Abstract
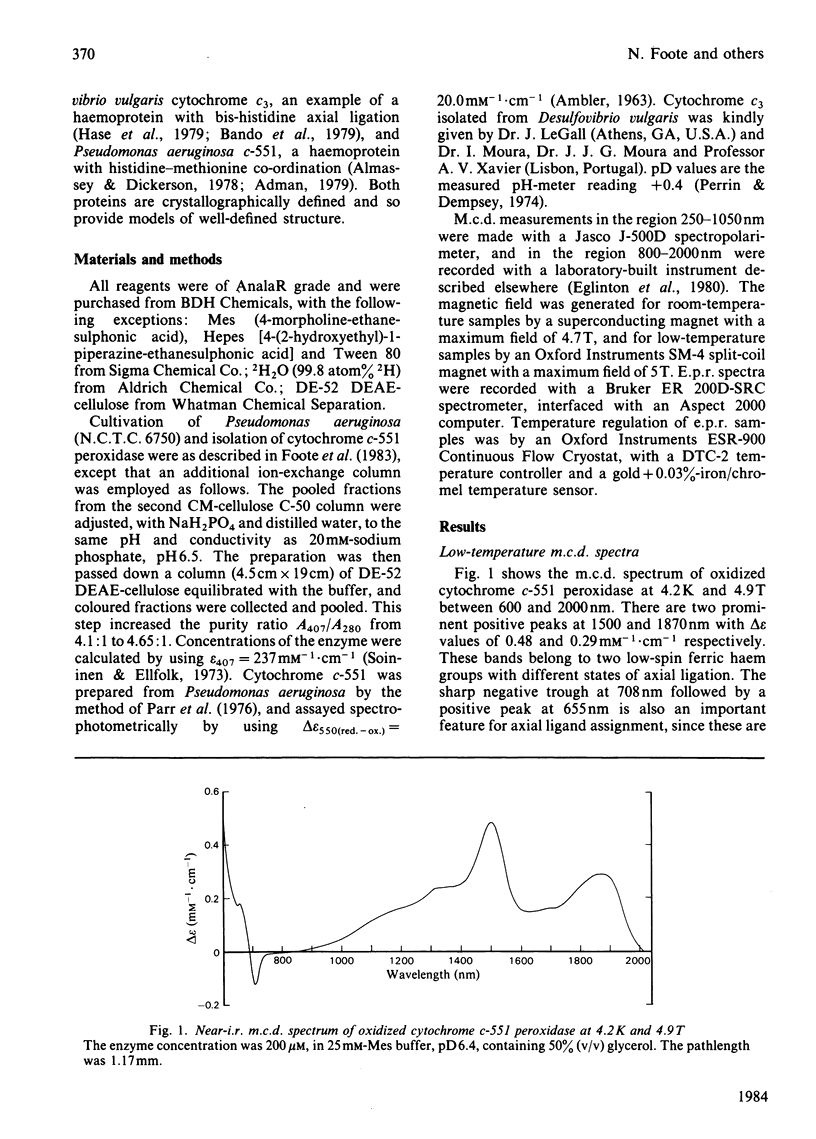
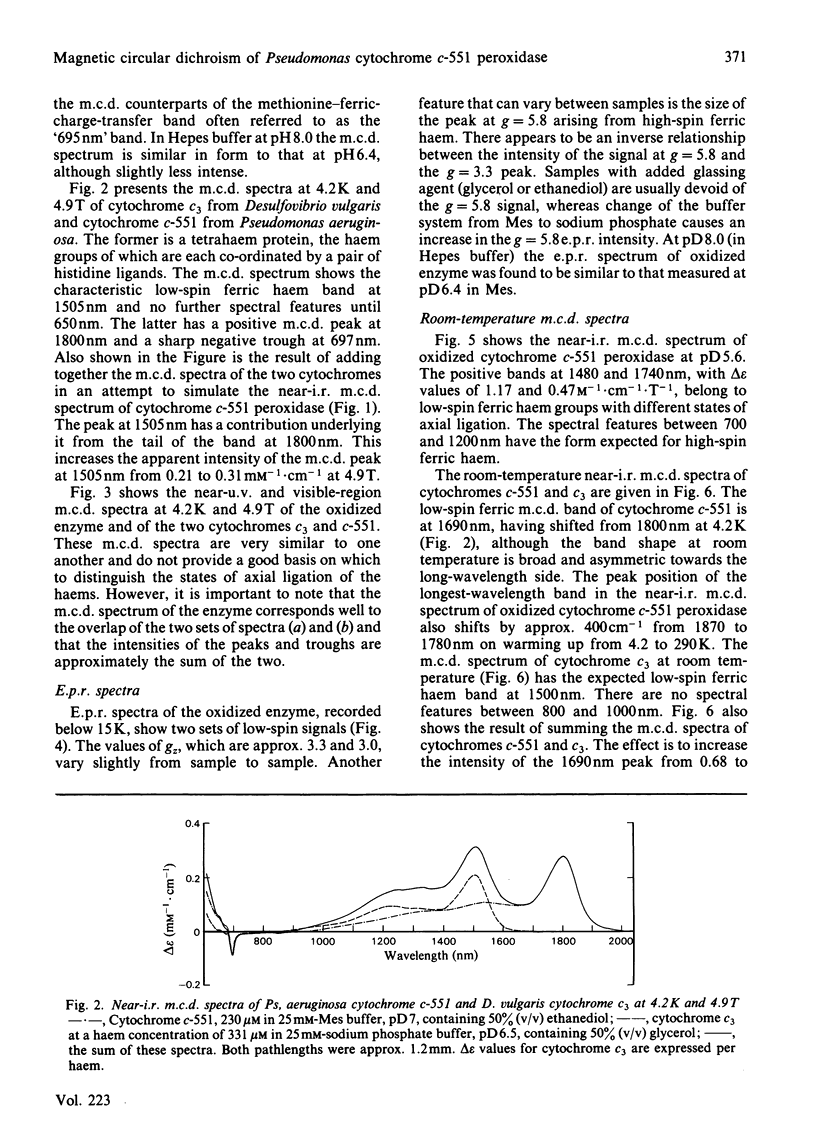
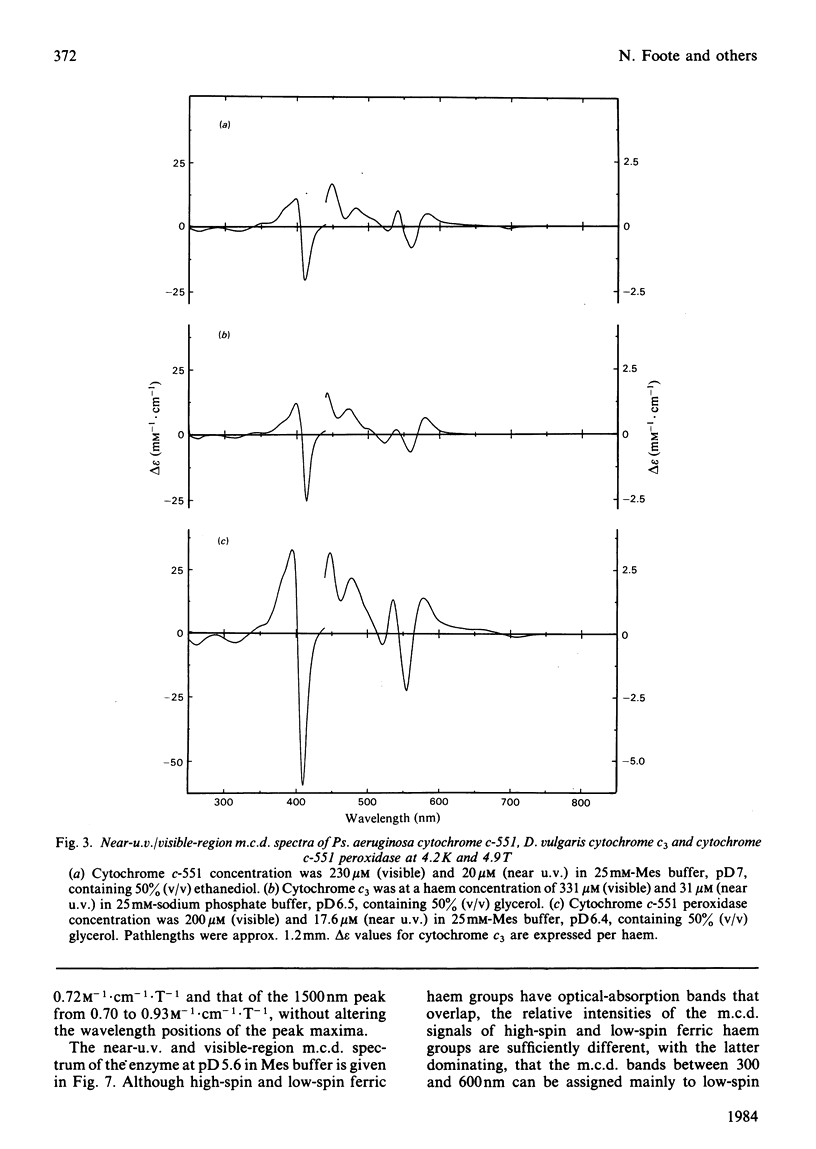
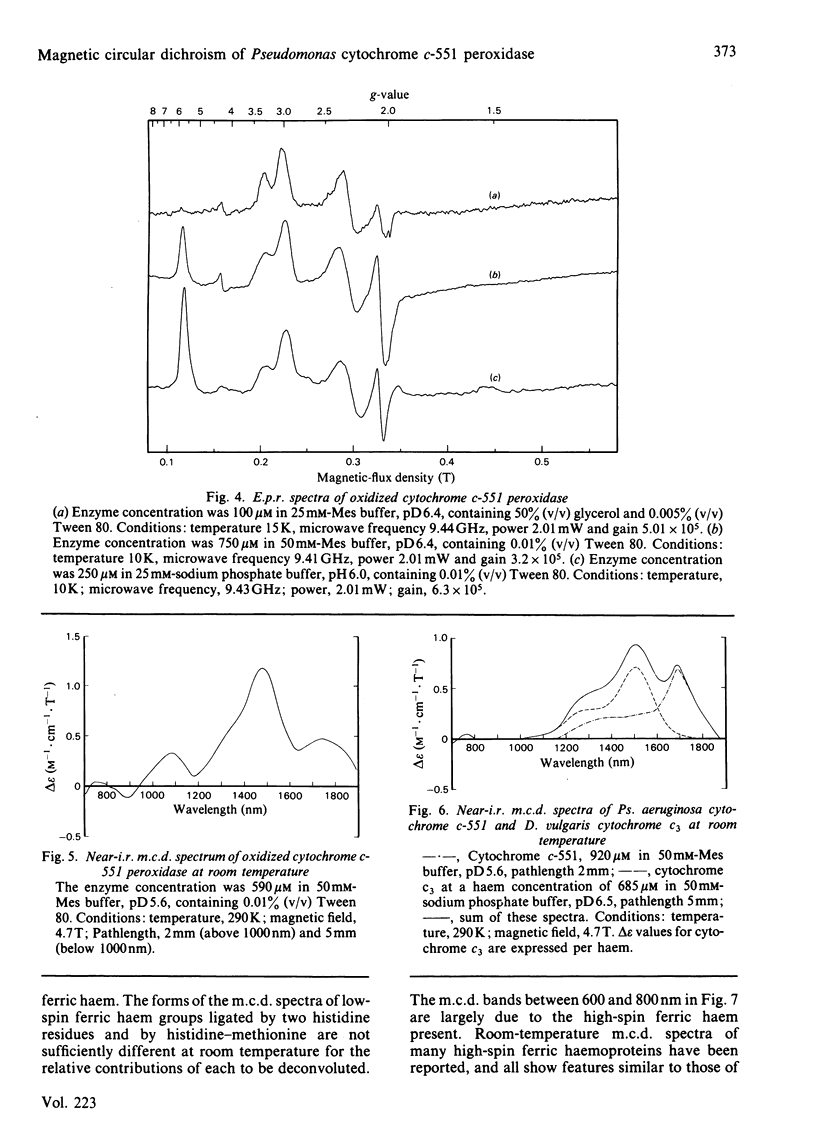
The magnetic properties at different temperatures of oxidized Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytochrome c-551 peroxidase were studied, with the use of the technique of magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. At 4.2K, both constituent haems were found to be low-spin, and the axial ligand pairs were identified as histidine-histidine and histidine-methionine. At room temperature high-spin signals were observed, amounting to less than 25% of the total haem present. These signals are concluded to arise mainly from a temperature-dependent spin-state equilibrium in the methionine-ligated haem.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE PURIFICATION AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:341–349. doi: 10.1042/bj0890341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasa R., Ellfolk N., Rönnberg M., Vänngärd T. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 29;670(2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adman E. T. A comparison of the structures of electron transfer proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):107–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almassy R. J., Dickerson R. E. Pseudomonas cytochrome c551 at 2.0 A resolution: enlargement of the cytochrome c family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2674–2678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bando S., Matsuura Y., Tanaka N., Yasuoka N., Kakudo M., Yagi T., Inokuchi H. Crystallographic data for cytochrome c3 from two strains of Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Miyazaki. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):269–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglinton D. G., Gadsby P. M., Sievers G., Peterson J., Thomson A. J. A comparative study of the low-temperature magnetic circular dichroism spectra of horse heart metmyoglobin and bovine liver catalase derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):648–658. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglinton D. G., Johnson M. K., Thomson A. J., Gooding P. E., Greenwood C. Near-infrared magnetic and natural circular dichroism of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):319–331. doi: 10.1042/bj1910319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellfolk N., Rönnberg M., Aasa R., Andréasson L. E., Vänngård T. Anion binding to resting and half-reduced Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 18;784(1):62–67. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellfolk N., Rönnberg M., Aasa R., Andréasson L. E., Vänngård T. Properties and function of the two hemes in Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 28;743(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellfolk N., Soininen R. Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. 3. The size and shape of the enzyme molecule. Acta Chem Scand. 1971;25(5):1535–1540. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.25-1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote N., Thompson A. C., Barber D., Greenwood C. Pseudomonas cytochrome C-551 peroxidase. A purification procedure and study of CO-binding kinetics. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2090701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Wilson M. T. Studies on ferricytochrome c. I. Effect of pH, ionic strength and protein denaturants on the spectra of ferricytochrome c. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):5–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haser R., Pierrot M., Frey M., Payan F., Astier J. P., Bruschi M., Le Gall J. Structure and sequence of the multihaem cytochrome c3. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):806–810. doi: 10.1038/282806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky L. S., Miller V. J., Davison A. J. Thermodynamic studies of the opening of the heme crevice of ferricytochrome c. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2215–2221. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Nozawa T., Hatano M. Magnetic circular dichroism studies on acid and alkaline forms of horseradish peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):340–351. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Structural basis for the variation in redox potential of cytochromes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80793-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa T., Yamamoto T., Hatano M. Infrared magnetic circular dichroism of myoglobin derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 18;427(1):28–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr S. R., Barber D., Greenwood C. A purification procedure for the soluble cytochrome oxidase and some other respiratory proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):423–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1570423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Blumberg W. E., Adler A. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of iron porphin and chlorin systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;206:310–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb43219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Stephens P. J., Nafie L. A., Kamen M. D. Near-infrared magnetic circular dichroism of cytochrome c'. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1725–1729. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg M., Ellfolk N. Heme-linked properties of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Evidence for non-equivalence of the hemes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 14;581(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg M., Osterlund K., Ellfolk N. Resonance Raman spectra of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senn H., Keller R. M., Wüthrich K. Different chirality of the axial methionine in homologous cytochromes c determined by 1H NMR and CD sectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 27;92(4):1362–1369. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sievers G., Gadsby P. M., Peterson J., Thomson A. J. Assignment of the axial ligands of the haem in milk lactoperoxidase using magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen R., Ellfolk N. Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. V. Absorption spectra of the enzyme and of its compounds with ligands. Inhibition of the enzyme by cyanide and azide. Acta Chem Scand. 1973;27(1):35–46. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. J., Johnson M. K. Magnetization curves of haemoproteins measured by low-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):411–420. doi: 10.1042/bj1910411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuk-Pavlović S., Benko B. The haem-enviroment in horseradish peroxidase as seen by proton magnetic relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1154–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


