Abstract
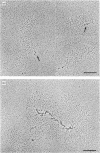
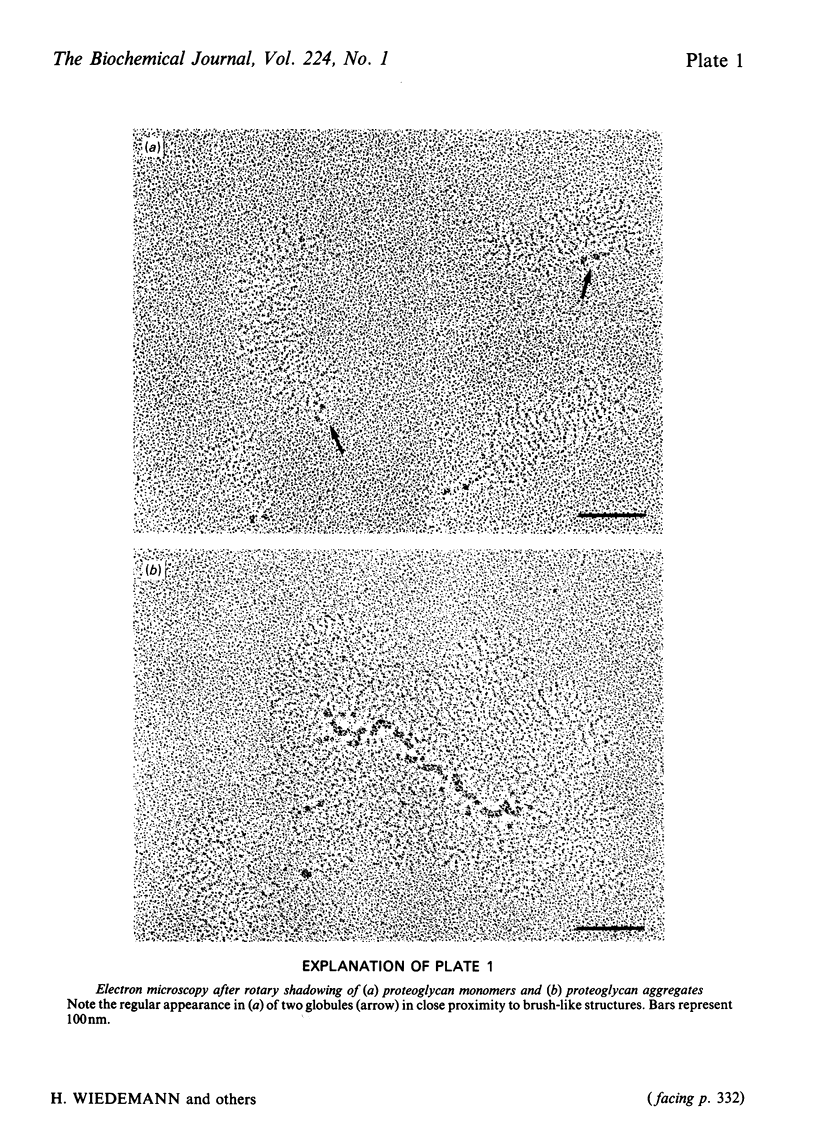
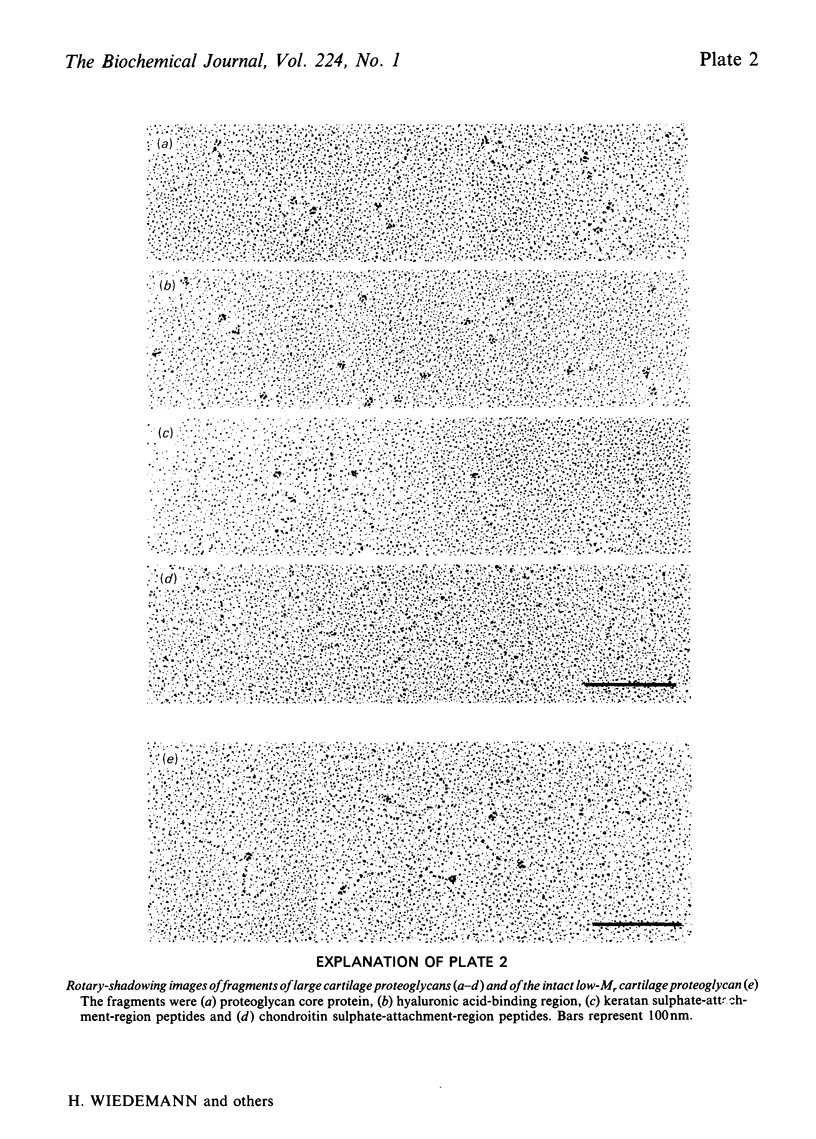
The rotary-shadowing technique for molecular electron microscopy was used to study cartilage proteoglycan structure. The high resolution of the method allowed demonstration of two distinct globular domains as well as a more strand-like portion in the core protein of large aggregating proteoglycans. Studies of proteoglycan aggregates and fragments showed that the globular domains represent the part of the proteoglycans that binds to the hyaluronic acid, i.e. the hyaluronic acid-binding region juxtapositioned to the keratan sulphate-attachment region. The strand-like portion represents the chondroitin sulphate-attachment region. Low-Mr proteoglycans from cartilage could be seen as a globule connected to one or two side-chain filaments of chondroitin sulphate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franzén A., Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate formation. Role of link protein. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1970669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Lustig A., Engel J. Structure and interactions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans from a mouse tumor basement membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):145–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Lohmander S., Thyberg J. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Electron-microscopic studies of native and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):913–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1750913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Paulsson M., Inerot S., Carlström C. A novel low-molecular weight chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan isolated from cartilage. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):355–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1970355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn K., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Risteli J., Dieringer H., Voss T., Glanville R. W. Macromolecular structure of basement membrane collagens. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 9;125(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Miller A., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Physical properties of the hyaluronate binding region of proteoglycan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Densitometric and small-angle neutron scattering studies of carbohydrates and carbohydrate-protein macromolecules. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):69–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Macromolecular models of proteinpolysaccharides from bovine nasal cartilage based on electron microscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4123–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Lohmander S., Heinegård D. Proteoglycans of hyaline cartilage: Electron-microscopic studies on isolated molecules. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):157–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]