 1982 Nov;14(6):889–895. doi: 10.1007/BF01005231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller A. C., Heijnen C. J., Ballieux R. E., Parwaresch M. R. Enzymehistochemical staining of T mu lymphocytes for glycyl-proline-4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamide-peptidase (DAP IV). Br J Haematol. 1982 Jun;51(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Demuth H. U., Barth A. N,O-diacylhydroxylamines as enzyme-activated inhibitors for serine proteases. Pharmazie. 1983 Apr;38(4):249–250. doi: 10.1002/chin.198341334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K., Fukasawa K. M., Hiraoka B. Y., Harada M. Purification and properties of dipeptidyl peptidase II from rat kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 30;745(1):6–11. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossrau R. Investigation of proteinases in the digestive tract using 4-methoxy-2-naphthylamine (MNA) substrates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Mar;29(3A):464–480. doi: 10.1177/29.3.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Sarimo S. R. Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase hydrolyzing glycyl-proline-naphthylamide. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Nov;348(11):1540–1550. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1967.348.1.1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Allison A. C., Ward P., Kight N. Identification of human mononuclear leucocyte populations by esterase staining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner J., Ansorge S., Bohhley P., Kirschke H., Hanson H. Intracellular protein breakdown. I. Activity determinations of endoipeptidases using protein substrates. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;26(5):935–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lojda Z. Studies on glycyl-proline naphthylamidase. I. Lymphocytes. Histochemistry. 1977 Dec 28;54(4):299–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00508273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnair D. C., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):379–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1790379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen M., Johnsen H. E., Hansen P. W., Christiansen S. E. Isolation of human T and B lymphocytes by E-rosette gradient centrifugation. Characterization of the isolated subpopulations. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(4):323–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Schwabe C. Dipeptidyl peptidase II of bovine dental pulp. Initial demonstration and characterization as a fibroblastic, lysosomal peptidase of the serine class active on collagen-related peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):68–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sannes P. L. Subcellular localization of dipeptidyl peptidases II and IV in rat and rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 May;31(5):684–690. doi: 10.1177/31.5.6341458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E. Proteolytic activities in plasma membrane preparations from rat liver. 2. Partial purification and characterization of membrane bound endopeptidases, dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase IV and aminopeptidase. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1983;42(5):451–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Simmons W. H., Yoshimoto T. Proline specific endo- and exopeptidases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Apr 18;30(2):111–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00227927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


