Abstract
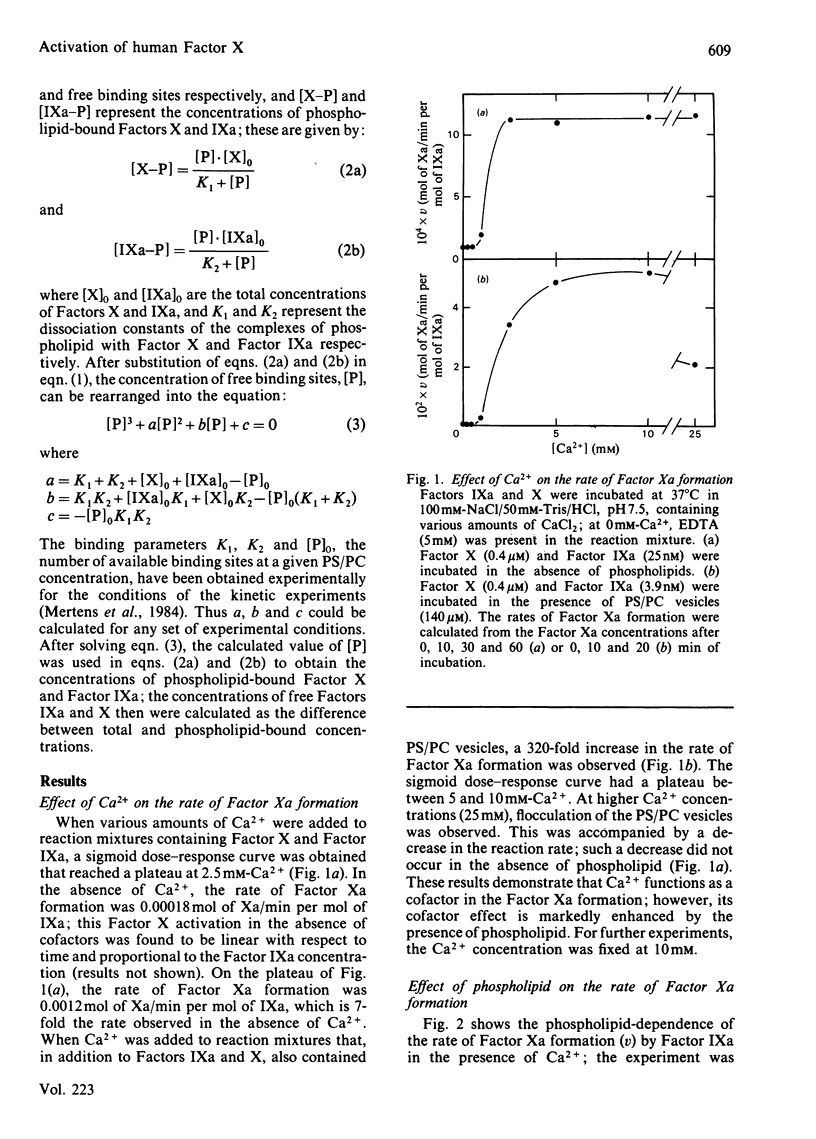
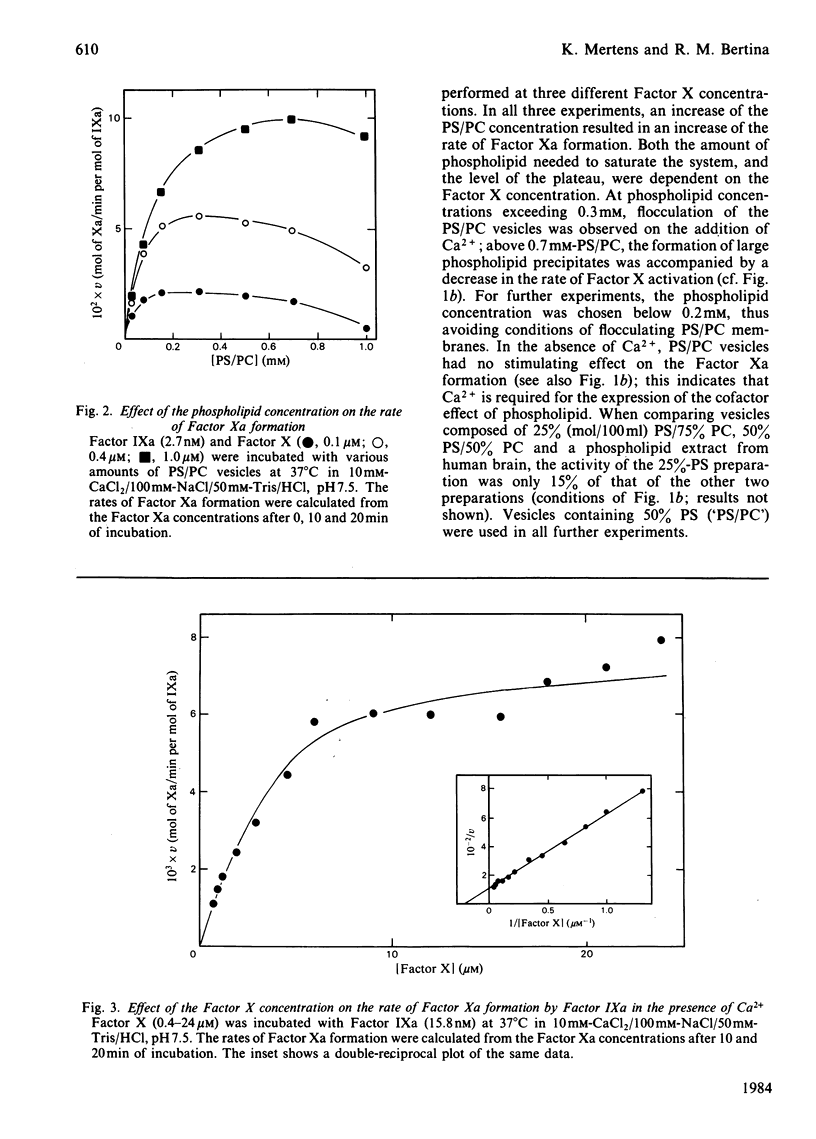
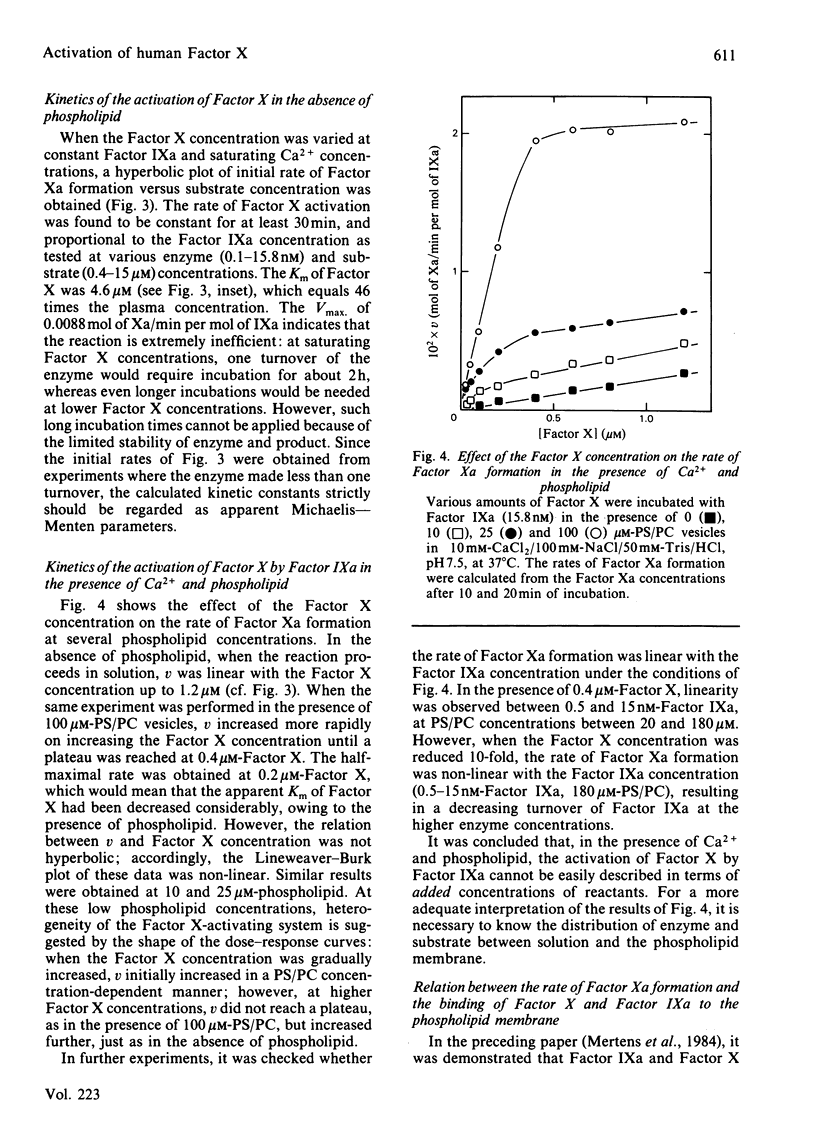
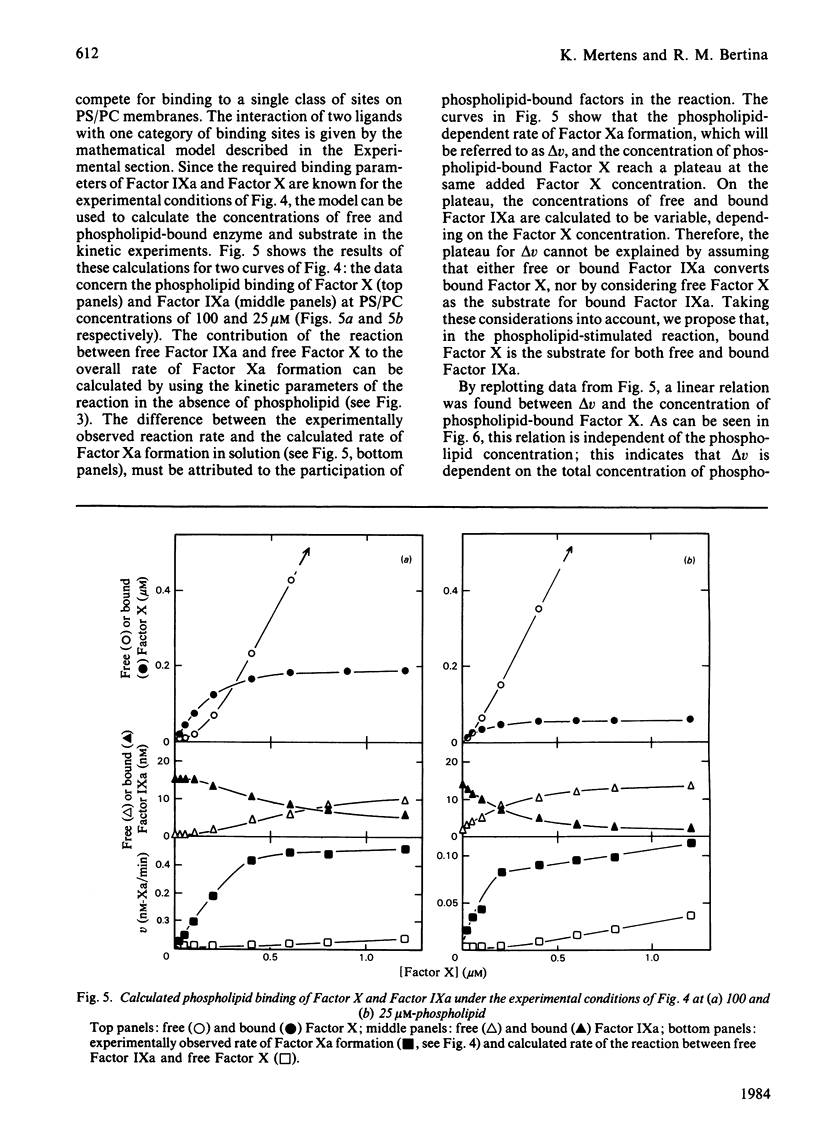
The role of the cofactors Ca2+ and phospholipid in the activation of human Factor X by Factor IXa was investigated. By use of a sensitive spectrophotometric Factor Xa assay, it was demonstrated that human Factor IXa can activate Factor X in the absence of cofactors. The presence of Ca2+ as the only cofactor resulted in a 7-fold stimulation of the Factor Xa formation. Kinetic analysis of the Ca2+-stimulated reaction showed that the apparent Km of Factor X was 4.6 microM, whereas the apparent Vmax. for Factor Xa formation was 0.0088 mol of Xa/min per mol of IXa. The presence of phospholipid as the only cofactor had no effect on the rate of Factor Xa formation. However, a several-hundred-fold stimulation was observed when Ca2+ and phospholipid were present in combination. The activation of Factor X in the presence of Ca2+ and phospholipid was found to be kinetically heterogeneous, involving both phospholipid-bound and free reactants. Quantitative data concerning the phospholipid binding of Factors IXa and X were used to study the relation between the rate of Factor Xa formation and the binding of enzyme and substrate to the phospholipid membrane. The results support the hypothesis that phospholipid-bound Factor X is the substrate in the phospholipid-stimulated reaction; however, phospholipid-bound and free Factor IXa seem to be equally efficient in catalysing the activation of phospholipid-bound Factor X.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amphlett G. W., Kisiel W., Castellino F. J. The interaction of Ca2+ with human Factor IX. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 May;208(2):576–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90546-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurell L., Friberger P., Karlsson G., Claeson G. A new sensitive and highly specific chromogenic peptide substrate for factor Xa. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P. Cooperative Ca2+ binding to human factor IX. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetic parameters of the activation of factor IX by factor XIa. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4127–4132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. F., Sargeant R. B., Hougie C. The intrinsic activation of factor X in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 19;273(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kurachi K., Kisiel W. The role of serine proteases in the blood coagulation cascade. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;48:277–318. doi: 10.1002/9780470122938.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrose F. A., Gitel S. N., Zawalich K., Jackson C. M. The association of bovine prothrombin fragment 1 with phospholipid. Quantitative characterization of the Ca2+ ion-mediated binding of prothrombin fragment 1 to phospholipid vesicles and a molecular model for its association with phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5027–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J., Reisner H. M., Lundblad R. L., Roberts H. R. Measurement of human factor IXa activity in an isolated factor X activation system. Thromb Res. 1982 Aug 1;27(3):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemker H. C., Kahn M. J. Reaction sequence of blood coagulation. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1201–1202. doi: 10.1038/2151201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobin F., Esnouf M. P. Studies on the formation of the prothrombin-converting complex. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):666–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1020666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindhout T., Govers-Riemslag J. W., van de Waart P., Hemker H. C., Rosing J. Factor Va-factor Xa interaction. Effects of phospholipid vesicles of varying composition. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5494–5502. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link R. P., Castellino F. J. Kinetic comparison of bovine blood coagulation factors IXa alpha and IXa beta toward bovine factor X. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4033–4041. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. Activation of human coagulation factor VIII by activated factor X, the common product of the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. Pathways in the activation of human coagulation factor X. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):647–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1850647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Cupers R., Van Wijngaarden A., Bertina R. M. Binding of human blood-coagulation Factors IXa and X to phospholipid membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):599–605. doi: 10.1042/bj2230599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Wortelboer M., van Dieijen G., Bertina R. M. Proteolysis of blood coagulation factor X by activated factor X: difference between the bovine and human proteins. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):174–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80844-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S., Robey F. A., Kosow D. P. Kinetic studies on the activation of human factor X. The role of metal ions on the reaction catalyzed by the venom coagulant protein of Viper russelli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4604–4608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal G. G., Chavin S. I. The role of factors VIII and IX in the activation of bovine blood coagulation factor X. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Kisiel W., Di Scipio R. G. Interaction of vitamin K dependent proteins with membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2134–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Eid S., Mann K. G. Assembly of the prothrombinase complex in the absence of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9874–9882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Tracy R. P., Mann K. G. "Clotspeed," a mathematical simulation of the functional properties of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1447–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Synthesis of intrinsic factor X activator. Inhibition of the function of formed activator by antibodies to factor VIII and to factor IX. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 14;9(8):1854–1861. doi: 10.1021/bi00810a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Nelsestuen G. L. The physical significance of Km in the prothrombinase reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):526–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90812-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent formation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:157–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomela H., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. The activation of factor X evaluated by using synthetic substrates. Thromb Res. 1977 Feb;10(2):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker M. M., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Differentiation of enzyme and substrate binding in the prothrombinase complex. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4540–4546. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


