Abstract
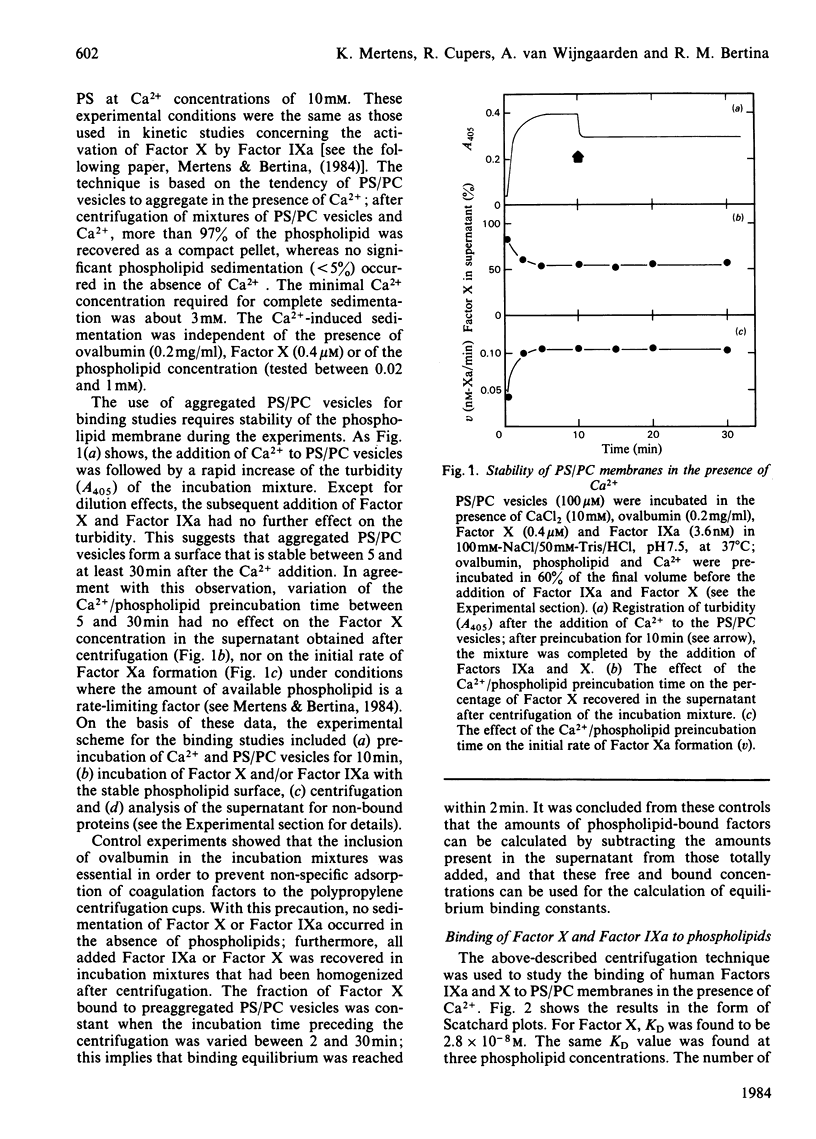
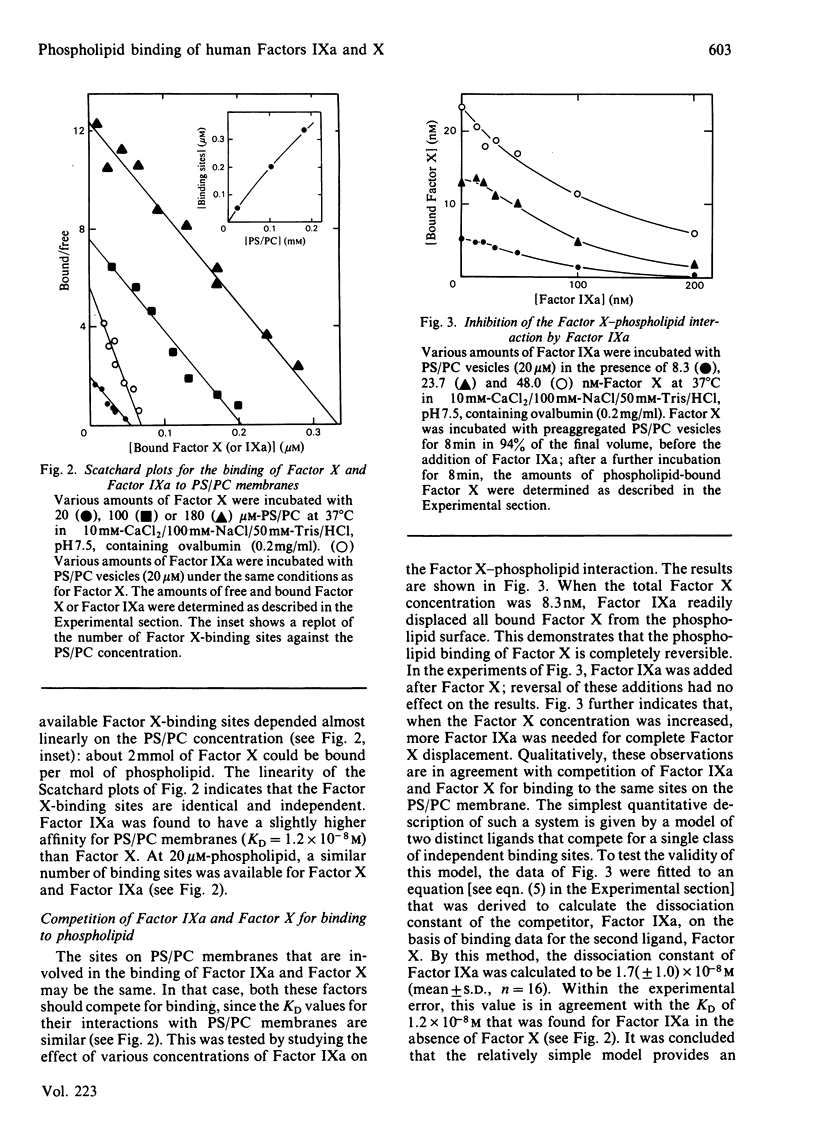
A simple centrifugation technique has been developed to study the interaction of human coagulation Factors IXa and X with phospholipid membranes. In the presence of Ca2+, equimolar phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine membranes form tight complexes with Factor X (KD = 2.8 X 10(-8) M); the KD is independent of the phospholipid concentration. Binding sites are available for about 2 mmol of Factor X/mol of phospholipid. Factor IXa has a slightly higher affinity for the phospholipid membrane (KD = 1.2 X 10(-8)M), and competes with Factor X for binding. The experimentally observed competition between Factor X and Factor IXa is in agreement with a model that describes the binding of two distinct ligands to a single class of independent binding sites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Brown J. E. Interaction of factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor with phospholipid vesicles. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2000161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. L., Begué-Cantón M. L., Blakeley R. L., Brubacher L. J., Feder J., Gunter C. R., Kézdy F. J., Killheffer J. V., Jr, Marshall T. H., Miller C. G. The determination of the concentration of hydrolytic enzyme solutions: alpha-chymotrypsin, trypsin, papain, elastase, subtilisin, and acetylcholinesterase. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Dec 20;88(24):5890–5913. doi: 10.1021/ja00976a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Veltkamp J. J. The abnormal factor IX of hemophilia B+ variants. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Oct 31;40(2):335–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Westhoek-Kuipers M. E., Alderkamp G. H. The inhibitor of prothrombin conversion in plasma of patients on oral anticoagulant treatment. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., van der Linden I. K. Inhibitor-neutralisation assay and electro-immuno assay of human factor IX (Christmas factor). Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jun 15;77(3):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Phospholipid-binding properties of bovine factor V and factor Va. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4419–4425. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne R., Link R. P., Castellino F. J. A kinetic evaluation of activated bovine blood coagulation factor IX toward synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5336–5341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong C. S., Colbow K. Light scattering and turbidity measurements on lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):260–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kurachi K., Kisiel W. The role of serine proteases in the blood coagulation cascade. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;48:277–318. doi: 10.1002/9780470122938.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day E. P., Ho J. T., Kunze R. K., Jr, Sun S. T. Dynamic light scattering study of calcium-induced fusion in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 1;470(3):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrose F. A., Gitel S. N., Zawalich K., Jackson C. M. The association of bovine prothrombin fragment 1 with phospholipid. Quantitative characterization of the Ca2+ ion-mediated binding of prothrombin fragment 1 to phospholipid vesicles and a molecular model for its association with phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5027–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Schwartz S. M. Binding of coagulation factors IX and X to the endothelial cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Factor X activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom: isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4901–4906. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajmanovich A., Hudry-Clergeon G., Freyssinet J. M., Marguerie G. Human factor VIII procoagulant activity and phospholipid interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 18;678(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Miller I. R., Elion J., Benarous R. Interaction of prothrombin and its fragments with monolayers containing phosphatidylserine. 1. Binding of prothrombin and its fragment I to phosphatidylserine-containing monolayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3434–3439. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist P. A., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent) and a protease from Russell's viper venom. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. Activation of human coagulation factor VIII by activated factor X, the common product of the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. Pathways in the activation of human coagulation factor X. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):647–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1850647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. The contribution of Ca2+ and phospholipids to the activation of human blood-coagulation Factor X by activated Factor IX. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):607–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2230607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Broderius M. Interaction of prothrombin and blood-clotting factor X with membranes of varying composition. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4172–4177. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Kisiel W., Di Scipio R. G. Interaction of vitamin K dependent proteins with membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2134–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Lim T. K. Equilibria involved in prothrombin- and blood-clotting factor X-membrane binding. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4164–4171. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S., Düzgüneş N., Leonards K. Phospholipid vesicle aggregation: effect of monovalent and divalent ions. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):2127–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Jacobson K., Poste G. Cochleate lipid cylinders: formation by fusion of unilamellar lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Waugh D. F. The purification of human prothrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Dec 1;16(3):468–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L. Titration of activated bovine Factor X. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2418–2423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent formation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:157–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokutomi S., Eguchi G., Ohnishi S. I. Disappearance of calcium-induced phase separation in phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylcholine membranes caused by protonation and by electric current. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 23;552(1):78–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltkamp J. J., Drion E. F., Loeliger E. A. Detection of the carrier state in hereditary coagulation disorders. I. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):279–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F. Membrane and lipid involvement in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):163–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


