Abstract
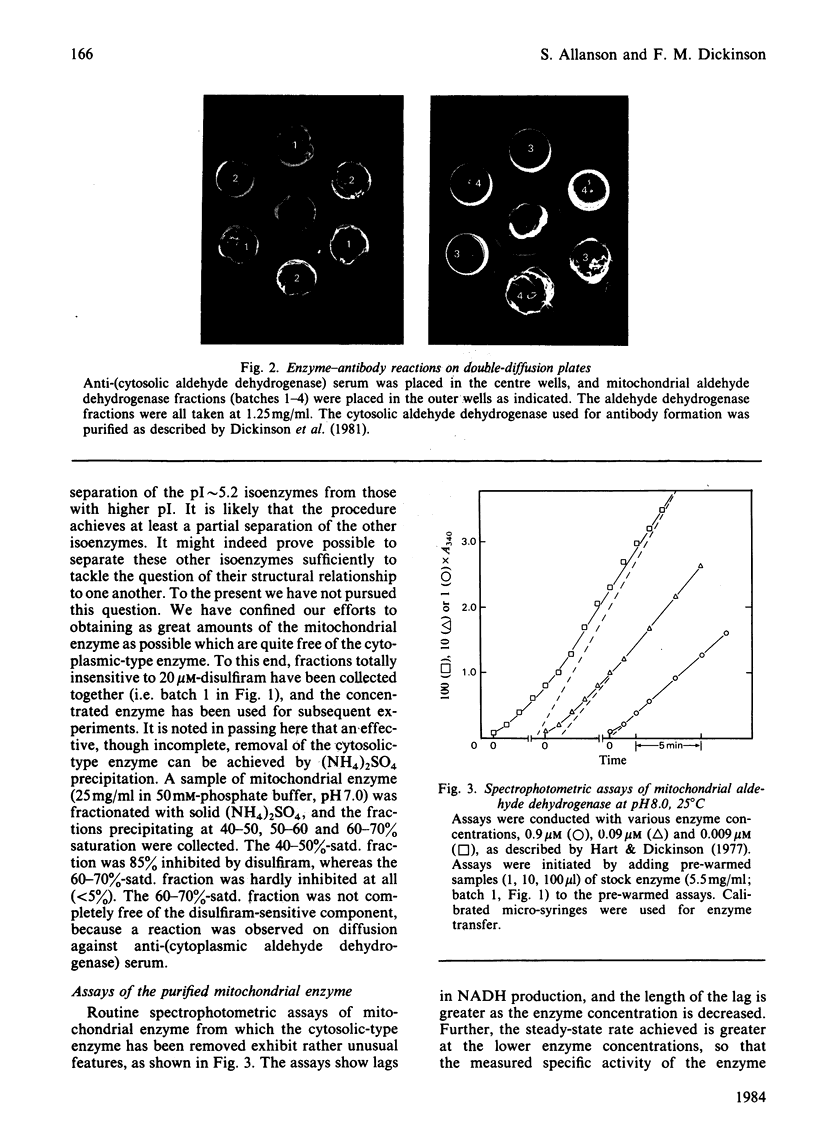
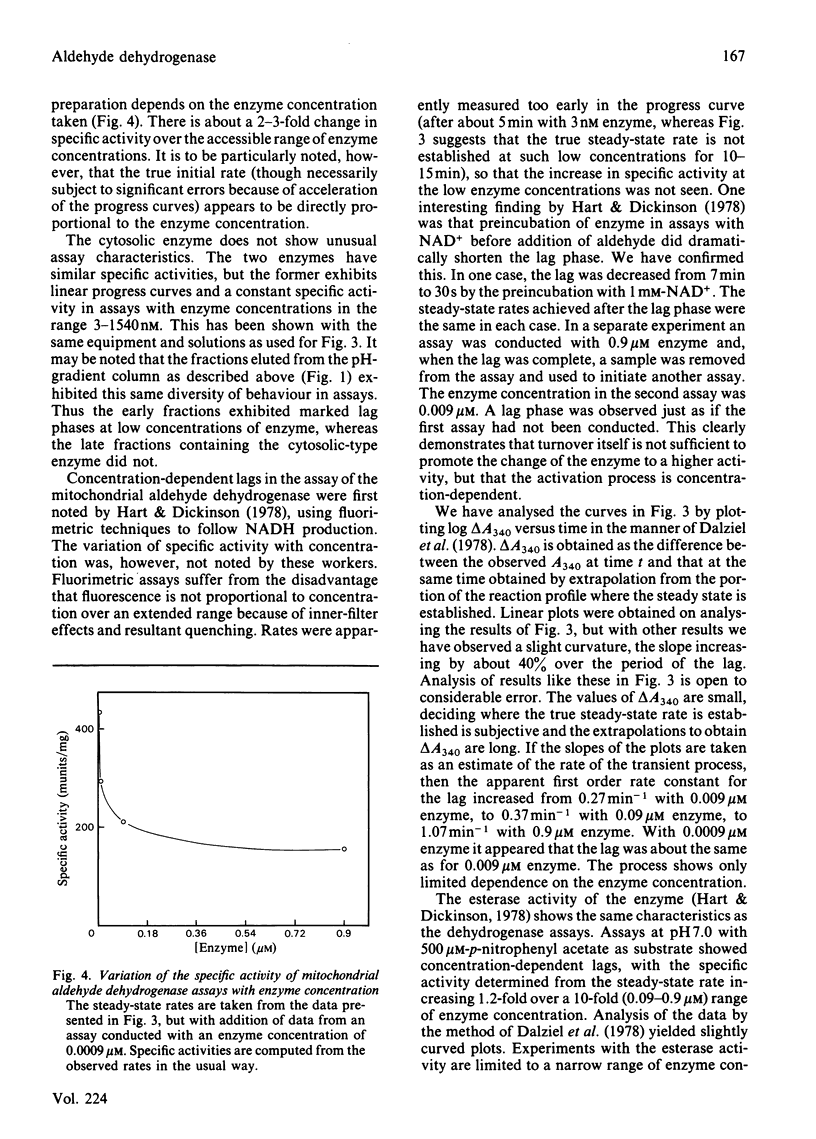
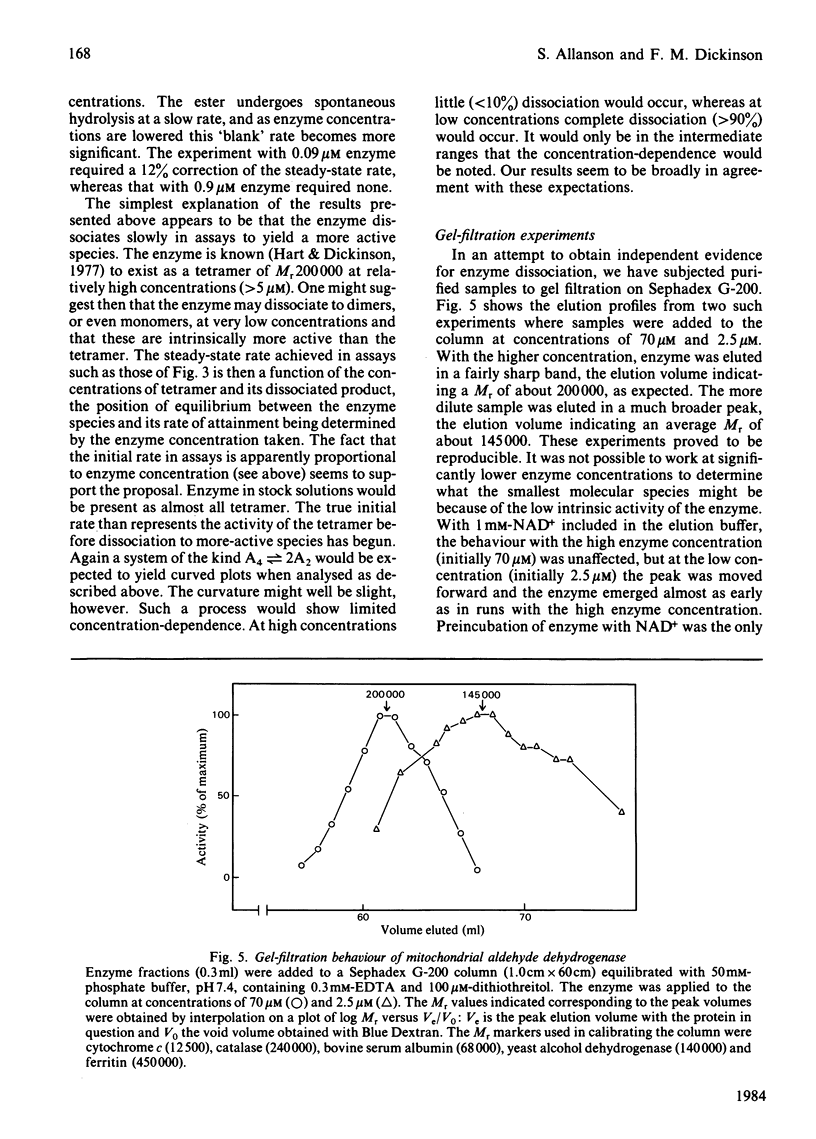
The pI approximately 5.2 isoenzymes of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase were separated from the other isoenzymes by pH-gradient chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel. The pI approximately 5.2 material is immunologically identical with cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase. It also shows sensitivity to 20 microM-disulfiram and insensitivity to 4M-urea in assays. These and other criteria seem to establish that the material is identical with the cytosolic enzyme. Mitochondrial enzyme that had been purified to remove pI approximately 5.2 isoenzymes shows concentration-dependent lag phases in assays. These effects are possibly due to the slow establishment of equilibrium between tetramer and either dimers or monomers, with the dissociated species being intrinsically more active than the tetramer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew K. E., Bennett A. F., Crow K. E., Greenway R. M., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. A reinvestigation of the purity, isoelectric points and some kinetic properties of the aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel K., McFerran N., Matthews B., Reynolds C. H. Transient kinetics of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from bovine heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):743–750. doi: 10.1042/bj1710743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Berrieman S. The separation of sheep liver cytoplasmic and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenases by isoelectric focusing, and observations on the purity of preparations of the cytoplasmic enzyme, and their sensitivity towards inhibition by disulfiram. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):709–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1790709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
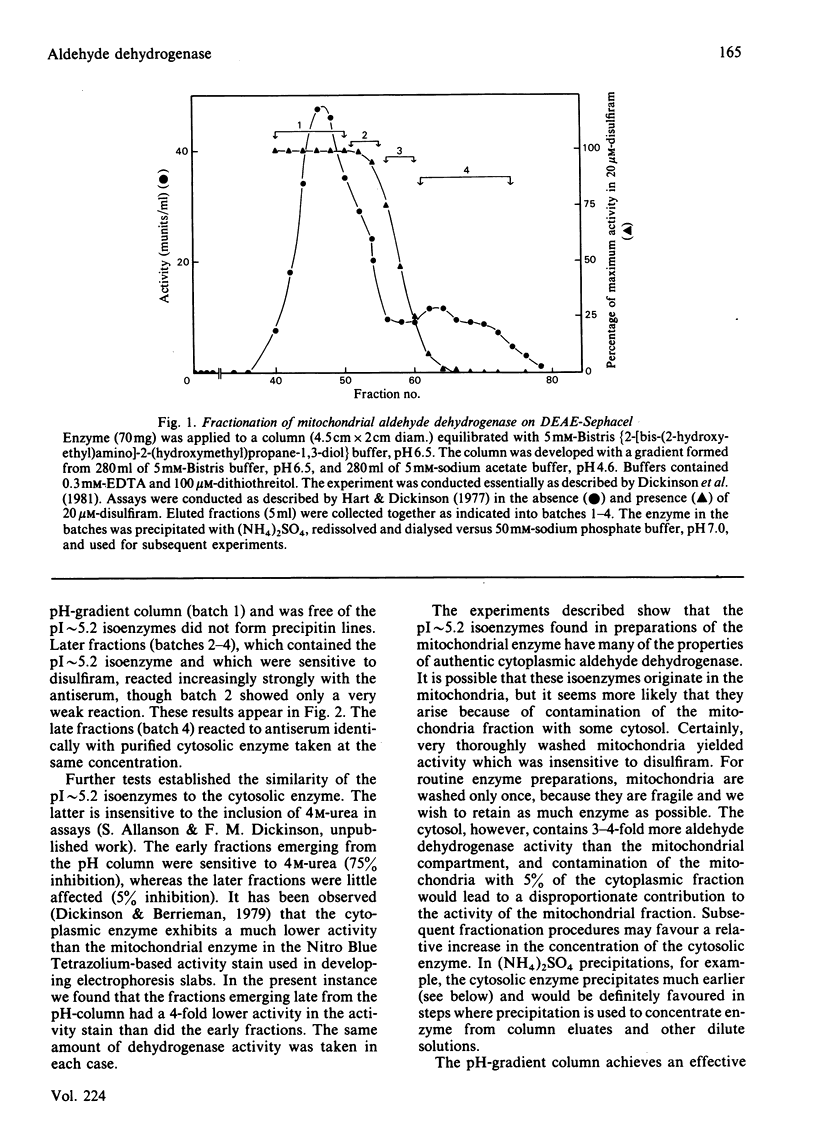
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):899–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1750899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1630261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. The coenzyme-binding characteristics of highly purified preparations of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):363–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2110363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H., Hu J. H. Increase in the stoichiometry of the functioning active sites of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase in the presence of magnesium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H. Magnesium stimulation of catalytic activity of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Changes in molecular weight and catalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8206–8209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]