Abstract
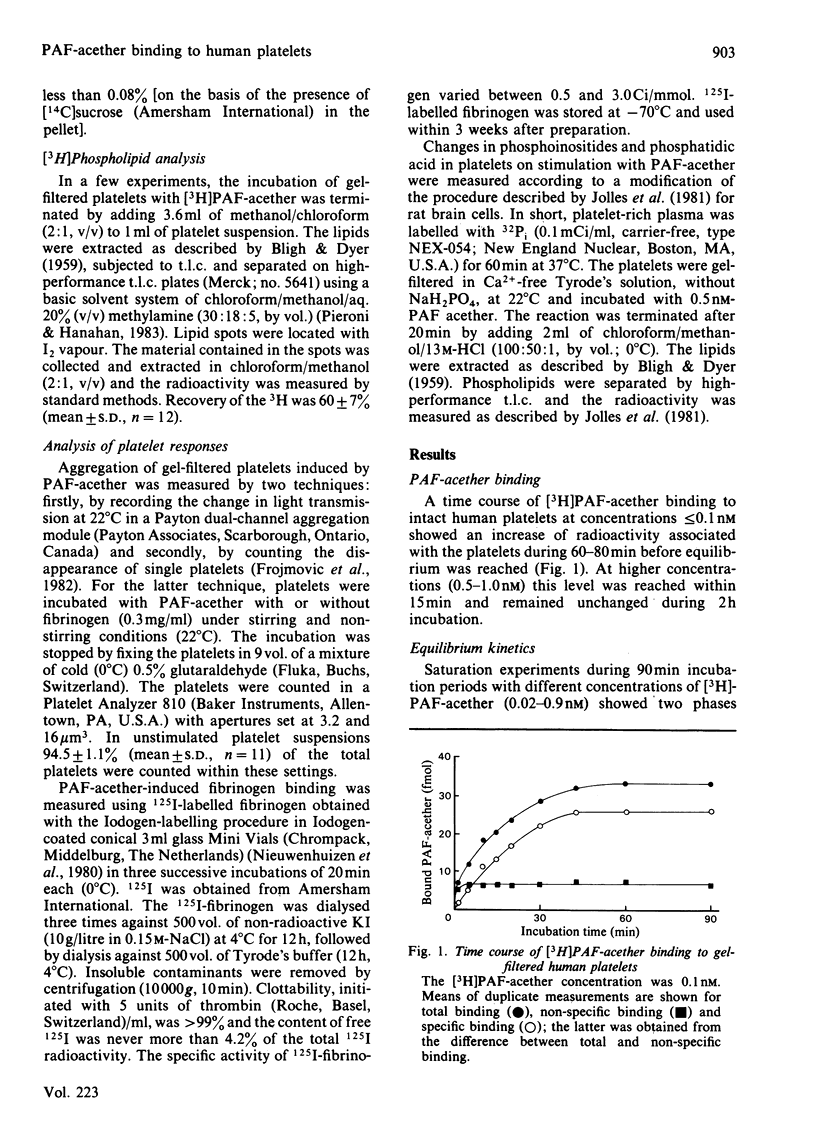
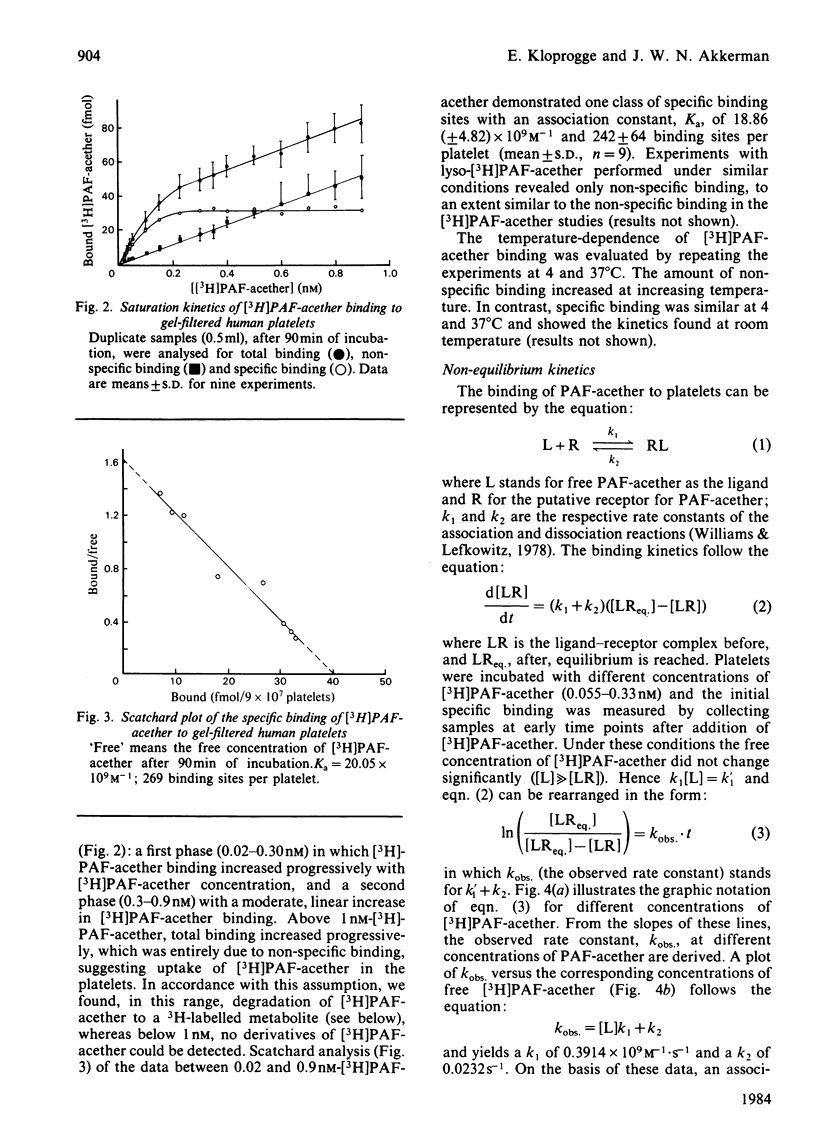
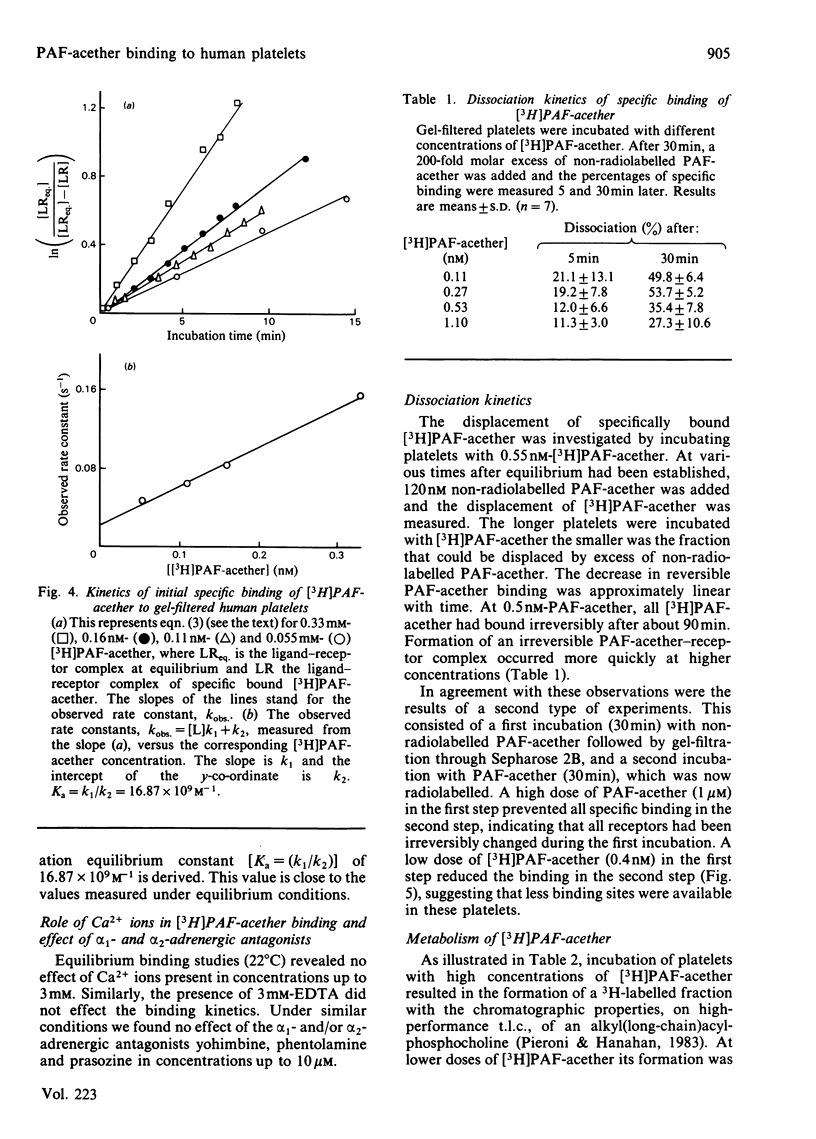
The binding of [3H]PAF-acether (1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) to intact human gel-filtered platelets was measured at 22 degrees C. Specific binding reached saturation within 15 min at high doses of [3H]PAF-acether (0.5-0.9 nM), whereas about 90 min were required when low doses (0.02-0.5 nM) were used. Above 1 nM, [3H]PAF-acether non-specific binding increased progressively, which together with the demonstration of a 3H-labelled metabolite suggested uptake and metabolism of [3H]PAF-acether. Equilibrium analysis revealed one class of specific receptors with a Ka of 18.86 +/- 4.82 X 10(9) M-1 and 242 +/- 64 binding sites per platelet. Non-equilibrium binding revealed a similar Ka (16.87 X 10(9) M-1). Specific binding became irreversible after prolonged incubation, a process that was enhanced at increasing concentrations of [3H]PAF-acether. Platelets made desensitized to PAF-acether by prior incubation with unlabelled PAF-acether failed to bind a second dose of PAF-acether (3H-labelled), suggesting that desensitization resulted from loss of available binding sites. Under the conditions of the binding studies, PAF-acether induced exposure of the fibrinogen receptor, aggregation (in a stirred suspension) and alterations in (poly)-phosphatidylinositides. These results suggest that PAF-acether initiates platelet responses via receptor-mediated processes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam I., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor by blood platelets and plasma. Lipids. 1983 Aug;18(8):534–538. doi: 10.1007/BF02535393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Tencé M., Varenne P., Bidault J., Boullet C., Polonsky J. Semi-synthèse et structure proposée du facteur activant les plaquettes (P.A.F.): PAF-acether, un alkyl ether analogue de la lysophosphatidylcholine. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Nov 26;289(14):1037–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Cress E. A., Lee T. C., Malone B., Surles J. R., Piantadosi C., Hajdu J., Snyder F. Structural features of platelet activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) required for hypotensive and platelet serotonin responses. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;38(1):3–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cejka J. Enzyme immunoassay for factor VIII-related antigen. Clin Chem. 1982 Jun;28(6):1356–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D. D., Byers L. W., Muirhead E. E. Effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) on human platelets. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):582–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Miller E. J. Affinity of fibronectin to collagens of different genetic types and to fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1584–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine K. M., Ashbrook P. C., Brigden L. P., Maldonado J. E., Didishelm P. Gel-filtered human platelets. Ultrastructure, function, and role of proteins in inhibition of aggregation by aspirin. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):11–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G., Duchastel A. Microscopic measurements of platelet aggregation reveal a low ADP-dependent process distinct from turbidometrically measured aggregation. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jun;101(6):964–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B. Interaction of platelet-derived growth factor with its fibroblast receptor. Demonstration of ligand degradation and receptor modulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4216–4221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Pinckard R. N. Platelet activating factor (PAF). A possible direct mediator of anaphylaxis in the rabbit and a trigger for the vascular deposition of circulating immune complexes. Monogr Allergy. 1977;12:13–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lee C. S., Cheah M. J., Shen T. Y. Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4756–4763. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Schrama L. H., Gispen W. H. Calcium-dependent turnover of brain polyphosphoinositides in vitro after prelabelling in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloprogge E., de Haas G. H., Gorter G., Akkerman J. W. Properties of PAF-acether-induced platelet aggregation and secretion. Studies in gel-filtered human platelets. Thromb Res. 1983 Mar 15;29(6):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Dubernard V., Caen J. Further characterization of human platelet ADP binding sites using 5' AMP. Demonstration of a highly reactive population of sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb R. H., Pool G. L., Bubacz D. G., Blank M. L., Snyder F. Spontaneous and protein-catalyzed transfer of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet-activating factor) between phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 7;750(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Phospholipid biosynthesis in human platelets. Formation of phosphatidylcholine from 1-acyl lysophosphatidylcholine by acyl-CoA:1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11278–11283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N. Pathobiology of the intravenous infusion of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC), a synthetic platelet-activating factor (PAF), in the rabbit. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2919–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuizen W., Emeis J. J., Vermond A., Kurver P., van der Heide D. Studies on the catabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in rats. Application of the Iodogen labelling technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Budzynski A. Z., Morinelli T. A., Brudzynski T. M., Stewart G. J. Exposure of fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by proteolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):917–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L., Miller C. H., Lewis J. C., Waite M., Bass D. A., McCall C. E., DeChatelet L. R. 1-O-Alkyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholines: a novel class of neutrophil stimulants. Am J Pathol. 1981 Apr;103(1):70–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni G., Hanahan D. J. Metabolic behavior of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine on interaction with rabbit platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky J., Tencé M., Varenne P., Das B. C., Lunel J., Benveniste J. Release of 1-O-alkylglyceryl 3-phosphorylcholine, O-deacetyl platelet-activating factor, from leukocytes: chemical ionization mass spectrometry of phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7019–7023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Henson P. M. The binding of rabbit basophil-derived platelet-activating factor to rabbit platelets. Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):791–810. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Pinckard R. N., Ferrigni K. S., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J. Activation of human neutrophils with 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine (platelet activating factor). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1250–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl A. M., Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Nicolaou K. C., Ahern D. Selective binding site for [3H]prostacyclin on platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):215–220. doi: 10.1172/JCI109292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Osler A. G. Destruction of rabbit platelets in the allergic response of sensitized leukocytes. I. Demonstration of a fluid phase intermediate. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1244–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J., Marfey P. Gel filtration. A new technique for separation of blood platelets from plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Jun 30;25(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashita Z., Tsushima S., Yoshioka Y., Nomura H., Inada Y., Nishikawa K. CV-3988 - a specific antagonist of platelet activating factor (PAF). Life Sci. 1983 Apr 25;32(17):1975–1982. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touqui L., Jacquemin C., Vargaftig B. B. Conversion of 3H-PAF acether by rabbit platelets is independent from aggregation: evidences for a novel metabolite. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):890–893. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Coles E., Reinhold V. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding of phospholipid platelet-activating factor by human platelets. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1637–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Chignard M., Benveniste J., Lefort J., Wal F. Background and present status of research on platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:119–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Fouque F., Benveniste J., Odiot J. Adrenaline and PAF-acether synergize to trigger cyclooxygenase-independent activation of plasma-free human platelets. Thromb Res. 1982 Nov 15;28(4):557–573. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. Albumin density gradient separation and washing of platelets and the study of platelet coagulant activities. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):205–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wykle R. L., Miller C. H., Lewis J. C., Schmitt J. D., Smith J. A., Surles J. R., Piantadosi C., O'Flaherty J. T. Stereospecific activity of 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine and comparison of analogs in the degranulation of platelets and neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun;100(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


